Saccharopine dehydrogenase (NADP+, L-glutamate-forming)
Two lysine biosynthesis pathway: ubiquitous diaminopimelate pathway found in plants, bacteria and lower fungi. And the alpha-aminoadipate pathway (AAA pathway) found in higher fungi and cyanobacteria. The AAA pathway synthesises lysine from alpha-ketoglutarate and it is a member of the glutamate family of amino acid biosynthetic pathways. A number of fungi using this lysine synthesis pathway are human and plant pathogens. Selective inhibition of the essential biosynthetic pathway of lysine can be a possible means of controlling these pathogens. Saccharopine reductase catalyses the penultimate step in the AAA pathway in which glutamate and alpha-aminoadipic-delta-semialdehyde are reversibly converted to saccharophine, using, in preference, NADPH as cofactor. But it can also utilise NADH though with low catalytic efficiency.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
Q9P4R4
 (1.5.1.10)
(1.5.1.10)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Magnaporthe oryzae 70-15 (Fungus)

- PDB
-
1e5q
- Ternary complex of saccharopine reductase from Magnaporthe grisea, NADPH and saccharopine
(2.1 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.30.360.10
 (see all for 1e5q)
(see all for 1e5q)
- Cofactors
- Nadph (1)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:1.5.1.10)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
In the forward reaction from glutamate and alpha-aminoadipic-delta-semialdehyde to saccharopine, first, the amino nitrogen atom of the glutamate acts as a nucleophile to attack the carbon atom of the aldehyde group of alpha-aminoadipate-delta-semialdehyde, resulting in the formation of carbinoamine. Second, elimination of a water molecule results in Schiff-base intermediate and finally, NADPH transfers hydrides to the intermediate to form saccharopine.
In the reverse reaction, the hydrolysis of the Schiff-base requires the nucleophilic attack of a water molecule on carbon C6 of saccharopine. Asp126 activates a water molecule to promote the hydrolysis.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1e5q) | ||
| Asp126 | Asp126C | It deprotonates a water molecule to allow its hydrolysis of the Schiff-base intermediate in the reverse reaction which saccharopine is converted back to glutamate and alpha-aminoadipic-delta-semialdehyde. |
Chemical Components
bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, proton transfer, elimination (not covered by the Ingold mechanisms), dehydration, aromatic unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, overall product formed, hydride transfer, rate-determining stepReferences
- Johansson E et al. (2000), Structure, 8, 1037-1047. Crystal Structure of Saccharopine Reductase from Magnaporthe grisea, an Enzyme of the α-Aminoadipate Pathway of Lysine Biosynthesis. DOI:10.1016/s0969-2126(00)00512-8. PMID:11080625.
- Almasi JN et al. (2011), Molecules, 16, 8569-8589. A QM/MM-based computational investigation on the catalytic mechanism of saccharopine reductase. DOI:10.3390/molecules16108569. PMID:21993247.
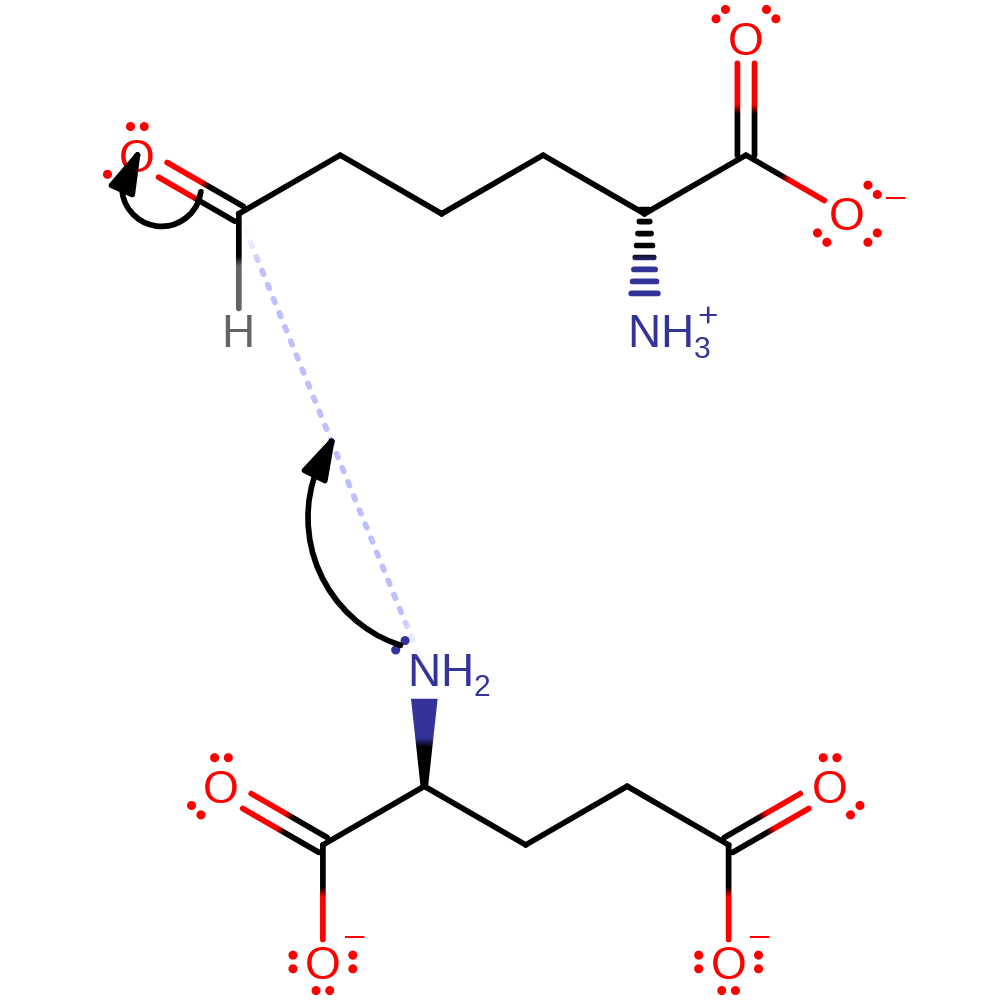
Step 1. The first step in the mechanism is nucleophilic attack of the glutamate amine nitrogen at the R-group carbonyl carbon of alpha-aminoadipate-delta-semialdehyde. This occurs with concomitant transfer of a proton to AASA's R group carbonyl oxygen and loss of a proton from the bridging amine to give a carbinolamine intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, proton transfer
Step 2. The carbinolamine intermediate undergoes a 1,3 intramolecular proton transfer to the hydroxyl group. There is then loss of water and formation of an unprotonated Schiff base intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|
Chemical Components
elimination (not covered by the Ingold mechanisms), dehydration, proton transfer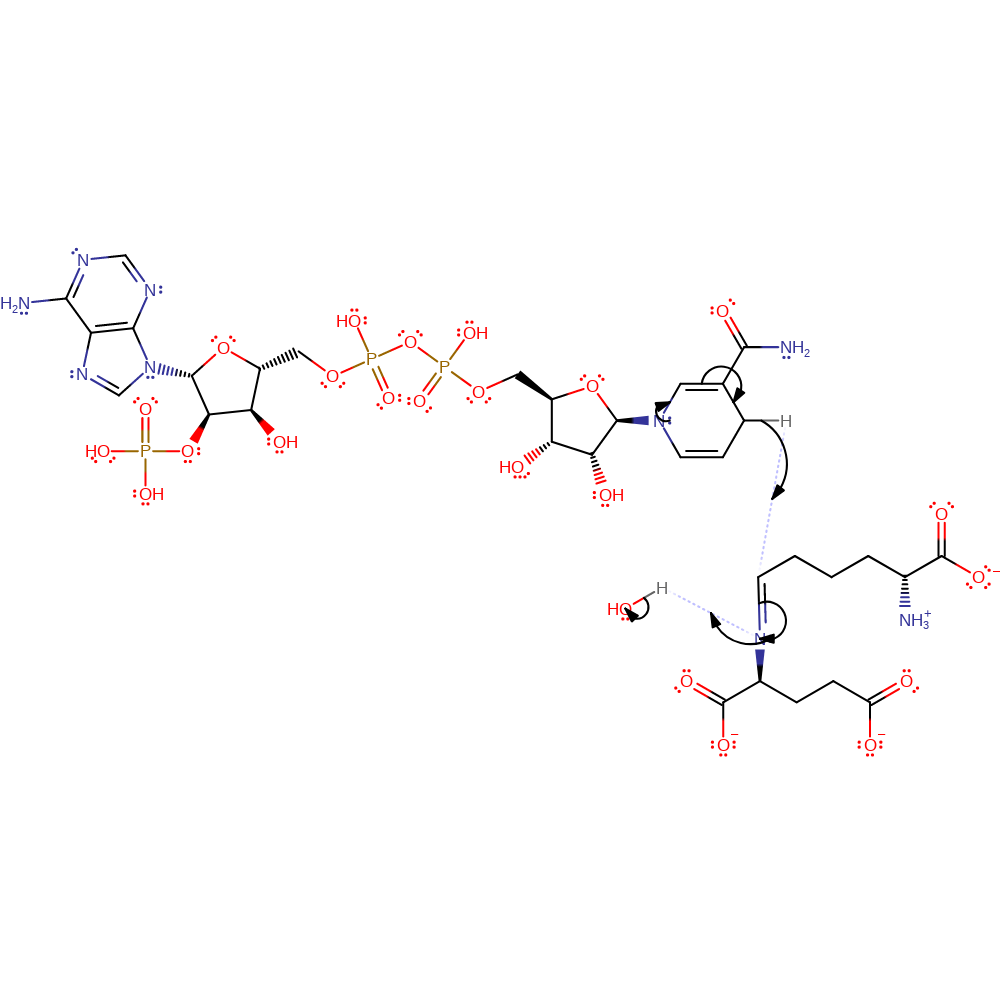
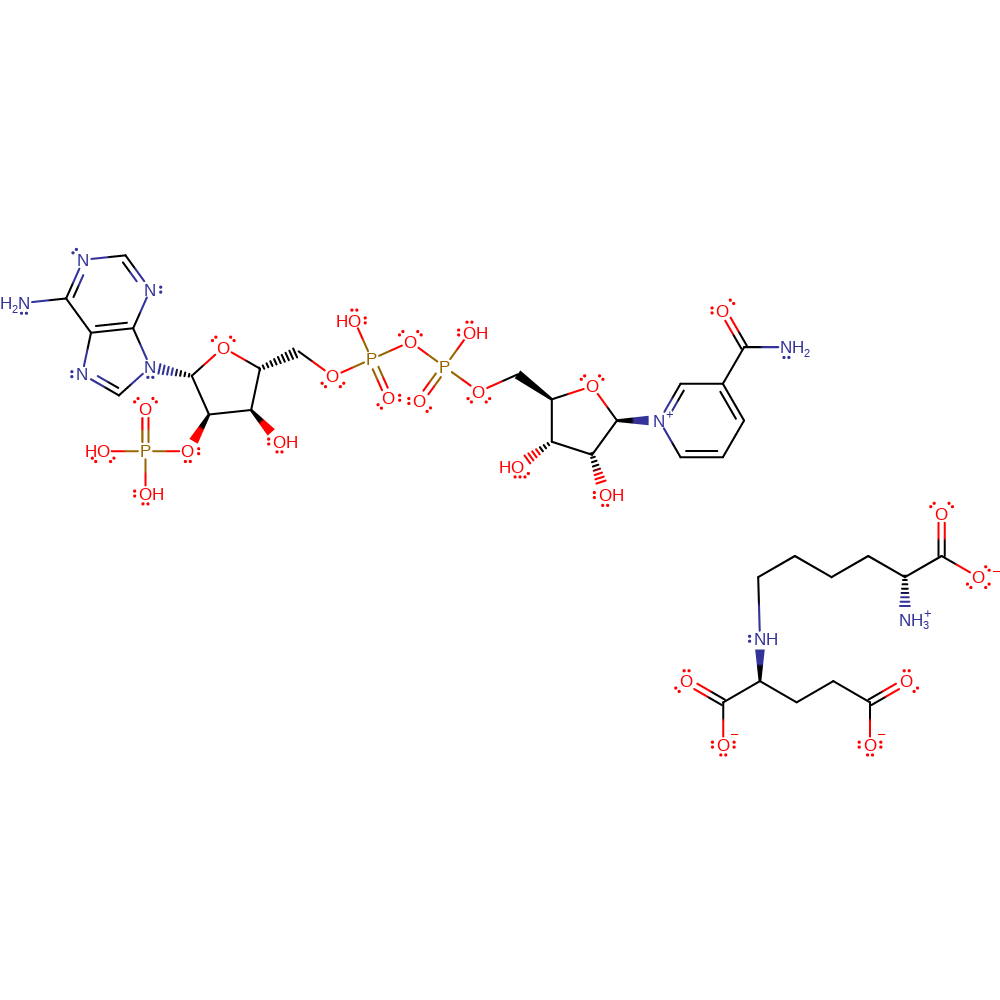
Step 3. The Schiff base intermediate is reduced via hydride transfer from NADPH with concomitant protonation of the developing amine nitrogen. The identity of the proton donor is currently unknown.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|







 Download:
Download: