Fumarate hydratase (class II)
Fumarase catalyses the reversible stereospecific hydration/dehydration of fumarate to L-malate during Kreb's cycle. Fumarase C is a member of the class II enzymes, a family which also includes aspartase, adenylosuccinate lyase and arginosuccinate, with high sequence similarity among its members. Fumarse C differs from the class I fumarase A and B enzymes in its lack of an apparent iron sulphur cluster.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P05042
 (4.2.1.2)
(4.2.1.2)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Escherichia coli K-12 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1fuq
- FUMARASE WITH BOUND 3-TRIMETHYLSILYLSUCCINIC ACID
(2.0 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
1.20.200.10
 (see all for 1fuq)
(see all for 1fuq)
- Cofactors
- Water (1)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:4.2.1.2)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The catalytic site is formed from residues which span three of the four enzyme subunits. In the direction of fumarate formation, a catalytic base, His188 (A) first activates a water molecule towards abstracting the C3 proton of the malate substrate. This generates an unstable carbanion which rearranges to the aci-carboxylate intermediate with concomitant proton donation to the enzyme, leaving the enzyme in a doubly protonated state. The catalytic Ser318 then acts as a general acid to a departing OH group from the C2 position, resulting in the loss of water and the formation of fumarate. The 'sticky' proton left on the enzyme is displaced by the binding of another malate molecule.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1fuq) | ||
| Ser318 | Ser318B | Acts as a general acid protonating the departing hydroxyl in the final step. | proton donor |
| His188 | His188A | The residue is catalytically important to the first step of the reaction, activating a water molecule to act as a base towards the C3 proton of malate. The residue its self is activated towards this role through an electrostatic interaction with Glu331, a connection which later in the reaction facilitates a proton relay from the enzyme to the solvent. | proton acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys324 | Lys324B | The residue's positively charged side chain is thought to stabilise the resulting carbanion from the initiated reaction step, and therefore facilitate the formation of the intermediate. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu331 | Glu331B | The residue is thought to activate His188 towards catalysis by modifying its pKa through electrostatic interactions. This interaction then forms the pathway for proton relay from the enzyme to the solvent when a second malate substrate molecule binds in the active site. | increase basicity |
Chemical Components
overall reactant used, proton transfer, charge delocalisation, intramolecular elimination, overall product formedReferences
- Weaver T et al. (1996), Biochemistry, 35, 13955-13965. Crystallographic Studies of the Catalytic and a Second Site in Fumarase C fromEscherichia coli†,‡. DOI:10.1021/bi9614702. PMID:8909293.
- Mechaly AE et al. (2012), FEBS Lett, 586, 1606-1611. Conformational changes upon ligand binding in the essential class II fumarase Rv1098c from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. DOI:10.1016/j.febslet.2012.04.034. PMID:22561013.
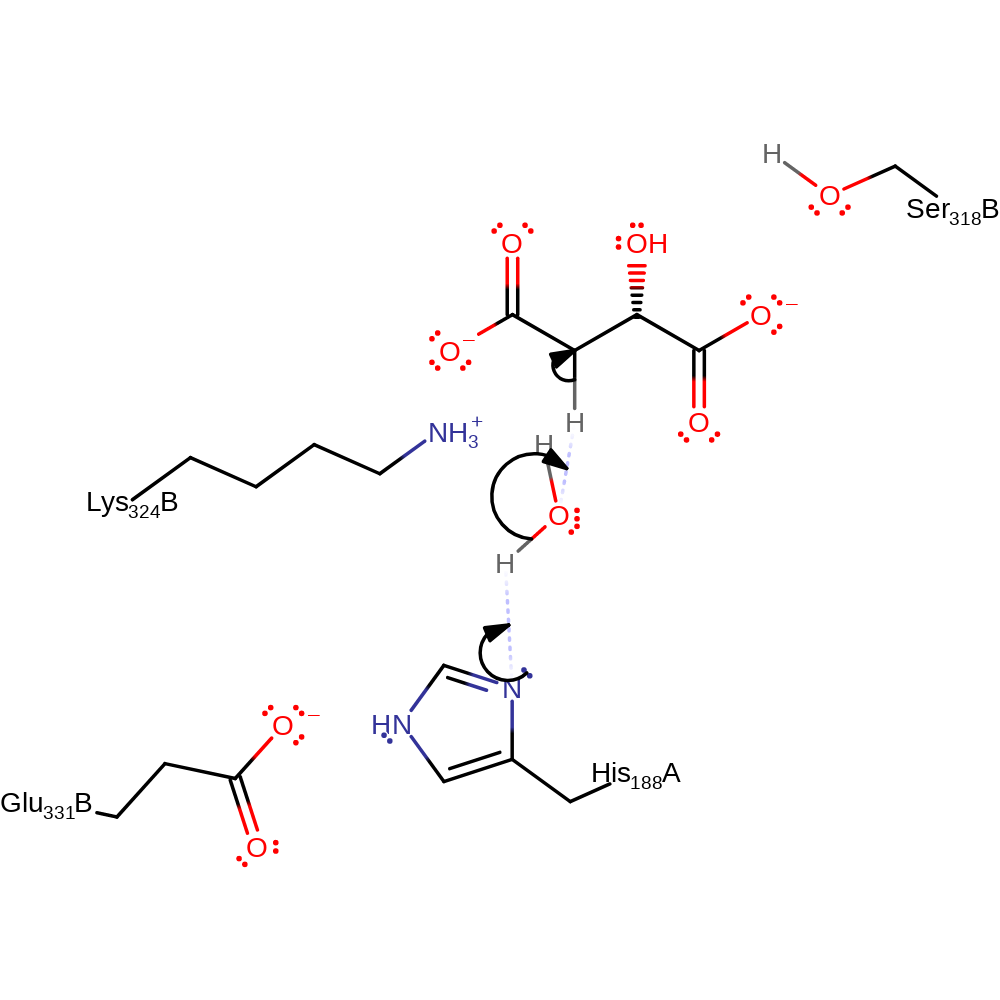
Step 1. His188 activates a water molecule which abstracts a proton from C3 of malate. Glu331 acts to increase the basicity of His188. A carboanion is formed which is stabilized by Lys324.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His188A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys324B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu331B | increase basicity |
| His188A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
overall reactant used, proton transfer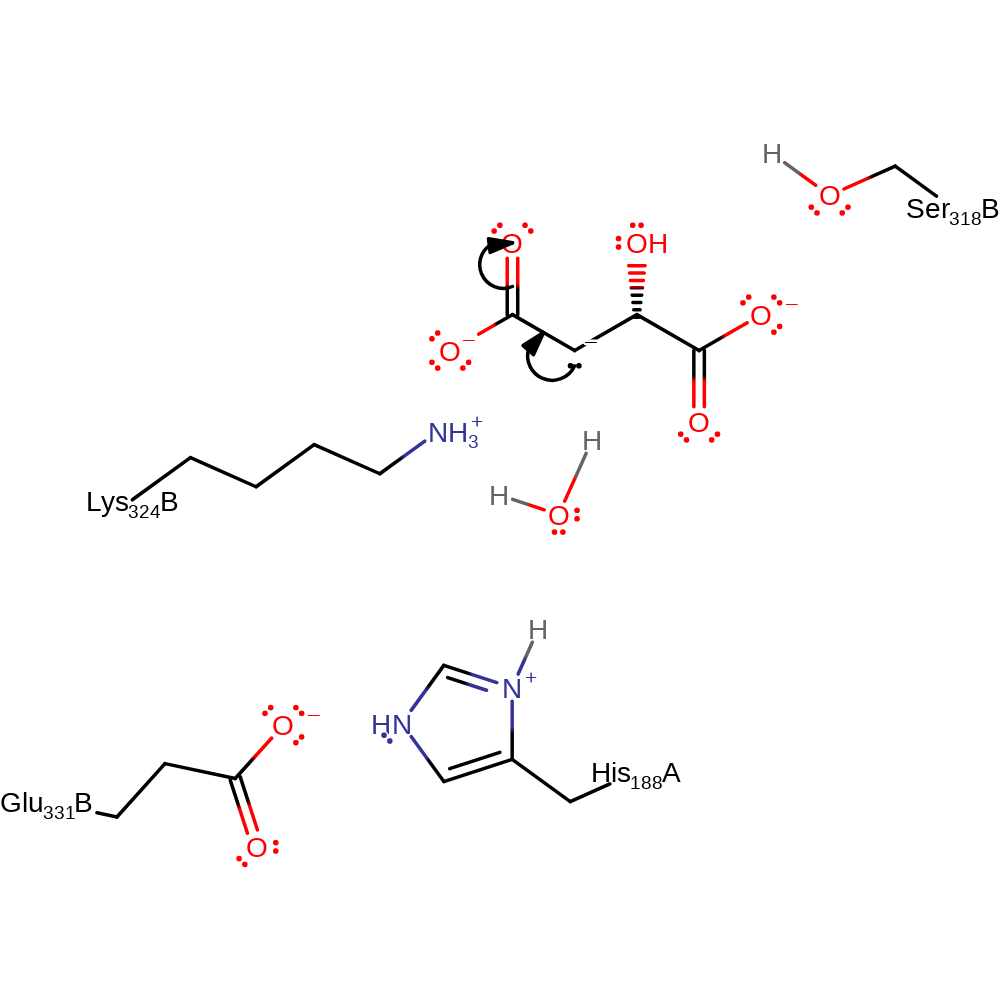
Step 2. The negative charge of the carboanion is delocalized to the carbonyl oxygen.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His188A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys324B | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
charge delocalisation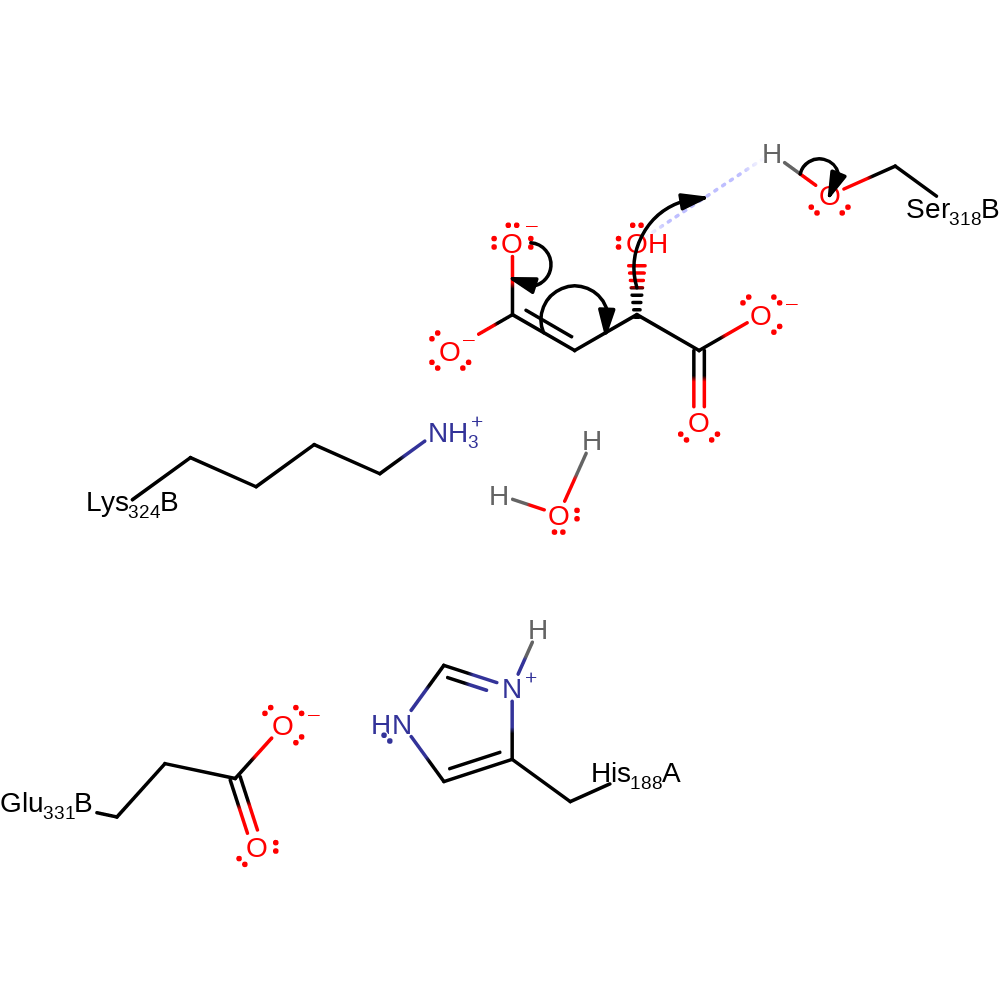
Step 3. Water is eliminated from C2 in an overall E1CB reaction with Ser318 acting as an acid protonating the hydroxyl.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His188A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys324B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser318B | proton donor |



 Download:
Download: