Ribose-5-phosphate isomerase
Ribose-5-phosphate isomerase is able to catalyse the interconversion of Ribose-5-phosphate and Ribulose-5-phosphate, an isomerisation reaction involving the open chain forms of the two sugars, important in the pentose phosphate pathway. In Escherichia coli there are two forms of the enzyme, which although they catalyse the same reaction, have entirely different mechanisms and catalytic residues. The less common Escherichia coli RpiB is described here.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P37351
 (5.3.1.6)
(5.3.1.6)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Escherichia coli K-12 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1nn4
- Structural Genomics, RpiB/AlsB
(2.2 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.1400.10
 (see all for 1nn4)
(see all for 1nn4)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:5.3.1.6)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The overall mechanism of the reaction is through concerted acid-base catalysis, similar to that employed by Triose Phosphate Isomerase. Initial deprotonation of the C2 atom of Ribose-5-phosphate by the catalytic base Cys 66 primed by Asp 9 leads to the formation of an enediolate intermediate. Protons are shuttled via Thr68 leaving the C1 oxygen protonated and the C2 oxygen deprotonated. The endiolate then tautomerises forming the product-D-ribulose 5-phosphate.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1nn4) | ||
| Thr68 | Thr68(81)A | Acts as a proton relay transferring a proton from the C2 hydroxyl to the C1 | proton relay, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| His99 | His99(112)D | Acts as a general acid leading to ring opening. | proton donor |
| His134 | His134(147)D | Acts as a general base leading to ring opening. | proton acceptor |
| Asp9 | Asp9(22)A | Activates Cys66 | proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Cys66 | Cys66(79)A | Acts as the general base in the abstraction of a proton from Ribose-5-phosphate, then protonates the intermediate to facilitate its collapse. | proton acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, decyclisation, assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, overall reactant used, overall product formed, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Zhang RG et al. (2003), J Mol Biol, 332, 1083-1094. The 2.2Å Resolution Structure of RpiB/AlsB from Escherichia coli Illustrates a New Approach to the Ribose-5-phosphate Isomerase Reaction. DOI:10.1016/j.jmb.2003.08.009. PMID:14499611.
- Roos AK et al. (2005), J Biol Chem, 280, 6416-6422. Competitive inhibitors of Mycobacterium tuberculosis ribose-5-phosphate isomerase B reveal new information about the reaction mechanism. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M412018200. PMID:15590681.
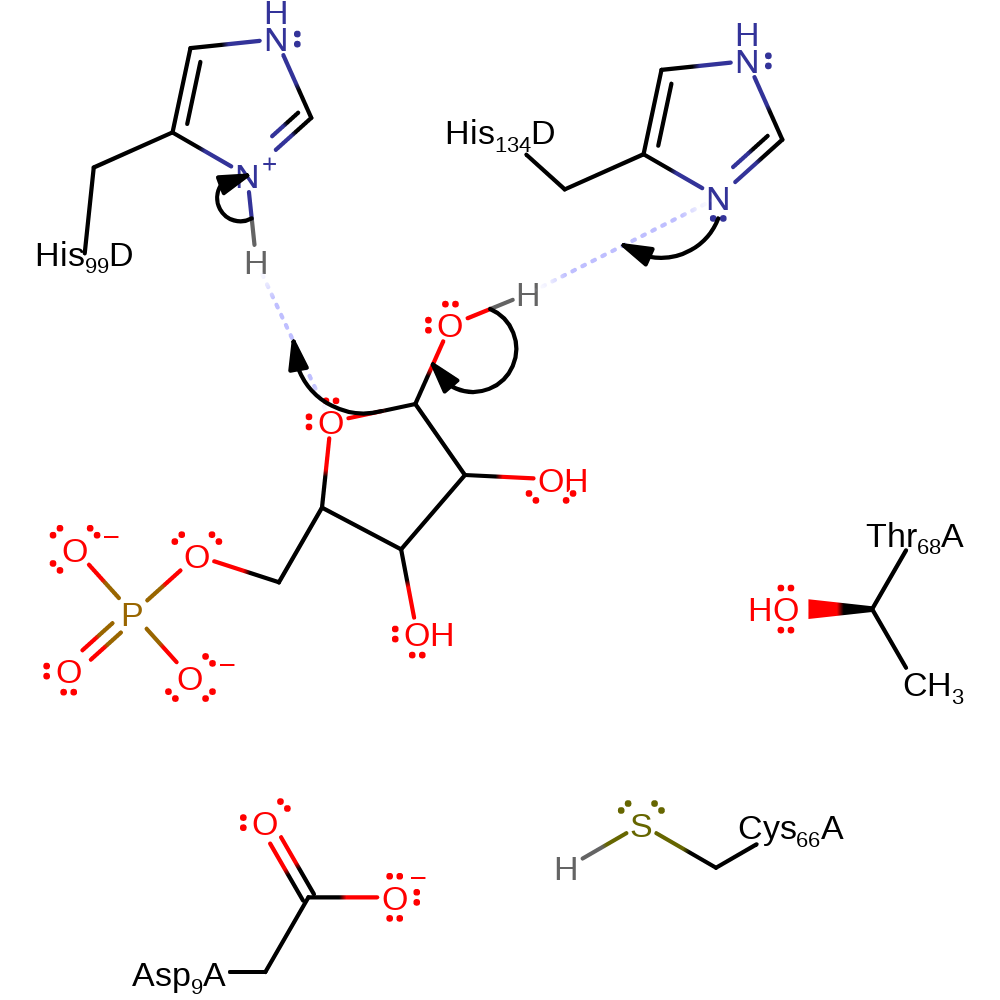
Step 1. Isomerization begins with the furanose ring being opened. His 134 accepts a proton from the carbon 1 hydroxyl oxygen and His 99 donates a proton to the ring oxygen. This causes the bond between carbon 1 and the ring oxygen to break.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His134(147)D | proton acceptor |
| His99(112)D | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, decyclisationCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp9(22)A | proton acceptor |
| Cys66(79)A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer
Step 3. The activated thiol group of Cys66 deprotonates the aldehydo-D-ribose 5-phosphate at carbon 2. This leads to tautomerisation forming an enediol intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys66(79)A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, proton transfer, overall reactant used
Step 4. Thr68 acts as a proton relay, leaving the hydroxyl oxygen on carbon 2 deprotonated.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Thr68(81)A | proton relay |
| Thr68(81)A | proton donor, proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer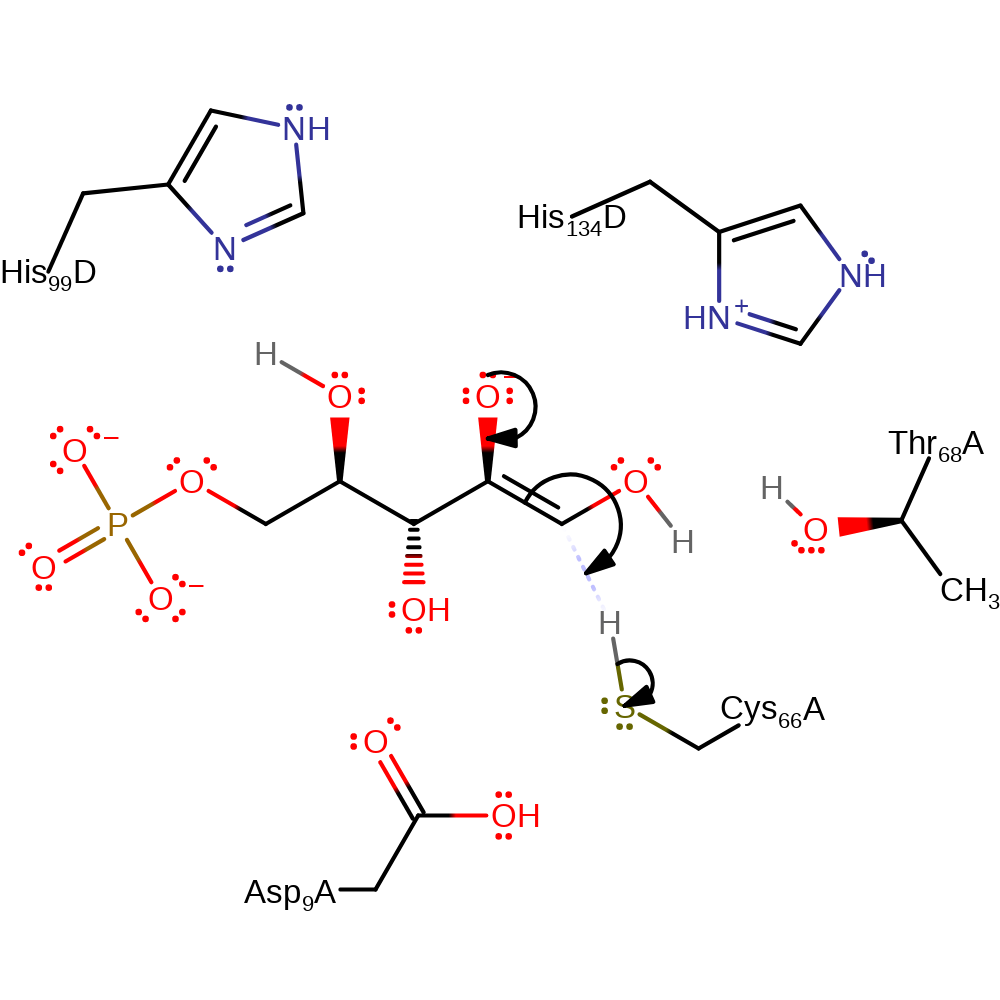
Step 5. The enediol intermediate accepts a proton from Cys66. This leads to a second tautomerisation reaction forming the product- D-ribulose 5-phosphate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys66(79)A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, overall product formed, assisted keto-enol tautomerisation
Step 6. Cys66 deprotonates Asp9, restoring these residues to their original states.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp9(22)A | proton donor |
| Cys66(79)A | proton acceptor |


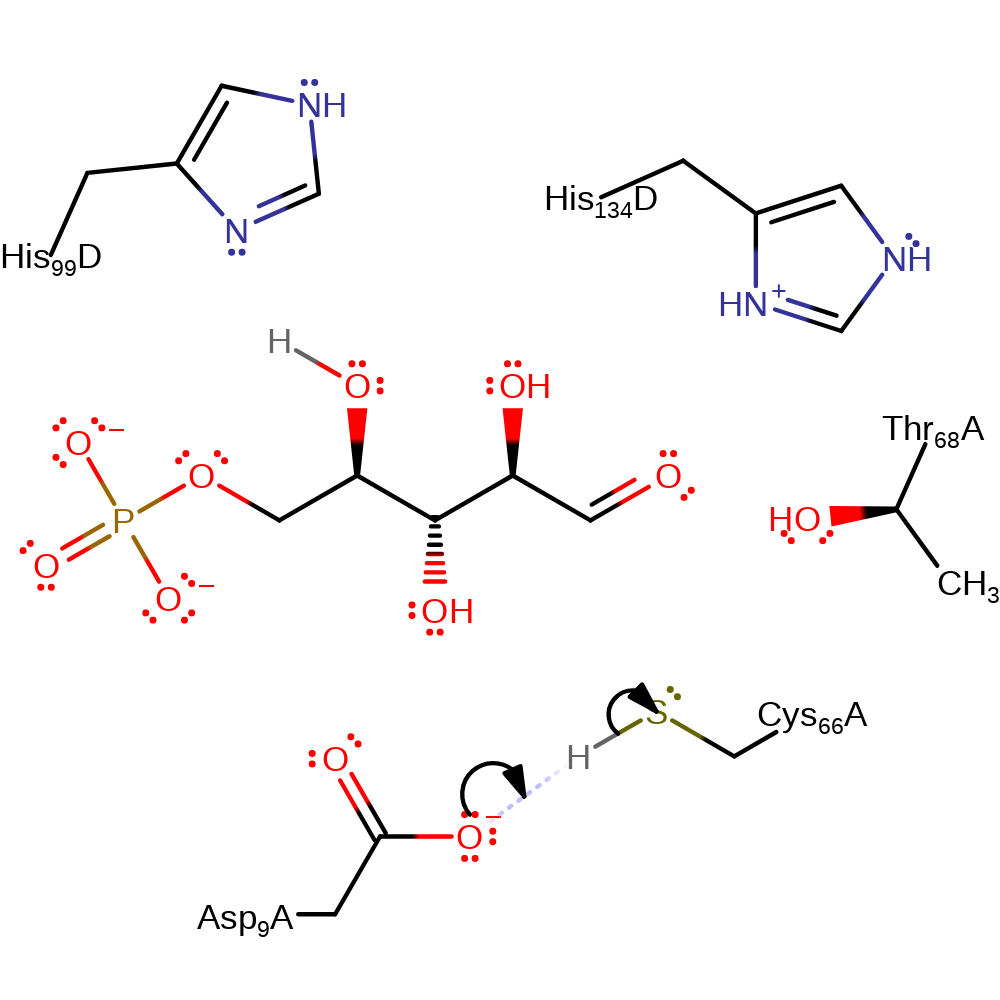
 Download:
Download: