Fructose-bisphosphatase
Fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase (FBPase) hydrolyses fructose 1,6-bis-phosphate to fructose 6-phosphate and phosphate. The enzyme plays a crucial role in gluconeogenesis, the formation of glucose from non-carbohydrate carbon containing substrates. The enzyme is only capable of catalysing the forward reaction, while phosphofructokinase catalyses the reverse reaction. Regulation of the two enzyme is performed by metabolites such as fructose 2,6 bis-phosphate, ensuring that enhances reactivity of one enzyme is accompanied by suppressed reactivity of the other.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P00636
 (3.1.3.11)
(3.1.3.11)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Sus scrofa (pig)

- PDB
-
1eyi
- FRUCTOSE-1,6-BISPHOSPHATASE COMPLEX WITH MAGNESIUM, FRUCTOSE-6-PHOSPHATE AND PHOSPHATE (R-STATE)
(2.32 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.30.540.10
 3.40.190.80
3.40.190.80  (see all for 1eyi)
(see all for 1eyi)
- Cofactors
- Magnesium(2+) (3)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:3.1.3.11)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
There are three divalent metal cations present within the catalytic site. Mg(2+) at site one is directly coordinated to the 1-(OH) of the 6 fructose phosphate product as a fifth coordinating ligand. The cation is thought to stabilise the negative charge of the hydroxide group before the transfer of a proton from Asp68, which relays a proton from the substrate neutralises the product. The second metal coordinates to a nucleophilic water molecule, also polarised through hydrogen bonds to Asp74 and Glu98, which abstracts a proton from a second coordinated water. The resulting hydroxide ion is the attacking nucleophile, displacing the 6 fructose phosphate in an SN2 mechanism. The resulting oxide is protonated as stated above.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1eyi) | ||
| Glu98 | Glu97A | Acts as a bidentate ligand for Mg1 and Mg2 magnesium binding sites. | metal ligand |
| Asp69 | Asp68A | The residue acts as a proton carrier from the substrate to the product. It initially forms a hydrogen bond with the proton of the 1-phosphate group, and after the SN2 displacement step has taken place, relays the proton to the anionic 6-fructose phosphate intermediate. | metal ligand, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Asp75 | Asp74A | Acts as the general acid/base that abstracts the proton from the catalytic water molecule. | proton acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser, proton donor |
| Asp119 | Asp118A | Acts as a bidentate ligand for the Mg2 and Mg3 magnesium binding sites. | metal ligand |
| Leu121 (main-C) | Leu120A (main-C) | Forms part of the Mg2 magnesium binding site. | metal ligand |
| Asp122, Glu281 | Asp121A, Glu280A | Forms part of the Mg3 magnesium binding site. | metal ligand |
| Glu99 | Glu98A | The residue's anionic carboxylic side chain hydrogen bonds to the basic water molecule in the close proximity Mg(2+) coordination sphere. The resulting polarisation enhances the basic character of the water molecule, activating it towards deprotonating a second, adjacent water molecule. | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, overall product formed, inferred reaction step, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Choe JY et al. (2000), Biochemistry, 39, 8565-8574. Crystal Structures of Fructose 1,6-Bisphosphatase: Mechanism of Catalysis and Allosteric Inhibition Revealed in Product Complexes†,‡. DOI:10.1021/bi000574g. PMID:10913263.
- Gao Y et al. (2013), Biochemistry, 52, 5206-5216. Mechanism of displacement of a catalytically essential loop from the active site of mammalian fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase. DOI:10.1021/bi400532n. PMID:23844654.
- Iancu CV et al. (2005), J Biol Chem, 280, 19737-19745. R-state AMP complex reveals initial steps of the quaternary transition of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M501011200. PMID:15767255.
- Choe JY et al. (2003), J Biol Chem, 278, 16015-16020. Metaphosphate in the active site of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M212395200. PMID:12595528.
- Choe JY et al. (2003), J Biol Chem, 278, 16008-16014. Interaction of Tl+ with product complexes of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M212394200. PMID:12595529.

Step 1. Asp74 abstracts a proton from the catalytic water, which attacks the metal bound phosphate and eliminates the F6P as a negatively charged intermediate in an SN2-type reaction. It is likely that the reaction proceeds via a pentavalent transition state.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp74A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu98A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp118A | metal ligand |
| Leu120A (main-C) | metal ligand |
| Glu97A | metal ligand |
| Asp68A | metal ligand |
| Asp121A | metal ligand |
| Glu280A | metal ligand |
| Asp74A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
Catalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp118A | metal ligand |
| Leu120A (main-C) | metal ligand |
| Glu97A | metal ligand |
| Asp68A | metal ligand |
| Asp121A | metal ligand |
| Glu280A | metal ligand |
| Glu98A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp68A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer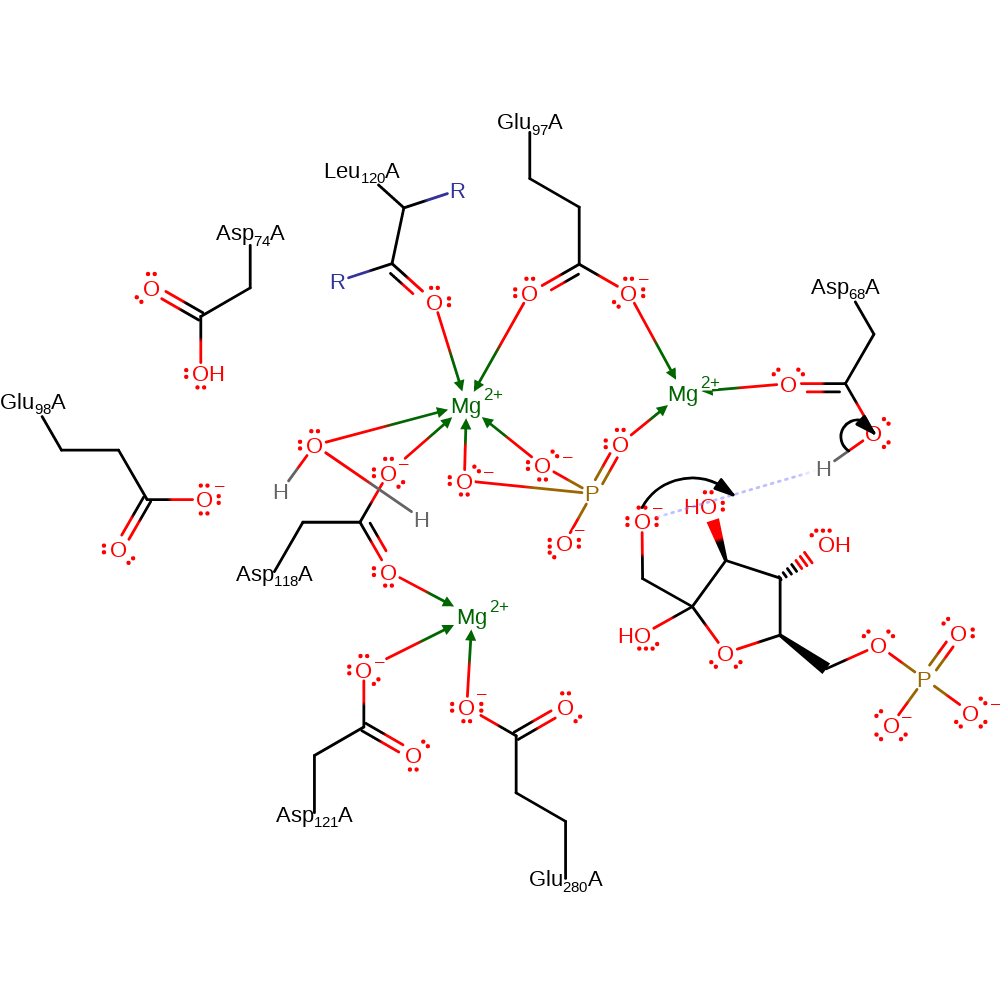
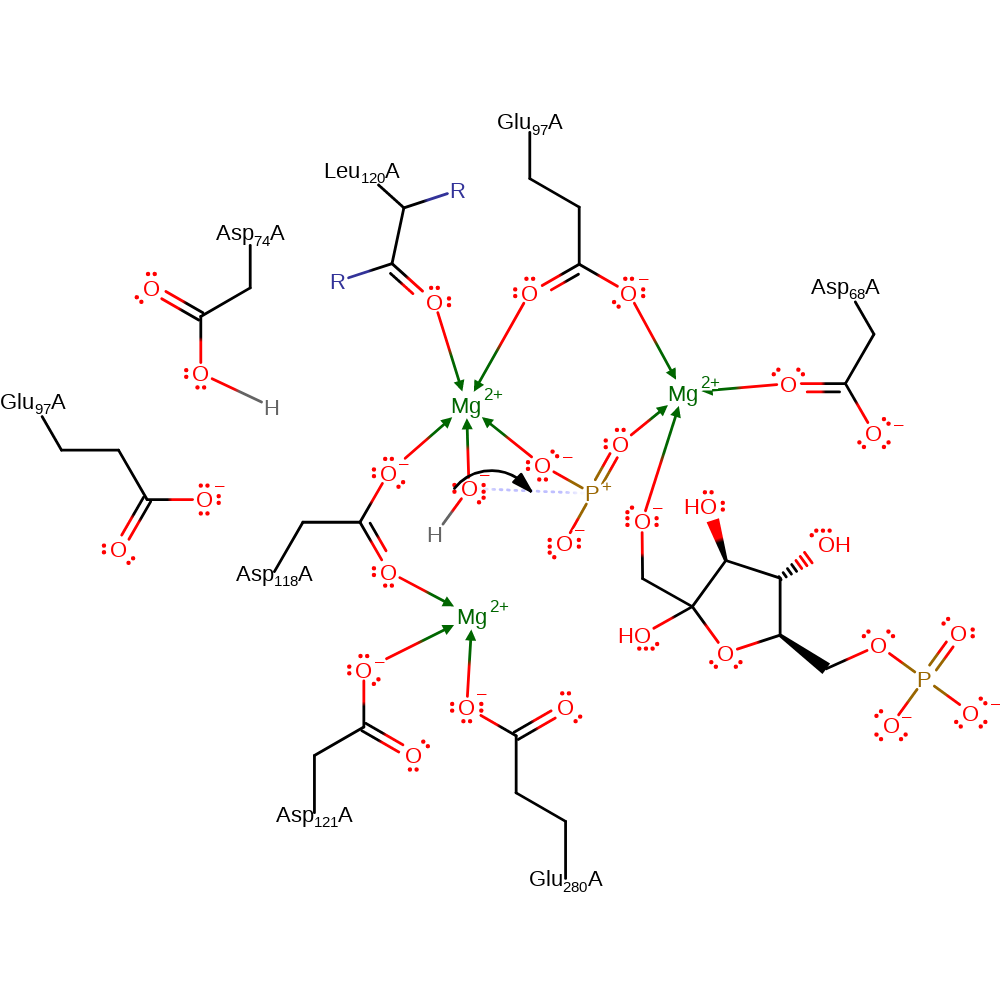
Step 3. F6P abstracts the proton from Asp68 to generate the final product.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp118A | metal ligand |
| Leu120A (main-C) | metal ligand |
| Glu97A | metal ligand |
| Asp68A | metal ligand |
| Asp121A | metal ligand |
| Glu280A | metal ligand |
| Glu98A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp68A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, overall product formed
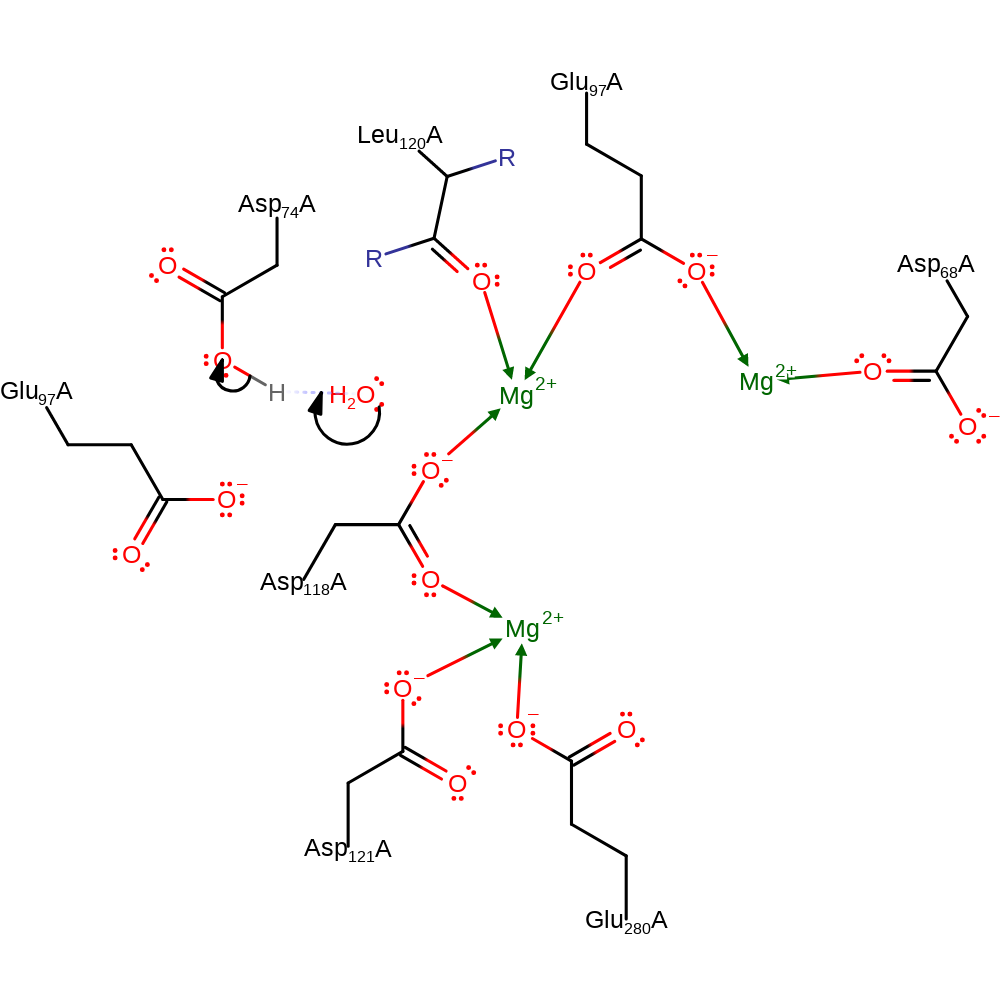
Step 4. Inferred return step. Asp74 returns a proton to water, which is then transferred to bulk solvent.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp118A | metal ligand |
| Leu120A (main-C) | metal ligand |
| Glu97A | metal ligand |
| Asp68A | metal ligand |
| Asp121A | metal ligand |
| Glu280A | metal ligand |
| Glu98A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp74A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, inferred reaction step, native state of enzyme regeneratedIntroduction
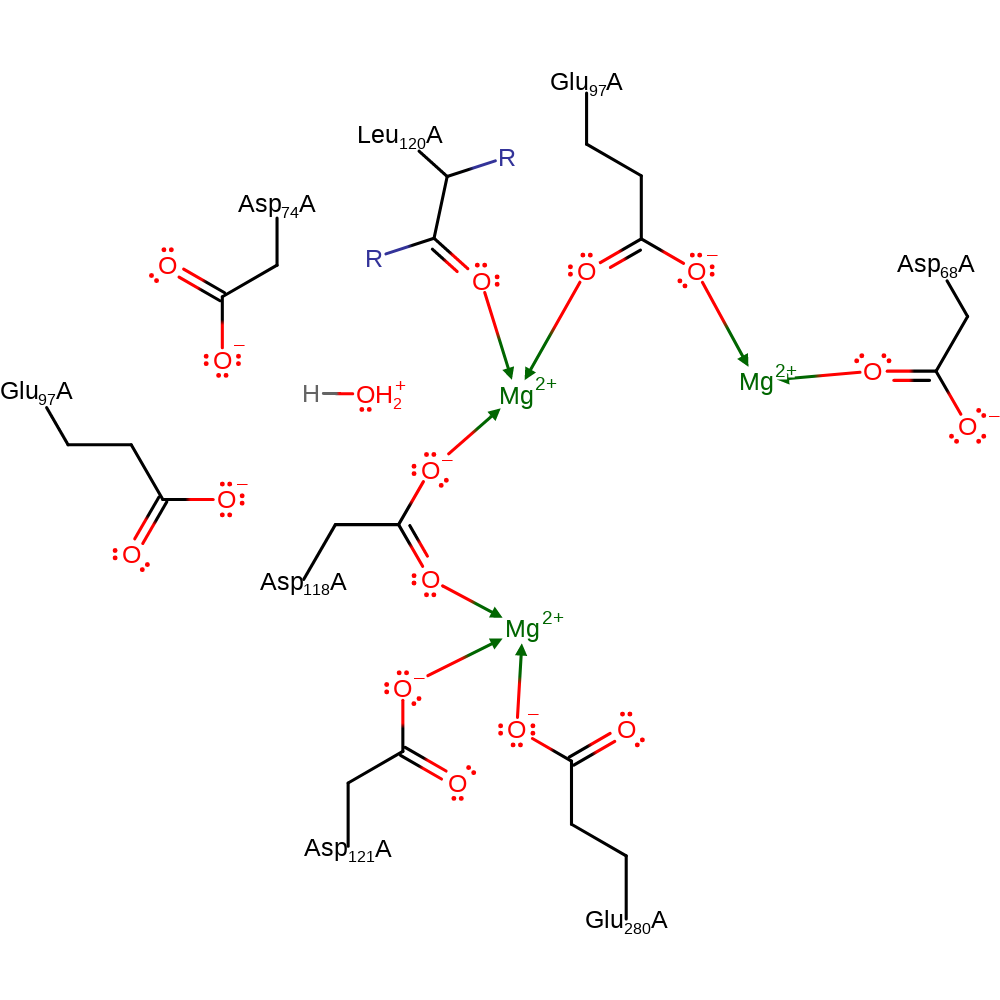
This represents the disassociative mechanism in which the P-O bond in fructose bisphosphate (FBP) breaks to form a postively charged phospho intermediate. Water is then activated by Asp74. The two reactive intermediates then combine for form a phosphate moiety.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1eyi) | ||
| Glu98 | Glu97A | Acts as a bidentate ligand for Mg1 and Mg2 magnesium binding sites. | metal ligand |
| Asp69 | Asp68A | The residue acts as a proton carrier from the substrate to the product. It initially forms a hydrogen bond with the proton of the 1-phosphate group, and after the displacement step has taken place, relays the proton to the anionic 6-fructose phosphate intermediate. | metal ligand, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Asp75 | Asp74A | Acts as a general acid/base that abstracts the proton from the catalytic water. | proton acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser, proton donor |
| Asp119 | Asp118A | Acts as a bidentate ligand for the Mg2 and Mg3 magnesium binding sites. | metal ligand |
| Leu121 (main-C) | Leu120A (main-C) | Forms part of the Mg2 magnesium binding site. | metal ligand |
| Asp122, Glu281 | Asp121A, Glu280A | Forms part of the Mg3 magnesium binding site. | metal ligand |
| Glu99 | Glu98A | The residue's anionic carboxylic side chain hydrogen bonds to the basic water molecule in the close proximity Mg(2+) coordination sphere. The resulting polarisation enhances the basic character of the water molecule, activating it towards deprotonating a second, adjacent water molecule. | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
heterolysis, overall reactant used, proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall product formed, inferred reaction step, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Choe JY et al. (2003), J Biol Chem, 278, 16015-16020. Metaphosphate in the active site of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M212395200. PMID:12595528.
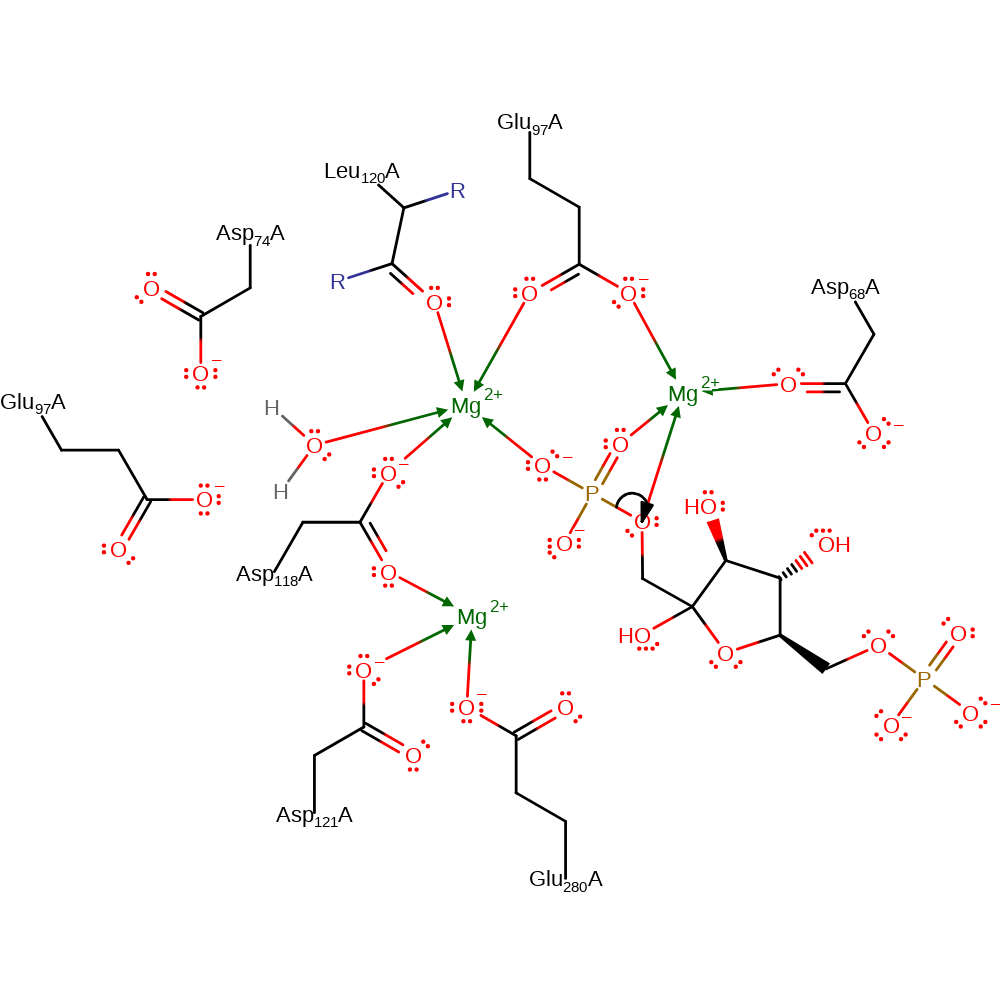
Step 1. The phsophate group dissociates from the FBP substrate to form the trigonal phosphate and negatively charged F6P intermediates.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu98A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp74A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp118A | metal ligand |
| Leu120A (main-C) | metal ligand |
| Glu97A | metal ligand |
| Asp68A | metal ligand |
| Asp121A | metal ligand |
| Glu280A | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
heterolysis, overall reactant usedCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp118A | metal ligand |
| Leu120A (main-C) | metal ligand |
| Glu97A | metal ligand |
| Asp68A | metal ligand |
| Asp121A | metal ligand |
| Glu280A | metal ligand |
| Glu98A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp74A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, overall reactant usedCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp118A | metal ligand |
| Leu120A (main-C) | metal ligand |
| Glu97A | metal ligand |
| Asp68A | metal ligand |
| Asp121A | metal ligand |
| Glu280A | metal ligand |
| Glu98A | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall product formed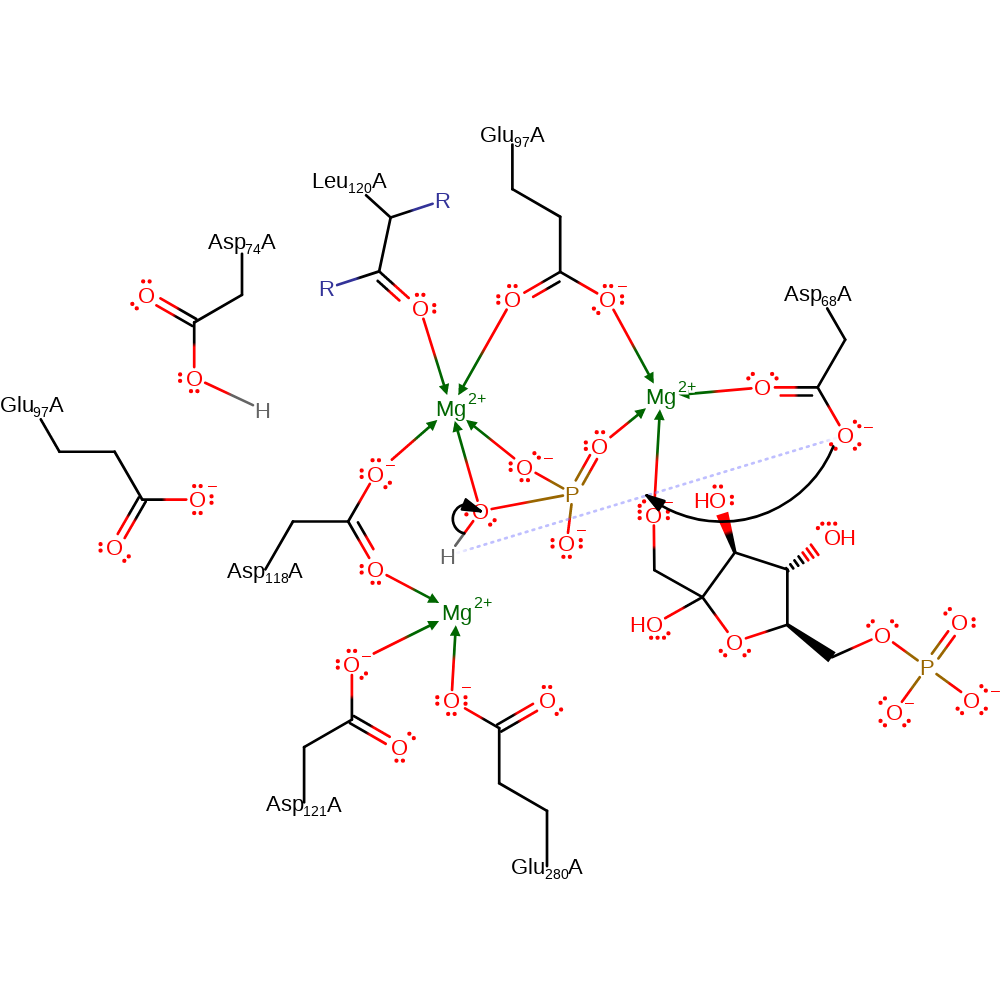
Step 4. The negatively charged F6P oxygen abstracts the proton from the phosphate group via Asp68. Not shown for clarity as it is assumed that this process is concerted.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp118A | metal ligand |
| Leu120A (main-C) | metal ligand |
| Glu97A | metal ligand |
| Asp68A | metal ligand |
| Asp121A | metal ligand |
| Glu280A | metal ligand |
| Glu98A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp68A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer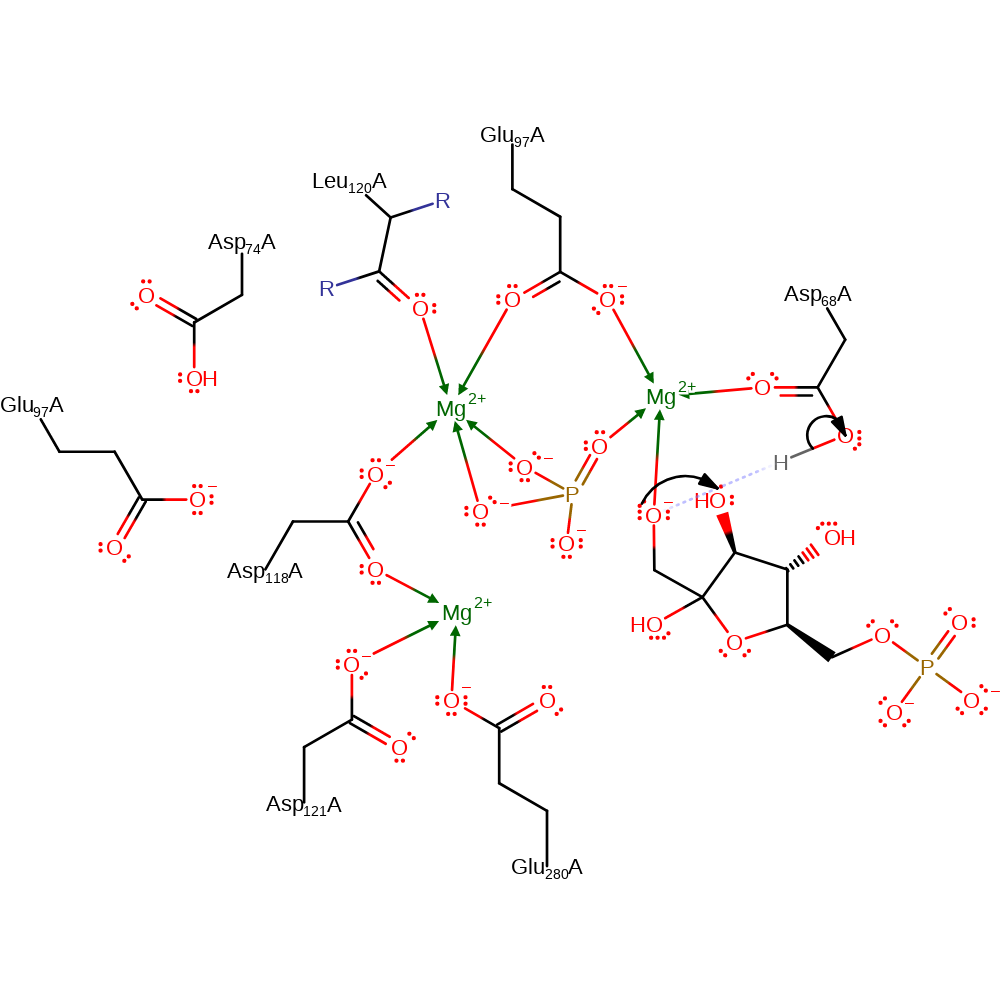
Step 5. F6P abstracts the proton from Asp68 to generate the final product.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp118A | metal ligand |
| Leu120A (main-C) | metal ligand |
| Glu97A | metal ligand |
| Asp68A | metal ligand |
| Asp121A | metal ligand |
| Glu280A | metal ligand |
| Glu98A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp68A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
overall product formed, proton transferCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp118A | metal ligand |
| Leu120A (main-C) | metal ligand |
| Glu97A | metal ligand |
| Asp68A | metal ligand |
| Asp121A | metal ligand |
| Glu280A | metal ligand |
| Asp74A | proton donor |





 Download:
Download: 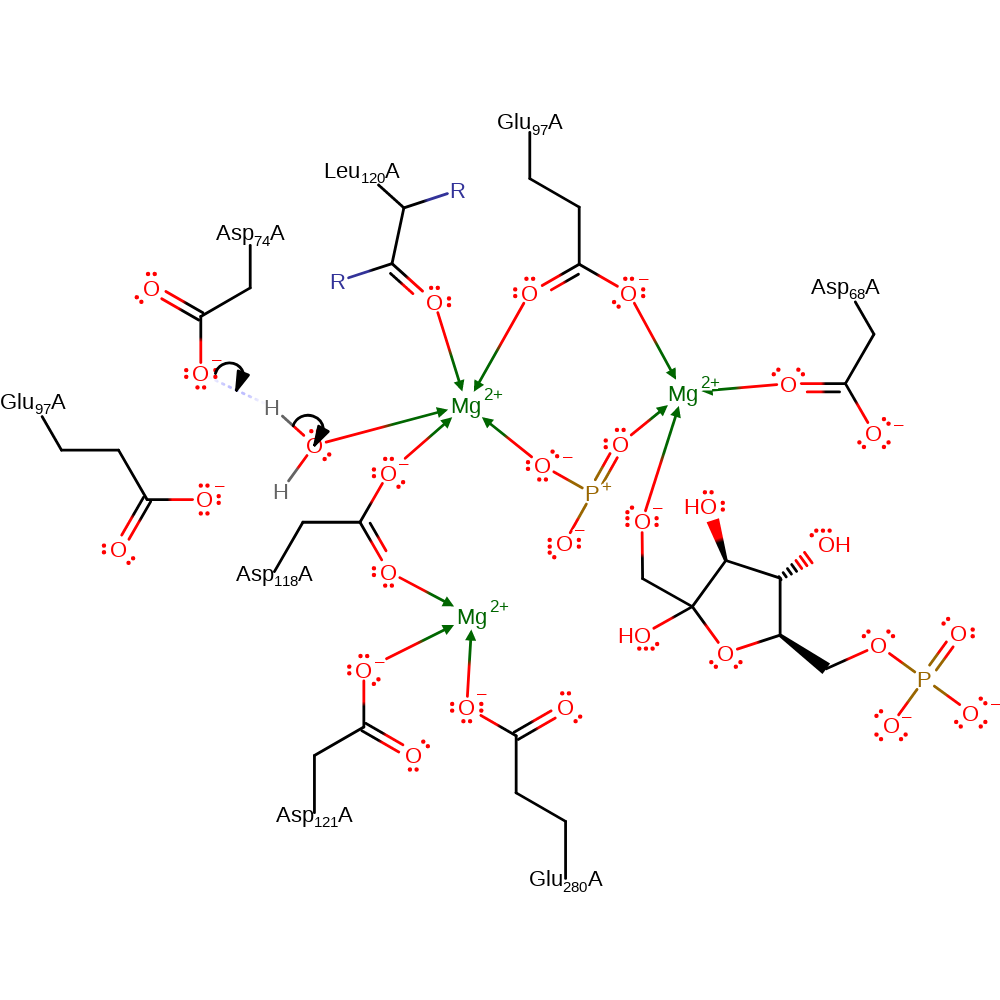
 Download:
Download: