Stromelysin 1
Human stromelysin-1 (matrix metalloproteinase 3, MMP-3) is one of the most attractive targets in drug discovery today because of its broad physiological specificity.This extracellular endopeptidase of vertebrate tissues degrades various proteoglycan components of the extracellular matrix as well as fibronectin and laminin. Stromelysin also plays a unique role among the MMPs because of its involvement in activation of other MMP proenzymes.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P08254
 (3.4.24.17)
(3.4.24.17)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Homo sapiens (Human)

- PDB
-
1hfs
- CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE CATALYTIC DOMAIN OF HUMAN FIBROBLAST STROMELYSIN-1 INHIBITED WITH THE N-CARBOXY-ALKYL INHIBITOR L-764,004
(1.7 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.390.10
 (see all for 1hfs)
(see all for 1hfs)
- Cofactors
- Zinc(2+) (1)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:3.4.24.17)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The general base role is assigned to the Glu202 in MMPs. The water molecule, coordinated to the metal in the reactant complex, is being extremely polarised between the glutamate base and zinc Lewis acid in the Glu-water- Zn bridge.Upon substrate delivery, the water oxygen performs a nucleophilic attack on the peptide carbon.Concertedly, the glutamate abstracts the proton from the water and shuttles it toward the nitrogen of the scissile amide. The tetrahedral gem -diolate intermediate is formed, bidentatelycoordinated to the metal. According to the classic proposals for zinc endopeptidases, the final breakdown of the C- N bond occurs only after the second proton transferred from the water oxygen, mediated again by the conserved glutamate; the oxyanion hole here is stabilised by His218, His222 and His228.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1hfs) | ||
| His218, His222, His228 | His201(114)A, His205(118)A, His211(124)A | Forms part of the Zinc binding site. | metal ligand |
| Glu219 | Glu202(115)A | Acts as a general base on water, to create nucleophile from attack on the amide carbonyl. | proton acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, coordination to a metal ion, intermediate formation, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate collapse, heterolysis, native state of enzyme regenerated, overall product formedReferences
- Pelmenschikov V et al. (2002), Inorg Chem, 41, 5659-5666. Catalytic Mechanism of Matrix Metalloproteinases: Two-Layered ONIOM Study. DOI:10.1021/ic0255656. PMID:12401069.
- Feliciano GT et al. (2015), J Mol Struct, 1091, 125-132. Unravelling the reaction mechanism of matrix metalloproteinase 3 using QM/MM calculations. DOI:10.1016/j.molstruc.2015.02.079.
- Kohno T et al. (2006), Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 344, 315-322. Crystal structures of the catalytic domain of human stromelysin-1 (MMP-3) and collagenase-3 (MMP-13) with a hydroxamic acid inhibitor SM-25453. DOI:10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.03.098. PMID:16603129.
- Manzetti S et al. (2003), J Comput Aided Mol Des, 17, 551-565. Modeling of enzyme–substrate complexes for the metalloproteases MMP-3, ADAM-9 and ADAM-10. DOI:10.1023/B:JCAM.0000005765.13637.38.
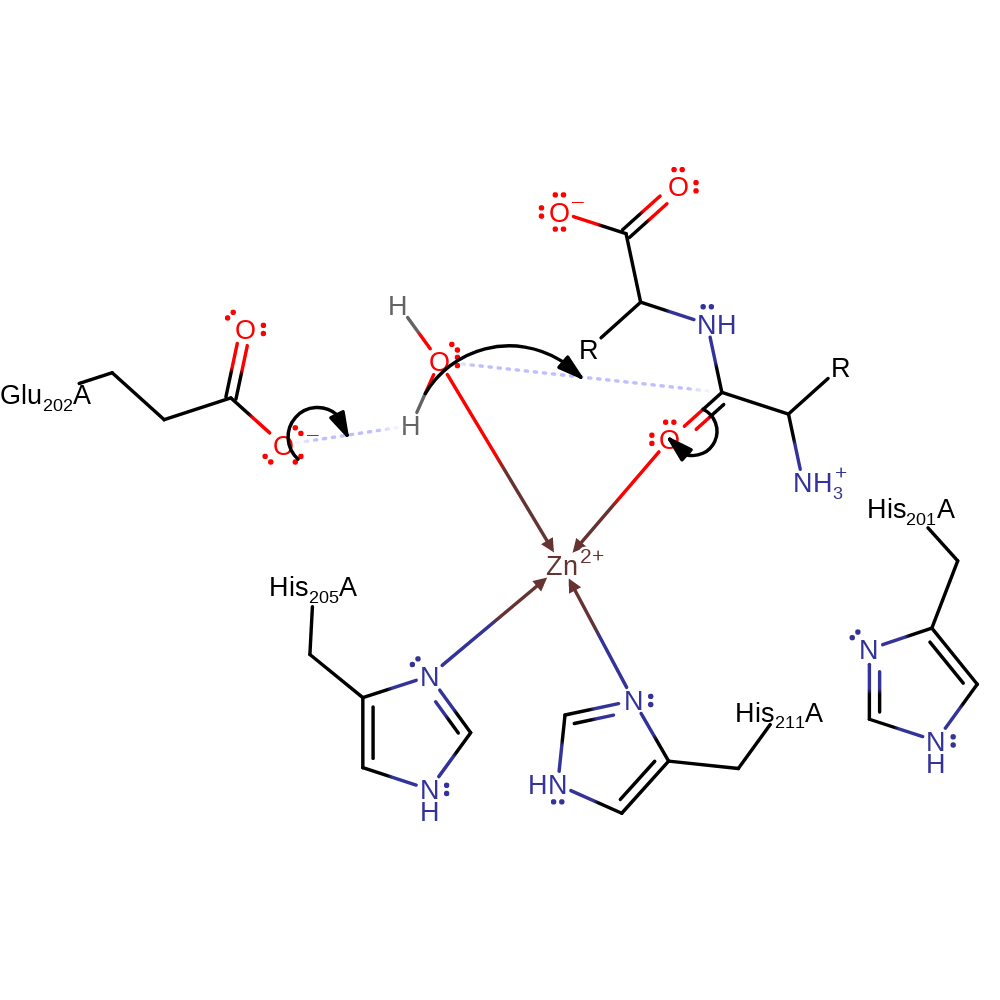
Step 1. Glu202 deprotonates water, which attacks the peptide bond in a nucleophilic addition. Zinc coordinates to water and carbonyl oxygen which means His218 is not coordinated to Zinc.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His205(118)A | metal ligand |
| His211(124)A | metal ligand |
| Glu202(115)A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, coordination to a metal ion, intermediate formation
Step 2. The oxyanion initiates an elimination that cleaves the peptide bond. The N-terminal product deprotonates Glu202. Zn is no longer coordinated to the carbonyl oxygen and so instead coordinates to His231.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His201(114)A | metal ligand |
| His205(118)A | metal ligand |
| His211(124)A | metal ligand |
| Glu202(115)A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate collapse, heterolysis, native state of enzyme regenerated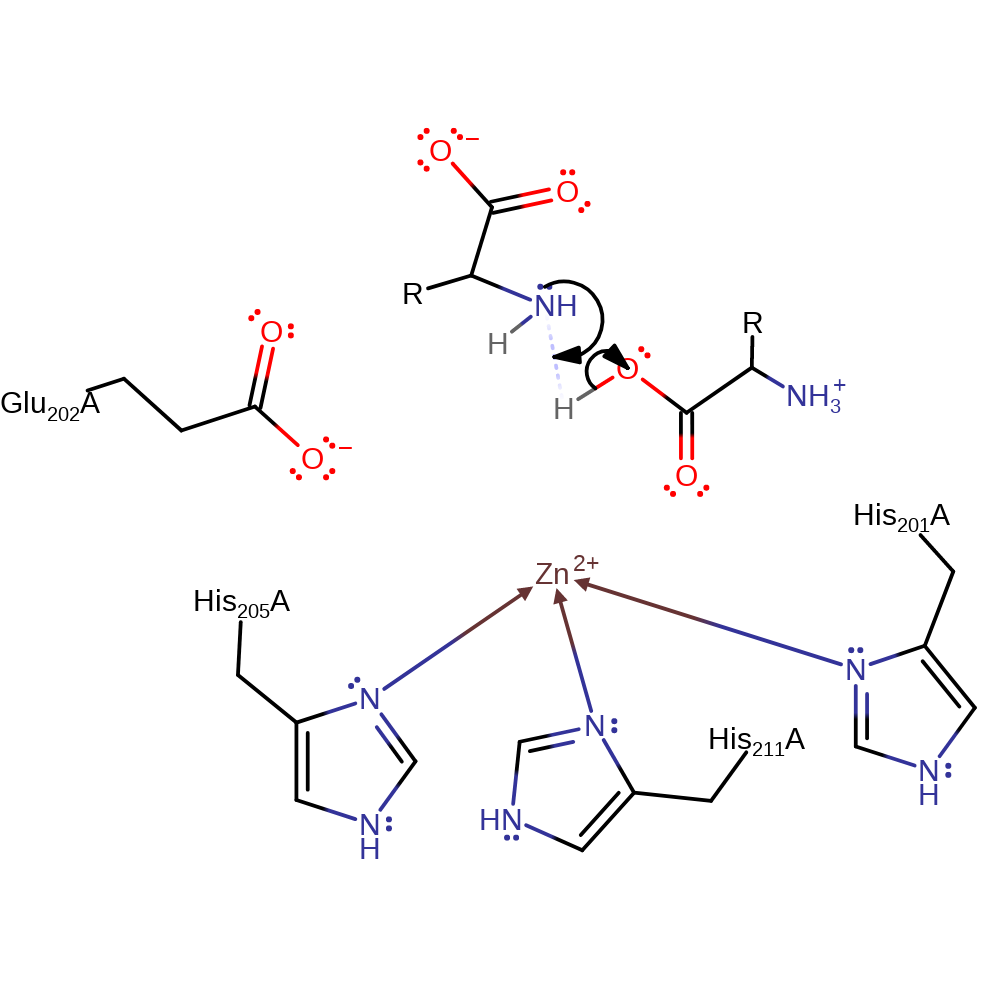
Step 3. The N-terminal product then deprotonates the C-terminal product to form the kinetically favourable products.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His201(114)A | metal ligand |
| His205(118)A | metal ligand |
| His211(124)A | metal ligand |



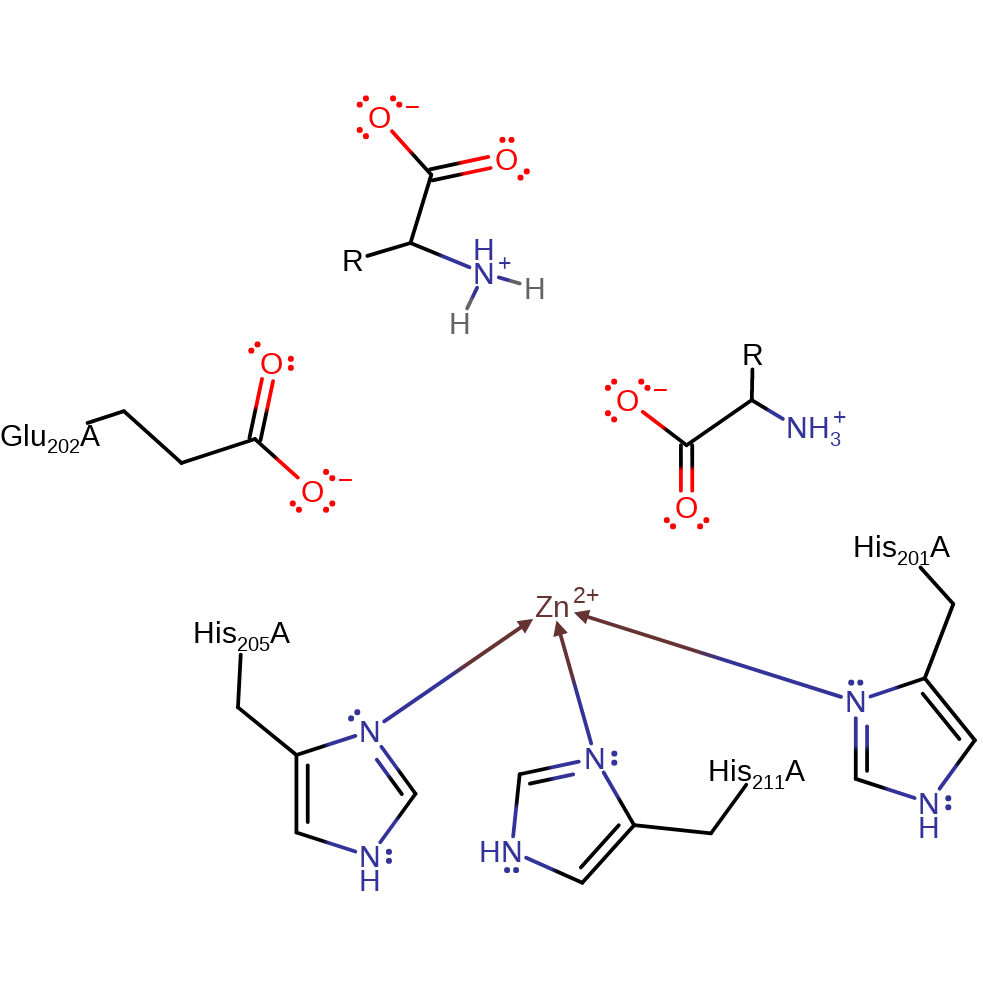 Download:
Download: