Formate dehydrogenase (nitrate-inducible)
Formate dehydrogenase-N (Fdn-N) isolated from Escherichia coli catalyses the oxidation of formate to carbon dioxide and a proton, coupled to the reduction of menaquinone to menaquinol. Fdn-N is involved in nitrate respiration and forms a redox loop with dissimilatory nitrate reductase (Nar). Together they pump protons across the membrane by reducing menaquinone at Fdn-N (taking up protons from the cytoplasm) and oxidising menaquinol at Nar, (releasing protons into the periplasm). They also generate a membrane potential by moving electrons from Fdn-N to Nar.
Fdn-N contains an active site for formate oxidation (alpha subunit) and an active site for menaquinone reduction (gamma subunit). They are linked by a redox chain containing two haem groups (gamma), five [4Fe-4S] clusters (FeS-0 in alpha and FeS-1 to FeS-4 in beta) and a molybdenum(VI) ion coordinated to two molybdopterin-guanine dinucleotides, the selenate group from Se-Cys196(alpha) and a hydroxide ion (alpha).
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequences
-
P24183
 (1.17.5.3)
(1.17.5.3)
P0AAJ3
P0AEK7
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Escherichia coli K-12 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1kqf
- FORMATE DEHYDROGENASE N FROM E. COLI
(1.6 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.228.10
 1.20.950.20
1.20.950.20  (see all for 1kqf)
(see all for 1kqf)
- Cofactors
- Molybdopterin guanine dinucleotide (2), Molybdenum(6+) (1), Tetra-mu3-sulfido-tetrairon (5), Heme b (2)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:1.17.5.3)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
Formate displaces the selenate group of Se-Cys196(alpha) from the Mo(VI) centre. His197(alpha) accepts a proton from formate, which leads to the formation of carbon dioxide (possibly via a selenium-carboxylated intermediate) and the reduction of the molybdenum centre to Mo(IV). The selenate group then re-coordinates to the metal centre. An electron is passed down a chain of iron-sulfur centres in the order FeS-0, FeS-1, FeS-4, FeS-2 and then FeS-3. It is transferred to haem bp, haem bc and then His169(gamma). Menaquinone accepts the electron from His169(gamma) and a proton through a water chain to form menasemiquinone. Mo(V) donates another electron and menasemiquinone is reduced to menaquinol and accepts a proton from His169(gamma). Menaquinol is released and His169(gamma) is protonated through a water channel.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1kqf) | ||
| Sec196 | Sec196A | The selenate group of Se-Cys196(alpha) is displaced from the molybdenum centre by formate. It is thought to be involved in a selenium-carboxylated intermediate before carbon dioxide is released. Once this has occurred the selenate can re-coordinate to the molybdenum centre. | covalently attached, nucleofuge, metal ligand |
| His197 | His197A | His197(alpha) accepts a proton during the two-electron oxidation of formate. | |
| His169 | His169C(CA) | His169(gamma) is a ligand for haem bc. It transfers electrons from the haem group to menaquinone/menasemiquinone. It also donates a proton to O-1 upon the reduction of menasemiquinone. It is reprotonated only after the menaquinol has been released and a water chain has formed. | single electron relay, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor, single electron acceptor, single electron donor |
Chemical Components
coordination to a metal ion, decoordination from a metal ion, decarboxylation, proton transfer, electron transfer, electron relay, intermediate formation, overall product formedReferences
- Jormakka M et al. (2002), Science, 295, 1863-1868. Molecular Basis of Proton Motive Force Generation: Structure of Formate Dehydrogenase-N. DOI:10.1126/science.1068186. PMID:11884747.
- Raaijmakers HC et al. (2006), J Biol Inorg Chem, 11, 849-854. Formate-reduced E. coli formate dehydrogenase H: the reinterpretation of the crystal structure suggests a new reaction mechanism. DOI:10.1007/s00775-006-0129-2. PMID:16830149.
- Blasco F et al. (2001), Cell Mol Life Sci, 58, 179-193. The coordination and function of the redox centres of the membrane-bound nitrate reductases. DOI:10.1007/pl00000846. PMID:11289300.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Sec196A | covalently attached |
| Sec196A | nucleofuge |
Chemical Components
coordination to a metal ion, decoordination from a metal ion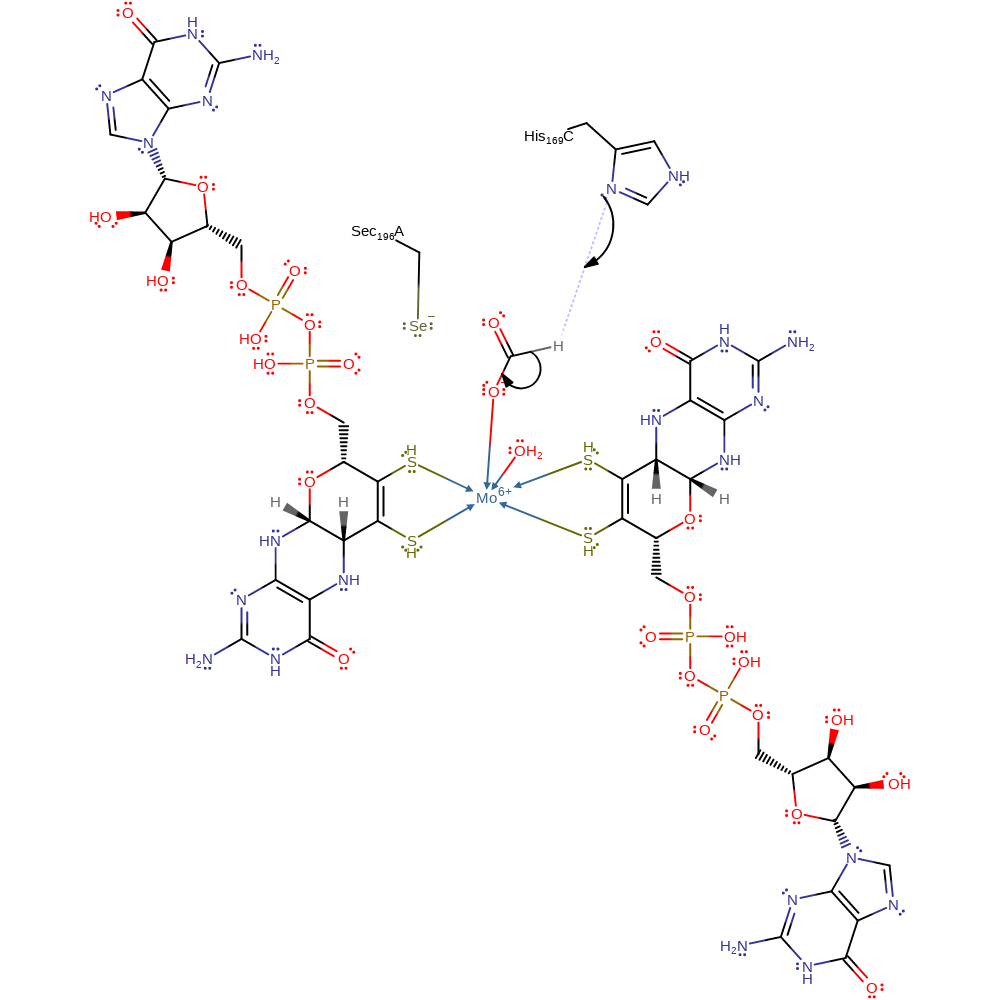
Step 2. His197 accepts a proton from formate, forming carbon dioxide and reducing the Mo centre to Mo(IV). The proton abstraction may proceed via a selenium-carboxylated intermediate. Following this step Sec196 re-coordinates to the metal centre.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His169C(CA) | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
decarboxylation, proton transfer, coordination to a metal ion, decoordination from a metal ion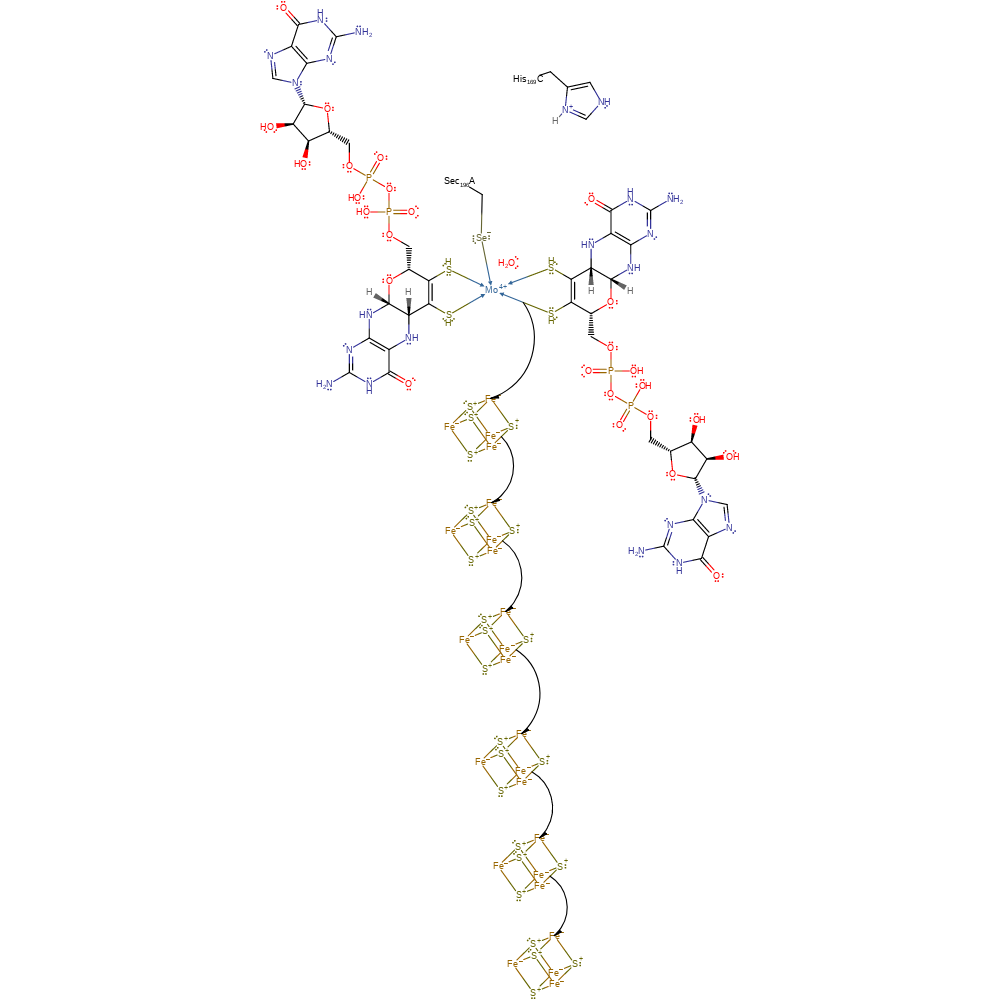
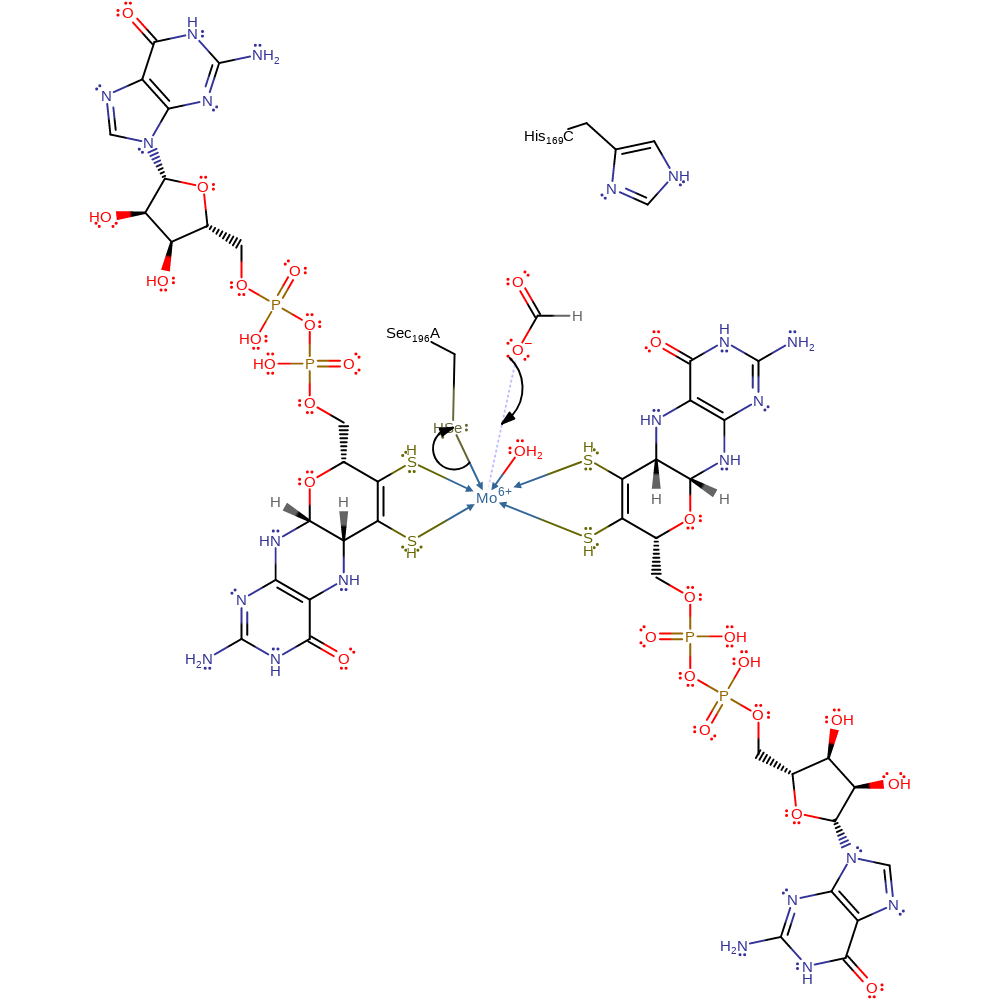
Step 3. An electron is passed down a chain of iron-sulfur centres in the alpha then beta subunit of the protein.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Sec196A | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
electron transfer, electron relay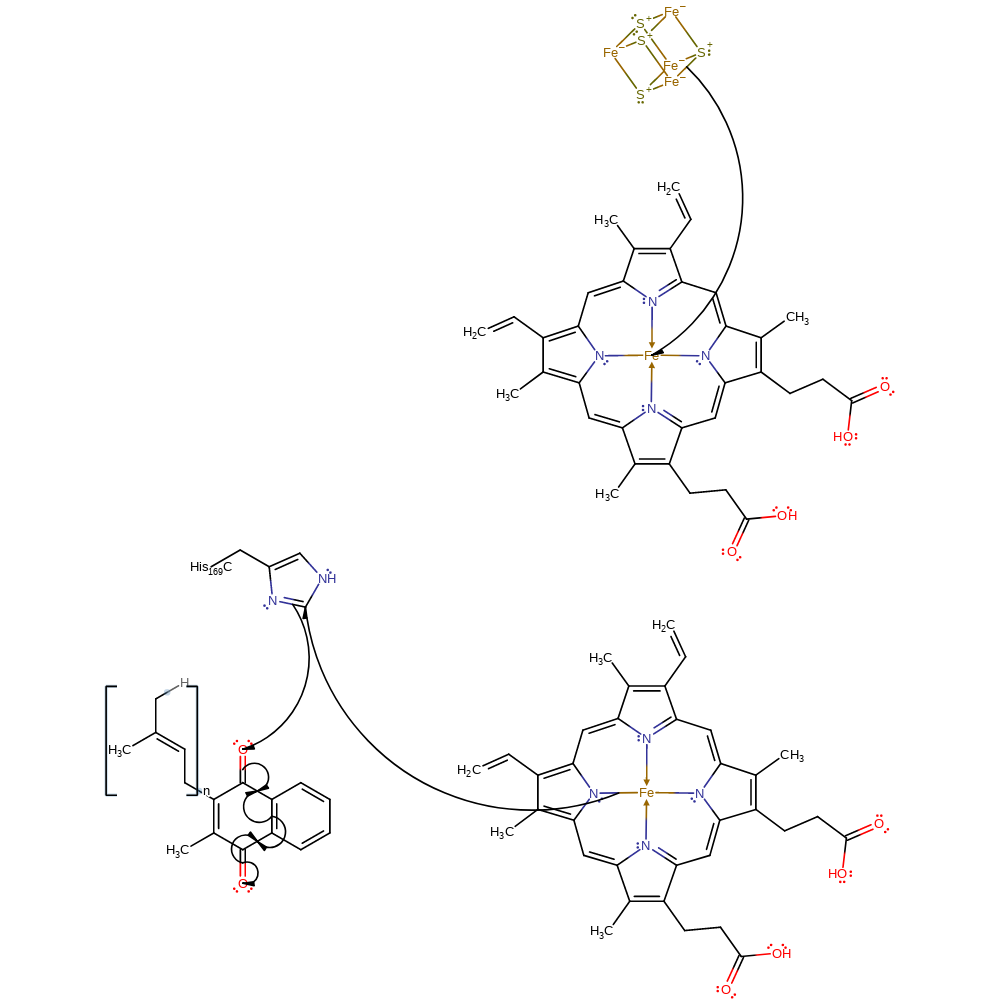
Step 4. The electron is then transferred to haem bp, haem bc, His169 then accepted by menaquinone in the gamma subunit of the protein. The oxygen accepts a proton through a water chain to form a radical menasemiquinone intermediate.The O1 atom of menaquinone accepts a hydrogen bond from His169.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His169C(CA) | hydrogen bond donor, single electron relay, single electron donor, single electron acceptor |
Chemical Components
electron relay, electron transfer, intermediate formation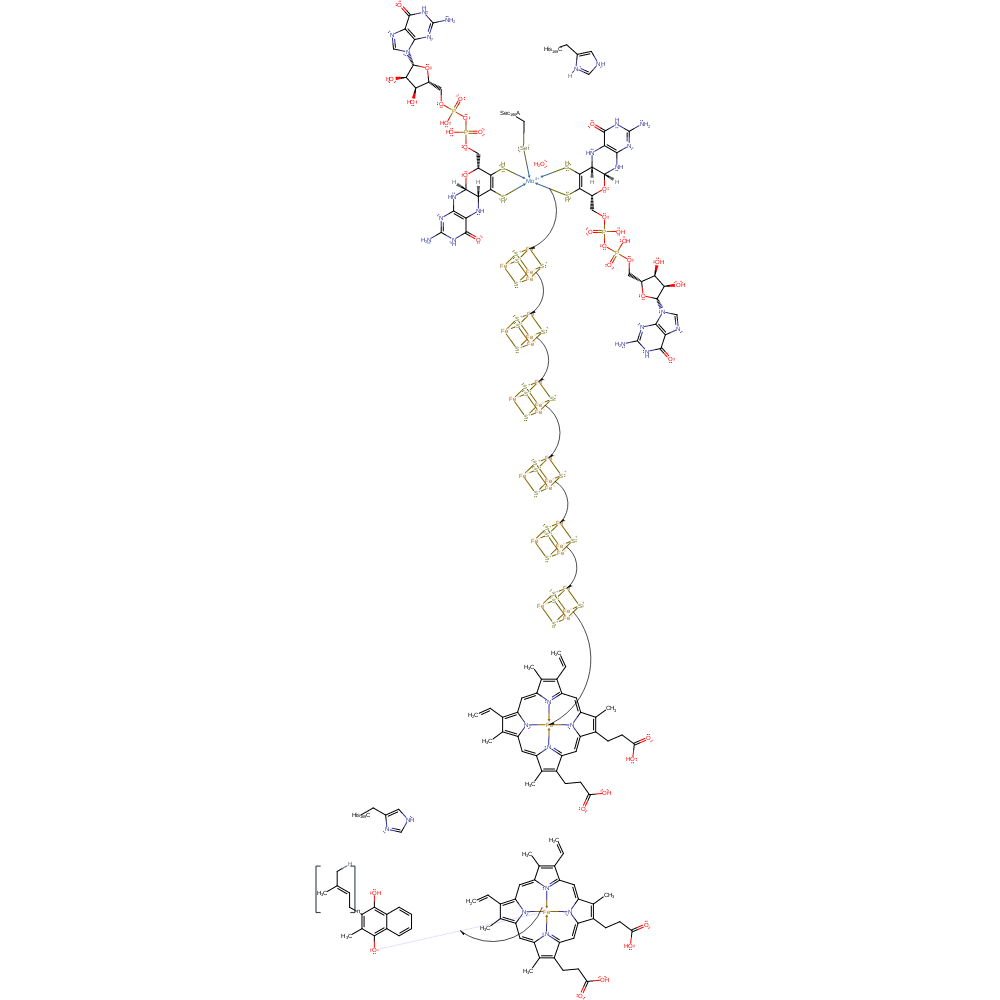
Step 5. Mo(V) donates another electron which is transferred through the iron sulfur clusters and haem cofactors to menasemiquinone. Mo(V) is oxidised to regenerate Mo(VI) and menasemiquinone is reduced.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Sec196A | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
electron transfer, electron relay, electron transfer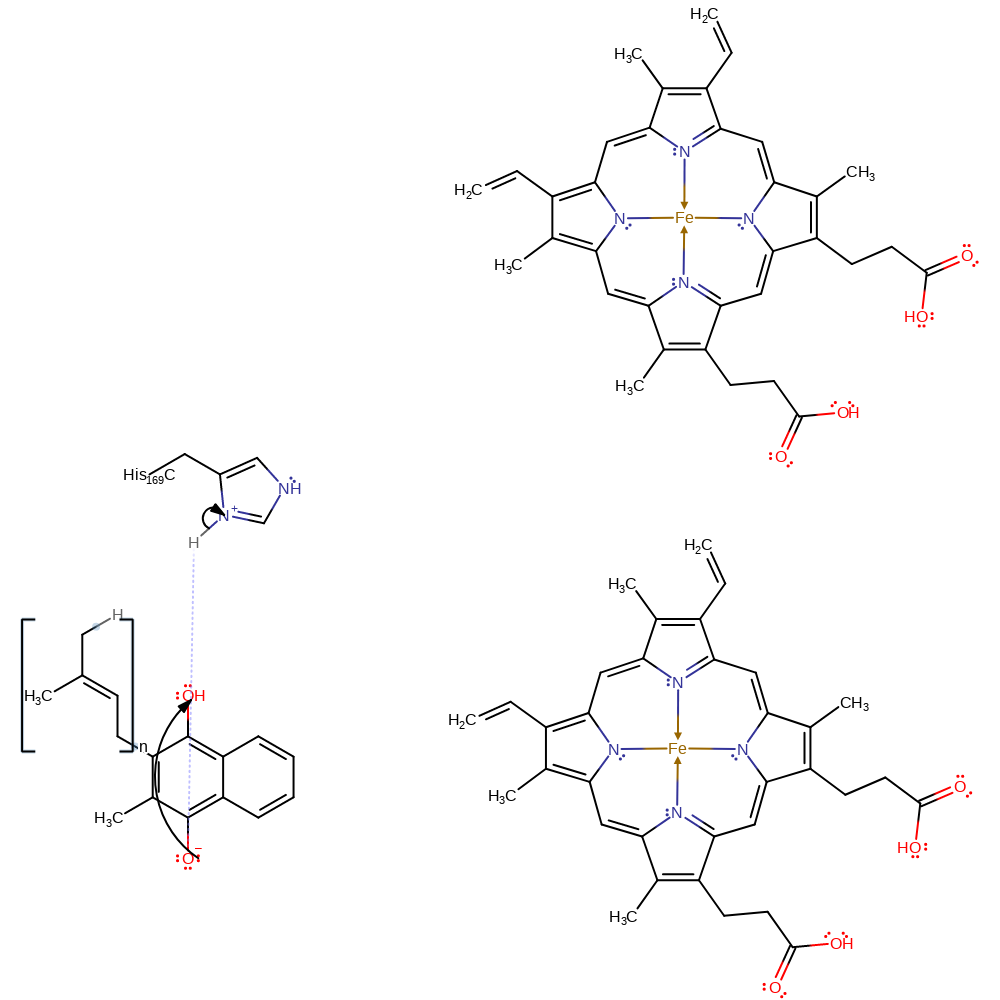
Step 6. The alkoxide accepts a proton from His169 and menaquinol is released. Deprotonated His169 is very unstable so it is immediately reprotonated via an extended water channel.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His169C(CA) | proton donor |





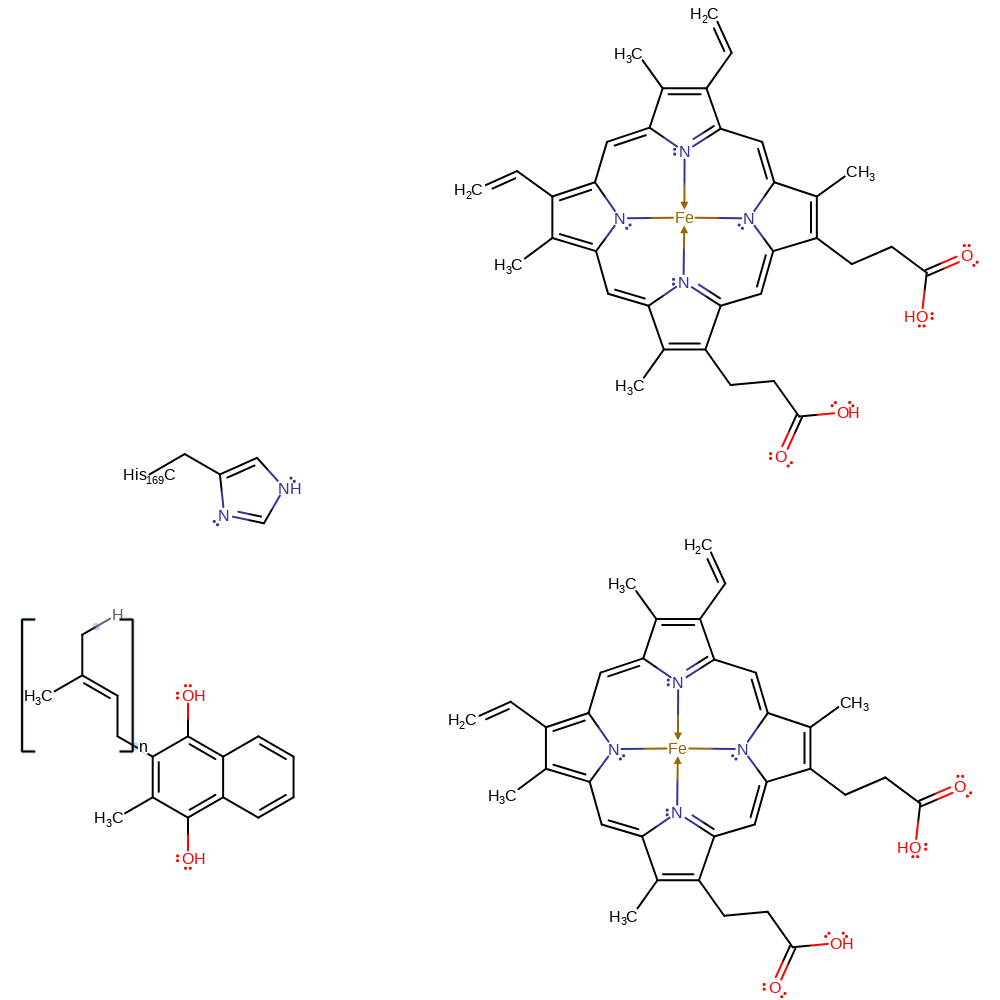 Download:
Download: