Mannuronate-specific alginate lyase
The enzyme alginate lyase from the bacteria Sphingomonas sp. is able to degrade the polymer alginate by eliminative cleavage. Alginate is made up of beta-d-mannuronate and beta-d-glucoronate linked together by a beta-1-4 glycosidic linkage, and alginate lyase is able to cleave this linkage to release two oligosaccharides. The enzyme may have potential therapeutic applications because one of the symptoms of cystic fibrosis is a thick layer of alginate that builds up inside the lungs making breathing difficult. The bacterial species produces three types of Alginate lyase, which are non-homologous but display similar organisation in the active site, suggesting that convergent evolution may account for their similar functions. Here, the structure and mechanism of Alginate lyase III is described.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
Q9KWU1

 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Sphingomonas sp. (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1qaz
- CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF ALGINATE LYASE A1-III FROM SPHINGOMONAS SPECIES A1 AT 1.78A RESOLUTION
(1.78 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
1.50.10.100
 (see all for 1qaz)
(see all for 1qaz)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:4.2.2.3)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
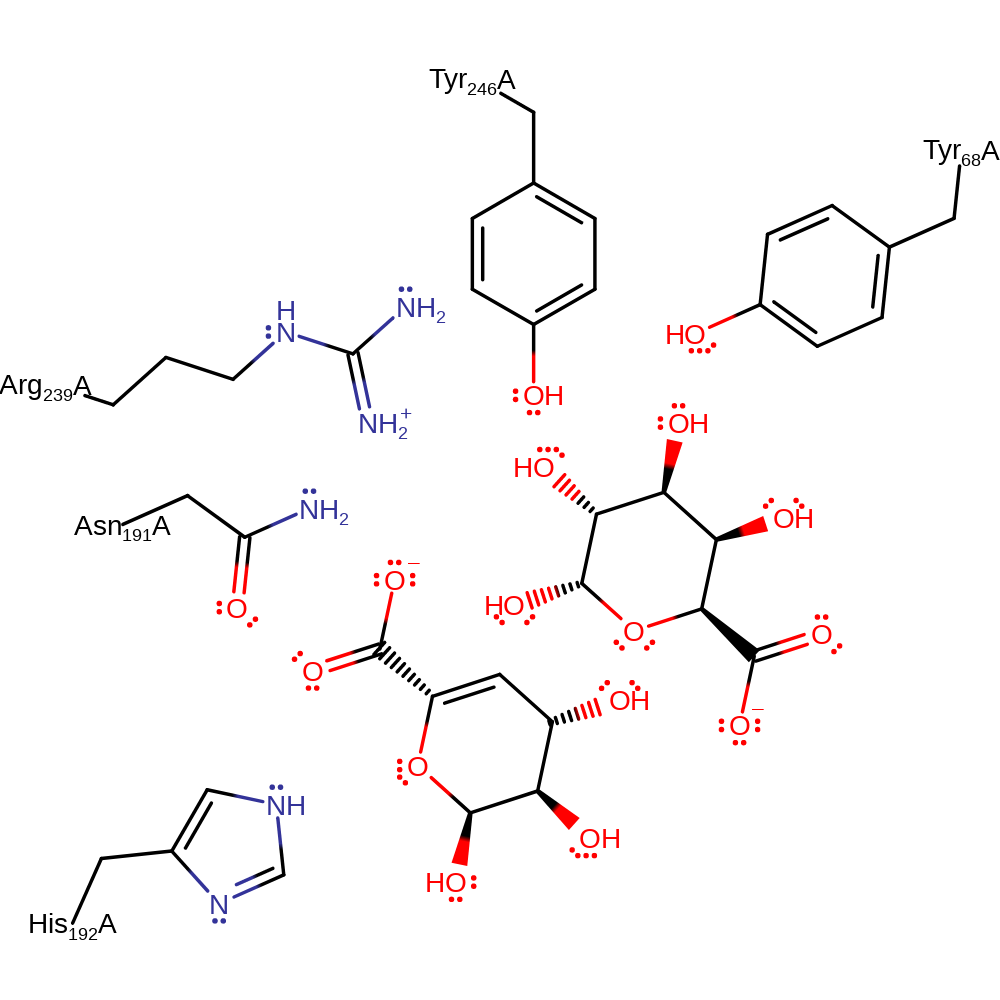
The alginate substrate is cleaved by elimination. To this end, Tyr 294 acts as a base for deprotonation of the mannuronate moiety at C5 resulting in a carbanion whose negative charge can be delocalised through the carboxylate group and is stabilised by Arg 287 and Asn 239. Arg 287 also acts to lower the pKa of Tyr 294 so that more molecules are in the ionised state at physiological pH. In addition Tyr 294 is stabilised by hydrogen bonding to Tyr 116 in the closed lid loop (which can only occur when the protein is in the closed lid form) which lowers the pKa of Tyr 294 which accelerates proton transfer. The bridging oxygen is then protonated by Tyr 294 to allow the cleavage of the glycosidic bond, resulting in the formation of a C4-C5 double bond. This releases the two oligosaccharide products.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1qaz) | ||
| His240 | His192(189)A | Hydrogen bonds to O2 and O5 mannuronate and causes slight distortion of the sugar ring to enable hydrogen abstraction. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr116 | Tyr68(65)A | When in the closed lid conformation Tyr 116 hydrogen bonds to Tyr 294 which lowers the pKa of Tyr 294 by stabilising the deprotonated form thereby accelerating proton transfer. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn239 | Asn191(188)A | Stabilises the carbanion transition state through electrostatic contacts. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg287 | Arg239(236)A | Stabilises the carbanion intermediate through electrostatic contacts. Also acts to lower the pKa of Tyr 294 thus allowing it to act as a base at physiological pH. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr294 | Tyr246(243)A | Acts as general base to deprotonate the 5 carbon. Then acts as general acid to protonate the bridging oxygen, allowing cleavage of the glycosidic bond. | proton relay, proton acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate formation, intermediate collapse, overall reactant used, overall product formedReferences
- Yoon HJ et al. (2001), J Mol Biol, 307, 9-16. Crystal structure of alginate lyase A1-III complexed with trisaccharide product at 2.0 Å resolution. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.2000.4509. PMID:11243798.
- Xu F et al. (2018), Appl Environ Microbiol, 84,Diversity of Three-Dimensional Structures and Catalytic Mechanisms of Alginate Lyases. DOI:10.1128/AEM.02040-17. PMID:29150496.
- Mikami B et al. (2012), Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr, 68, 1207-1216. Induced-fit motion of a lid loop involved in catalysis in alginate lyase A1-III. DOI:10.1107/S090744491202495X. PMID:22948922.
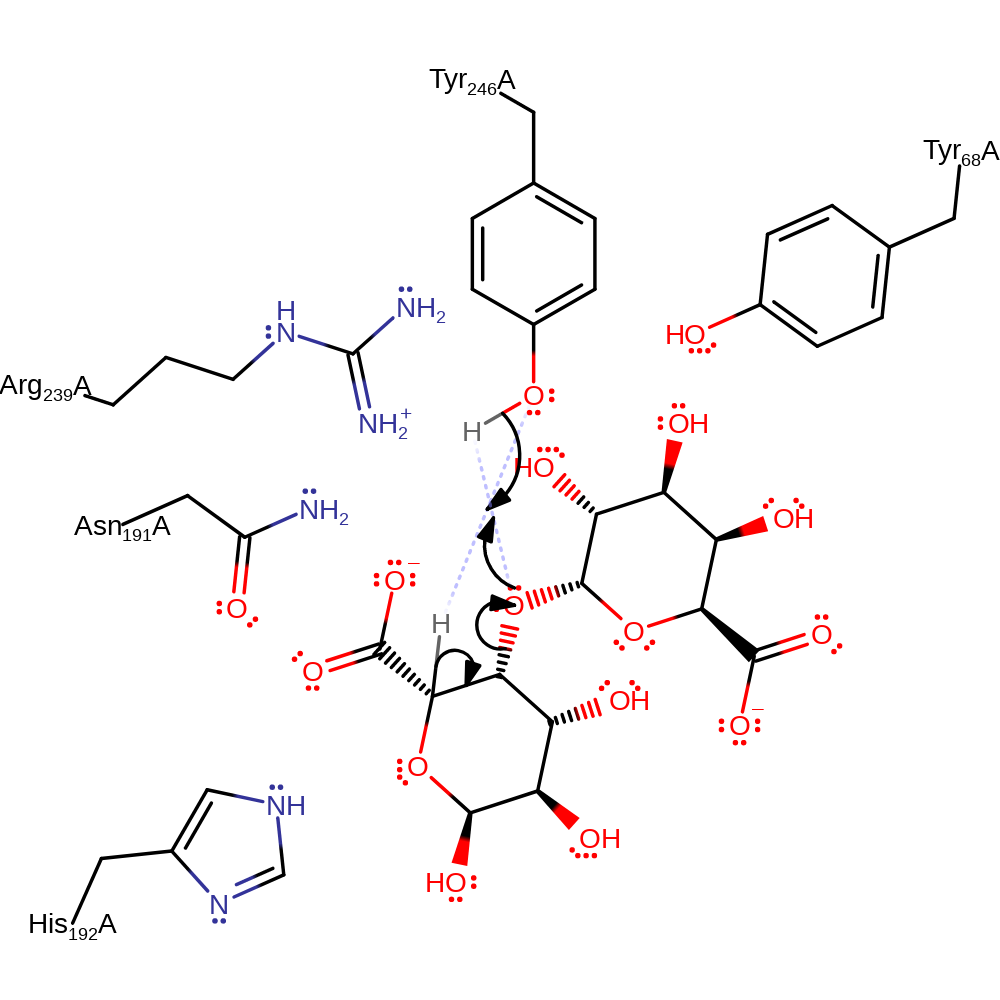
Step 1. The negative charge on the C5 carboxylate group is first neutralized by Arg287 and Asn239 so that the C5 proton can be more easily removed. Tyr294 extracts a proton from C5 of mannuronic acid, forming a carboxylate dianion intermediate. Tyr294 donates a proton to the oxygen of the glycosidic bond, forming a double bond between C4 and C5
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asn191(188)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg239(236)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr68(65)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His192(189)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr246(243)A | proton acceptor, proton relay, proton donor |



 Download:
Download: