Cytochrome P450 (BM-3)
Cytochromes P450, a gene superfamily of heme proteins found in all eukaryotes, most prokaryotes, and Archaea, catalyse the mono-oxygenation of a wide variety of organic molecules. P450 reactions of biological significance include steroid bio-genesis, drug metabolism, procarcinogen activation, xenobiotic detoxification, and fatty acid metabolism. P450BM-3 consists of heme (BMP) and FMN/FAD containing reductase domains linked together by a single polypeptide.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P14779
 (1.6.2.4, 1.14.14.1)
(1.6.2.4, 1.14.14.1)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Bacillus megaterium NBRC 15308 = ATCC 14581 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1bu7
- CRYOGENIC STRUCTURE OF CYTOCHROME P450BM-3 HEME DOMAIN
(1.65 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
1.10.630.10
 (see all for 1bu7)
(see all for 1bu7)
- Cofactors
- Fadh2(2-) (1), Heme b (1), Fmnh2(2-) (1)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:1.14.14.1)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
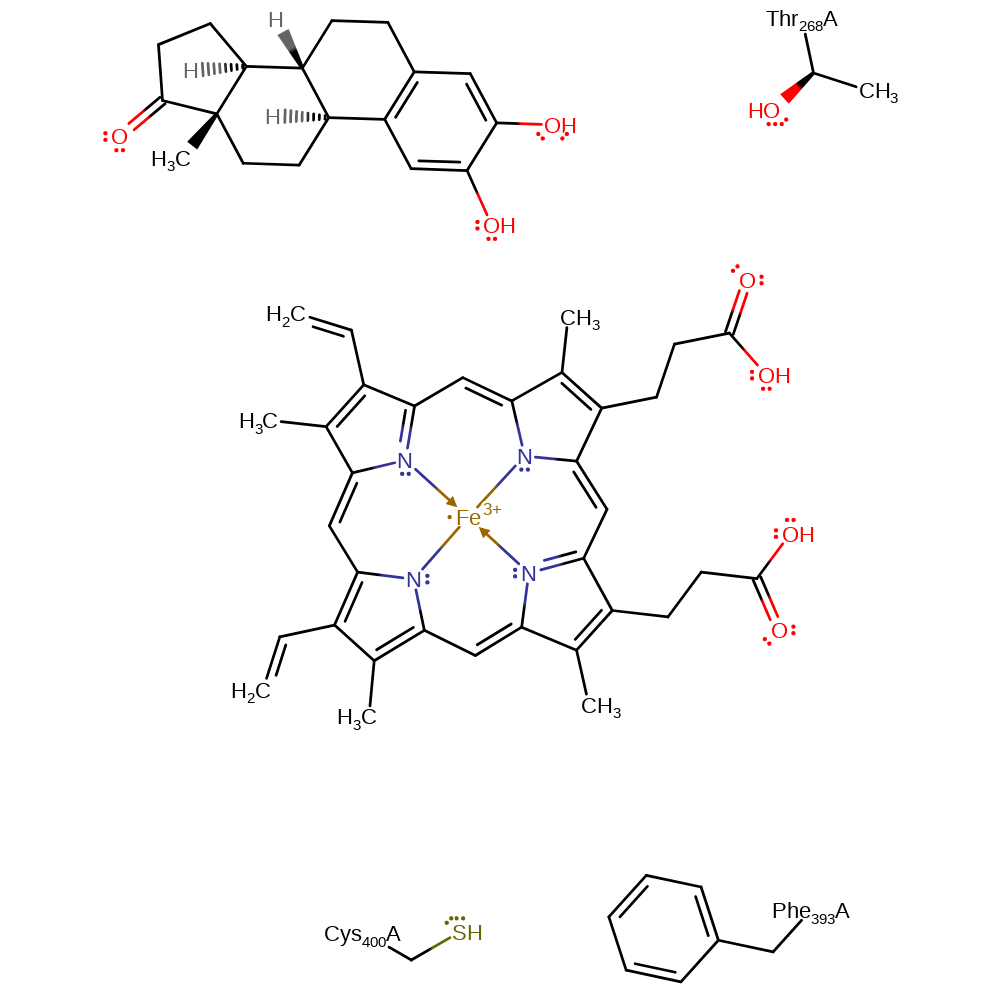
Electron transfer from a redox partner to the P450 is a key step in the P450 catalytic cycle. The redox partner for P450BM-3 is a covalently bound FAD/FMN-dependent NADPH-cytochrome P450 oxidoreductase (CPR). In CPR, FAD serves as an electron acceptor from NADPH, passes them to FMN which interacts with and reduces the P450BM-3 haem group. Binding of the substrate promotes electron transfer to P450 haem, reducing the iron from Fe(III) to Fe(II). Dioxygen binds and thus Fe(II) is oxidised back to Fe(III). A second electron is passed to the haem forming a superoxide species rapidly followed by proton donation by catalytic water. A second proton is delivered causing either non productive peroxide formation or loss of water and the formation of the low spin Fe(IV) oxo complex. The rebound mechanism forms the alcohol group on the substrate. The Fe(IV)-oxo complex undergoes spin inversion to form a radical oxo group which removes a hydrogen from the substrate to form a radical carbon centre and an alcohol group on Fe(IV). The new radical then attacks the oxygen to form the alcohol group and Fe(III), completing the catalytic cycle.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1bu7) | ||
| Phe394 | Phe393B | Acts to increase the redox potential of the haem iron by increasing the electron density around cys400. | electrostatic stabiliser, steric role |
| Cys401 | Cys400B | Acts to increase the redox potential of the haem iron with the aid of residue 383. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Thr269 | Thr268B | Required for a robust framework that positions water appropriately during the reaction to prevent peroxide formation. | steric role, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
redox reaction, electron transfer, intermediate formation, proton transfer, heterolysis, overall reactant used, radical formation, overall product formed, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Clark JP et al. (2006), J Inorg Biochem, 100, 1075-1090. The role of Thr268 and Phe393 in cytochrome P450 BM3. DOI:10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2005.11.020. PMID:16403573.
- Dubey KD et al. (2018), J Am Chem Soc, 140, 683-690. Choreography of the Reductase and P450BM3 Domains Toward Electron Transfer Is Instigated by the Substrate. DOI:10.1021/jacs.7b10072. PMID:29277994.
- Lonsdale R et al. (2016), Chem Res Toxicol, 29, 963-971. Quantum Mechanics/Molecular Mechanics Modeling of Drug Metabolism: Mexiletine N-Hydroxylation by Cytochrome P450 1A2. DOI:10.1021/acs.chemrestox.5b00514. PMID:27064685.
- Roccatano D (2015), J Phys Condens Matter, 27, 273102-. Structure, dynamics, and function of the monooxygenase P450 BM-3: insights from computer simulations studies. DOI:10.1088/0953-8984/27/27/273102. PMID:26061496.
- Verma R et al. (2014), Biopolymers, 101, 197-209. Insight into the redox partner interaction mechanism in cytochrome P450BM-3 using molecular dynamics simulations. DOI:10.1002/bip.22301. PMID:23754593.
- Cryle MJ et al. (2008), Chembiochem, 9, 261-266. The Role of the Conserved Threonine in P450BM3 Oxygen Activation: Substrate-Determined Hydroxylation Activity of the Thr268Ala Mutant. DOI:10.1002/cbic.200700537. PMID:18161730.
- Hlavica P (2004), Eur J Biochem, 271, 4335-4360. Models and mechanisms of O-O bond activation by cytochrome P450. A critical assessment of the potential role of multiple active intermediates in oxidative catalysis. DOI:10.1111/j.1432-1033.2004.04380.x. PMID:15560776.
- Ost TW et al. (2003), J Am Chem Soc, 125, 15010-15020. Oxygen Activation and Electron Transfer in Flavocytochrome P450 BM3. DOI:10.1021/ja035731o. PMID:14653735.
- Sevrioukova IF et al. (1999), Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 96, 1863-1868. Structure of a cytochrome P450-redox partner electron-transfer complex. DOI:10.1073/pnas.96.5.1863. PMID:10051560.
- Li H et al. (1999), Biochim Biophys Acta, 1441, 141-149. Fatty acid metabolism, conformational change, and electron transfer in cytochrome P-450BM-3. DOI:10.1016/s1388-1981(99)00161-4. PMID:10570242.
- Yeom H et al. (1995), Biochemistry, 34, 14733-14740. The role of Thr268 in oxygen activation of cytochrome P450BM-3. DOI:10.1021/bi00045a014. PMID:7578081.
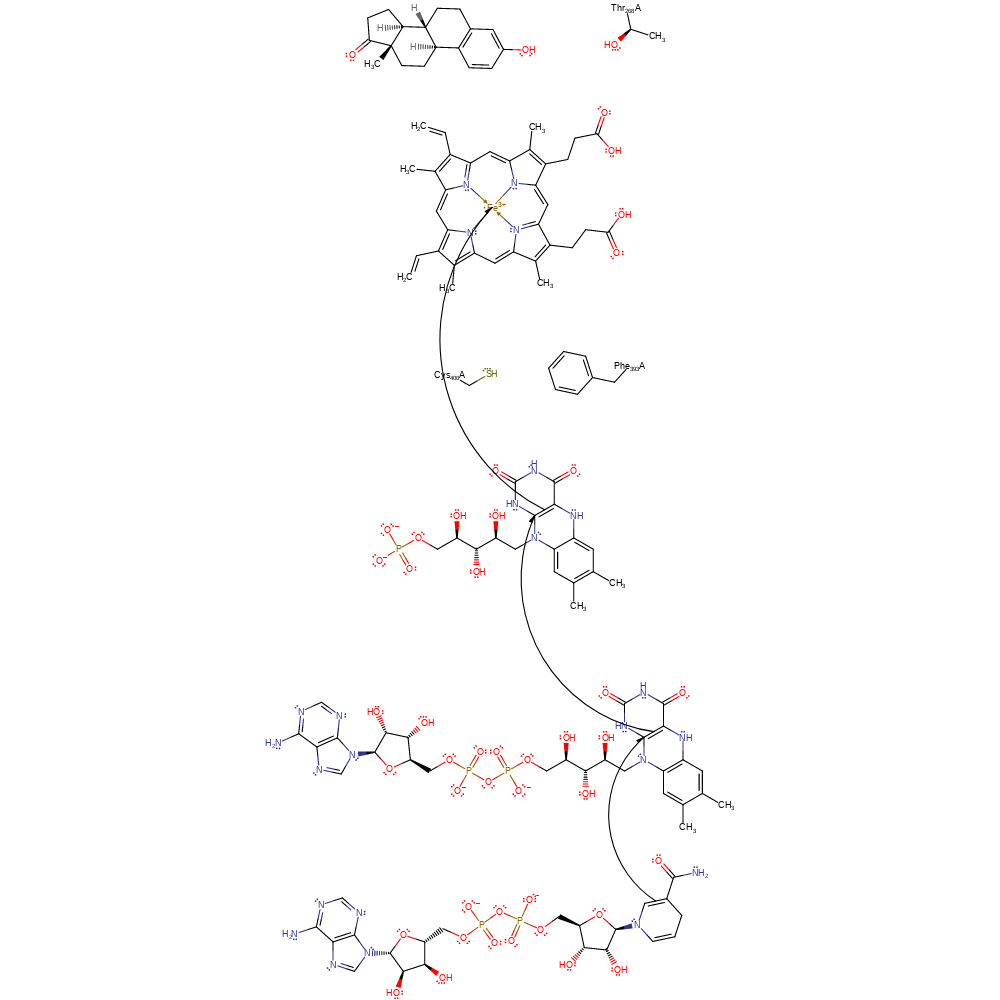
Step 1. The substrate binds to the active site. Fe(III) is reduced to Fe(II) by an electron which is transferred from the FAD/FMN domain via NADH, FAD and FMN.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Thr268B | steric role |
| Cys400B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Phe393B | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
redox reaction, electron transfer
Step 2. Oxygen binds to the heme group and Fe(II) is oxidised back to Fe(III).
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Phe393B | steric role |
| Thr268B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys400B | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
redox reaction, electron transfer, intermediate formation
Step 3. A second electron is transferred to the heme from NADH, forming NAD and a superoxide species.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|
Chemical Components
intermediate formation, electron transfer
Step 4. The superoxide is rapidly protonated by a water molecule to form a hyroperoxide.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|
Chemical Components
proton transfer, intermediate formation
Step 5. Further protonation of the hydroperoxide oxygen atom leads to heterolysis of the O-O bond and release of water.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Phe393B | steric role |
| Thr268B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys400B | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
heterolysis, electron transferCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Phe393B | steric role |
| Thr268B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys400B | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
overall reactant used, intermediate formation, radical formation
Step 7. The carbon radical attacks the oxygen of the hydroxyl group and forms the product. Fe(IV) is reduced back to Fe(III) and the native state of the enzyme is restored.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|








 Download:
Download: