Ribokinase
Ribokinase catalyses the phosphorylation of ribose to ribose-5-phosphate using ATP. The reaction is the first step in ribose metabolism and acts partly to trap ribose within the cell after uptake. Phosphorylation also prepares the sugar for use in the synthesis of nucleotides, histidine and for entry into the pentose phosphate pathway. Ribokinase is apart of the Ribokinase superfamily (also known as the PfkB family) alongside fructokinase and adenosine kinase which share two conserved motifs at the N and C terminus.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P0A9J6
 (2.7.1.15)
(2.7.1.15)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Escherichia coli K-12 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1rk2
- E. COLI RIBOKINASE COMPLEXED WITH RIBOSE AND ADP, SOLVED IN SPACE GROUP P212121
(2.25 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.1190.20
 (see all for 1rk2)
(see all for 1rk2)
- Cofactors
- Magnesium(2+) (2), Water (7)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:2.7.1.15)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
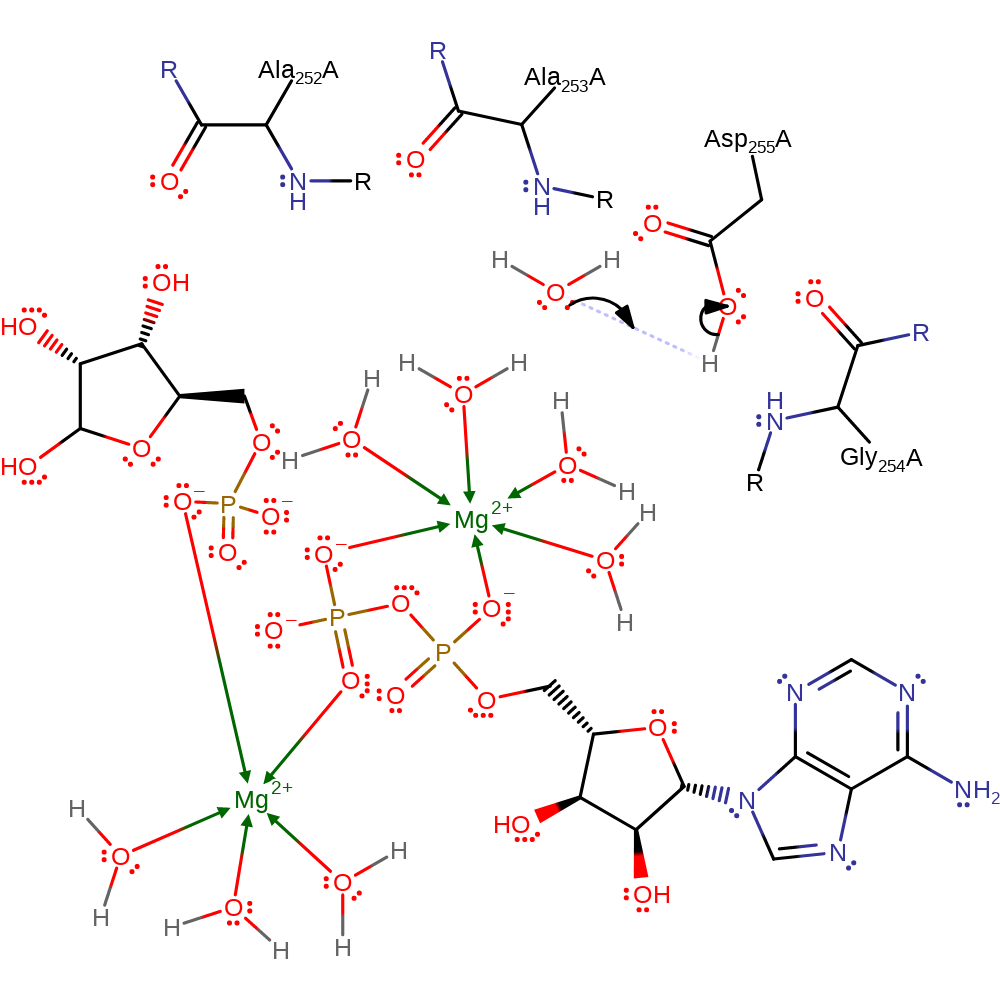
Asp255 acts as a base to deprotonate the O5'-hydroxyl group of ribose. The negatively charged O5' atom then makes a direct nucleophilic attack on the gamma-phosphate group of ATP in an in-line mechanism. An anion hole formed by backbone amide group of residues 252-255 (Ala252, Ala253, Gly254, Asp255) stabilise the transition state. Ribokinase has two Mg2+ ions present in its active site. Mg2+A coordinating to the alpha and beta phosphates is thought to promote ADP as a leaving group white Mg2+B coordinates to the beta and gamma phosphate, stabilising the developing negative charges in the reaction transition state. It is also thought to be activated by a monovalent cation such as K+ and interact with a phosphate ion.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1rk2) | ||
| Ala252 (main-N), Ala253 (main-N), Gly254 (main-N) | Ala252A (main-N), Ala253A (main-N), Gly254A (main-N) | It forms an oxyanion hole to stabilise the transition state. | electrostatic stabiliser, polar interaction |
| Asp255 | Asp255A | Its side chain acts as a base to deprotonate the O5'-hydroxyl group of ribose to promote its nucleophilic attack on the gamma-phosphate group of ATP. Its backbone amide forms an oxyanion hole to stabilise the transition state. | proton acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser, proton donor |
Chemical Components
bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, proton transfer, overall product formed, overall reactant used, inferred reaction step, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Sigrell JA et al. (1998), Structure, 6, 183-193. Structure of Escherichia coli ribokinase in complex with ribose and dinucleotide determined to 1.8 å resolution: insights into a new family of kinase structures. DOI:10.1016/s0969-2126(98)00020-3. PMID:9519409.
- Merino F et al. (2012), Biochimie, 94, 516-524. Catalytic and regulatory roles of divalent metal cations on the phosphoryl-transfer mechanism of ADP-dependent sugar kinases from hyperthermophilic archaea. DOI:10.1016/j.biochi.2011.08.021. PMID:21906652.
- Park J et al. (2008), Cell Mol Life Sci, 65, 2875-2896. Adenosine kinase and ribokinase--the RK family of proteins. DOI:10.1007/s00018-008-8123-1. PMID:18560757.
- Miallau L et al. (2007), J Biol Chem, 282, 19948-19957. Structures of Staphylococcus aureus D-tagatose-6-phosphate kinase implicate domain motions in specificity and mechanism. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M701480200. PMID:17459874.
- Andersson CE et al. (2002), J Mol Biol, 315, 409-419. Activation of ribokinase by monovalent cations. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.2001.5248. PMID:11786021.
- Maj MC et al. (2002), Biochemistry, 41, 4059-4069. Pentavalent Ions Dependency Is a Conserved Property of Adenosine Kinase from Diverse Sources: Identification of a Novel Motif Implicated in Phosphate and Magnesium Ion Binding and Substrate Inhibition†. DOI:10.1021/bi0119161.

Step 1. Asp255 deprotonates the 5' OH on ribose. This increases the group's nucleophilicity to then attack the gamma phosphate on ATP.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gly254A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp255A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ala253A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ala252A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ala252A (main-N) | polar interaction |
| Ala253A (main-N) | polar interaction |
| Gly254A (main-N) | polar interaction |
| Asp255A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, proton transfer, overall product formed, overall reactant usedCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp255A | proton donor |





 Download:
Download: