D-Ala-D-Ala dipeptidase
VanX is a Zn(II)-containing metalloenzyme that cleaves D-alanyl-D-alanine dipeptide (D-ala-D-ala), increasing the cytoplasmic pool of free D-ala available for use by VanA to form D-ala-D-lac. The enzyme is stereospecific and is found in solution as a mixture of monomers and dimers. The dipeptidase is a critical component of a system that mediates transposon-based, high-level vancomycin resistance in enterococci. Vancomycin acts by binding to the terminal D-ala-D-ala moiety of the bacterial peptidoglycan precursor, interfering with growth of the peptidoglycan chain and normal cell wall formation. The substitution of D-ala-D-ala by D-ala-D-lac at the extracellular terminus of the peptidoglycan chain diminishes the affinity of vancomycin by 1000-fold.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
Q06241
 (3.4.13.22)
(3.4.13.22)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Enterococcus faecium (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1r44
- Crystal Structure of VanX
(2.25 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.30.1380.10
 (see all for 1r44)
(see all for 1r44)
- Cofactors
- Zinc(2+) (1)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:3.4.13.22)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
An incoming peptide displaces a zinc-bound water molecule towards Glu181, giving a six-coordinated metal ion. The nucleophilic hydroxide is generated by zinc and Glu181 from the water molecule, and the nucleophile attacks the polarised carbonyl to form a tetrahedral intermediate. This forms a bidentate complex with the zinc and is stabilised further by interactions with Arg71. It is likely that Glu181 donates a proton to the scissile nitrogen, completing the reaction and yielding D-ala, although it is possible that the source of the proton may be from the nucleophile or another active site residue.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1r44) | ||
| His116, Asp123, His184 | His116A, Asp123A, His184A | Form the Zinc binding site. | metal ligand |
| Arg71 | Arg71A | Arg71 is a key residue in stabilising the tetrahedral transition state by formation of a salt link to one of the phosphonate oxygens. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu181 | Glu181A | Glu181 acts as a catalytic base, deprotonating the water molecule to form the nucleophile. The residue is thought to donate a proton to the scissile nitrogen to complete the reaction. | proton acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, coordination to a metal ion, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, rate-determining step, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate collapse, decoordination from a metal ion, native state of enzyme regenerated, overall product formedReferences
- Matthews ML et al. (2006), J Am Chem Soc, 128, 13050-13051. Probing the Reaction Mechanism of thed-ala-d-ala Dipeptidase, VanX, by Using Stopped-Flow Kinetic and Rapid-Freeze Quench EPR Studies on the Co(II)-Substituted Enzyme. DOI:10.1021/ja0627343. PMID:17017774.
- Meziane-Cherif D et al. (2014), Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 111, 5872-5877. Structural basis for the evolution of vancomycin resistance D,D-peptidases. DOI:10.1073/pnas.1402259111. PMID:24711382.
- Breece RM et al. (2005), J Biol Chem, 280, 11074-11081. A five-coordinate metal center in Co(II)-substituted VanX. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M412582200. PMID:15657055.
- Bussiere DE et al. (1998), Mol Cell, 2, 75-84. The Structure of VanX Reveals a Novel Amino-Dipeptidase Involved in Mediating Transposon-Based Vancomycin Resistance. DOI:10.1016/s1097-2765(00)80115-x. PMID:9702193.
- McCafferty DG et al. (1997), Biochemistry, 36, 10498-10505. Mutational Analysis of Potential Zinc-Binding Residues in the Active Site of the Enterococcald-Ala-d-Ala Dipeptidase VanX†. DOI:10.1021/bi970543u. PMID:9265630.

Step 1. Glu181 deprotonates a water which alongside Zn polarising the hydroxide activates it so it can attack the carbon of the carbonyl in a nucleophilic addition. The incoming pe-ptide also coordinates to the Zinc which further stabilises the tetrahedral intermediate produced.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg71A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His116A | metal ligand |
| Asp123A | metal ligand |
| His184A | metal ligand |
| Glu181A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, coordination to a metal ion, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, rate-determining step
Step 2. The oxyanion initiates an elimination which results in the cleavage of the peptide bond. The N-terminal product then accepts a proton from Glu181.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His116A | metal ligand |
| Asp123A | metal ligand |
| His184A | metal ligand |
| Arg71A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu181A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, proton transfer, intermediate collapse, decoordination from a metal ion, native state of enzyme regenerated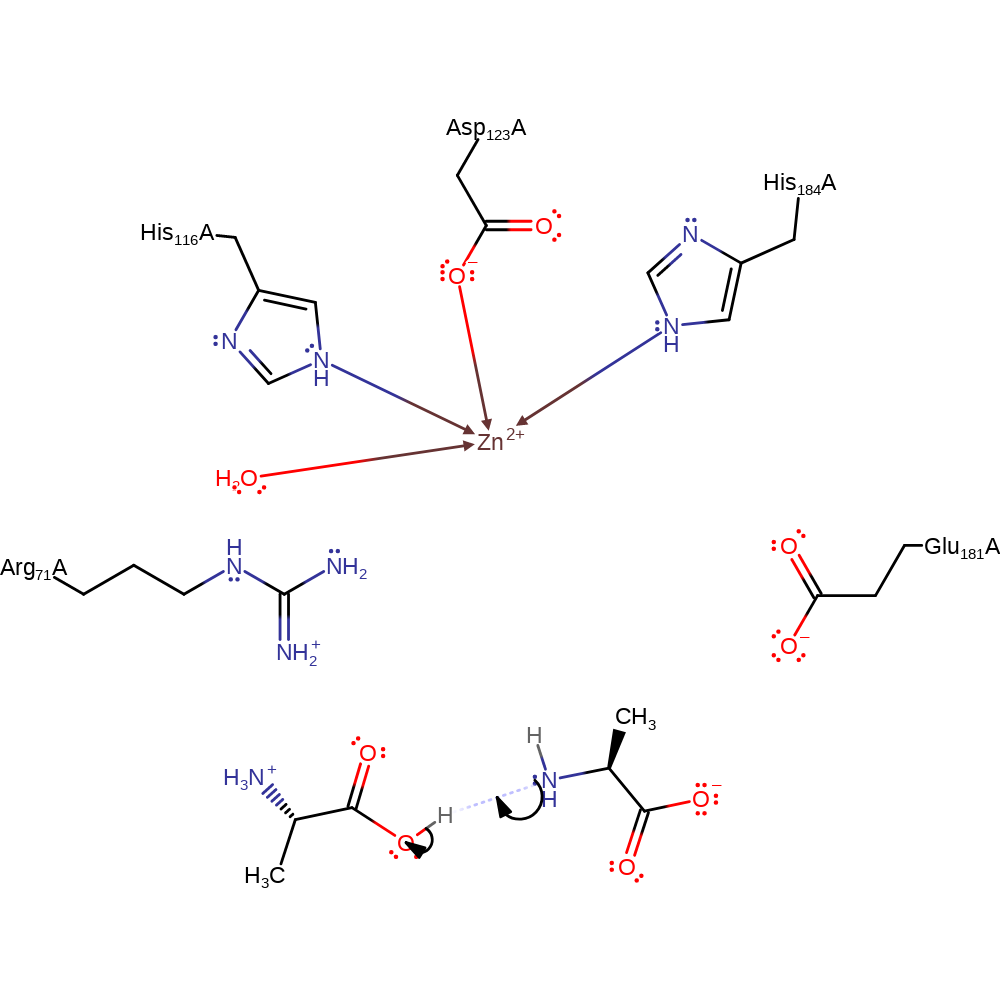
Step 3. The N-terminal product accepts a proton from the C-terminal product to produce the kinetically favourable products.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His116A | metal ligand |
| Asp123A | metal ligand |
| His184A | metal ligand |
| Arg71A | electrostatic stabiliser |



 Download:
Download: