Histone-lysine N-methyltransferase (Suvar3-9 subfamily)
Histone lysine methylation is part of the histone code that regulates chromatin function. Histone lysine methyltransferases (HKMT) differ both in their substrate specificity for the various acceptor lysines as well as in their product specificity for the number of methyl groups (one, two, or three) they transfer. Known targets for HKMT include Lys4, 9, 27, 36, and 79 in histone H3 and Lys20 in histone H4. DIM-5 of N. crassa generates primarily trimethyl Lys9, which marks chromatin regions for DNA methylation.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequences
-
Q8X225
 (2.1.1.355)
(2.1.1.355)
P61830
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Neurospora crassa OR74A (Fungus)

- PDB
-
1peg
- Structural basis for the product specificity of histone lysine methyltransferases
(2.59 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
2.170.270.10
 (see all for 1peg)
(see all for 1peg)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:2.1.1.43)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
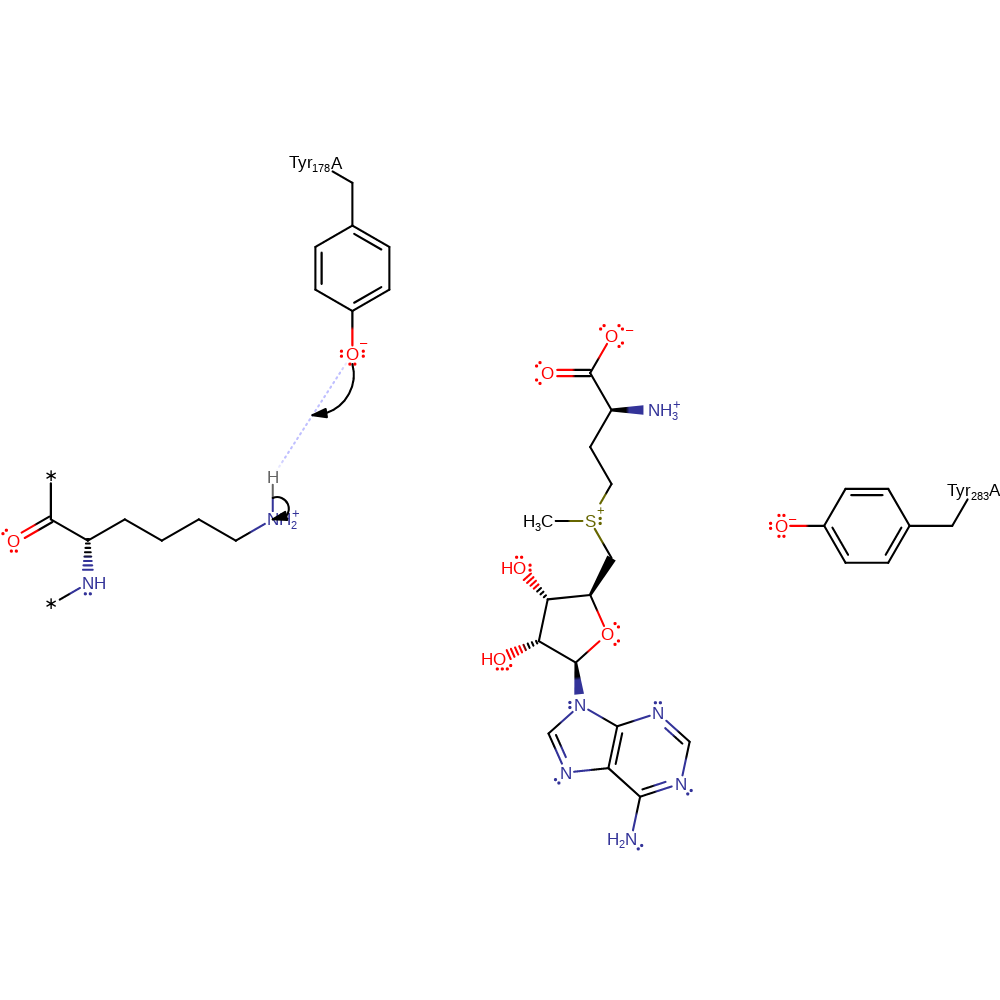
At the optimum pH the catalytic Tyr178 is deprotonated and so able to act as a general base, abstracting a proton from the target lysine in the first round of methylation (or target methyl/dimethyl lysine in subsequent rounds). The lysine may then perform a direct nucleophilic attack on the S=adenosyl-L-methionine (SAM) methyl group. Methyl lysine is formed which, in the case of N. crassa DIM-5, generally remains in the active site while the used cofactor S-adenosyl homocystine (SAH) is exchanged for new SAM.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1peg) | ||
| Tyr296 | Tyr283(267)A | Electrostatic interation with the sulfur on SAM acts to stabilise the charged cofactor. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr191 | Tyr178(162)A | Abstracts a proton from the amine group of the lysine side chain. | proton acceptor, activator, electrostatic stabiliser, proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, overall reactant used, intramolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall product formed, native state of enzyme regenerated, inferred reaction stepReferences
- Zhang X et al. (2003), Mol Cell, 12, 177-185. Structural basis for the product specificity of histone lysine methyltransferases. DOI:10.2210/pdb1peg/pdb. PMID:12887903.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr283(267)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr178(162)A | activator, proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, overall reactant used
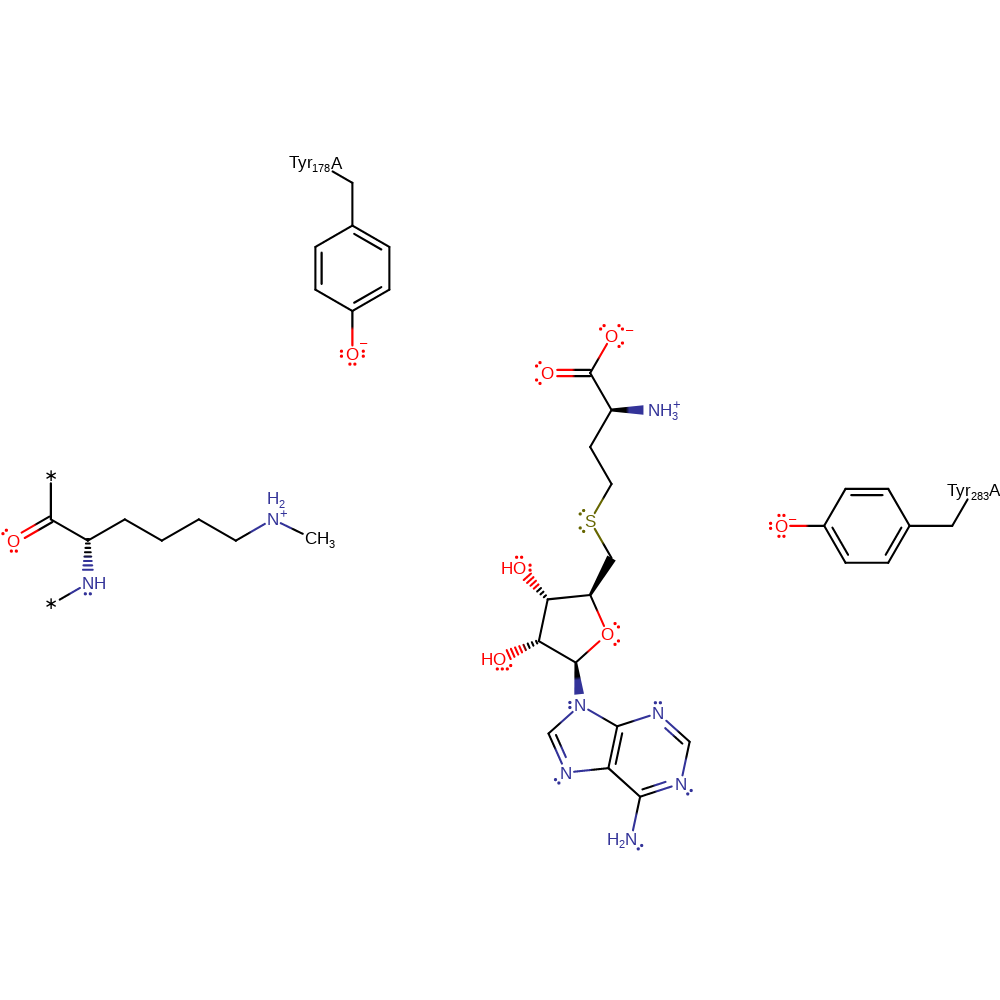
Step 2. In an SN2 reaction the amine group of the lysine residue attacks the methyl of SAM, forming the secondary amine product and SAH.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr178(162)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr283(267)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
ingold: intramolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall product formed
Step 3. In an inferred reaction step Tyr178 is deprotonated to regenerate the native state of the enzyme.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr178(162)A | proton donor |





 Download:
Download: