Classical-complement-pathway C3/C5 convertase
C3/C5 convertase is part of the complement system which is a major defence system in blood plasma against pathogens. The pathway activates the proteases C3 and C5 convertase which cleave proteins C3 and C5 respectively so that the cleaved products can attract phagocytes to the site of infection and tags target cells for elimination by phagocytosis. Also C5 convertase initiates the terminal phase of the complement system, leading to the assembly of the membrane attack complex (MAC). The membrane attack complex creates a pore on the target cell's membrane, inducing cell lysis and death.
Both C3 and C5 convertase are made up of the subunits, C2a and C4b. However, C5 convertase in addition to these subunits also has the cleaved product of C3 convertase, C3b, which enables C5 convertase to cleave C5 components. The catalytic subunit of the convertase is C2a which displays the classic serine protease catalytic triad of serine, histidine and aspartate which are key for the mechanism of hydrolysis of peptide bonds with this convertase being specific to Arg-Ser bonds.
Interestingly both C3b and C4b subunits contain a specific binding component on their alpha-chain, a thiolacetone ring, made up of the residues -Cys-Gly-Glu-Gln- which can react with hydroxyl or amino groups and enable the binding of this subunit to other molecules, including membranes and other protein subunits. The thiolacetone ring is usually buried in the protein however after cleavage of the alpha-chain by a protease it is exposed and so is liable to attack by nucleophiles such as hydroxyl and amino groups. Both the C4b and C3b subunit of C3/C5 convertases serve as a platform for the assembly of the proteolytically active convertases that mediate downstream activation of the complement system by cleavage of C3 and C5.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
Q5JP69

 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Homo sapiens (Human)

- PDB
-
2odq
- Complement component C2a, the catalytic fragment of C3- and C5-convertase of human complement
(2.3 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
2.40.10.10
 (see all for 2odq)
(see all for 2odq)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:3.4.21.43)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The catalytic subunit of C3/C5 convertases, C2a, is a serine protease and contains the key catalytic triad of serine, histidine and aspartate. His 507 acts as a general acid/base which is enabled by the hydrogen bonding to Asp 561 which lowers the pKa of Histidine so that it accepts a proton more willingly. This proton is donated by Ser 679 and upon deprotonation Ser 679 is activated and can nucleophilically attack the carbon of the peptide bond forming the oxyanion intermediate. The negative charge of the oxyanion is stabilised by the oxyanion hole which is made up of the amide backbone of Ser 679. Upon protonation of the nitrogen of the peptide bond the tetrahedral intermediate collapse releasing the serine product. The acylenzyme intermediate is hydrolysed by a water molecule, activated by His 507, to release the arginine product and restore the enzyme to its active state.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (2odq) | ||
| Asp561 | Asp541(318)A | Stabilises His 507 through hydrogen bonding which lowers histidine's pKa so it more readily accepts a proton. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His507 | His487(264)A | Acts as general acid/base and through deprotonation of Ser 679 and water, activates each of these molecules so that they in turn can act as a nucleophile. | proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Ser679 | Ser659(436)A | When activated by His 507, serves as a nucleophile which attacks the substrate carbonyl. | nucleofuge, nucleophile, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Ser679 (main-N) | Ser659(436)A (main-N) | Forms the oxyanion hole and stabilises the negative charge of the oxyanion through hydrogen bonding. | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, rate-determining step, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate collapse, overall product formed, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Krishnan V et al. (2007), J Mol Biol, 367, 224-233. The crystal structure of C2a, the catalytic fragment of classical pathway C3 and C5 convertase of human complement. DOI:10.1016/j.jmb.2006.12.039. PMID:17234210.
- Rawal N et al. (2003), J Biol Chem, 278, 38476-38483. Formation of high affinity C5 convertase of the classical pathway of complement. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M307017200. PMID:12878586.

Step 1. His 507 deprotonates Ser 679 which activates it to nucleophilically attack the carbon of the carbonyl to produce the oxyanion intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp541(318)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser659(436)A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His487(264)A | proton acceptor |
| Ser659(436)A | proton donor, nucleophile |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, rate-determining step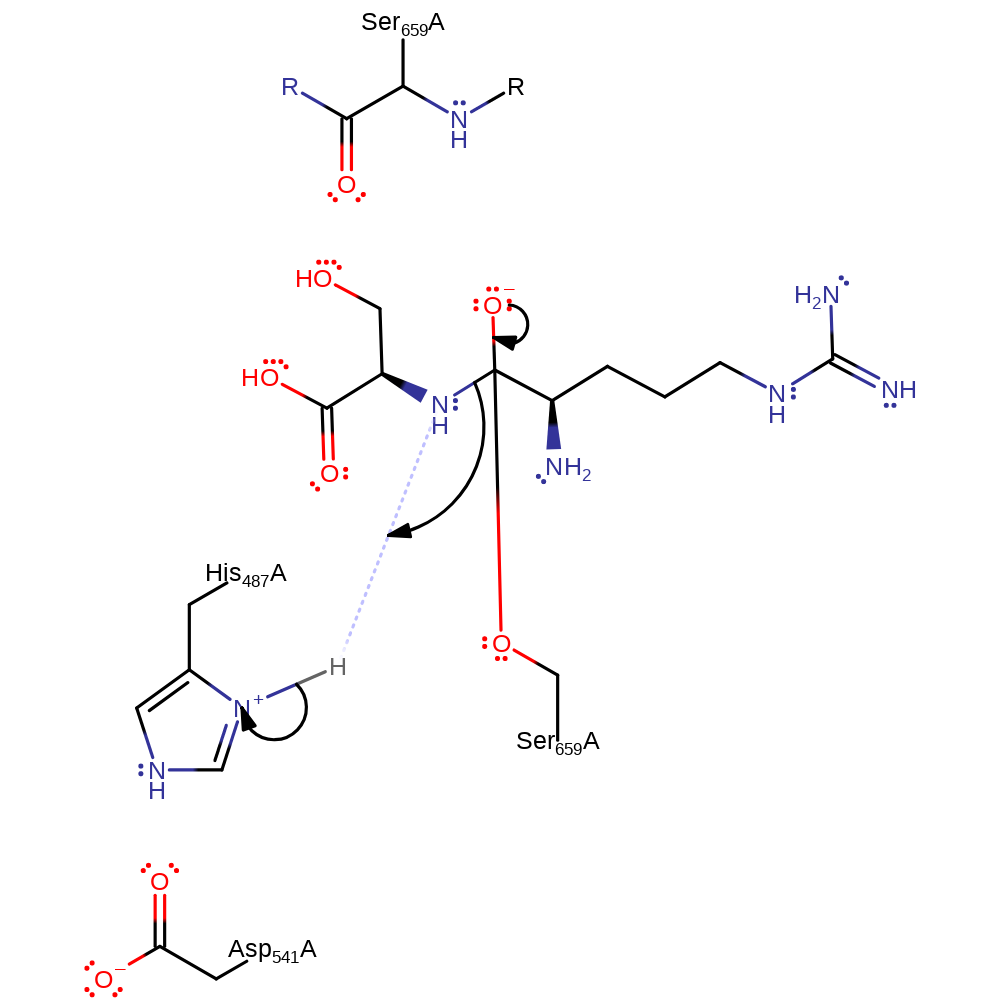
Step 2. The tetrahedral intermediate collapse upon protonation of the amine by His 507 which releases the serine product and forms the acyl-enzyme.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp541(318)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser659(436)A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His487(264)A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate collapse, overall product formed
Step 3. His 507 abstracts a proton from a water which activates it to attack the carbon of the ester bond in a nucleophilic addition and once again produces the oxyanion intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp541(318)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser659(436)A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His487(264)A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, overall reactant used
Step 4. The tetrahedral intermediate once again collapse releasing Ser 679 and the Arginine product. Ser 679 then accepts a proton from His 507 which returns the active site to its native state.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp541(318)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser659(436)A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser659(436)A | proton acceptor |
| His487(264)A | proton donor |
| Ser659(436)A | nucleofuge |




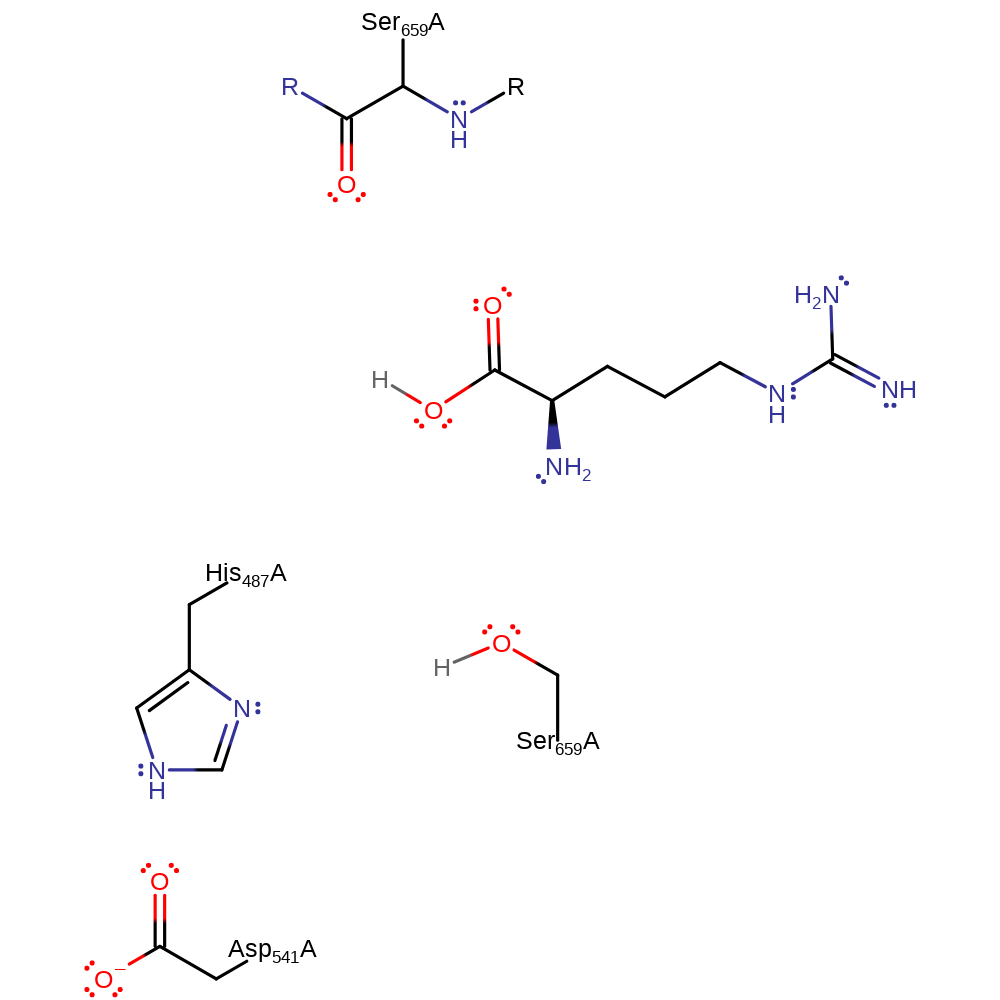 Download:
Download: