Cellulase (GH45)
Endoglucanase V (EGV) from Humicola insolens is a cellulase, catalysing the hydrolysis of the beta-(1,4) glycosidic bond of cellulose. Although the active site resembles lysozyme, with six hexose binding sites and similarly placed acidic residues, the enzymes are structurally different and produce products with different stereochemistries. It is a member of the glycoside hydrolase family 45.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P43316
 (3.2.1.4)
(3.2.1.4)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Humicola insolens (Fungus)

- PDB
-
2eng
- ENDOGLUCANASE V
(1.5 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
2.40.40.10
 (see all for 2eng)
(see all for 2eng)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:3.2.1.4)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
Asp 10 activates a water molecule via general base catalysis. The activated water can attack the electrophilic acetal carbon as hydroxide. SN2-type displacement of the linking oxygen occurs, with a protonated Asp 121 acting as a general acid donor to the oxygen. The products are a hemiacetal and secondary alcohol.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (2eng) | ||
| Asp10 | Asp10A | Asp 10 acts as a general base, deprotonating water to activate it as a nucleophile. | activator, increase nucleophilicity, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Asp121 | Asp121A | Asp 121 acts as a general acid to the linking oxygen of the breaking glycosidic bond. | promote heterolysis, proton acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
overall product formed, overall reactant used, proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, hydrolysis, inferred reaction step, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Davies GJ et al. (1993), Nature, 365, 362-364. Structure and function of endoglucanase V. DOI:10.1038/365362a0. PMID:8377830.
- Hirvonen M et al. (2003), J Mol Biol, 329, 403-410. Crystal Structure of a Family 45 Endoglucanase from Melanocarpus albomyces: Mechanistic Implications Based on the Free and Cellobiose-bound Forms. DOI:10.1016/S0022-2836(03)00467-4.
- Davies GJ et al. (1996), Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr, 52, 7-17. Structure determination and refinement of the Humicola insolens endoglucanase V at 1.5 Å Resolution. DOI:10.1107/s0907444995009280. PMID:15299721.
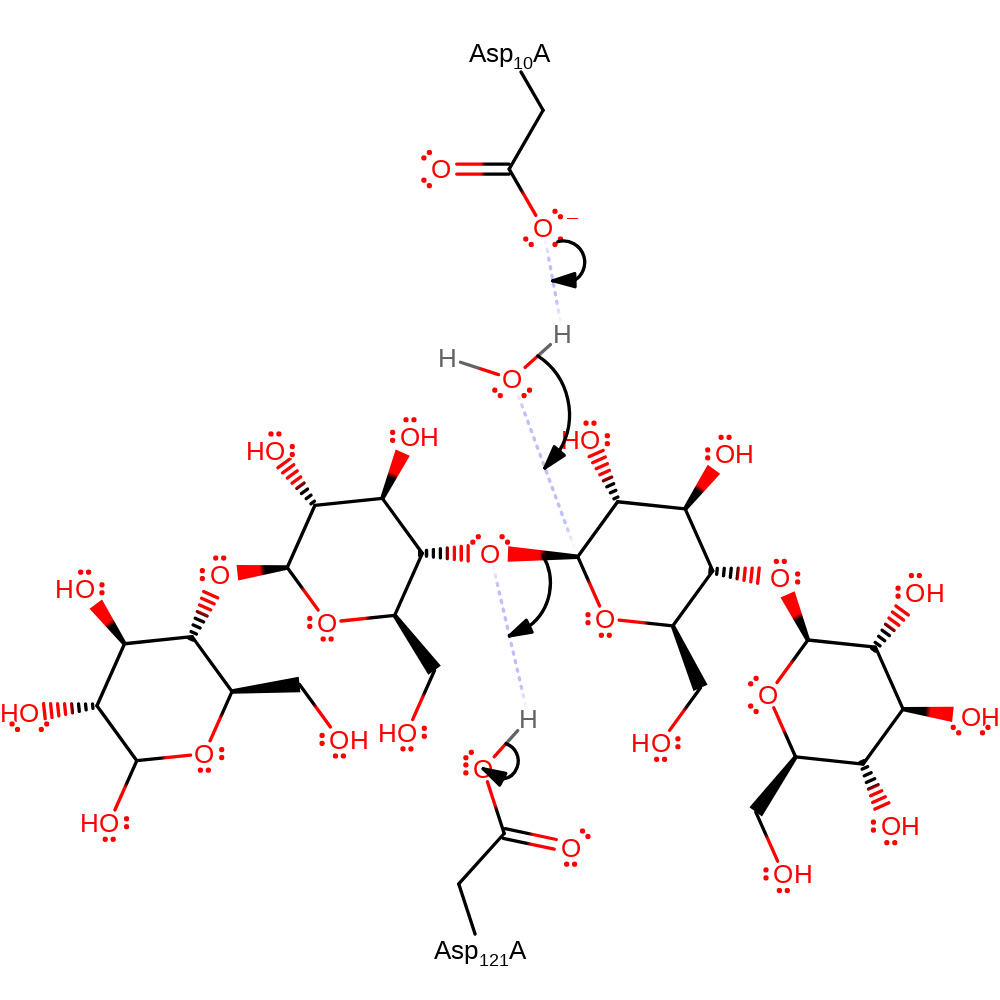
Step 1. Asp10 activates a water molecule which attacks the anomeric carbon causing the cleavage of the glycosidic bond upon protonation by Asp121.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp10A | activator, increase nucleophilicity |
| Asp121A | promote heterolysis |
| Asp10A | proton acceptor |
| Asp121A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
overall product formed, overall reactant used, proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, hydrolysisCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp10A | proton donor |
| Asp121A | proton acceptor |




 Download:
Download: