Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (NAD(P)+) (phosphorylating)
Archaebacterial glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase is able to catalyse the conversion of glycerate-1-3-bisphophate to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate using NADPH or NADH as the cofactor. It displays homology with the family of GAPDH dehydrogenases including both bacterial and human forms, but is unique in its resistance to extremes of temperature.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P10618
 (1.2.1.59)
(1.2.1.59)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Methanothermus fervidus (Archaea)

- PDB
-
1cf2
- THREE-DIMENSIONAL STRUCTURE OF D-GLYCERALDEHYDE-3-PHOSPHATE DEHYDROGENASE FROM THE HYPERTHERMOPHILIC ARCHAEON METHANOTHERMUS FERVIDUS
(2.1 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.30.360.10
 (see all for 1cf2)
(see all for 1cf2)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:1.2.1.59)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The reaction proceeds via initial nucleophilic addition-elimination by cysteine on glycerate-1-3-bisphosphate resulting in the thioacyl enzyme intermediate. Hydride transfer to the intermediate from the cofactor results in a further hemithiolaceto enzyme intermediate, with protonation by histidine stabilising this state. Collapse of this intermediate results in the product being released.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1cf2) | ||
| Cys140 | Cys140P(A) | Acts as nucleophile to attack substrate resulting in the elimination fo the phosphate group and formation of the thioacyl-enzyme intermediate which then collapses to give the product. | covalently attached, nucleofuge, nucleophile, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| His219 | His219P(A) | Acts to increase nucleophilicity of cys 140 by accepting a proton. Also acts to allow hydride transfer to the substrate by stabilising the hemithioacetal intermediate through hydrogen bonding. Finally protonates the cysteine residue to facilitate collapse of this intermediate. | proton acceptor, modifies pKa, electrostatic stabiliser, proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, enzyme-substrate complex formation, aromatic bimolecular nucleophilic addition, hydride transfer, intermediate collapse, cofactor used, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, overall product formed, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, inferred reaction step, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Charron C et al. (2000), J Mol Biol, 297, 481-500. The crystal structure of d-glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Methanothermus fervidus in the presence of NADP+ at 2.1 Å resolution. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.2000.3565. PMID:10715215.
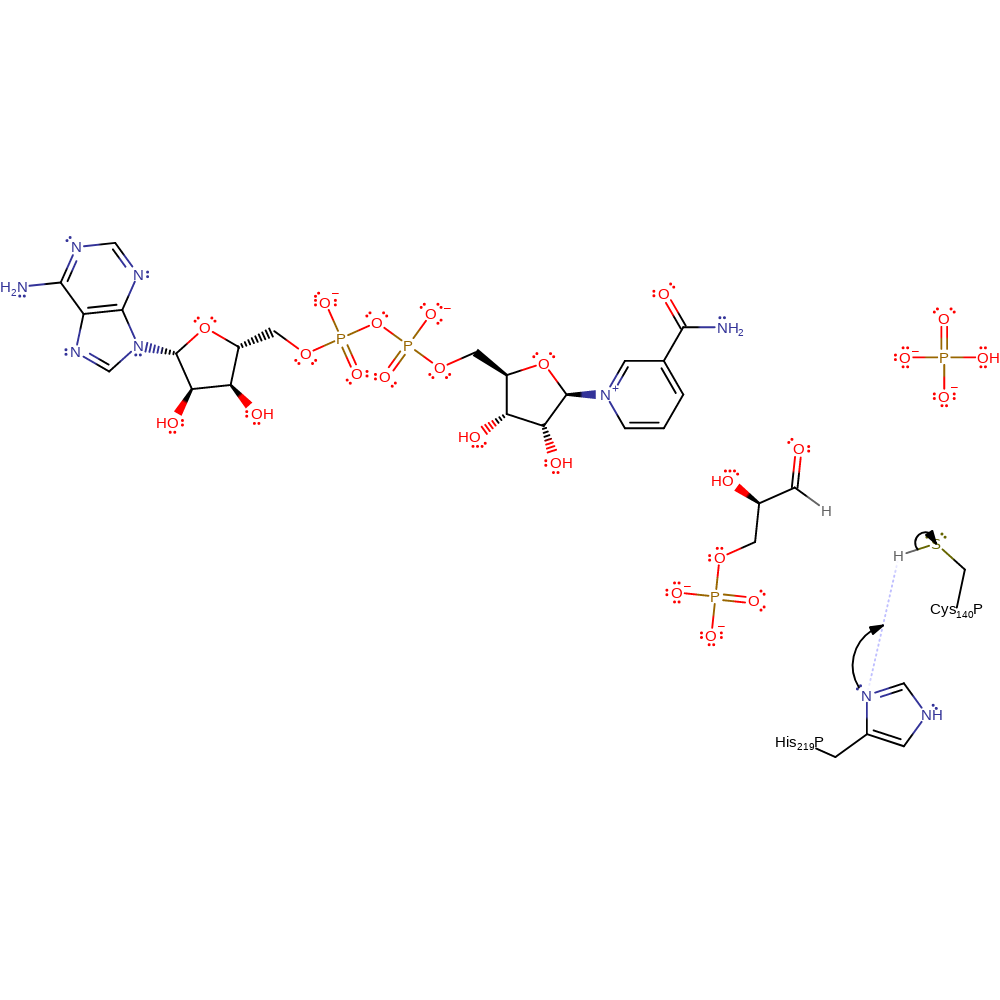
Step 1. His219 decreases the pKa of Cys140 and deprotonates the thiol group.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His219P(A) | modifies pKa, proton acceptor |
| Cys140P(A) | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer
Step 2. Cys140 attacks D-glyceraldehyde in a nucleophilic bimolecular addition reaction.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys140P(A) | covalently attached, nucleophile |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, enzyme-substrate complex formation
Step 3. A hydride is transferred from the thioacyl enzyme intermediate to NAD and the tetrahedral intermediate collapses. Hydride transfer is promoted by His219, either as a base catalyst or as a stabilizer of the deprotonated hemithioacetal intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys140P(A) | covalently attached |
| His219P(A) | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
ingold: aromatic bimolecular nucleophilic addition, hydride transfer, intermediate collapse, cofactor used
Step 4. The phosphate attacks the intermediate in a nucleophilic addition reaction.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys140P(A) | covalently attached |
| His219P(A) | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation
Step 5. The tetrahedral intermediate collapses, forming the product and eliminating Cys140.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys140P(A) | nucleofuge |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate collapse, overall product formed, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage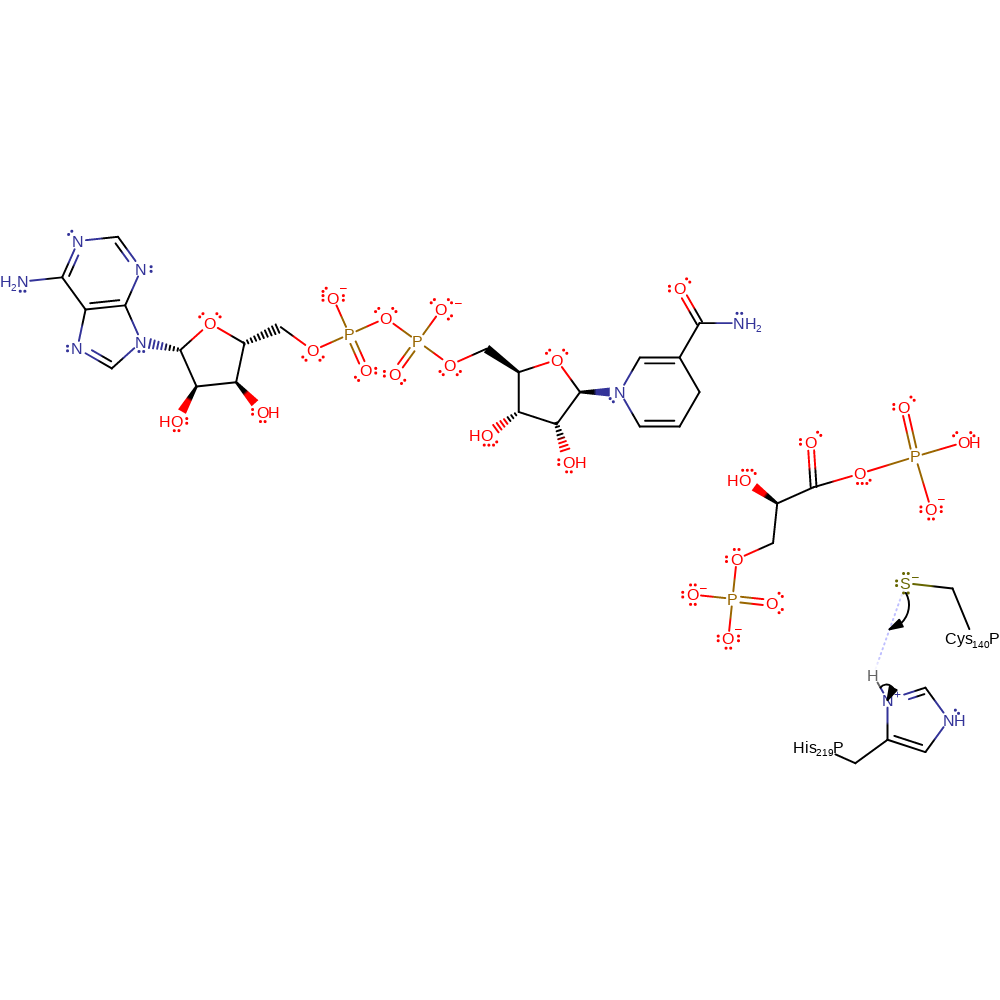
Step 6. In an inferred step the native state of the active site is regenerated after proton transfer to Cys140 and from His219.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His219P(A) | proton donor |
| Cys140P(A) | proton acceptor |






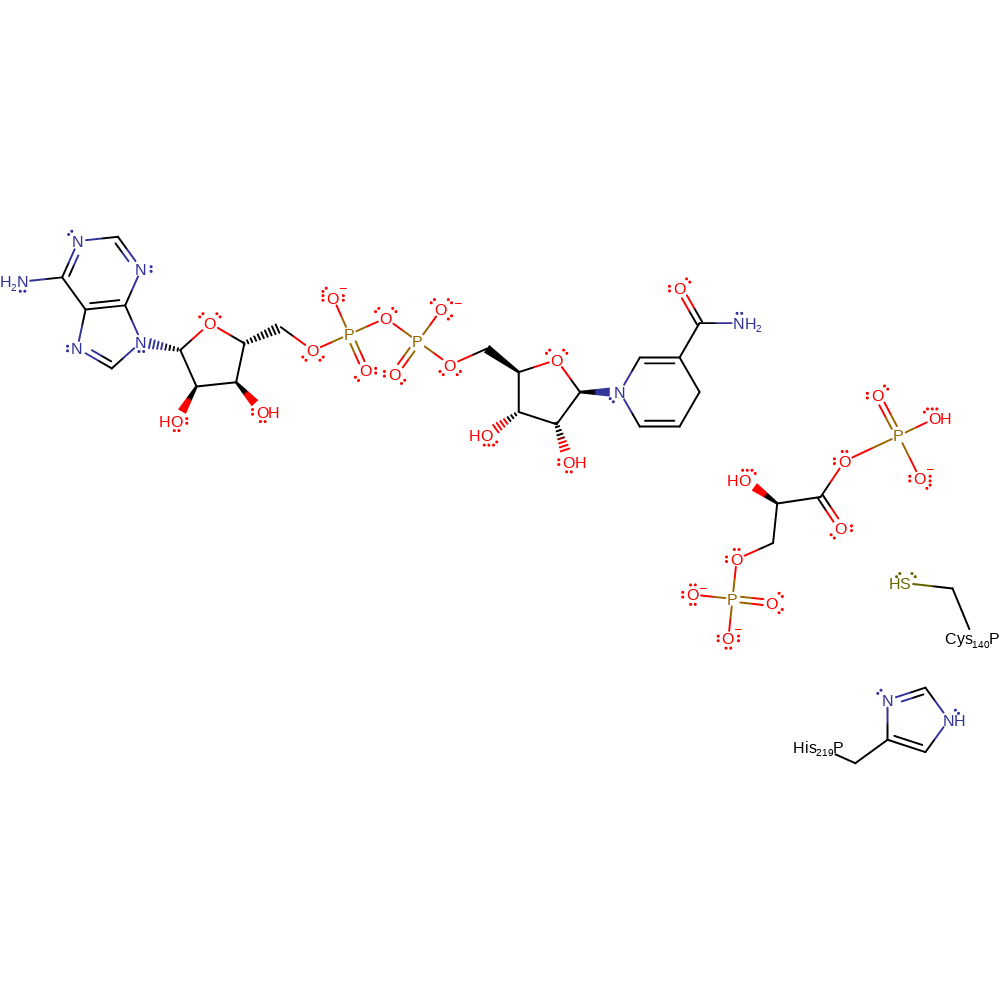 Download:
Download: