Scytalidopepsin B
Scytalidopepsin-B is a member of a group of fungal pepstatin-insensitive glutamic peptidases known as the eqolsins. The enzyme has been shown to cleave angiotensin II and the oxidised insulin B chain, and operates most efficiently in acidic conditions. The eqolsins show no sequence homology to the well known pepsin-like or retroviral aspartic peptidases.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P15369
 (3.4.23.32)
(3.4.23.32)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Scytalidium lignicola (Fungus)

- PDB
-
1s2k
- Structure of SCP-B a member of the Eqolisin family of Peptidases in a complex with a Tripeptide Ala-Ile-His
(2.0 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
2.60.120.700
 (see all for 1s2k)
(see all for 1s2k)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:3.4.23.32)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
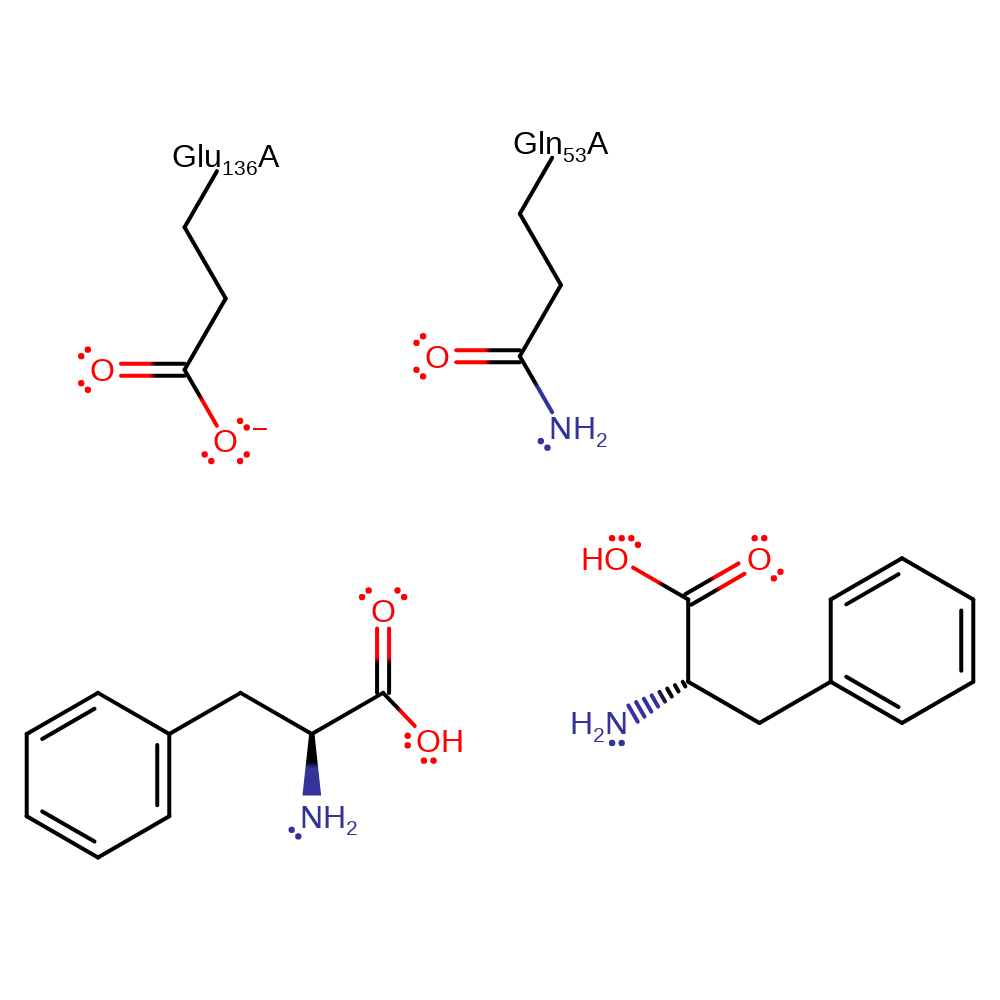
Glu 136 removes a proton from a water molecule which acts as a nucleophile to attack the peptide carbonyl. The tetrahedral intermediate and transition state leading to it is stabilised by hydrogen bonding from the side chain amide of Gln 53. Collapse of the intermediate with protonation of the departing nitrogen by Glu 136 completes the reaction.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1s2k) | ||
| Gln107 | Gln53A | Stabilises the tetrahedral intermediate/transition state. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu190 | Glu136A | Removes a proton from a water molecule which then attacks the peptide carbonyl. Later protonates the departing amine leaving group. | proton acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, rate-determining step, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate collapse, heterolysis, overall product formed, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Fujinaga M et al. (2004), Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 101, 3364-3369. The molecular structure and catalytic mechanism of a novel carboxyl peptidase from Scytalidium lignicolum. DOI:10.1073/pnas.0400246101. PMID:14993599.
- Pillai B et al. (2007), J Mol Biol, 365, 343-361. Crystal structure of scytalidoglutamic peptidase with its first potent inhibitor provides insights into substrate specificity and catalysis. DOI:10.1016/j.jmb.2006.09.058. PMID:17069854.
- Kataoka Y et al. (2005), FEBS Lett, 579, 2991-2994. Catalytic residues and substrate specificity of scytalidoglutamic peptidase, the first member of the eqolisin in family (G1) of peptidases. DOI:10.1016/j.febslet.2005.04.050. PMID:15907842.

Step 1. Glu136 abstracts a proton from water which activates it to nucleophilically attack the carbonyl carbon.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gln53A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu136A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, rate-determining step
Step 2. The amide nitrogen is protonated by Glu136 which initiates an elimination from the oxyanion which results in the cleavage of the peptide bond.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gln53A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu136A | proton donor |



 Download:
Download: