6-deoxyerythronolide B hydroxylase
6-deoxyerythronolide B hydroxylase (P450eryF) is a heme-thiolate protein (P-450). P-450s are a superfamily of heme proteins found in all eukaryotes, most prokaryotes, and Archaea and catalyse the monooxygenation of a wide variety of organic molecules. P450 reactions of biological significance include steroid biogenesis, drug metabolism, procarcinogen activation, xenobiotic detoxification, and fatty acid metabolism. P450eryF catalyses the NADPH-dependent conversion of 6-deoxyerythronolide B (6-DEB) to erythronolide B (EB) by the insertion of an oxygen at the 6S position of 6-DEB. Function requires the participation of a ferredoxin and a ferredoxin reductase for the transfer of electrons from NADPH to the monooxygenase.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
Q00441
 (1.14.15.35)
(1.14.15.35)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Saccharopolyspora erythraea NRRL 2338 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1oxa
- CYTOCHROME P450 (DONOR:O2 OXIDOREDUCTASE)
(2.1 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
1.10.630.10
 (see all for 1oxa)
(see all for 1oxa)
- Cofactors
- Heme b (1)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:1.14.15.35)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The catalytic cycle of all cytochrome P450s is conserved. Electrons are delivered to the haem centre from NADH, permitting oxygen reduction. This is illustrated as a general electron donor. Binding of the substrate promotes electron transfer to P450 haem, reducing the iron from Fe(III) to Fe(II). Dioxygen binds and thus Fe(II) is oxidised back to Fe(III). A second electron is passed to the haem forming a superoxide species, followed by donation of two protons. Catalytic water (Wat564), and uniquely the C5 hydroxyl group of 6-DEB, provide the protons to the distil oxygen. This results in the loss of water and the formation of the low spin Fe(IV) oxo complex. Reprotonation of the catalytic water and 6-DEB after protonation of dioxygen occurs via a hydrogen bonded network presumed to be in contact with the bulk solvent during the course of the reaction. The rebound mechanism forms the alcohol group on the substrate once the oxo group is formed. The Fe(IV)-oxo complex undergoes spin inversion to form a radical oxo group which removes a hydrogen from the substrate to form a radical carbon centre and an alcohol group on Fe(IV). The new radical then attacks the oxygen to form the alcohol group and Fe(III), completing the catalytic cycle.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1oxa) | ||
| Ala241 (main-C) | Ala241(240)A (main-C) | Involved in a hydrogen bond network with Glu360, Ser246 and a water molecule which is responsible for protonating the peroxy-complex intermediate. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys351 | Cys351(350)A | Coordinated to the Fe ion in heme b. | metal ligand |
| Ser246 | Ser246(245)A | Member of the hydrogen bonded network which replenishes the protons in the active site. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, metal ligand, proton acceptor, proton donor, proton relay, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu360 | Glu360(359)A | Member of the hydrogen bonded network which replenishes the protons in the active site. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, proton donor |
Chemical Components
redox reaction, decoordination from a metal ion, coordination to a metal ion, electron transfer, proton transfer, proton relay, intermediate formation, heterolysis, radical formation, overall reactant used, overall product formed, radical termination, aromatic bimolecular nucleophilic additionReferences
- Nagano S et al. (2005), J Biol Chem, 280, 22102-22107. Crystal Structures of the Ferrous Dioxygen Complex of Wild-type Cytochrome P450eryF and Its Mutants, A245S and A245T: INVESTIGATION OF THE PROTON TRANSFER SYSTEM IN P450eryF. DOI:10.1074/jbc.m501732200. PMID:15824115.
- Sen K et al. (2014), J Phys Chem B, 118, 2810-2820. Role of Two Alternate Water Networks in Compound I Formation in P450eryF. DOI:10.1021/jp411272h. PMID:24564366.
- Muralidhara BK et al. (2007), J Am Chem Soc, 129, 2015-2024. Dissecting the Thermodynamics and Cooperativity of Ligand Binding in Cytochrome P450eryF. DOI:10.1021/ja066303w. PMID:17256854.
- Choonkeun K et al. (2000), Bioorg Chem, 28, 306-314. The Role of Serine-246 in Cytochrome P450eryF-Catalyzed Hydroxylation of 6-Deoxyerythronolide B. DOI:10.1006/bioo.2000.1187. PMID:11133149.
- Cupp-Vickery JR et al. (1996), Nat Struct Biol, 3, 632-637. Substrate-assisted catalysis in cytochrome P450eryF. DOI:10.1038/nsb0796-632. PMID:8673608.
- Cupp-Vickery JR et al. (1995), Nat Struct Biol, 2, 144-153. Structure of cytochrome P450eryF involved in erythromycin biosynthesis. PMID:7749919.

Step 1. After the substrate binds a water molecule is released from the active site which increases the redox potential. This facilitates the first one electron reduction of Fe(III) to Fe(II) by NADPH (illustrated here as transfer from a general donor).
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys351(350)A | metal ligand |
| Ala241(240)A (main-C) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser246(245)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ala241(240)A (main-C) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser246(245)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Ala241(240)A (main-C) | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Ser246(245)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu360(359)A | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
Chemical Components
redox reaction, decoordination from a metal ion
Step 2. Molecular oxygen binds to Fe(II) to form the oxyferrous intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys351(350)A | metal ligand |
| Ala241(240)A (main-C) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser246(245)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu360(359)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ala241(240)A (main-C) | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Ser246(245)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu360(359)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Ala241(240)A (main-C) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser246(245)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu360(359)A | hydrogen bond donor |
Chemical Components
coordination to a metal ion, redox reactionCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys351(350)A | metal ligand |
| Ala241(240)A (main-C) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser246(245)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu360(359)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ala241(240)A (main-C) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser246(245)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu360(359)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Ala241(240)A (main-C) | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Ser246(245)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu360(359)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
Chemical Components
redox reaction, electron transfer
Step 4. The peroxy oxygen accepts a proton from the C5 hydroxyl group of 6-DEB.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ala241(240)A (main-C) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser246(245)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu360(359)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ala241(240)A (main-C) | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Ser246(245)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu360(359)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Ala241(240)A (main-C) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser246(245)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu360(359)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser246(245)A | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
proton transfer
Step 5. A second proton transfer is facilitated by a hydrogen bond network involving Ala241, Ser246 and Glu360.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys351(350)A | metal ligand |
| Ser246(245)A | proton relay, proton donor |
| Glu360(359)A | proton donor |
| Ser246(245)A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, proton relay, intermediate formation
Step 6. There is fission of the O-O bond and loss of a water molecule. The proton abstraction from 5-OH by O2 transiently forms a substrate alkoxide. After O–O bond fission, the C5 alkoxide is reprotonated, most likely by the solvent.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys351(350)A | metal ligand |
| Ala241(240)A (main-C) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser246(245)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu360(359)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ala241(240)A (main-C) | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Ser246(245)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu360(359)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Ala241(240)A (main-C) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser246(245)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu360(359)A | hydrogen bond donor |
Chemical Components
heterolysis, proton transfer, proton relay
Step 7. The Fe(IV)-oxo complex undergoes spin inversion to form a radical oxo group which removes a hydrogen from the substrate to form a radical carbon centre and an alcohol group on Fe(IV).
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys351(350)A | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
radical formation, overall reactant used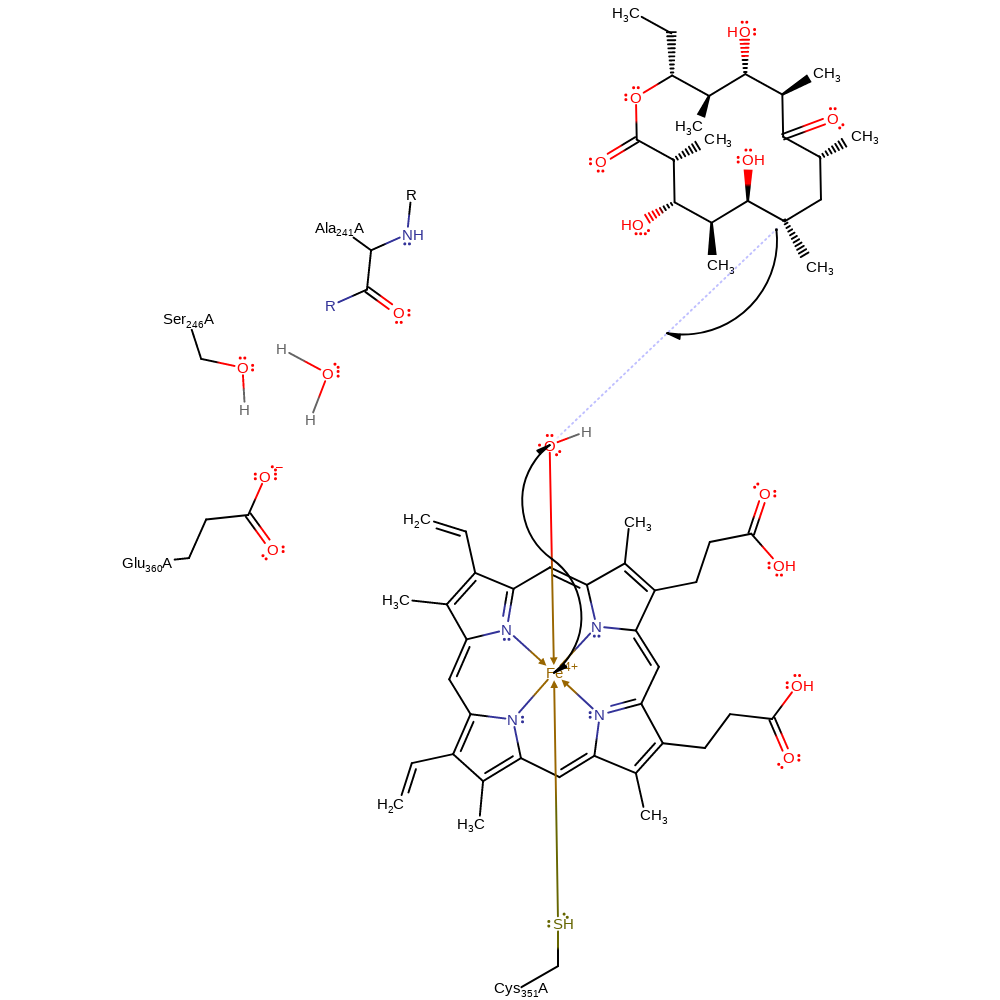
Step 8. The carbon radical attacks the hydroxyl group to form the alcohol product and reduce Fe(IV) to Fe(III).
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys351(350)A | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
overall product formed, radical termination, ingold: aromatic bimolecular nucleophilic additionIntroduction
The catalytic cycle of all cytochrome P450s is conserved. Electrons are delivered to the haem centre by NADH, permitting oxygen reduction. Binding of the substrate promotes electron transfer to P450 haem, reducing the iron from Fe(III) to Fe(II). Dioxygen binds and thus Fe(II) is oxidised back to Fe(III). A second electron is passed to the haem forming a superoxide species, followed by donation of two protons. Catalytic water involved in a Glu244 proton transfer pathway, and uniquely the C5 hydroxyl group of 6-DEB, provide the protons to the distil oxygen. This results in the loss of water and the formation of the low spin Fe(IV) oxo complex. Reprotonation of the catalytic water and 6-DEB after protonation of dioxygen occurs via a hydrogen bonded network presumed to be in contact with the bulk solvent during the course of the reaction. The rebound mechanism forms the alcohol group on the substrate once the oxo group is formed. The Fe(IV)-oxo complex undergoes spin inversion to form a radical oxo group which removes a hydrogen from the substrate to form a radical carbon centre and an alcohol group on Fe(IV). The new radical then attacks the oxygen to form the alcohol group and Fe(III), completing the catalytic cycle.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1oxa) | ||
| Glu244 | Glu244(243)A | Glu244 is involved in the first proton transfer that converts the peroxo to the hydroperoxo intermediate. | hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor, proton relay, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys351 | Cys351(350)A | Coordinated to the Fe ion in heme b. | covalently attached, metal ligand |
Chemical Components
redox reaction, electron transfer, decoordination from a metal ion, coordination to a metal ion, overall reactant used, proton transfer, proton relay, homolysis, overall product formed, radical formation, radical termination, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Sen K et al. (2014), J Phys Chem B, 118, 2810-2820. Role of Two Alternate Water Networks in Compound I Formation in P450eryF. DOI:10.1021/jp411272h. PMID:24564366.
- Nagano S et al. (2005), J Biol Chem, 280, 22102-22107. Crystal Structures of the Ferrous Dioxygen Complex of Wild-type Cytochrome P450eryF and Its Mutants, A245S and A245T: INVESTIGATION OF THE PROTON TRANSFER SYSTEM IN P450eryF. DOI:10.1074/jbc.m501732200. PMID:15824115.
- Cupp-Vickery JR et al. (1996), Nat Struct Biol, 3, 632-637. Substrate-assisted catalysis in cytochrome P450eryF. DOI:10.1038/nsb0796-632. PMID:8673608.
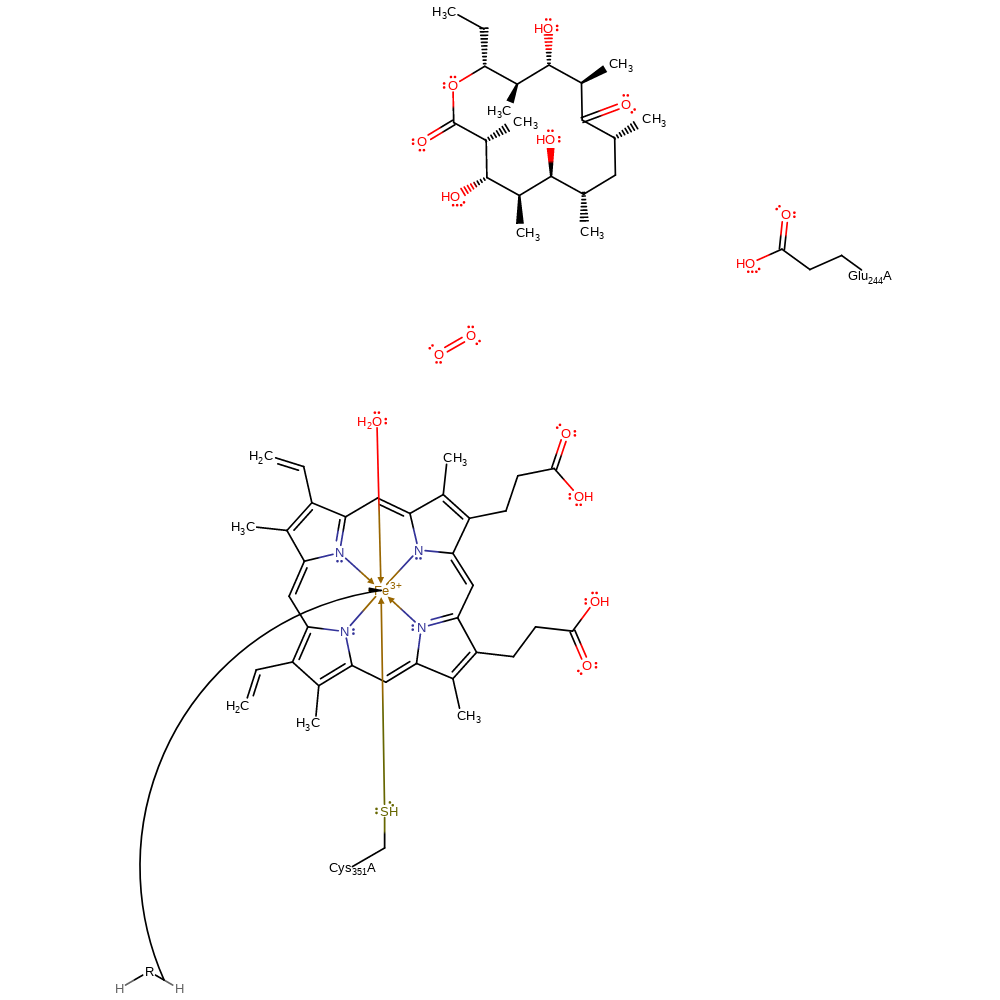
Step 1. After the substrate binds a water molecule is released from the active site which increases the redox potential. This facilitates the first one electron reduction of Fe(III) to Fe(II) by NADPH. Electron transfer is illustrated from a general donor.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys351(350)A | metal ligand |
| Glu244(243)A | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
Chemical Components
redox reaction, electron transfer, decoordination from a metal ion
Step 2. Molecular oxygen binds to Fe(II) to form the oxyferrous intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys351(350)A | metal ligand |
| Glu244(243)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
redox reaction, coordination to a metal ion, overall reactant usedCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys351(350)A | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
redox reaction, electron transfer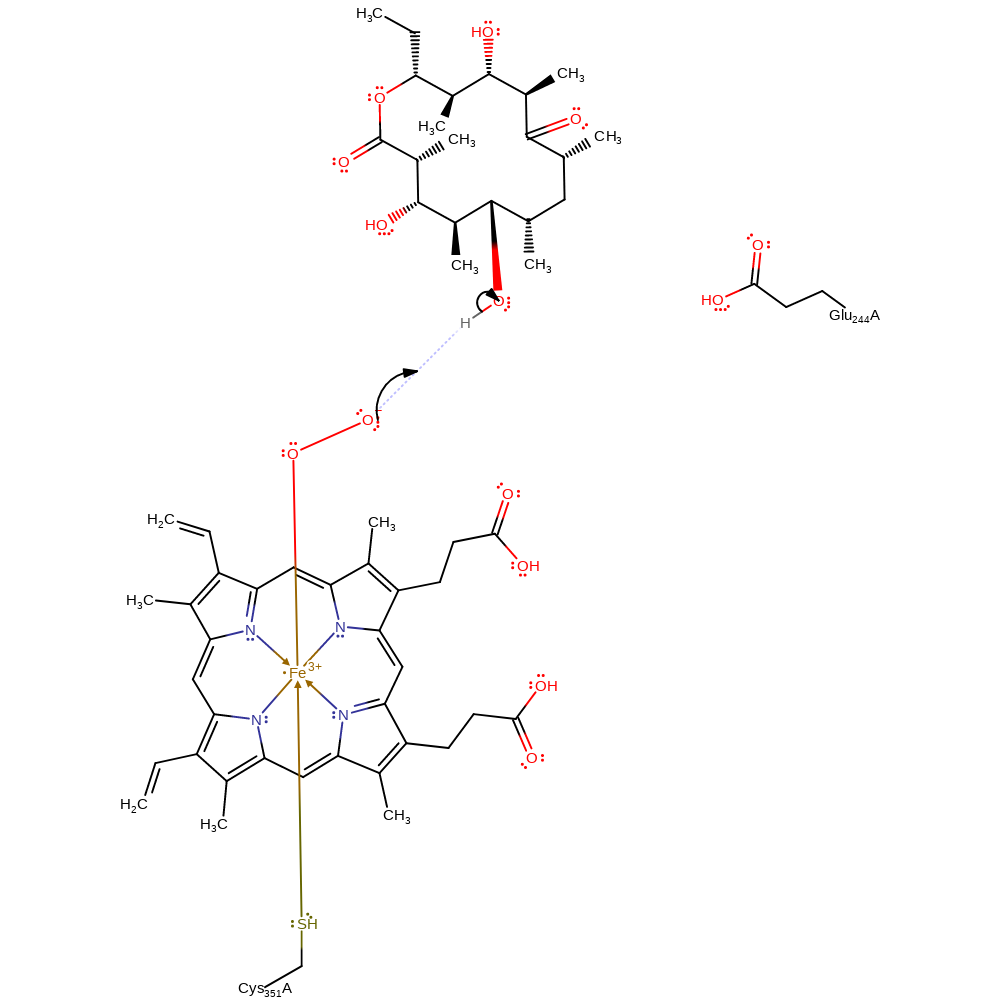
Step 4. The peroxy oxygen accepts a proton from the C5 hydroxyl group of 6-DEB.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys351(350)A | metal ligand |
| Glu244(243)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer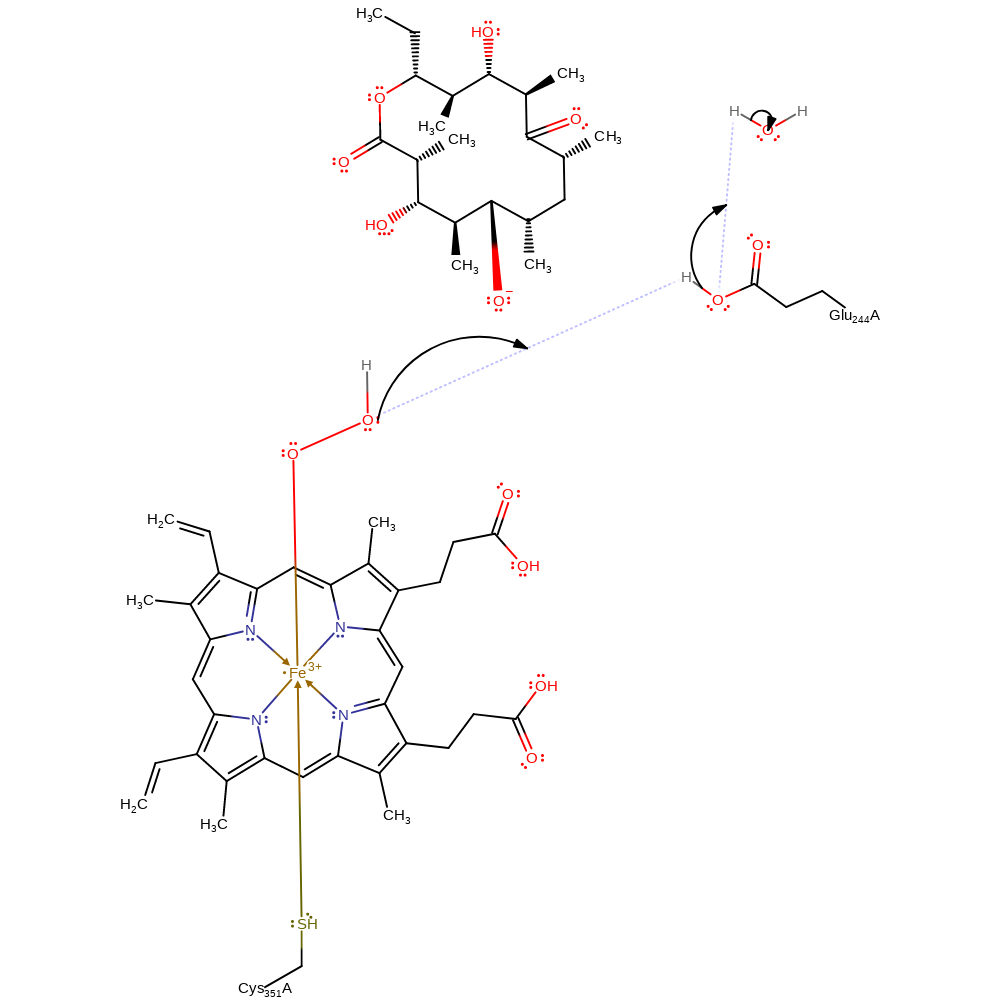
Step 5. A second proton transfer from Glu244 occurs. Glu244 is well connected to bulk water and can easily replenish its proton from bulk water.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys351(350)A | metal ligand |
| Glu244(243)A | proton relay, proton acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, proton relay
Step 6. The O-O bond breaks, releasing water from the metal centre and Fe(III) is oxidised to Fe(IV). The C5 hydroxyl group of DEB is reprotonated. This is likely to be by the solvent.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys351(350)A | metal ligand |
| Glu244(243)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
homolysis, overall product formed, proton transfer, electron transfer, redox reaction
Step 7. The Fe(IV)-oxo complex undergoes spin inversion to form a radical oxo group which removes a hydrogen from the substrate to form a radical carbon centre and an alcohol group on Fe(IV).
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys351(350)A | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
radical formation
Step 8. The carbon radical attacks the hydroxyl group to form the alcohol product and reduce Fe(IV) to Fe(III).
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys351(350)A | covalently attached |







 Download:
Download: 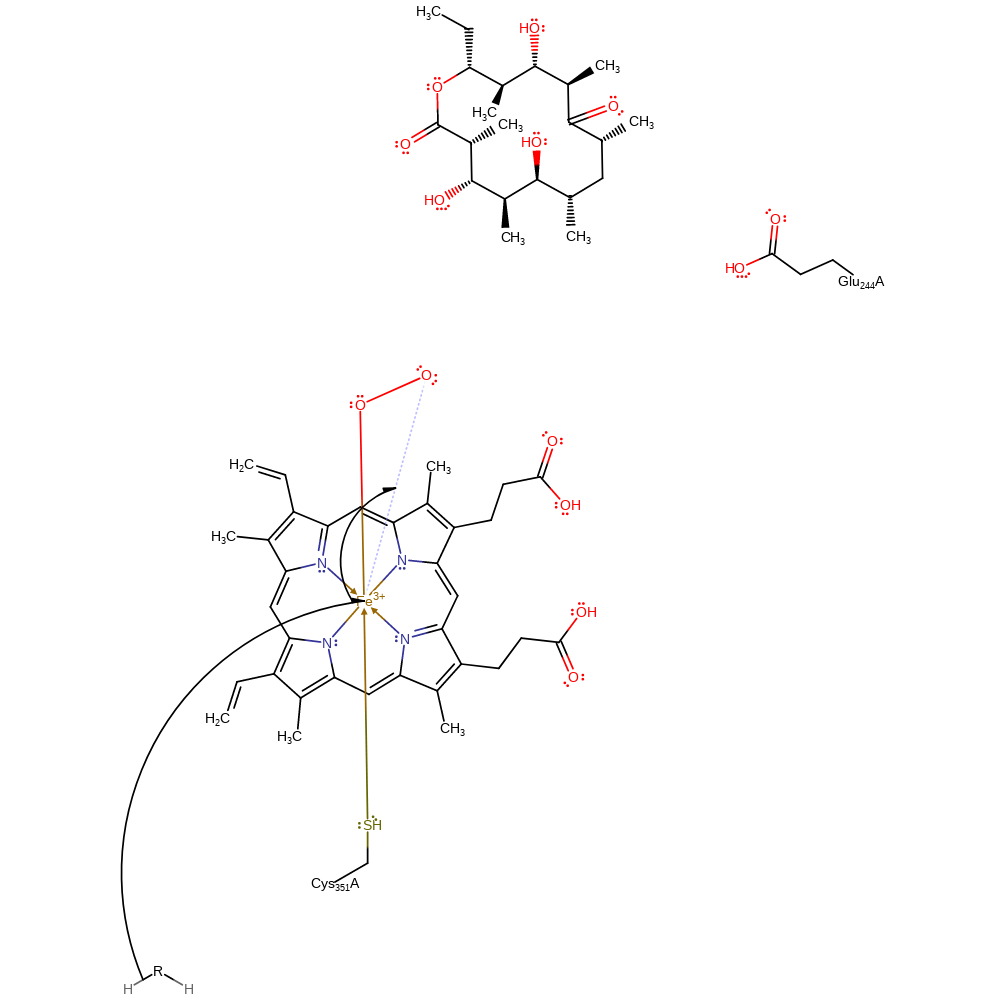
 Download:
Download: