Anthocyanidin synthase
The 2-oxoglutarate dependent enzyme anthocyanidin synthase is able to catalyse the synthesis of anthocyanidin from quercetin, a vital step in the synthesis of flavoids and flavones in plant cells. The reaction is coupled to the decarboxylation of 2-oxoglutarate to form succinate. It is part of the family of 2OG dependent non-haem iron oxygenases, which use 2-oxoglutarate as a cosubstrate and Iron (II) as a cofactor in their reaction mechanisms. The enzyme is of particular interest to geneticists as a mutated form is responsible for the original tall/dwarf dimorphism observed in peas by Mendel.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
Q96323
 (1.14.20.4)
(1.14.20.4)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Arabidopsis thaliana (Thale cress)

- PDB
-
1gp5
- Anthocyanidin synthase from Arabidopsis thaliana complexed with trans-dihydroquercetin
(2.2 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
2.60.120.330
 (see all for 1gp5)
(see all for 1gp5)
- Cofactors
- Iron(3+) (1)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:1.14.20.4)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
In the first stage of the reaction the iron (II) ion acts as a nucleophile to attack molecular oxygen, thus reducing it to a peroxide radical, and oxidising iron (II) to iron (III). The radical then reacts with the 2C of the 2 oxoglutarate to create an unstable intermediate which loses CO2 to give iron IV with a double bond formed to oxygen. The reduction of iron to Fe (III) then allows the double bond to break, so that the oxygen can strip a proton from the substrate quercetin to leave a radical. The radical then allows the OH to break its bond to the iron, forming iron (II) and an acetal. Deprotonation of the acetal by Lys 213 results in the return of the OH to the Iron (II), now acting as a Lewis acid, and forms the product Anthocyanidin.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1gp5) | ||
| His232, His288, Asp234 | His232A, His288A, Asp234A | The residues are coordinated to the Fe(II) ion centre. | metal ligand |
| Lys213 | Lys213A | Deprotonates quercetin to allow a double bond to form so that dehydration occurs resulting in the Anthrocyadin product. | proton relay, proton acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
electron transfer, coordination to a metal ion, intermediate formation, decarboxylation, overall product formed, intermediate collapse, radical formation, radical termination, bimolecular elimination, keto-enol tautomerisation, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Wilmouth RC et al. (2002), Structure, 10, 93-103. Structure and Mechanism of Anthocyanidin Synthase from Arabidopsis thaliana. DOI:10.1016/s0969-2126(01)00695-5. PMID:11796114.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His232A | metal ligand |
| Asp234A | metal ligand |
| His288A | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
electron transfer, coordination to a metal ionCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His232A | metal ligand |
| Asp234A | metal ligand |
| His288A | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
intermediate formation, electron transfer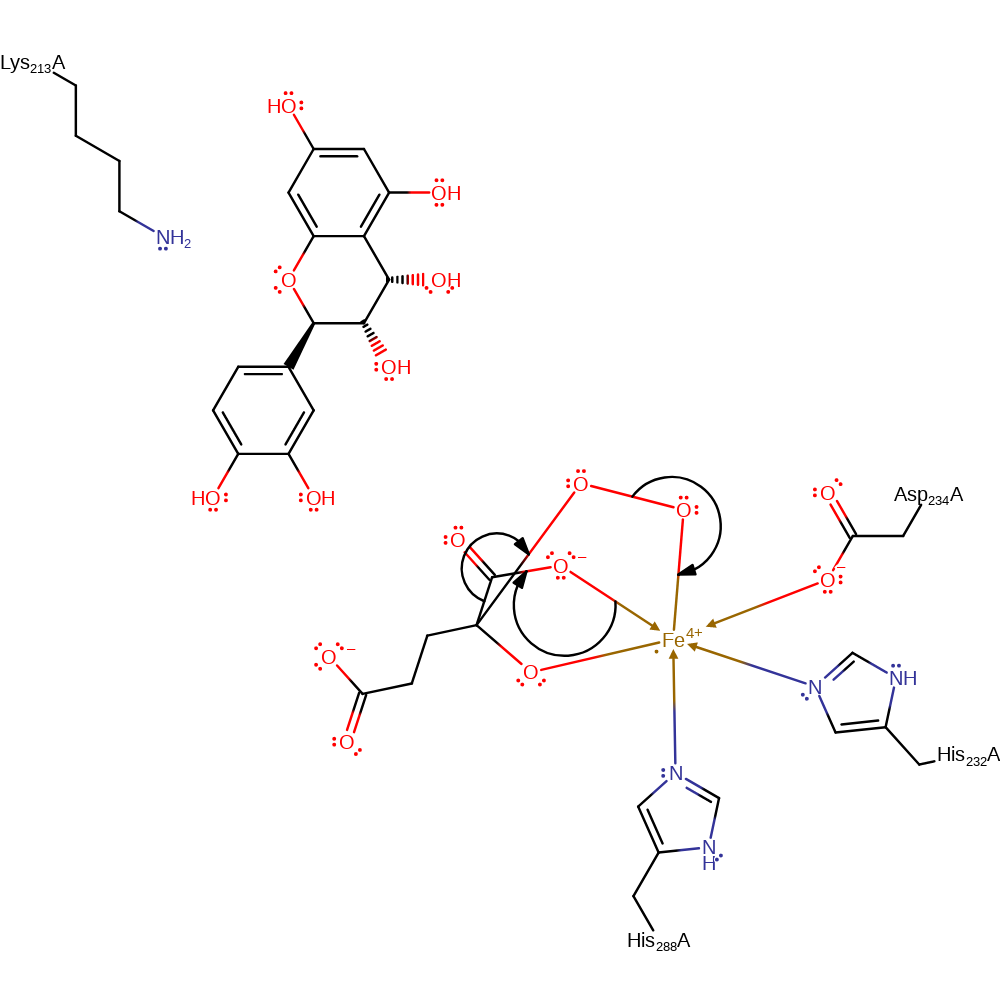
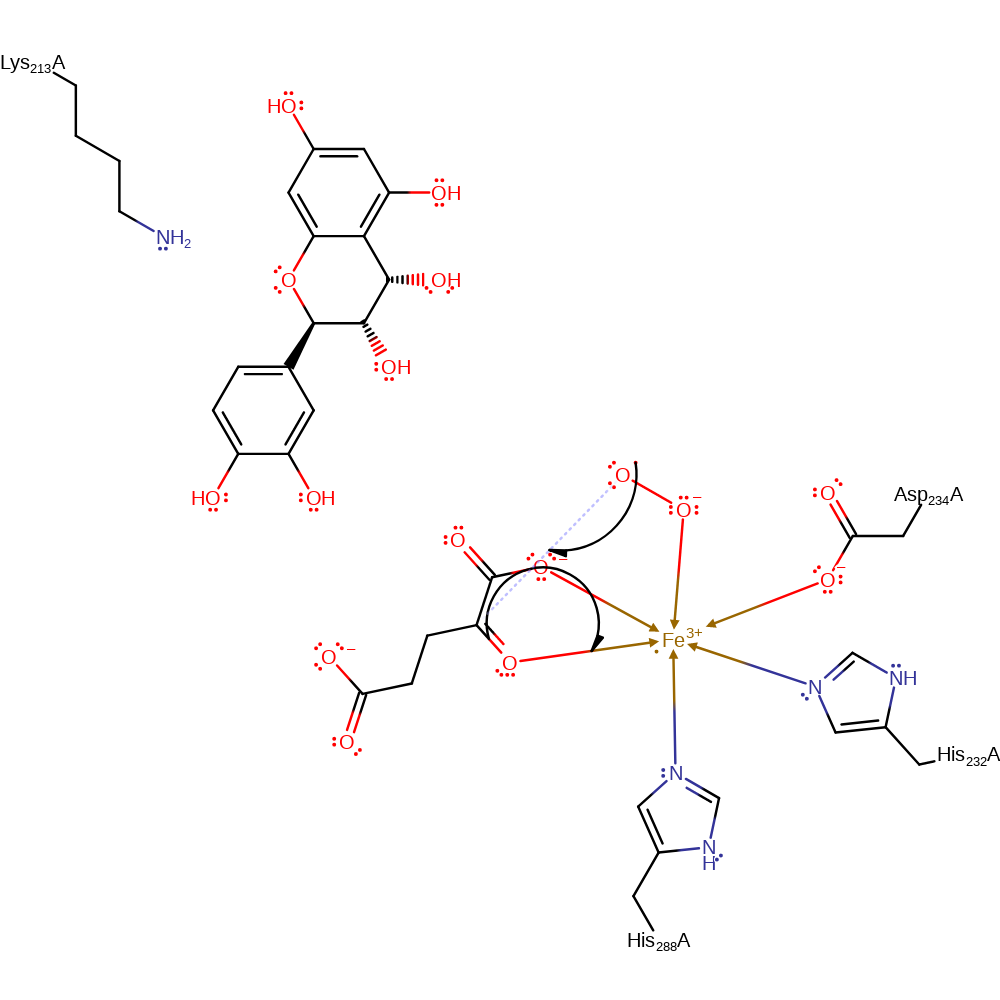
Step 3. There is oxidative decarboxylation, resulting in the formation of succinate, CO2 and the ferryl species.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His232A | metal ligand |
| Asp234A | metal ligand |
| His288A | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
decarboxylation, overall product formed, intermediate collapse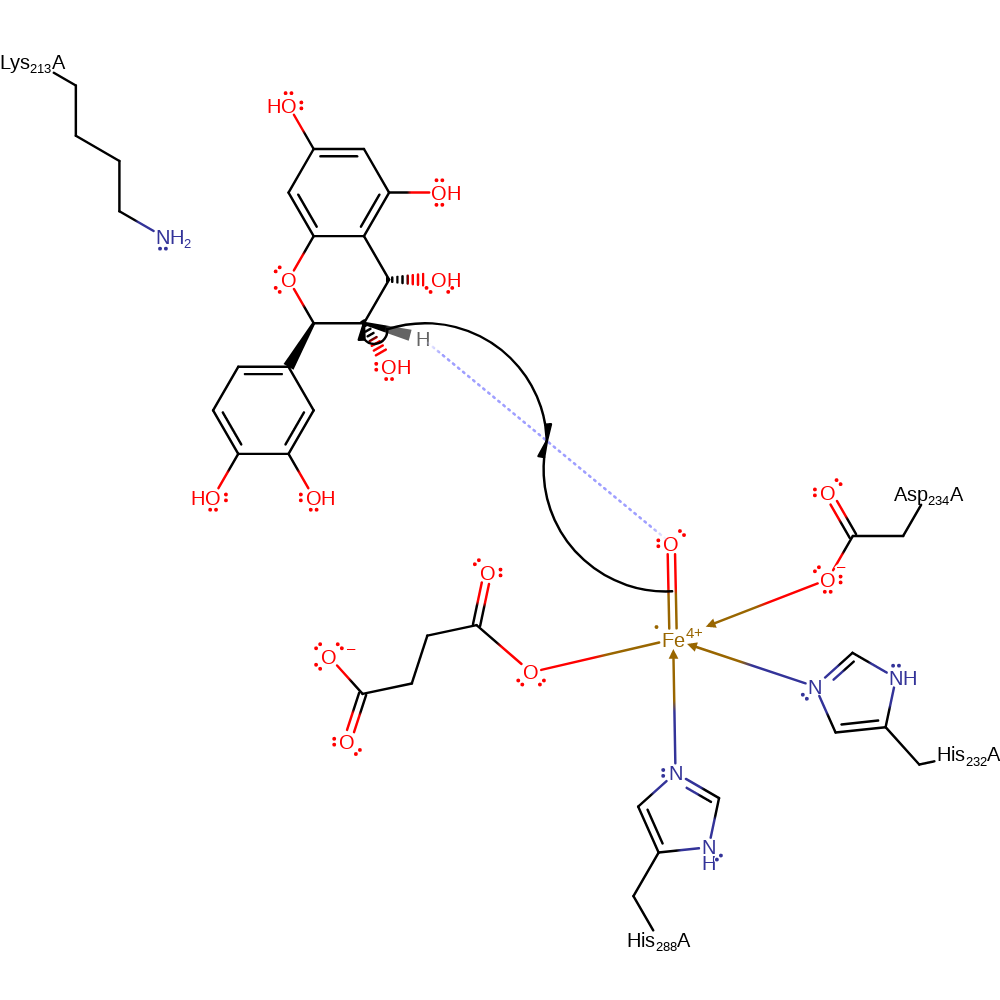
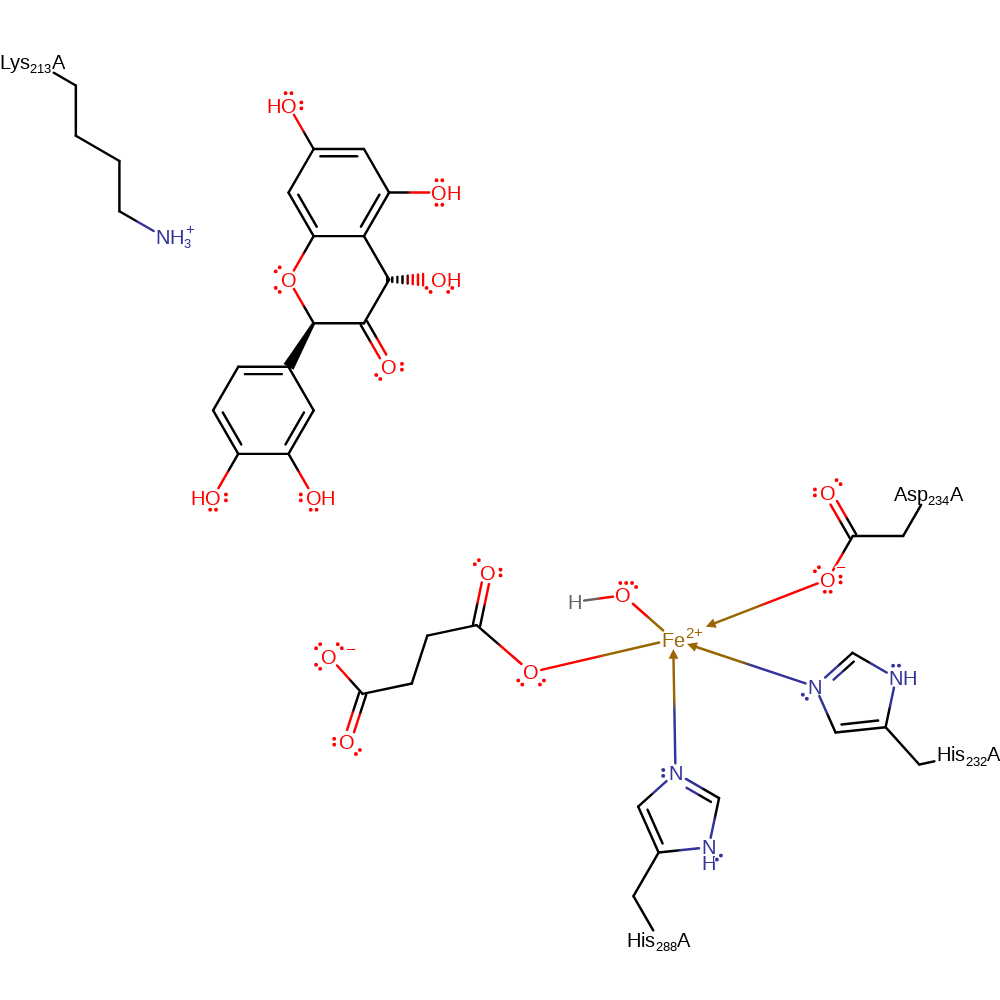
Step 4. The ferryl oxygen abstracts a proton from leucocyanidin to form a radical intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His232A | metal ligand |
| Asp234A | metal ligand |
| His288A | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
radical formation, intermediate formation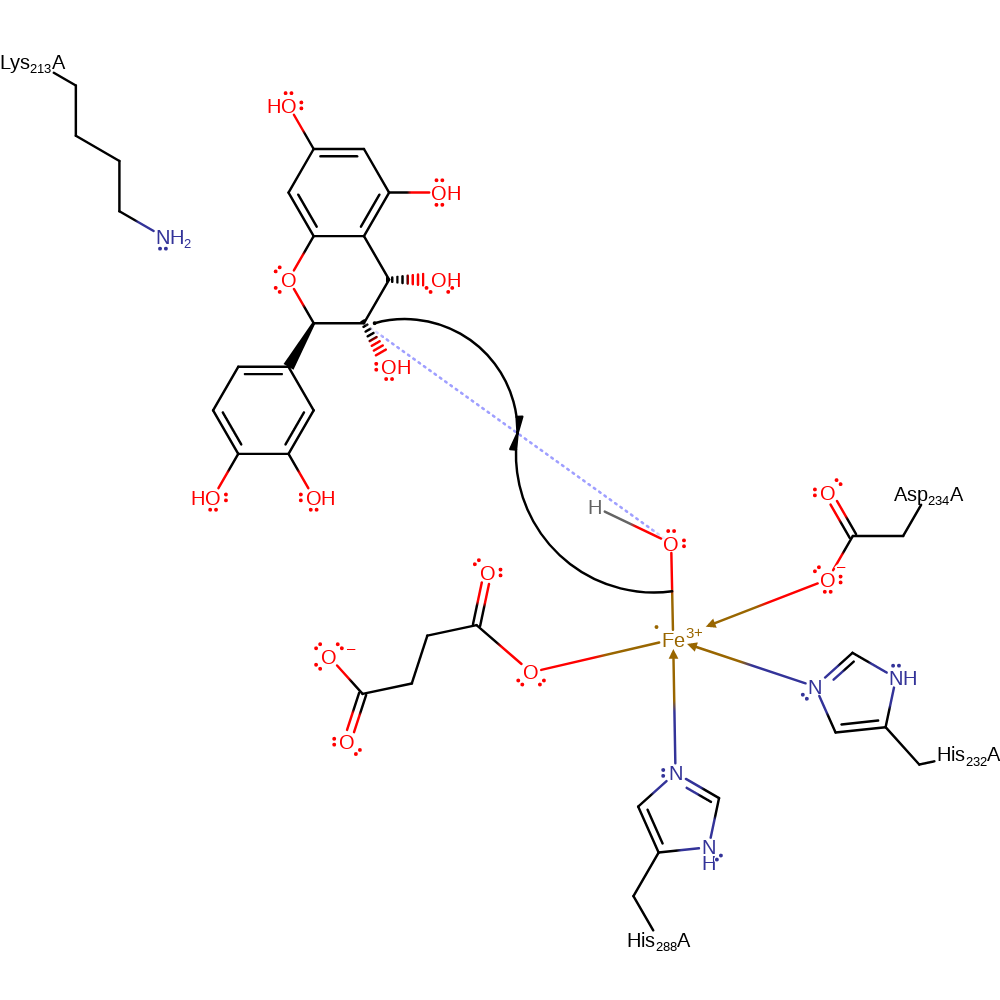
Step 5. The hydroxide adds to the radical intermediate, reducing Fe(III) to Fe(II) and forming an acetal.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His232A | metal ligand |
| Asp234A | metal ligand |
| His288A | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
radical termination, intermediate formation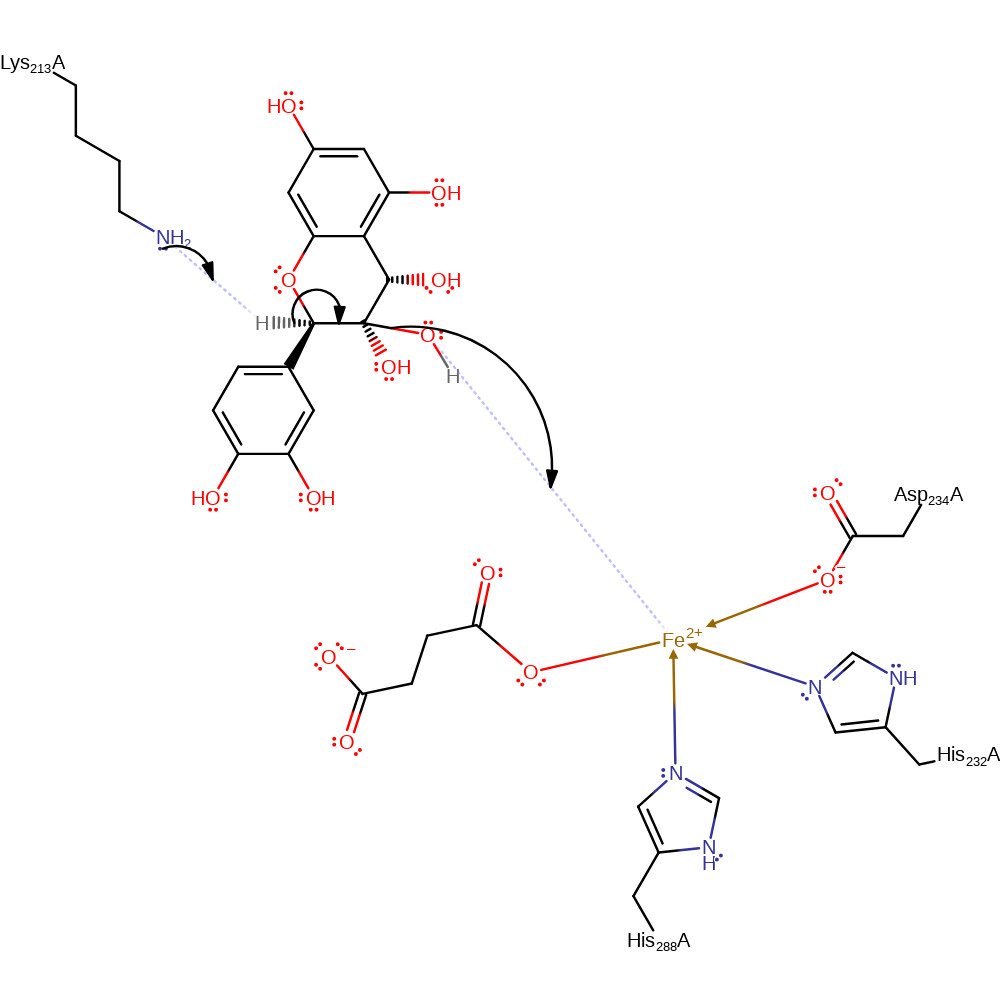
Step 6. Lys213 acts as a base to deprotonate the acetal intermediate, causing the elimination of the hydroxyl and formation of a carbon-carbon double bond.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His232A | metal ligand |
| Asp234A | metal ligand |
| His288A | metal ligand |
| Lys213A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular elimination, overall product formed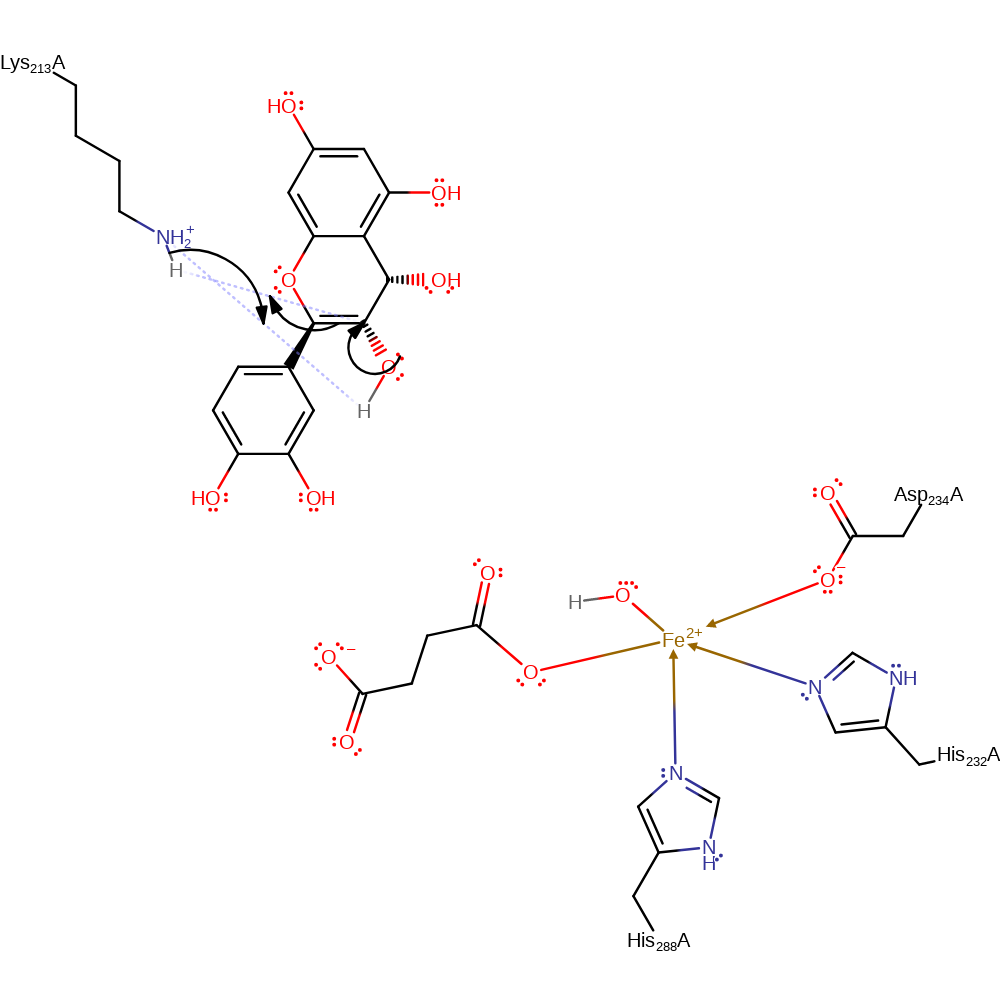
Step 7. In an inferred step the product of step 6 tautomerises to form the taxifolin product. The succinate product and hydroxyl are released from the Fe(II) centre and the native state of the enzyme is restored.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His232A | metal ligand |
| Asp234A | metal ligand |
| His288A | metal ligand |
| Lys213A | proton relay, proton donor, proton acceptor |







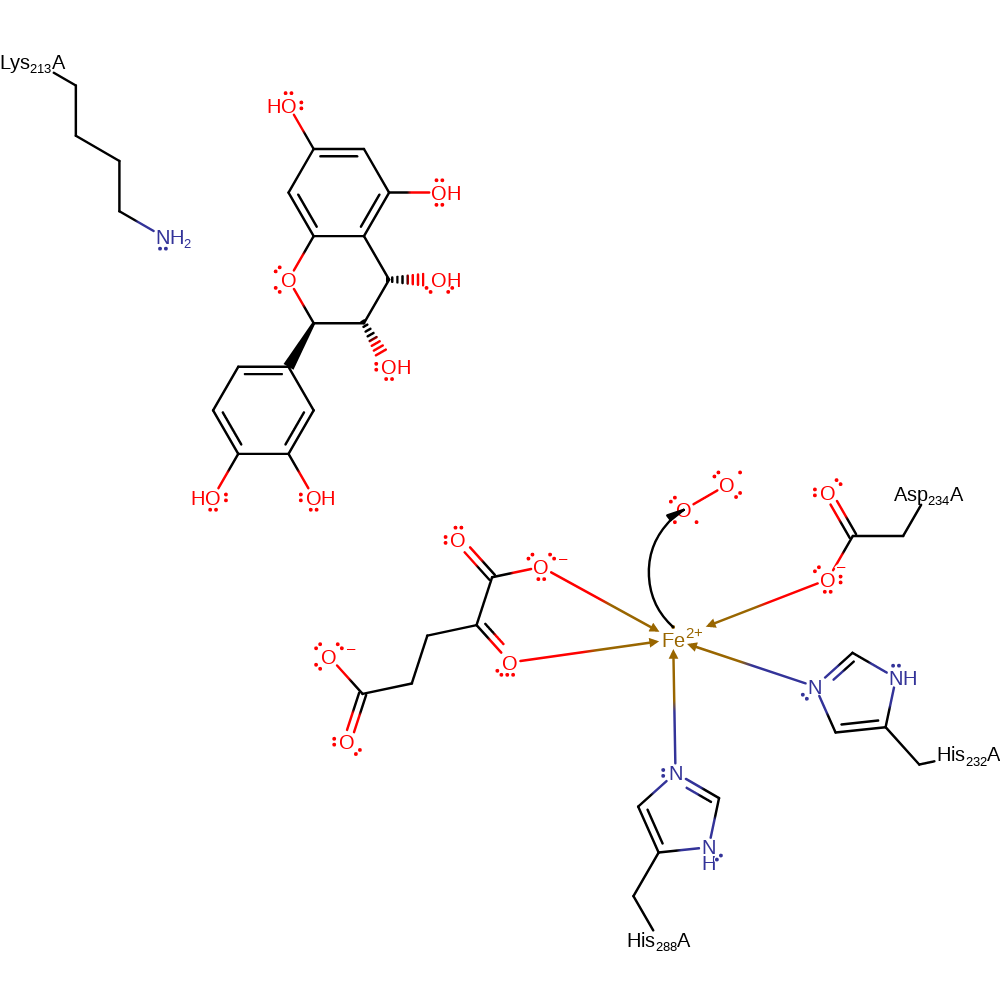
 Download:
Download: