Malate dehydrogenase (type 1)
Malonate dehydrogenase (MDHase) catalyses the reversible oxidation of malonate to oxaloacetate, a reaction dependent upon the oxidation/reduction of NAD cofactor. The enzyme functions as an important component in the citric acid cycle in the prokaryotic cytoplasm and the malate/aspartate shuttle in eukaryotic cytoplasm.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P61889
 (1.1.1.37)
(1.1.1.37)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Escherichia coli K-12 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1emd
- CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF A TERNARY COMPLEX OF ESCHERICHIA COLI MALATE DEHYDROGENASE, CITRATE AND NAD AT 1.9 ANGSTROMS RESOLUTION
(1.9 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.90.110.10
 (see all for 1emd)
(see all for 1emd)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:1.1.1.37)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The enzyme catalyses the interconversion of malonate and oxaloacetate with the oxidation and reduction of the NAD cofactor. A histidine-aspartate pair form a proton relay system in the active site, which allows the histidine to act as both a general acid and general base to the substrate. In the direction of reduction, a water molecule acts as the proton donor while in the direction of oxidation the 2-hydroxy group of the substrate acts as the donor.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1emd) | ||
| His177 | His177A | The residue acts as a general base towards the 2-hydroyl group of the oxaloacetate in the direction of oxidation, and as a general acid in the direction of reduction. It is involved in a proton relay mechanism with Asp 150. | proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Asp150 | Asp150A | The residue acts to relay a proton from a water molecule to the His 195 residue in reduction of oxaloacetate to malate. | modifies pKa |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, hydride transfer, overall reactant used, overall product formed, inferred reaction step, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Goward CR et al. (1994), Protein Sci, 3, 1883-1888. Malate dehydrogenase: A model for structure, evolution, and catalysis. DOI:10.1002/pro.5560031027. PMID:7849603.
- Zaitseva J et al. (2009), Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun, 65, 866-869. Structure of Escherichia coli malate dehydrogenase at 1.45 A resolution. DOI:10.1107/S1744309109032217. PMID:19724119.
- Bell JK et al. (2001), J Biol Chem, 276, 31156-31162. Structural analyses of a malate dehydrogenase with a variable active site. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M100902200. PMID:11389141.
- Chapman AD et al. (1999), J Mol Biol, 285, 703-712. Structural basis of substrate specificity in malate dehydrogenases: crystal structure of a ternary complex of porcine cytoplasmic malate dehydrogenase, α-Ketomalonate and TetrahydoNAD. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.1998.2357. PMID:10075524.
- Hall MD et al. (1993), J Mol Biol, 232, 213-222. Crystal Structure of a Ternary Complex of Escherichia coli Malate Dehydrogenase Citrate and NAD at 1·9 Å Resolution. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.1993.1377. PMID:8331658.
- Hall MD et al. (1992), J Mol Biol, 226, 867-882. Crystal structure of Escherichia coli malate dehydrogenase. A complex of the apoenzyme and citrate at 1.87 A resolution. PMID:1507230.
- Birktoft JJ et al. (1983), J Biol Chem, 258, 472-482. The presence of a histidine-aspartic acid pair in the active site of 2-hydroxyacid dehydrogenases. X-ray refinement of cytoplasmic malate dehydrogenase. DOI:10.2210/pdb2mdh/pdb. PMID:6848515.

Step 1. His177, activated by Asp150, abstracts a proton from the hydroxyl group, with concomitant elimination of a hydride to the NAD(P) cofactor.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp150A | modifies pKa |
| His177A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, hydride transfer, overall reactant used, overall product formed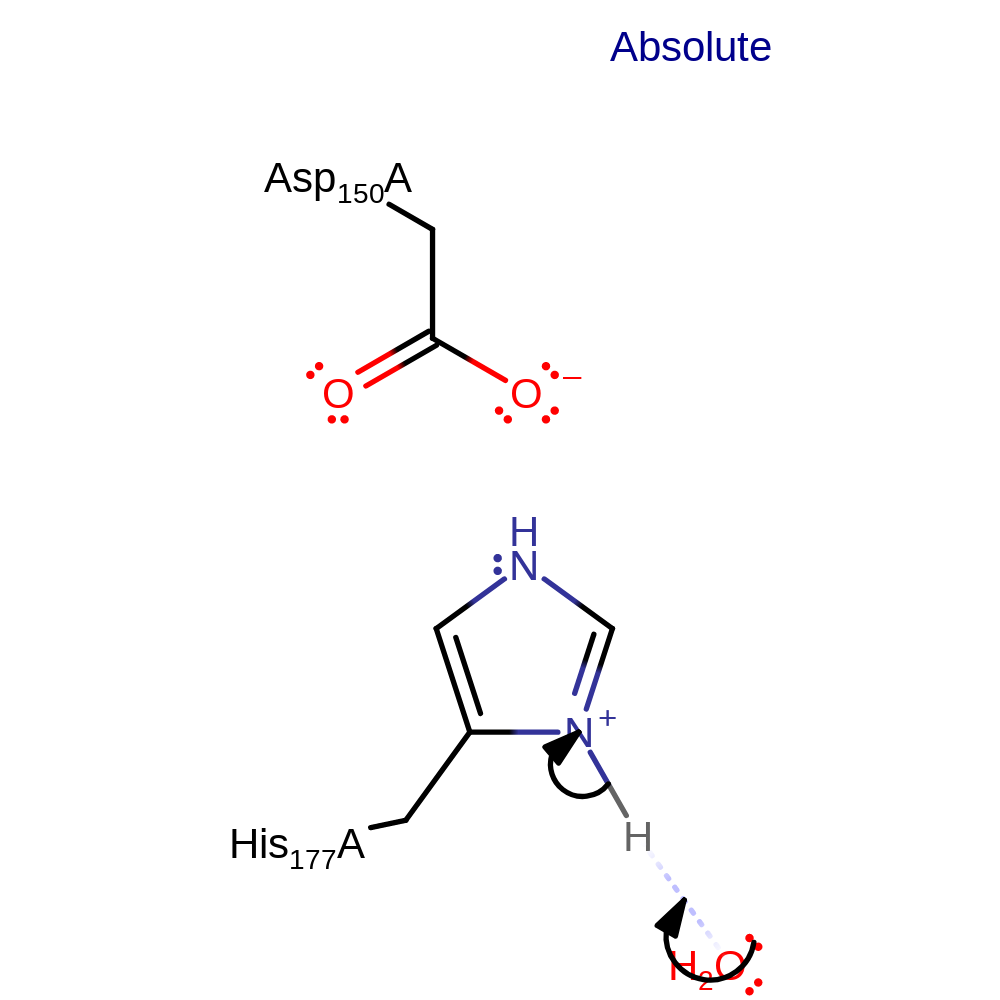
Step 2. Inferred step in which water abstracts a proton from the catalytic histidine.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp150A | modifies pKa |
| His177A | proton donor |





 Download:
Download: