Bontoxilysin
Botulinum neurotoxin acts by inhibiting neurotransmitter release. It binds to peripheral neuronal synapses, is internalised and moves by retrograde transport up the axon into the spinal cord where it can move between postsynaptic and presynaptic neurons. It disrupts neurotransmitter release by acting as a zinc endopeptidase that cleaves the 76-Gln-|-Phe-77 bond of synaptobrevin-2(Sb2), one of three SNARE proteins involved in neuronal synaptic vesicle fusion.
There are in total 7 serotypes of botulinum neurotoxin. All seven serotypes possess an identical Zn2+-binding motif, HEXXH, but are unique either in substrate selection or in their cleavage site. Their catalytic domains share high degree of sequence homology and holotoxin structures of serotype A and serotype B have been reported to be structurally similar. Botulinum belongs to the same class of neurotoxin with tetanus neurotoxin and they share significant sequence homology. They possess similar structural and functional domains and have a similar mechanism of toxicity. However, Botulinum neurotoxins acts at the neuromuscular junction causing flaccid paralysis by inhibiting the release of acetylcholine into the synapse, while tetanus toxin acts at the central nervous system causing spastic paralysis. In addition botulinum neurotoxin is the protein also known as Botox which is widely used in the cosmetics industry for the reduction of facial wrinkles through relaxation of the muscles.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P10844
 (3.4.24.69)
(3.4.24.69)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Clostridium botulinum (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1epw
- CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF CLOSTRIDIUM NEUROTOXIN TYPE B
(1.9 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.90.1240.10
 (see all for 1epw)
(see all for 1epw)
- Cofactors
- Zinc(2+) (1)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
Glu231 is abase which deprotonates water and in conjugation with polarization by Zn2+ activates water so that it can act as a nucleophile and attack the carbonyl of the peptide bond. Arg369 and Zn2+ stabilise the transition state by interacting with the negatively charged carbonyl oxygen atom of the tetrahedral intermediate. The collapse of the oxyanion results in the cleavage of the peptide bond and the kinetically favoured products of this reaction are the carboxyanion and the amine cation, thus in a final step the N-terminal amine deprotonates the C-terminal carboxyacid.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1epw) | ||
| Glu231 | Glu230A | Acts as a general base on water, to create nucleophile from attack on the amide carbonyl. | proton acceptor, proton donor |
| His230, His234, Glu268 | His229A, His233A, Glu267A | Form the Zinc binding site in the enzyme | metal ligand |
| Arg370 | Arg369A | It stabilises the transition state by stabilising the negative charge developed on the substrate carbonyl oxygen atom. | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, coordination, coordination to a metal ion, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, rate-determining step, cofactor used, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, heterolysis, intermediate collapse, decoordination from a metal ion, native state of cofactor regenerated, native state of enzyme regenerated, overall product formedReferences
- Swaminathan S et al. (2000), Nat Struct Biol, 7, 693-699. Structural analysis of the catalytic and binding sites of Clostridium botulinum neurotoxin B. PMID:10932256.
- Ahmed SA et al. (2008), Protein J, 27, 151-162. Identification of residues surrounding the active site of type A botulinum neurotoxin important for substrate recognition and catalytic activity. DOI:10.1007/s10930-007-9118-8. PMID:18213512.
- Swaminathan S et al. (2004), Mov Disord, 19 Suppl 8, S17-S22. Structure and enzymatic activity of botulinum neurotoxins. DOI:10.1002/mds.20005. PMID:15027050.
- Breidenbach MA et al. (2004), Nature, 432, 925-929. Substrate recognition strategy for botulinum neurotoxin serotype A. DOI:10.1038/nature03123. PMID:15592454.
- Rigoni M et al. (2001), Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 288, 1231-1237. Site-Directed Mutagenesis Identifies Active-Site Residues of the Light Chain of Botulinum Neurotoxin Type A. DOI:10.1006/bbrc.2001.5911. PMID:11700044.
- Hanson MA et al. (2000), Nat Struct Biol, 16, 795-795. Retraction: Cocrystal structure of synaptobrevin-II bound to botulinum neurotoxin type B at 2.0 Å resolution. DOI:10.1038/nsmb0709-795. PMID:10932255.
- Schiavo G et al. (1992), J Biol Chem, 267, 23479-23483. Botulinum neurotoxins are zinc proteins. PMID:1429690.
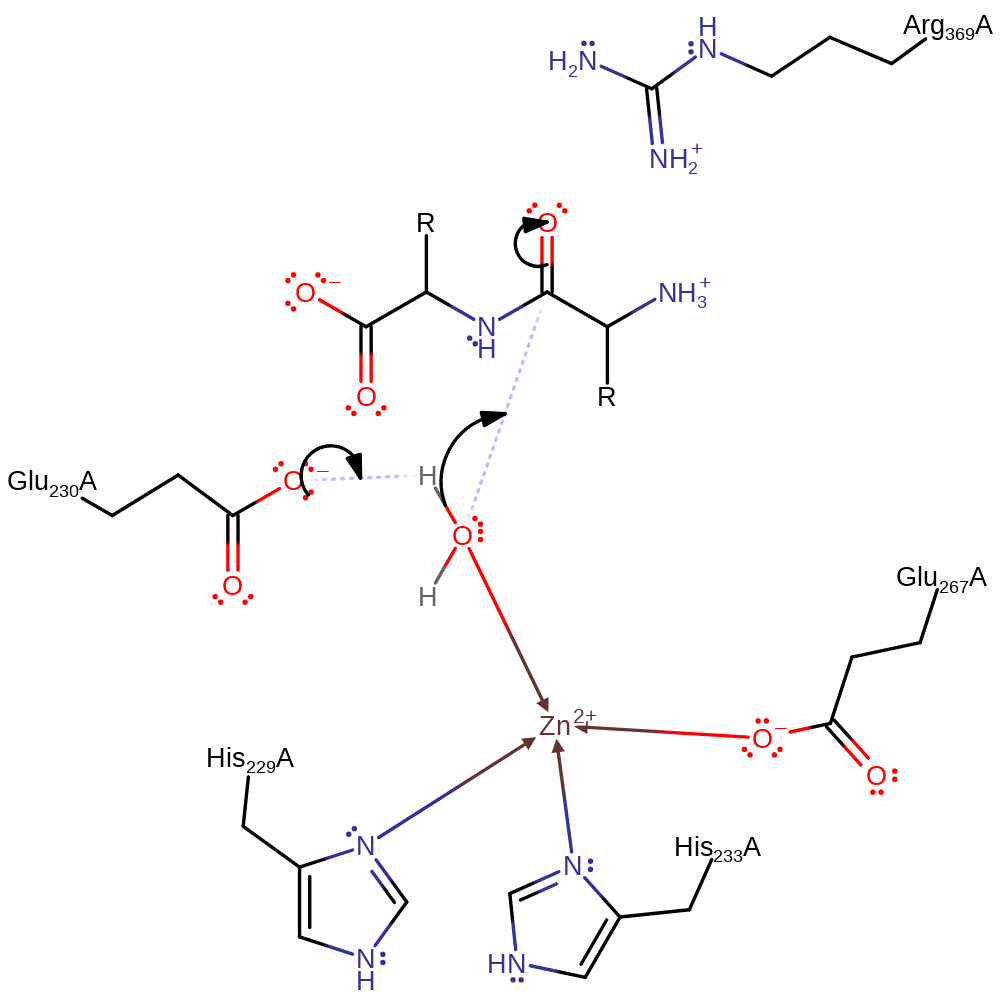
Step 1. Glu231 deprotonates water which then attacks the peptide bond in a nucleophilic addition. This results in the oxyanion coordinating to the Zinc. Arg369 stabilises the transition state by interacting with the negatively charged carbonyl of the tetrahedral intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg369A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His229A | metal ligand |
| His233A | metal ligand |
| Glu267A | metal ligand |
| Glu230A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, coordination, coordination to a metal ion, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, rate-determining step, cofactor used
Step 2. The oxyanion initiates an elimination that results in the cleavage of the peptide bond. The N-terminal product accepts a proton from Glu231.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg369A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His229A | metal ligand |
| His233A | metal ligand |
| Glu267A | metal ligand |
| Glu230A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, heterolysis, intermediate collapse, decoordination from a metal ion, native state of cofactor regenerated, native state of enzyme regenerated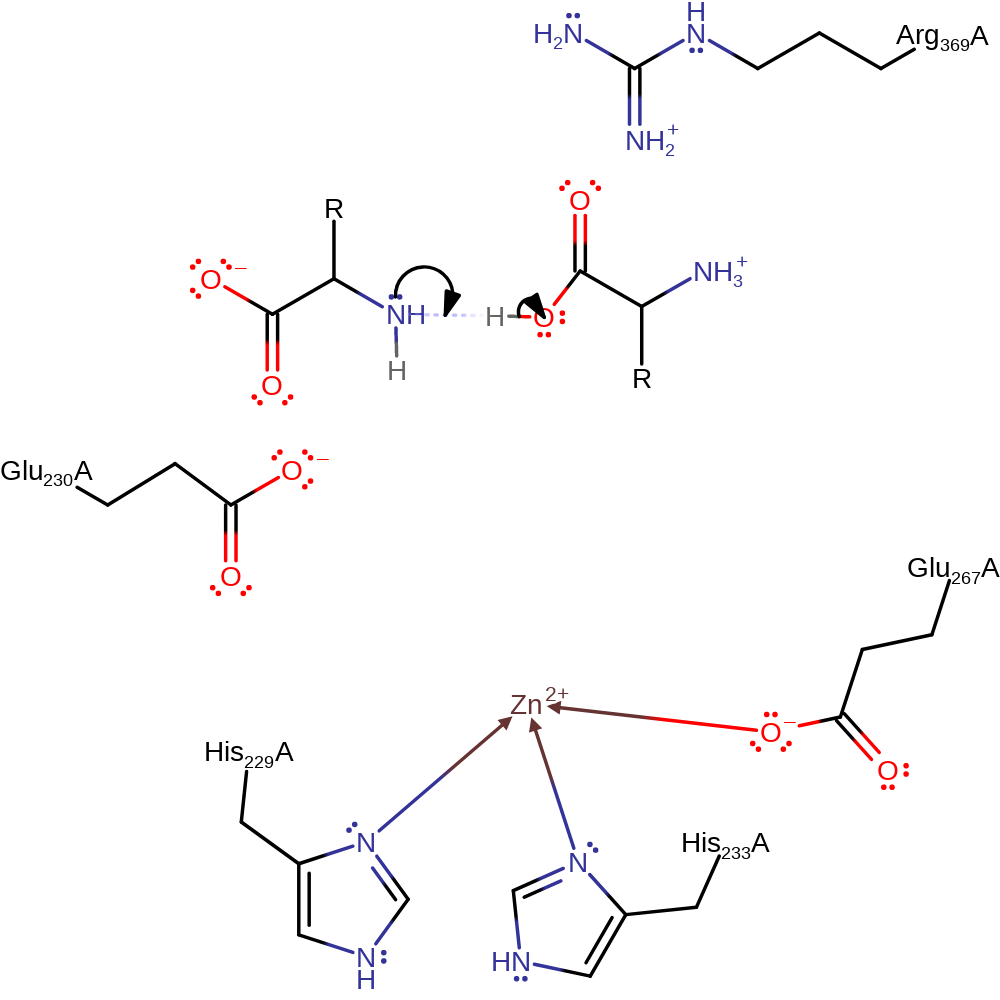
Step 3. The N-terminal product deprotonates the C-terminal product to produce kinetically favourable products.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg369A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His229A | metal ligand |
| His233A | metal ligand |
| Glu267A | metal ligand |



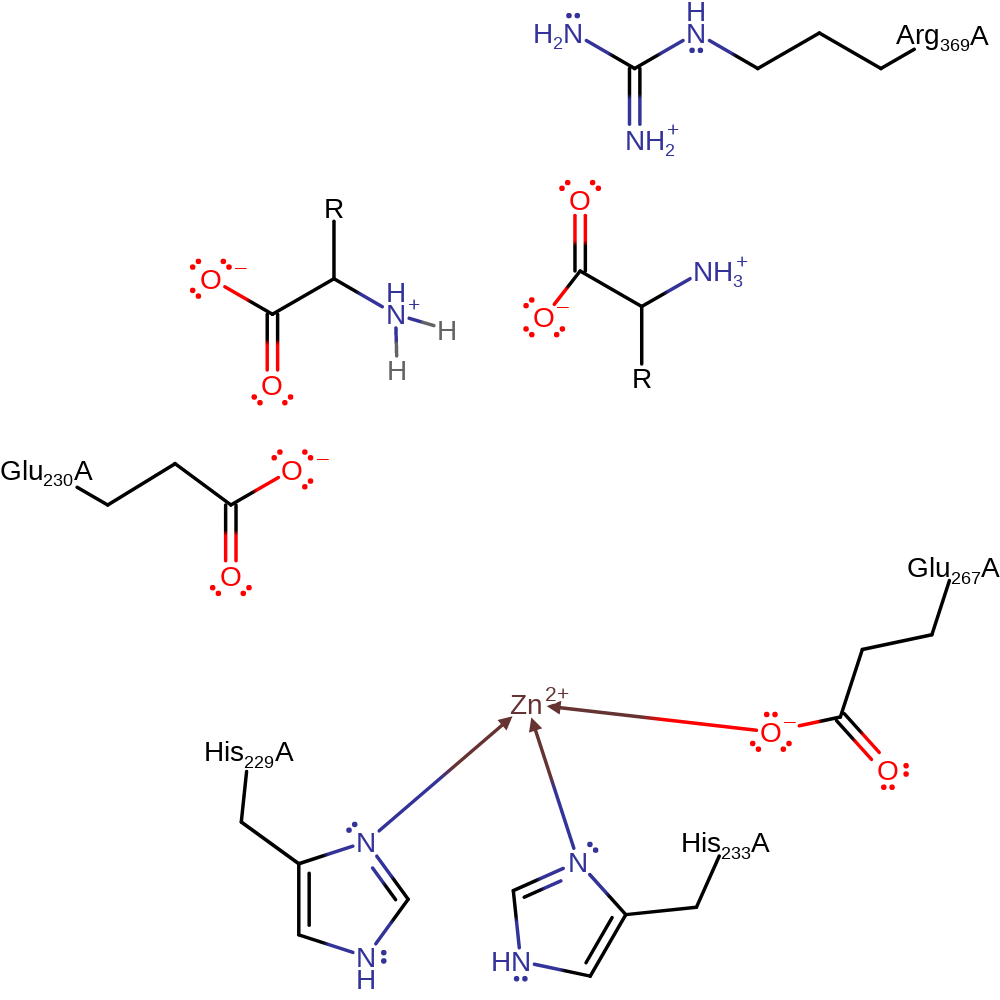 Download:
Download: