L-lactate dehydrogenase
Lactate dehydrogenase catalyses the interconversion of L-lactate and pyruvate in the glycolytic pathway, coupled with the reduction/oxidation of NAD+ and NADH. The enzyme crystallised from dogfish is a homotetramer. There has been some debate about whether the enzyme mechanism is concerted or stepwise.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P00341
 (1.1.1.27)
(1.1.1.27)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Squalus acanthias (spiny dogfish)

- PDB
-
1ldm
- Refined crystal structure of dogfish M4 apo-lactate dehydrogenase
(2.1 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.90.110.10
 3.40.50.720
3.40.50.720  (see all for 1ldm)
(see all for 1ldm)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:1.1.1.27)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
In the forward direction a proton is abstracted from lactate and a hydride donated to NAD+. In the reverse direction a proton is donated to pyruvate and a hydride ion donated from NADH. The proton donor/abstractor depending on direction is His193, which is regulated via hydrogen-bond to Asp166. The hydride is donated/abstracted by NADH/NAD+. It is likely that the reaction proceeds in a stepwise manner with Arg169 stabilising the charge via a strong salt bridge to the substrate, and possibly via electrostatic interactions from Arg106.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1ldm) | ||
| His194 | His193A | Acts as a general acid/base. | proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Arg107, Arg170 | Arg106A, Arg169A | Stabilise the reactive intermediates and transition states formed during the course of the reaction. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp167 | Asp166A | Forms a dyad with His193, enhancing its reactivity. | enhance reactivity |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, hydride transfer, overall reactant used, overall product formed, cofactor used, native state of enzyme regenerated, inferred reaction stepReferences
- Abad-Zapatero C et al. (1987), J Mol Biol, 198, 445-467. Refined crystal structure of dogfish M4 apo-lactate dehydrogenase. DOI:10.1016/0022-2836(87)90293-2. PMID:3430615.
- Cameron A et al. (2004), J Biol Chem, 279, 31429-31439. Identification and activity of a series of azole-based compounds with lactate dehydrogenase-directed anti-malarial activity. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M402433200. PMID:15117937.

Step 1. His193 abstracts a proton from the hydroxyl group of the substrate. NAD accepts a hydride in a nucleophilic addition reaction.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp166A | enhance reactivity |
| Arg106A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg169A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His193A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, hydride transfer, overall reactant used, overall product formed, cofactor used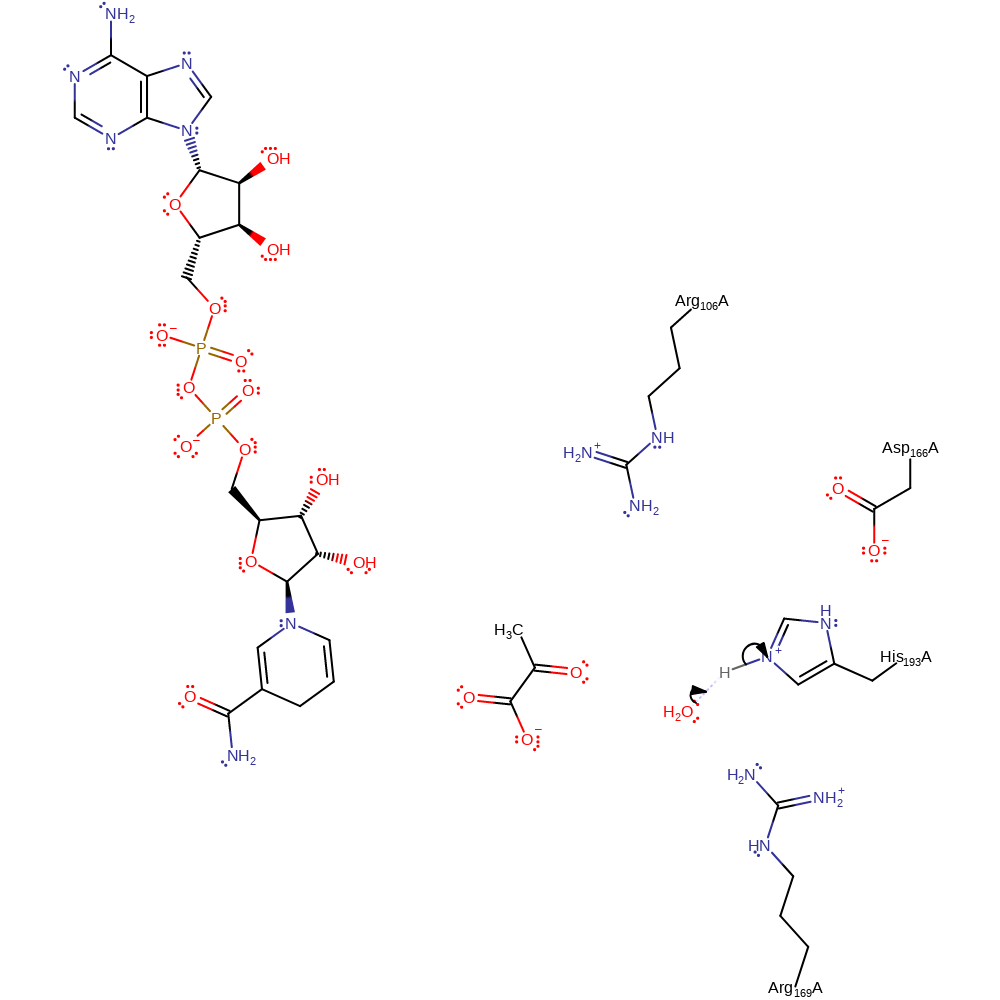
Step 2. In an inferred step his193 is deprotonated to regenerate the native state of the enzyme.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His193A | proton donor |





 Download:
Download: