Glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (NAD+)
Glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase catalyses the interconversion of glycerol-3-phosphate (G3P) and Dihydroxyacetone-3-phosphate (DHAP), which is vital in the mitochondrial NAD/NADH shuttle. The dehydrogenase isolated from Leishmania mexicana (trypanosome) displays little sequence homology with the human system, thus may be a target for drug design.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P90551
 (1.1.1.8)
(1.1.1.8)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Leishmania mexicana (Leishmania)

- PDB
-
1evy
- CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF LEISHMANIA MEXICANA GLYCEROL-3-PHOSPHATE DEHYDROGENASE
(1.75 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
1.10.1040.10
 (see all for 1evy)
(see all for 1evy)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:1.1.1.8)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
Lys 210 acts as the general base for the extraction of a proton from G3P, forming an intermediate with negative charge on the oxygen, stabilised by contacts with Thr 267. This intermediate then collapses via hydride transfer to the NAD+ cofactor to form the DHAP product.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1evy) | ||
| Thr267 | Thr267A | Makes favourable contacts with the negatively charged oxygen of the intermediate to stabilise the transition state. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys210 | Lys210A | Acts as a general base to extract a proton from G3P to form the charged intermediate thus facilitating hydride transfer from the substrate to NAD+ | proton acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, aromatic bimolecular nucleophilic addition, hydride transfer, overall product formed, intermediate collapse, inferred reaction step, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Choe J et al. (2003), J Mol Biol, 329, 335-349. Leishmania mexicana Glycerol-3-phosphate Dehydrogenase Showed Conformational Changes Upon Binding a Bi-substrate Adduct. DOI:10.1016/s0022-2836(03)00421-2. PMID:12758080.
- Suresh S et al. (2000), Structure, 8, 541-552. A potential target enzyme for trypanocidal drugs revealed by the crystal structure of NAD-dependent glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase from Leishmania mexicana. DOI:10.1016/s0969-2126(00)00135-0. PMID:10801498.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Thr267A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys210A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, intermediate formation, overall reactant used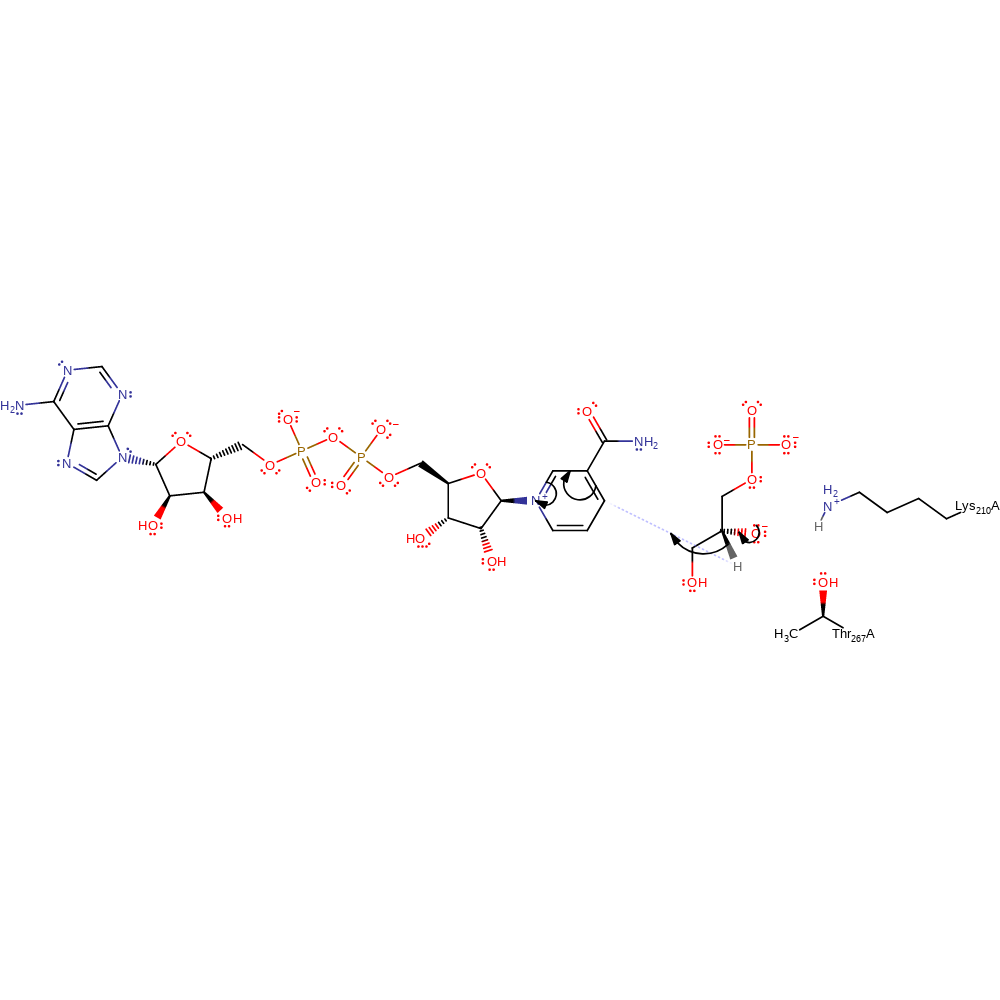
Step 2. A hydride is transferred from G3P to NAD+ in an aromatic bimolecular nucleophilic addition reaction and the product is formed.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|
Chemical Components
ingold: aromatic bimolecular nucleophilic addition, hydride transfer, overall product formed, intermediate collapse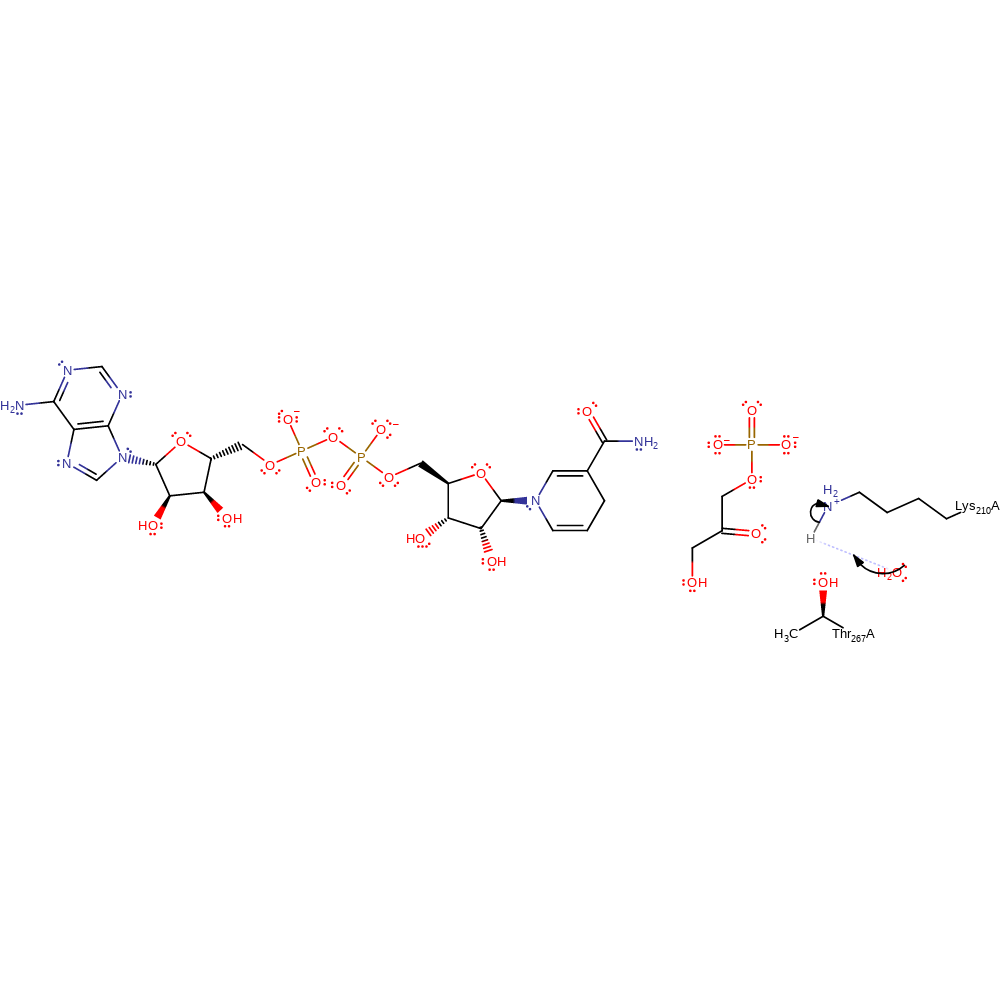
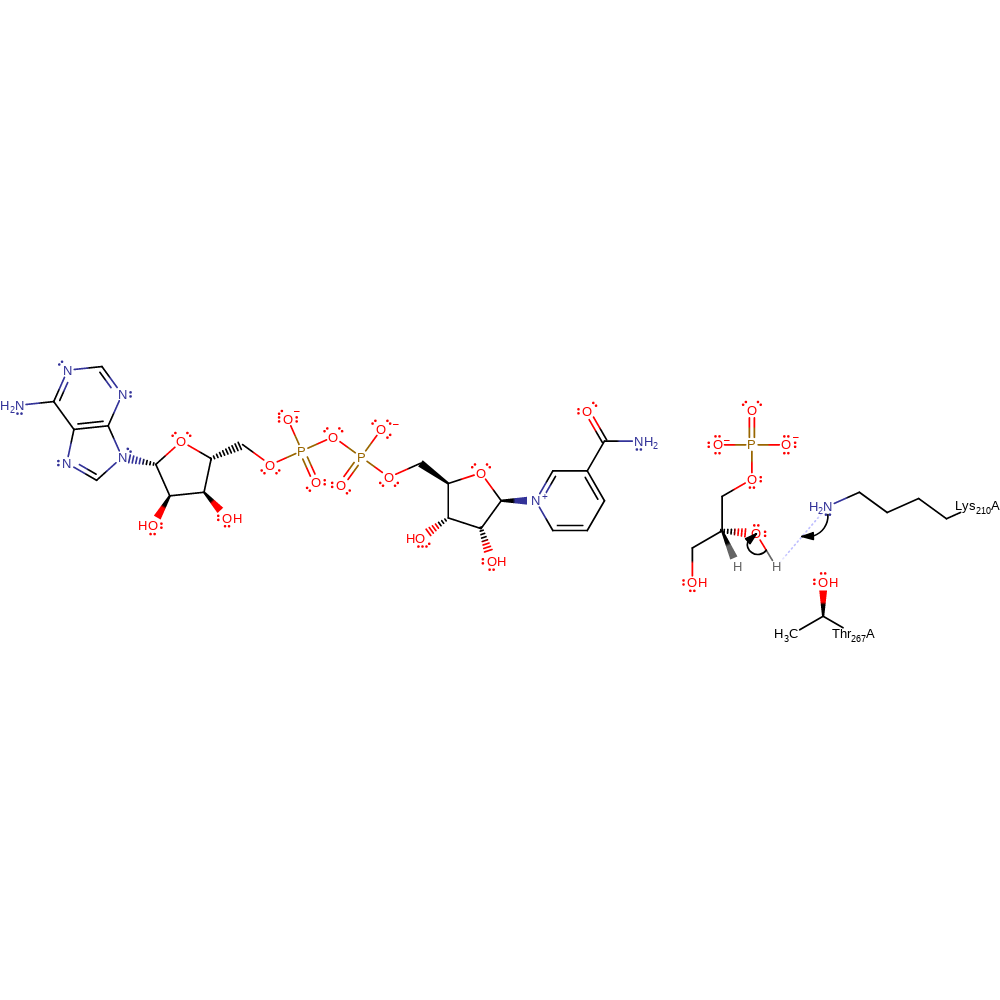
Step 3. In an inferred reaction step Lys210 is deprotonated to regenerate the native state of the enzyme.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys210A | proton donor |





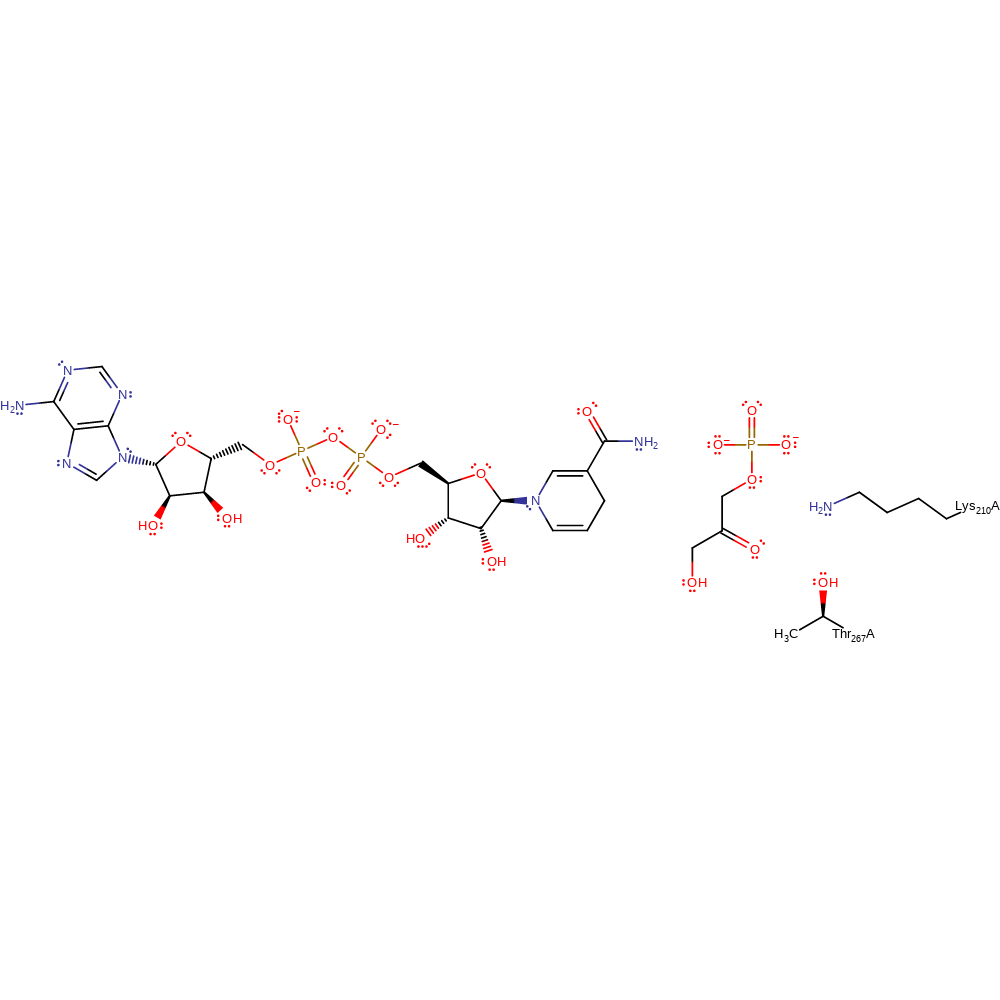 Download:
Download: