Phospholipase D
Phospholipase D catalyses the hydrolysis of phospholipids (normally phosphatidyl choline) into phosphatidic acid (PA) and the polar head group (normally choline). The PA generated can be converted into second messengers such as diacylglycerol (DAG) and is also suggested to cause changes in lipid bilayer properties. Phospholipase D will additionally catalyse transphosphatidylation reactions in vitro when an alcohol is present as the nucleophilic donor. It has been shown to be part of a superfamily that includes cardiolipin synthases, phosphatidyl serine synthases, poxvirus envelope proteins and several endonucleases.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P84147
 (3.1.4.4)
(3.1.4.4)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Streptomyces sp. PMF (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1v0y
- Phospholipase D from Streptomyces sp. strain PMF soaked with the substrate dibutyrylphosphatidylcholine.
(1.71 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.30.870.10
 (see all for 1v0y)
(see all for 1v0y)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:3.1.4.4)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The catalysed hydrolysis reaction occurs in two steps. First, nucleophilic attack by His 170 on the substrate phosphate leads to displacement of the alcohol head group (e.g. choline if the substrate is phosphatidyl choline) and formation of a His-phosphatidate intermediate with a covalent P-N bond to His 170 N-epsilon. The departing polar head group is protonated by His 448. In the second step, His 448 deprotonates a water molecule that attacks the His-phosphatidate intermediate to displace His 170 and produce phosphatidate. Asp 473 and Asp 202 interact with and modify the pKa values of His 170 and His 448 respectively.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1v0y) | ||
| His167 | His170(167)A | Attacks phosphate of substrate to form a covalent His-Phosphatidate intermediate that is subsequently hydrolysed. | covalently attached, nucleofuge, nucleophile |
| Asp199 | Asp202(199)A | Modifies pKa of His 448. | modifies pKa, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His440 | His448(440)A | Protonates departing alcohol group (eg choline) during formation of the His-Phosphatidate intermediate. Later deprotonates the water molecule that attacks this intermediate. | increase nucleophilicity, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Asp465 | Asp473(465)A | Modifies pKa of His 170. | increase nucleophilicity, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
overall reactant used, intermediate formation, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall product formed, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, proton transfer, intermediate terminated, bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Leiros I et al. (2004), J Mol Biol, 339, 805-820. The Reaction Mechanism of Phospholipase D from Streptomyces sp. Strain PMF. Snapshots along the Reaction Pathway Reveal a Pentacoordinate Reaction Intermediate and an Unexpected Final Product. DOI:10.1016/j.jmb.2004.04.003. PMID:15165852.
- Mahankali M et al. (2015), Cell Signal, 27, 69-81. Mechanism of enzymatic reaction and protein-protein interactions of PLD from a 3D structural model. DOI:10.1016/j.cellsig.2014.09.008. PMID:25308783.
- Gottlin EB et al. (1998), Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 95, 9202-9207. Catalytic mechanism of the phospholipase D superfamily proceeds via a covalent phosphohistidine intermediate. DOI:10.1073/pnas.95.16.9202. PMID:9689058.
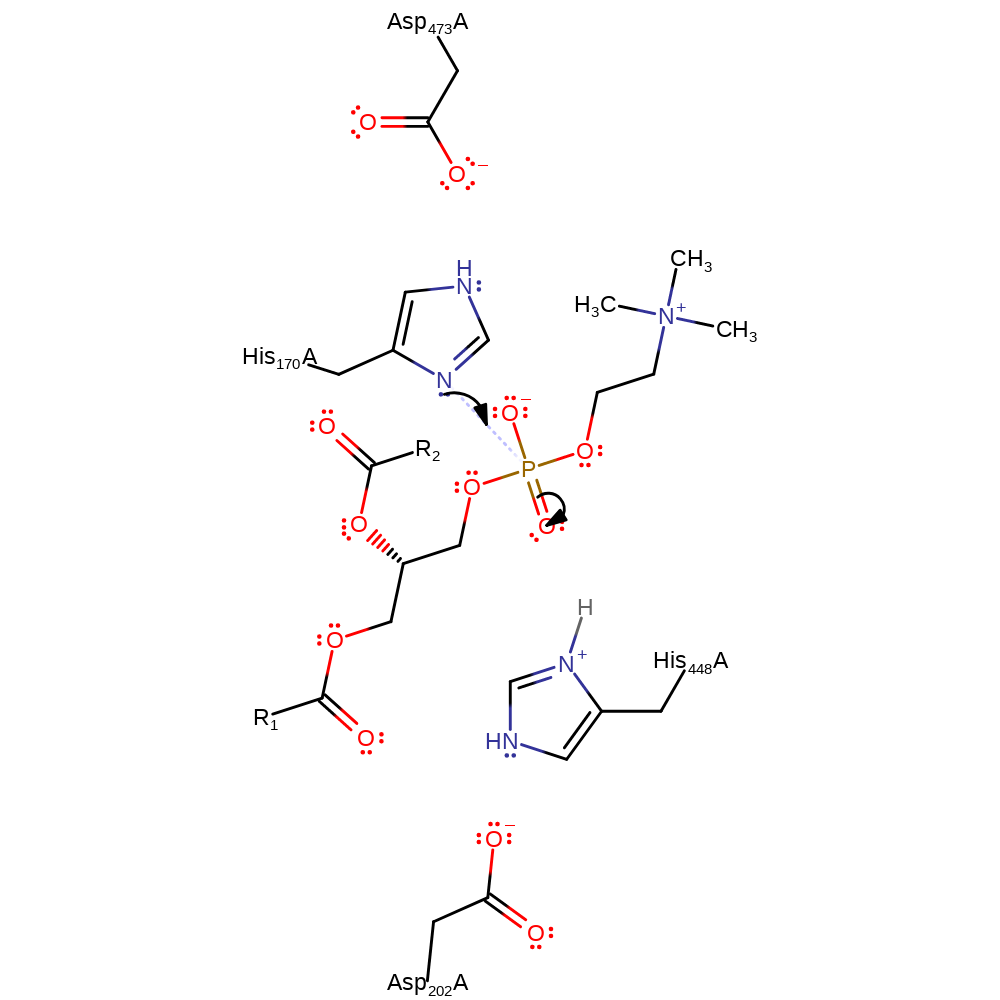
Step 1. His170 attacks the phosphate forming a penta-covalent intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp473(465)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His170(167)A | covalently attached |
| Asp473(465)A | increase nucleophilicity |
| His170(167)A | nucleophile |
Chemical Components
overall reactant used, intermediate formation, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition
Step 2. The penta-covalent intermediate collapses and His448 donates a proton to the choline leaving group.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His170(167)A | covalently attached |
| Asp202(199)A | electrostatic stabiliser, modifies pKa |
| His448(440)A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
overall product formed, ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, proton transfer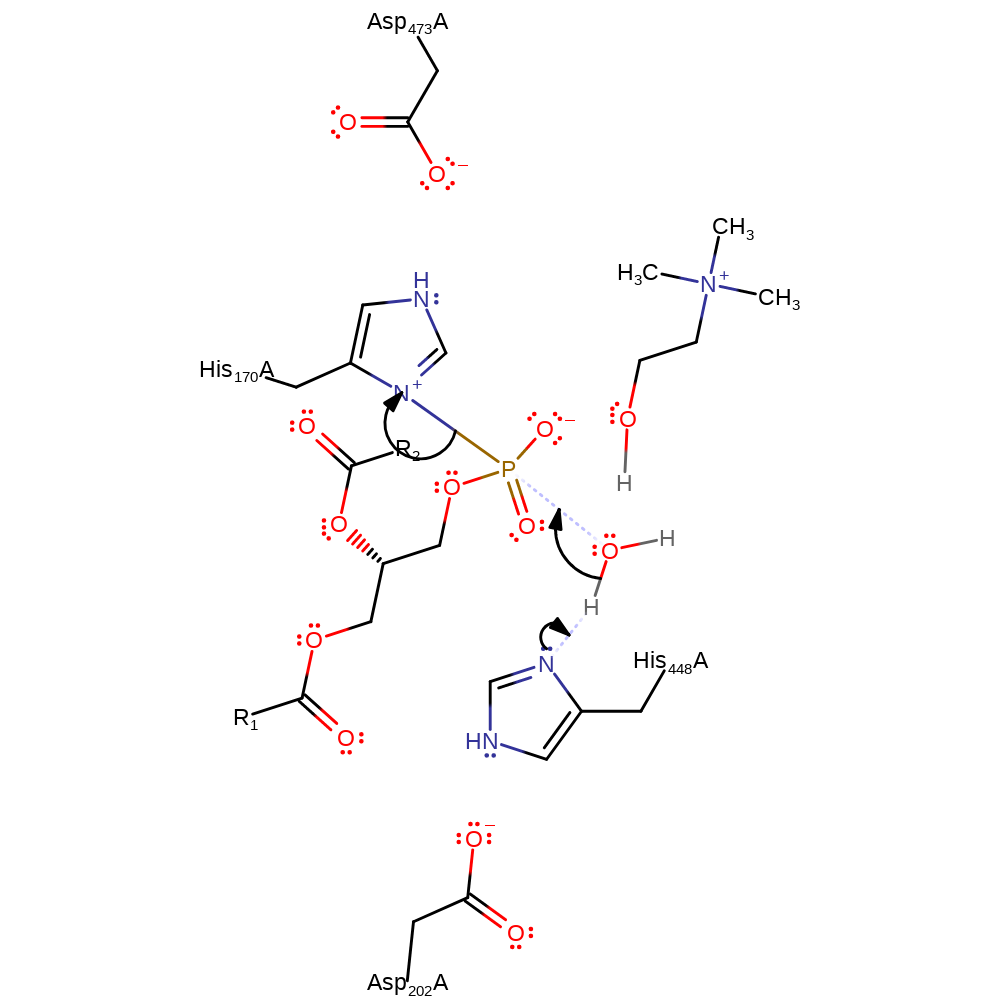
Step 3. His448 deprotonates a water molecule, activating it for nucleophilic attack on the phosphate. This causes His170 to be displaced.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp202(199)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp473(465)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp202(199)A | modifies pKa |
| His448(440)A | increase nucleophilicity |
| His170(167)A | nucleofuge |
| His448(440)A | proton acceptor |





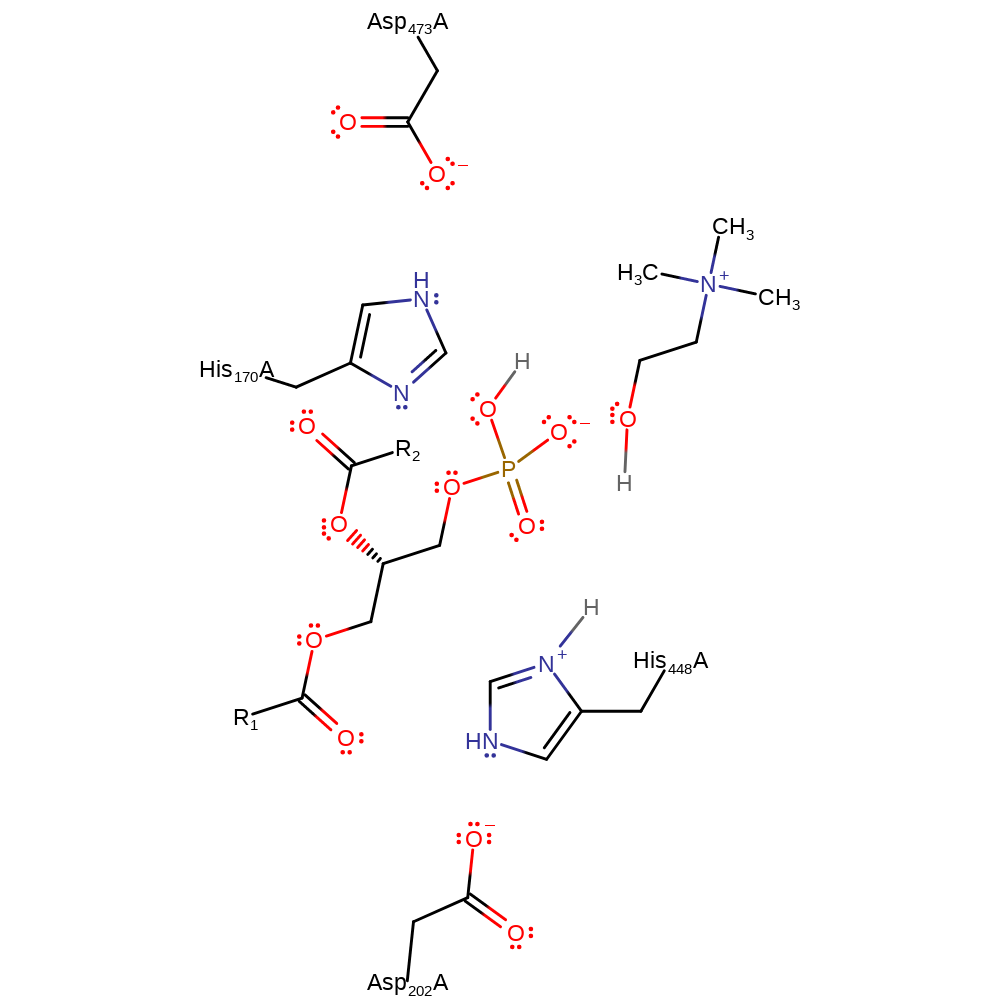 Download:
Download: