S-(hydroxymethyl)glutathione synthase
Glutathione-dependent formaldehyde-activating enzyme (Gfa) is a carbon-sulphur lyase enzyme that catalyses the first step of a pathway that metabolises toxic formaldehyde to yield formate as a product. Gfa catalyses the condensation of formaledhyde and glutathione to form an adduct, S-hydroxymethylglutathione.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
Q51669
 (4.4.1.22)
(4.4.1.22)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Paracoccus denitrificans (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1xa8
- Crystal Structure Analysis of Glutathione-dependent formaldehyde-activating enzyme (Gfa)
(2.4 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.90.1590.10
 (see all for 1xa8)
(see all for 1xa8)
- Cofactors
- Glutathione (1), Zinc(2+) (1)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:4.4.1.22)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
Catalysis uses a zinc redox switch mechanism, in which a zinc molecule moves in a ping-pong fashion between its coordination state and its dislocated state. Formation of a disulphide bond between a glutathione molecule in its oxidised form (GSSG) and a zinc-coordinating thiol (Cys56) releases zinc into its dislocated state. In its dislocated state, zinc exerts its actual catalytic function by activating the coordinated formaldehyde and glutathione (GSH) for nucleophilic addition. The proposed mechanism involves the GSSG reacting with Cys56, resulting in the formation of a disulphide-bonded Gfa-glutathione intermediate and the displacement of zinc. The zinc-glutathione complex acts as a formaldehyde scavenger. In this complex, the carbonyl bond of the formaldehyde and the sulfinyl bond of GSH are polarised by zinc and activated for the final nucleophilic addition to form S-hydroxymethylglutathione, relocate zinc into the catalytic site and regenerate GSSG.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1xa8) | ||
| Cys52, Cys57 | Cys54A, Cys59A | Coordinate to zinc in the initial state | metal ligand |
| Cys54 | Cys56A | Cys 56 forms a ligand interaction with zinc and also forms a disulphide bridge with GSSG, which is important in the displacement of zinc forming a highly dynamic zinc redox switch which is crucial for the reaction. Sulphur ligands, such as Cys56, are needed to create an oxidoreductive environment in which the ligands (not the metal) are oxidised and reduced with concomitant release and binding of zinc. | nucleophile, nucleofuge, metal ligand |
Chemical Components
bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, decoordination from a metal ion, coordination, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, enzyme-substrate complex formation, native state of enzyme regenerated, overall product formed, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, proton transfer, intermediate terminated, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, native state of cofactor regeneratedReferences
- Neculai AM et al. (2005), J Biol Chem, 280, 2826-2830. A Dynamic Zinc Redox Switch. DOI:10.1074/jbc.c400517200. PMID:15548539.
- Hopkinson RJ et al. (2015), PLoS One, 10, e0145085-. Studies on the Glutathione-Dependent Formaldehyde-Activating Enzyme from Paracoccus denitrificans. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0145085. PMID:26675168.
- Goenrich M et al. (2002), J Biol Chem, 277, 3069-3072. A Glutathione-dependent Formaldehyde-activating Enzyme (Gfa) from Paracoccus denitrificans Detected and Purified via Two-dimensional Proton Exchange NMR Spectroscopy. DOI:10.1074/jbc.c100579200. PMID:11741920.
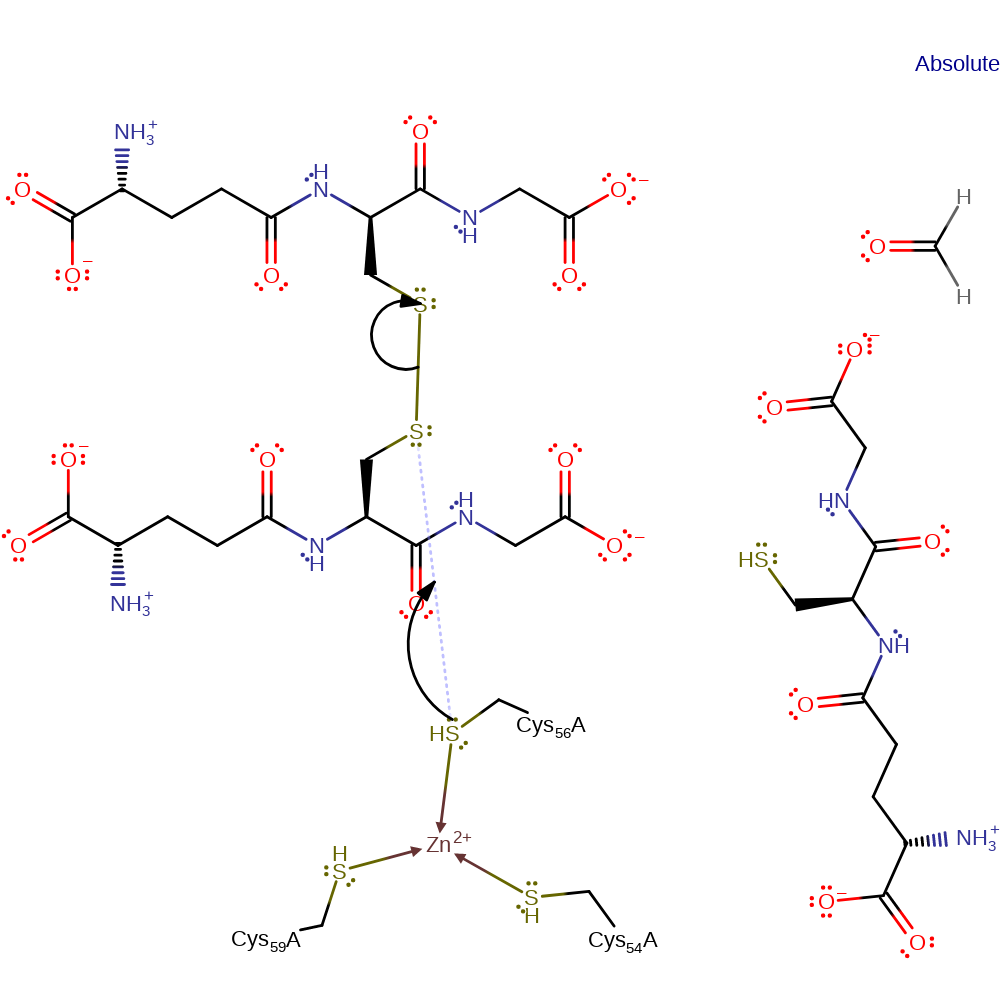
Step 1. In the initial state Gfa exists in the presence of both oxidized and reduced glutathione, with the zinc being coordinated to the three cys residues in a trigonal planar conformation. Cys56 forms a disulphide bond with glutathione by performing a nucleophilic attack on the oxidized form. This results in the zinc being dislocated from the cys residues.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys54A | metal ligand |
| Cys56A | metal ligand |
| Cys59A | metal ligand |
| Cys56A | nucleophile |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, decoordination from a metal ion, coordination, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, enzyme-substrate complex formation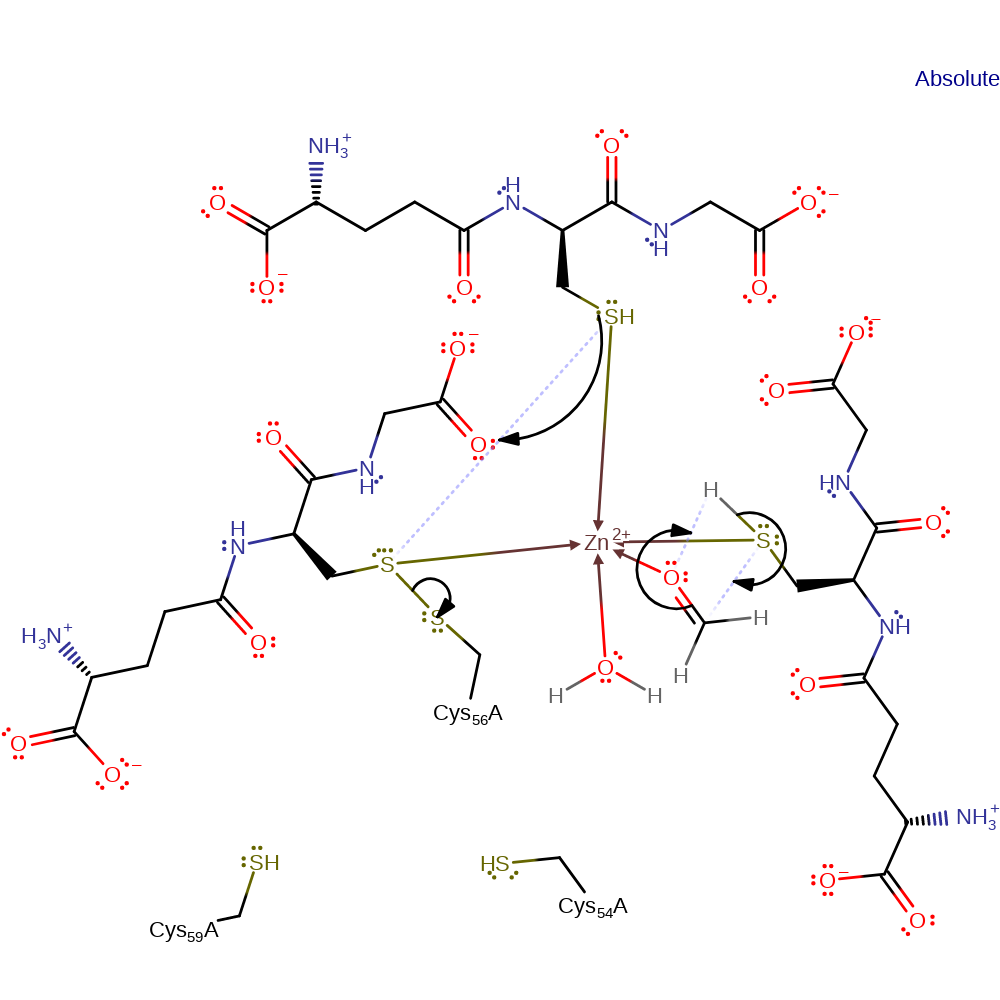
Step 2. The zinc is now coordinated to three glutathiones, a ligand thought to be either water or histidine, and the formaldehyde. The zinc polarizes the thiol group of one of the reduced glutathiones as well as the formaldehyde. This facillitates the nucelophilic attack of the thiol onto the formaldehyde carbonyl. Forming the product. The other reduced glutathione forms a disulphide bond with the Cys56 bound glutathione restoring the enzyme to the state seen in step one.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys56A | nucleofuge |



 Download:
Download: