Phospholipase A2 (prokaryotic/fungal)
The secreted phospholipase A2 (PLA2) from Streptomyces violaceoruber is the first identified prokaryotic PLA2. This Ca II dependent, lipolytic enzyme hydrolyses the 2-acyl ester bonds of 1,2-diacylglycero-3-phospholipids. The very high catalytic activities of secreted PLA2's relative to the aggregated substrates when compared to the monomeric substrates is due to interfacial activation.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
Q6UV28

 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Streptomyces violaceoruber (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1it4
- Solution structure of the prokaryotic Phospholipase A2 from Streptomyces violaceoruber
(solution nmr
Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
1.20.90.10
 (see all for 1it4)
(see all for 1it4)
- Cofactors
- Water (3), Calcium(2+) (1)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:3.1.1.4)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
Prokaryotic PLA2 is Ca II dependent and catalyses the hydrolysis of the 2-acyl ester bonds of 1,2-diacylglycero-3-phospholipids. According to the enzyme model of interfacial activation, the conformational change in PLA2 induced by phospholipid binding optimises the active site and enhances catalysis in the enzyme. A catalytic dyad is formed between His 93 and Asp 114, and the hydrogen bonding network extends from these catalytic residues to the C-terminal region. His 93 is hydrogen bonded to Wat 260 via the His N-delta-1 atom. His 93 abstracts a proton from this water molecule, activating it towards nucleophilic attack of the carbonyl carbon of the substrate. Asp 114, which forms a hydrogen bond with His 93 Ne2 neutralises the positive charge of His 93 created by the ester bond cleavage during catalysis. The calcium binding site is formed by Asp 94 carboxylate, Asp 72 carboxylate, Leu 73 carbonyl oxygen and three water molecules. The Ca II is neccessary for enzymatic activity and helps to stabilise the His 93.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1it4) | ||
| Asp72, Asp94, Leu73 (main-N) | Asp43A, Asp65A, Leu44A (main-N) | Coordinate the calcium ion. | metal ligand |
| His93 | His64A | The His 64 is hydrogen bonded to Wat 260 via the His N-delta-1 atom. His 64 abstracts a proton from this water molecule, activating it towards nucleophilic attack of the carbonyl carbon of the substrate. The histidine is aslo hydrogen bonded to Asp 85, forming the catalytic dyad. His 64 interacts electrostatically with the Ca II cofactor for stabilisation. |
proton acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser, proton donor |
| Asp114 | Asp85A | Asp 85, which forms a hydrogen bond with His 64 Ne2 neutralises the positive charge of His 64 created by the ester bond cleavage during catalysis. | increase basicity, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, coordination to a metal ion, decoordination from a metal ion, overall product formed, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate baseReferences
- Sugiyama M et al. (2002), J Biol Chem, 277, 20051-20058. A Novel Prokaryotic Phospholipase A2. CHARACTERIZATION, GENE CLONING, AND SOLUTION STRUCTURE. DOI:10.1074/jbc.m200264200. PMID:11897786.
- Matoba Y et al. (2003), Proteins, 51, 453-469. Atomic resolution structure of prokaryotic phospholipase A2: Analysis of internal motion and implication for a catalytic mechanism. DOI:10.1002/prot.10360. PMID:12696056.
- Matoba Y et al. (2002), J Biol Chem, 277, 20059-20069. The crystal structure of prokaryotic phospholipase A2. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M200263200. PMID:11897785.
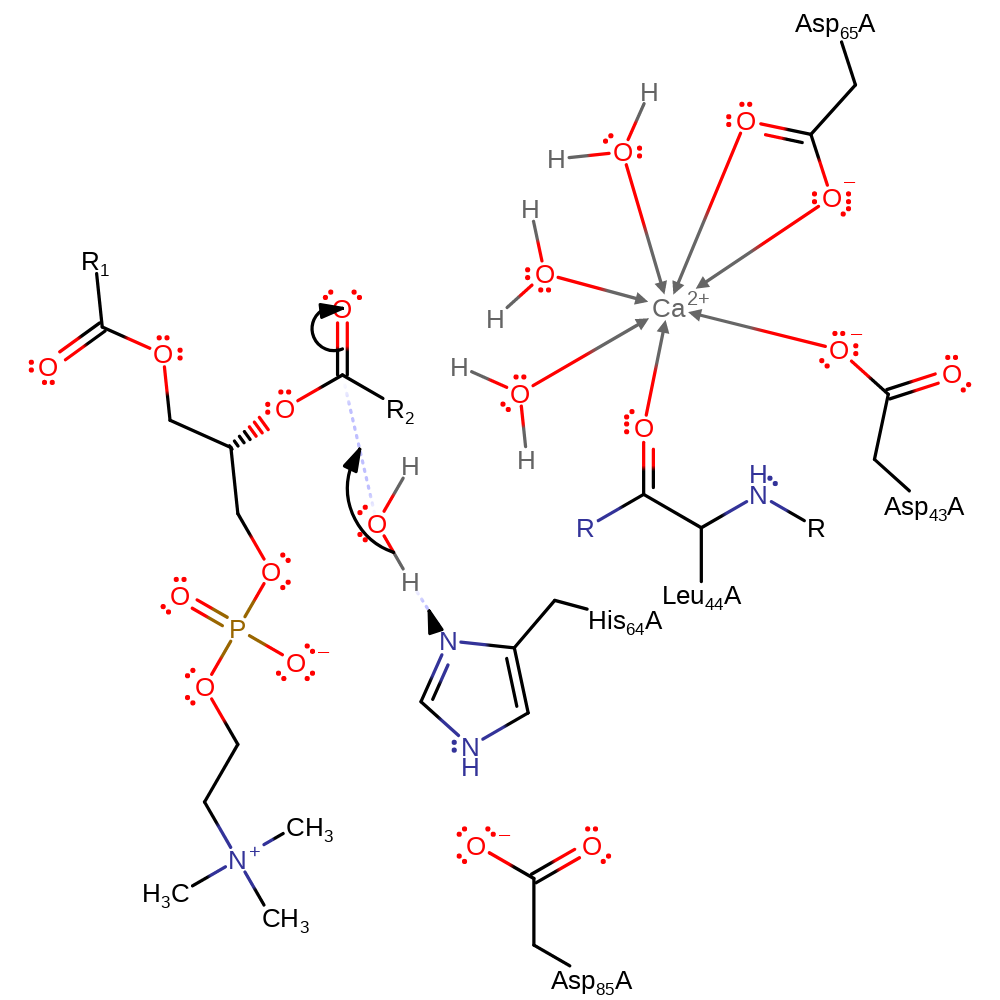
Step 1. The His93 and Asp114 dyad activates a water molecule which performs a nucleophilic attack on the ester carbonyl carbon. This results in an oxyanion intermediate forming which is stabilized by the calcium ion- the oxyanion becomes ligated to the calcium in the place of one of the water molecules.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His64A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp85A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp85A | increase basicity |
| Asp43A | metal ligand |
| Leu44A (main-N) | metal ligand |
| Asp65A | metal ligand |
| His64A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, coordination to a metal ion, decoordination from a metal ion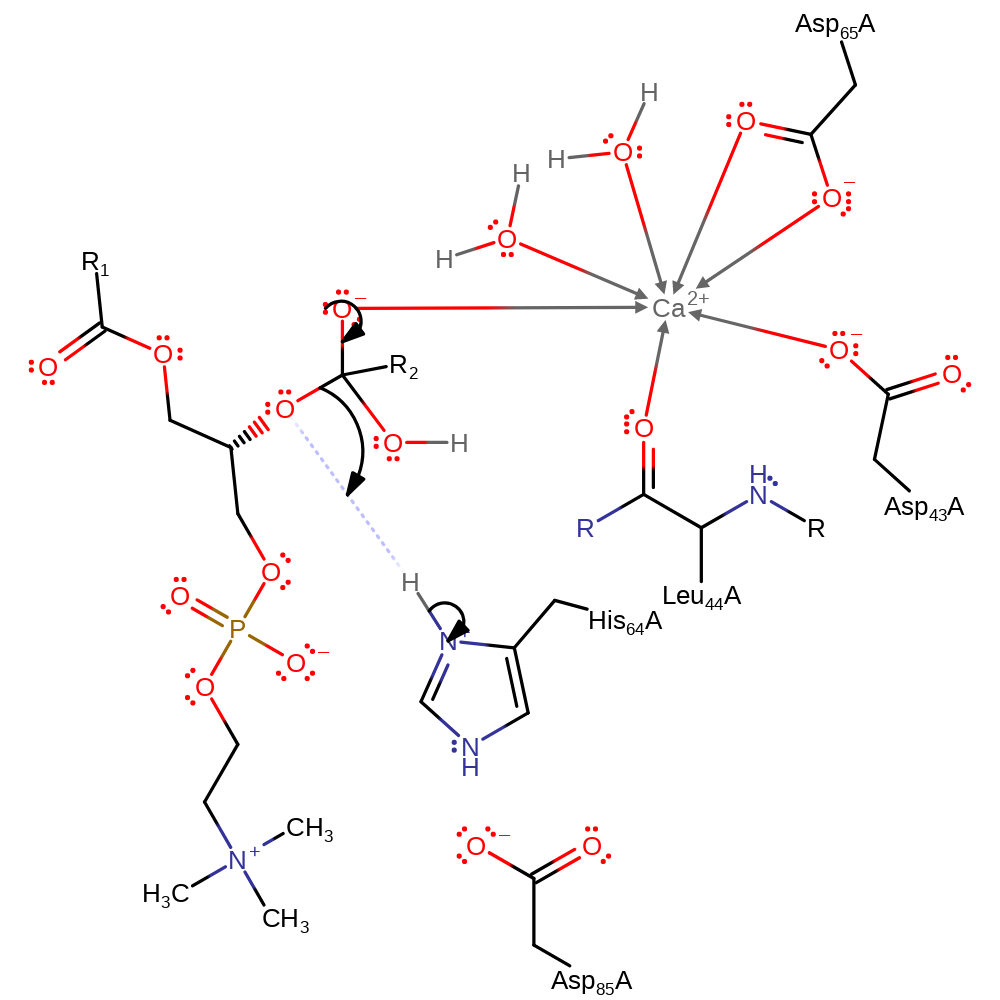
Step 2. The tetrahedral intermediate collapses with His93 protonating the leaving group- generating the products.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp85A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp43A | metal ligand |
| Leu44A (main-N) | metal ligand |
| Asp65A | metal ligand |
| His64A | proton donor |





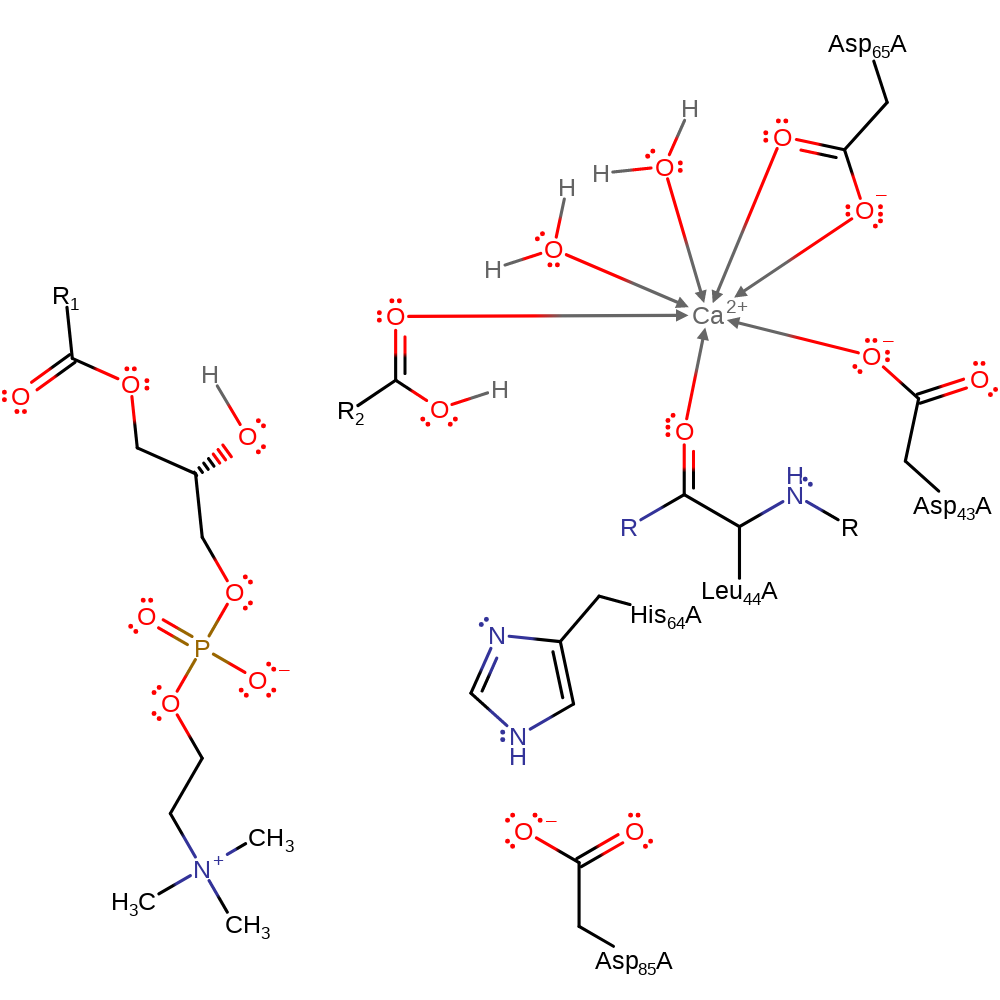 Download:
Download: