O-succinylbenzoate synthase
o-Succinylbenzoate synthase (OSBS) is a member of the muconate lactonising enzyme subgroup of the enolase superfamily. It catalyses the exergonic dehydration reaction in the menaquinone biosynthesis pathway in which 2-succinyl-6-hydroxy-2,4-cyclohexadiene-1-carboxylate (SHCHC) is converted to o-succinylbenzoate.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P29208
 (4.2.1.113)
(4.2.1.113)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Escherichia coli K-12 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1r6w
- Crystal structure of the K133R mutant of o-Succinylbenzoate synthase (OSBS) from Escherichia coli. Complex with SHCHC
(1.62 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.20.20.120
 (see all for 1r6w)
(see all for 1r6w)
- Cofactors
- Magnesium(2+) (1)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:4.2.1.113)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The dehydration is initiated by the abstraction of a proton from the C1, the carbon adjacent to the carboxylate group by Lys133, forming an enediolate anion intermediate. The negatively charged intermediate is stabilised by Lys235 through a cation-pi interaction to the cyclohexadienyl moiety and by Mg(II) ion through a bidentate coordination to the carboxylate group. Lys133 is also responsible for protonation of the departing water molecule.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1r6w) | ||
| Lys133 | Arg133(135)A | It removes a proton from C1 to initiate the dehydration. It then donates a proton to the departing water molecule. | proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Asp161, Glu190, Asp213 | Asp161(163)A, Glu190(192)A, Asp213(215)A | Forms part of the magnesium binding site. | metal ligand |
| Lys235 | Lys235(237)A | It stabilises the transition state by the a cation-pi interaction with the enediolate intermediate. | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, overall reactant used, dehydration, aromatic unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, overall product formed, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Klenchin VA et al. (2003), Biochemistry, 42, 14427-14433. Evolution of Enzymatic Activity in the Enolase Superfamily: Structural and Mutagenic Studies of the Mechanism of the Reaction Catalyzed byo-Succinylbenzoate Synthase fromEscherichia coli†,‡. DOI:10.1021/bi035545v. PMID:14661953.
- Sánchez-Tarín M et al. (2015), J Phys Chem B, 119, 1899-1911. Enzyme promiscuity in enolase superfamily. Theoretical study of o-succinylbenzoate synthase using QM/MM methods. DOI:10.1021/jp511147b. PMID:25556698.
- Zhu WW et al. (2012), Biochemistry, 51, 6171-6181. Residues required for activity in Escherichia coli o-succinylbenzoate synthase (OSBS) are not conserved in all OSBS enzymes. DOI:10.1021/bi300753j. PMID:22775324.
- Thompson TB et al. (2000), Biochemistry, 39, 10662-10676. Evolution of enzymatic activity in the enolase superfamily: structure of o-succinylbenzoate synthase from Escherichia coli in complex with Mg2+ and o-succinylbenzoate. PMID:10978150.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys235(237)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu190(192)A | metal ligand |
| Asp161(163)A | metal ligand |
| Asp213(215)A | metal ligand |
| Arg133(135)A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, overall reactant used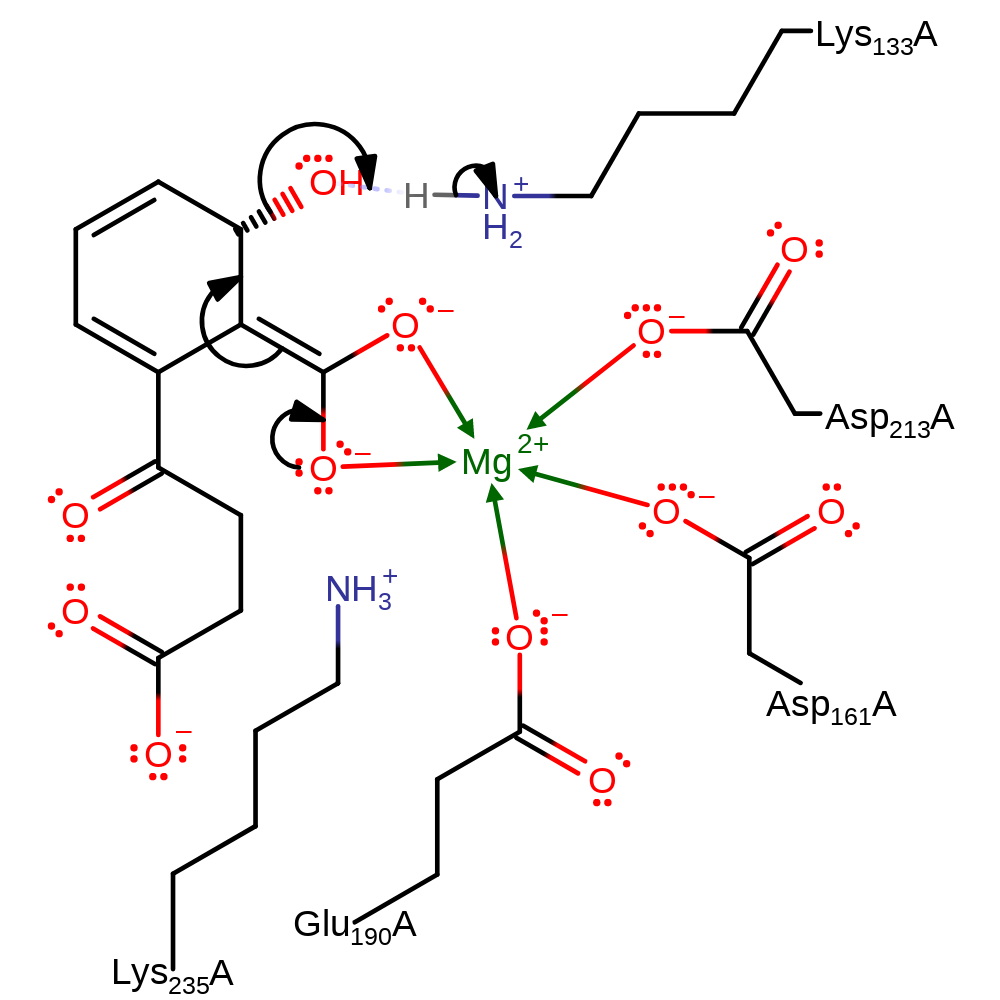
Step 2. The intermediate eliminates water with concomitant deprotonation of Lys133 to form the final product and regenerate the enzyme's active site.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu190(192)A | metal ligand |
| Asp161(163)A | metal ligand |
| Asp213(215)A | metal ligand |
| Lys235(237)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg133(135)A | proton donor |




 Download:
Download: