Diphosphate---fructose-6-phosphate 1-phosphotransferase
The Lyme disease causing Spirochete Borrelia burgdorferi uses pyrophosphate (PPi) rather than ATP as the source of phosphate for the phosphorylation of Fructose-6-phosphate to Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate in glycolysis. This strategy, common to many anaerobic bacteria, allows ATP to be conserved for other processes such as maintaining a proton gradient. The enzyme catalysing this process shares around 23% sequence identity to the E. coli PFK and many structural features differ between the two enzymes. However, the active sites do share a similar structure with conservation of key residues, so the mechanism of the reaction is almost certainly the same for each.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P70826
 (2.7.1.90)
(2.7.1.90)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Borrelia burgdorferi B31 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1kzh
- Structure of a pyrophosphate-dependent phosphofructokinase from the Lyme disease spirochete Borrelia burgdorferi
(2.55 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.50.450
 (see all for 1kzh)
(see all for 1kzh)
- Cofactors
- Magnesium(2+) (1)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:2.7.1.90)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
Fructose-6-phosphate's 1COH acts as the nucleophile to attack the terminal phosphate of PPi. Its nucleophilicity is increased by the action of Asp 206 which removes a hydrogen ion from the attacking hydroxyl, allowing a pentavalent phosphate transition state to form, stabilised by Mg2+ and several conserved residues at the active site (Gly 82, Arg 146, Thr 204 and Lys 203). Collapse of the transition state results in the overall phosphoryl transferfrom PPi to fructose-6-phosphate. It is still unclear the exact location and coordination of the magnesium ion due to not being present in the crystal structure.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1kzh) | ||
| Asp177 | Asp177A | Important in substrate specificity for pyrophosphate (not ATP) as the phosphate donor, indirectly coordinating to the magnesium cofactor via a water molecule. | polar interaction |
| Gly82 (main-N) | Gly82A (main-N) | The amide on the polypeptide backbone forms a strong hydrogen bond to the pyrophosphate thus stabilising the pentavalent phosphate transition state. | electrostatic stabiliser, polar interaction |
| Arg146 | Arg146A | Contacts PPi through its positively charged side chain, thus stabilises the pentavalent phosphate transition state. | electrostatic stabiliser, polar interaction |
| Lys203 | Lys203A | Stabilises the pentavalent phosphate transition state through electrostatic interactions. | electrostatic stabiliser, polar interaction |
| Thr204 | Thr204A | Forms hydrogen bond to the PPi, thus can act to stabilise the negative charge that develops in formation of the pentavalent phosphate transition state. | electrostatic stabiliser, polar interaction |
| Asp206 | Asp206A | Activates the 1-OH group of fructose-6-phosphate to allow the nucleophilic attack on the terminal phosphate of PPi which leads to the in-line phosphoryl transfer. | proton acceptor, proton donor, polar interaction, activator, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, proton transfer, overall reactant used, overall product formed, inferred reaction stepReferences
- Moore SA et al. (2002), Structure, 10, 659-671. The structure of a pyrophosphate-dependent phosphofructokinase from the Lyme disease spirochete Borrelia burgdorferi. DOI:10.2210/pdb1kzh/pdb. PMID:12015149.
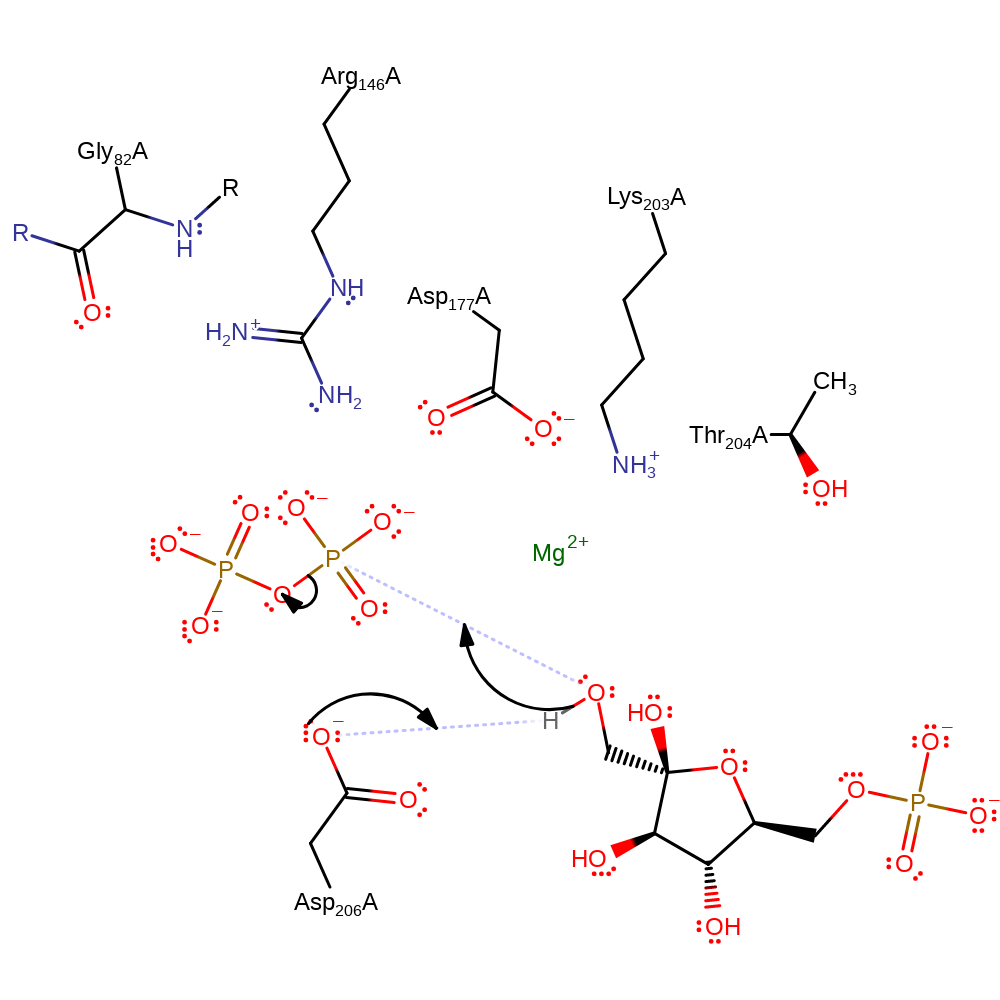
Step 1. Asp206 deprotonates Fructose-6-phosphate's 1C hydroxyl. This increases its nucleophilicity to then attack the terminal PPi phosphate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Thr204A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp206A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly82A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys203A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg146A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp206A | activator |
| Gly82A (main-N) | polar interaction |
| Arg146A | polar interaction |
| Asp177A | polar interaction |
| Lys203A | polar interaction |
| Thr204A | polar interaction |
| Asp206A | polar interaction |
| Asp206A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, proton transfer, overall reactant used, overall product formedCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gly82A (main-N) | polar interaction |
| Arg146A | polar interaction |
| Asp177A | polar interaction |
| Lys203A | polar interaction |
| Thr204A | polar interaction |
| Asp206A | polar interaction, proton donor |




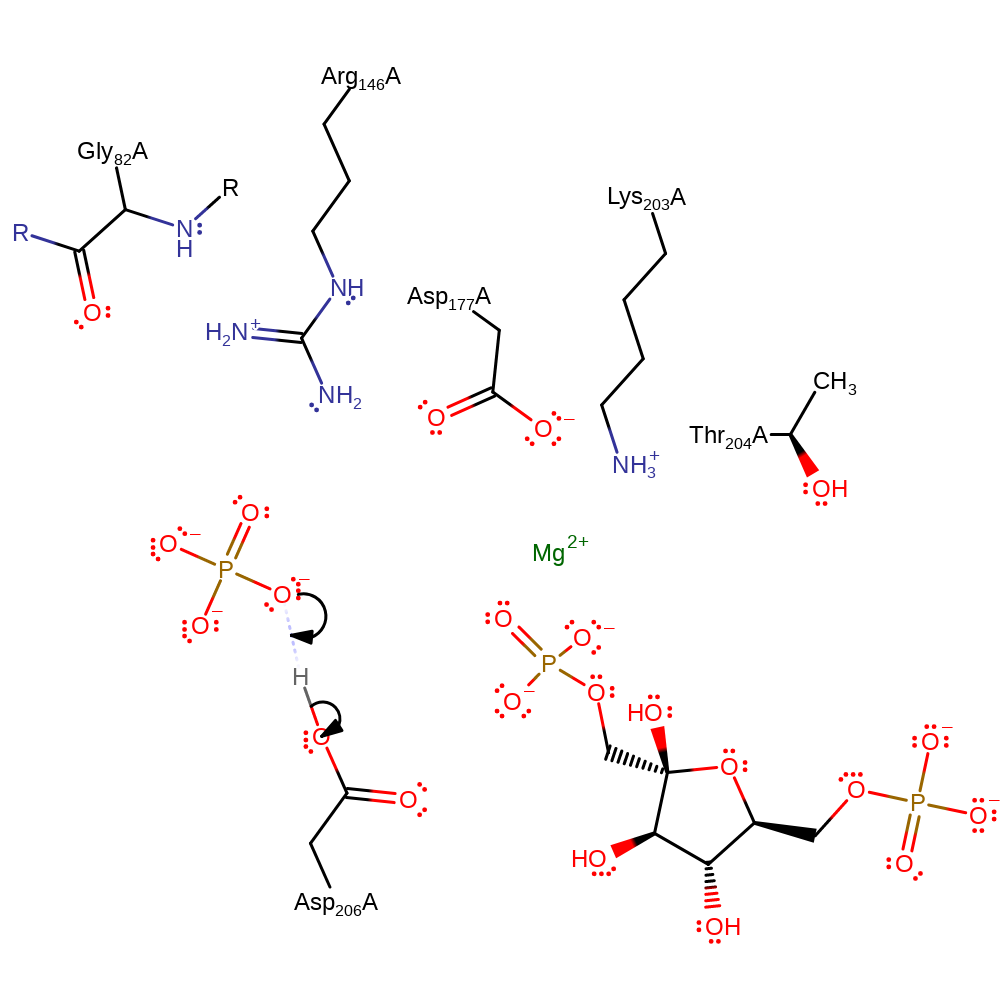
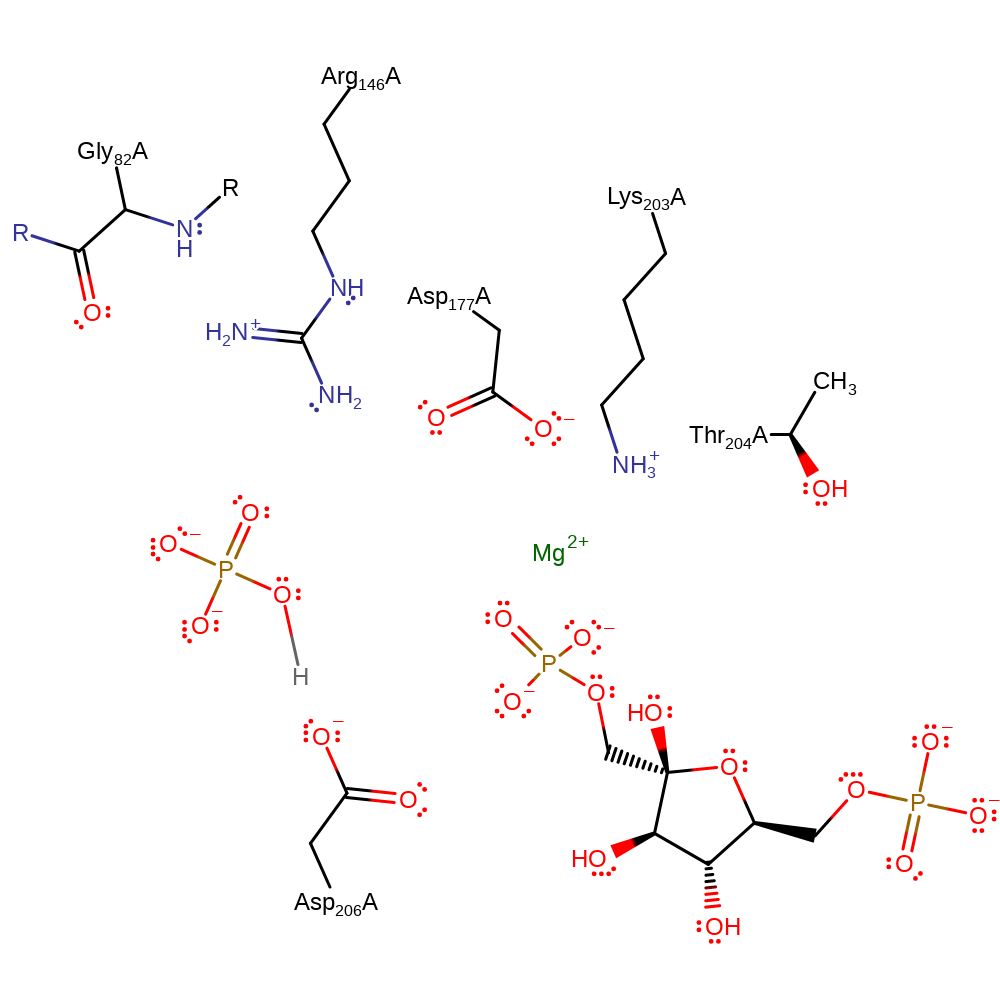 Download:
Download: