Triacylglycerol lipase (Pseudomonas family)
Member of the Pseudomonas lipase family, and an alpha-beta hydrolase superfamily member. Also requires calcium for catalysis to occur. Catalyses the hydrolysis of triglycerides.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
Q05489
 (3.1.1.3)
(3.1.1.3)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Burkholderia glumae (Pseudomonas glumae)

- PDB
-
1tah
- THE CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF TRIACYLGLYCEROL LIPASE FROM PSEUDOMONAS GLUMAE REVEALS A PARTIALLY REDUNDANT CATALYTIC ASPARTATE
(3.0 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.50.1820
 (see all for 1tah)
(see all for 1tah)
- Cofactors
- Calcium(2+) (1)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:3.1.1.3)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
This protein is a member of the alpha-beta hydrolase superfamily and is known to function via a classical Ser-His-Asp triad mechanism. Here the histidine of the triad activates the serine, which acts as a nucleophile, forming a covalent intermediate, which then collapses to eliminate the first product. Hydrolysis of the enzyme-substrate bond results in the release of the final product and regeneration of the active site.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1tah) | ||
| Leu56 (main-N), Gln127 (main-N) | Leu17(16)B(A) (main-N), Gln88(87)B(A) (main-N) | Form the oxyanion hole that stabilises the negatively charged intermediates and transition states formed. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp302 | Asp263(262)B(A) | Part of the Ser-His-Asp catalytic triad. Activates the histidine. | increase basicity, modifies pKa, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser126 | Ser87(86)B(A) | Part of the Ser-His-Asp catalytic triad. Acts as the nucleophile. | covalently attached, nucleofuge, nucleophile, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| His324 | His285(284)B(A) | Part of the Ser-His-Asp catalytic triad. Acts as a general acid/base to activate the serine. | proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Val334 (main-C), Gln330, Asp326, Asp280 | Val295(294)B(A) (main-C), Gln291(290)B(A), Asp287(286)B(A), Asp241(240)B(A) | Forms part of the calcium binding site. | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
bimolecular nucleophilic addition, proton transfer, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, overall product formed, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, native state of enzyme regenerated, intermediate terminatedReferences
- Schrag JD et al. (1997), Structure, 5, 187-202. The open conformation of a Pseudomonas lipase. DOI:10.1016/s0969-2126(97)00178-0. PMID:9032074.
- Chiou S et al. (2009), QSAR Comb Sci, 28, 267-273. QSAR for Inhibition ofPseudomonasSpecies Lipase by 1-Acyloxy-3-N-n-octylcarbamyl-benzenes. DOI:10.1002/qsar.200810031.

Step 1. His285 acts as a general base activating the Ser87 hydroxyl group for nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl carbon of the ester bond. The third component of this catalytic triad- Asp263 acts to increase the basicity of the histidine. The oxyanion intermediate formed is stabilized by the amide groups of Gln88 and Leu17. The calcium ion may also play a role in stabilization.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Leu17(16)B(A) (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gln88(87)B(A) (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp241(240)B(A) | metal ligand |
| Asp287(286)B(A) | metal ligand |
| Gln291(290)B(A) | metal ligand |
| Val295(294)B(A) (main-C) | metal ligand |
| Asp263(262)B(A) | modifies pKa, electrostatic stabiliser, increase basicity |
| Ser87(86)B(A) | proton donor |
| His285(284)B(A) | proton acceptor |
| Ser87(86)B(A) | nucleophile |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, proton transfer, intermediate formation, overall reactant used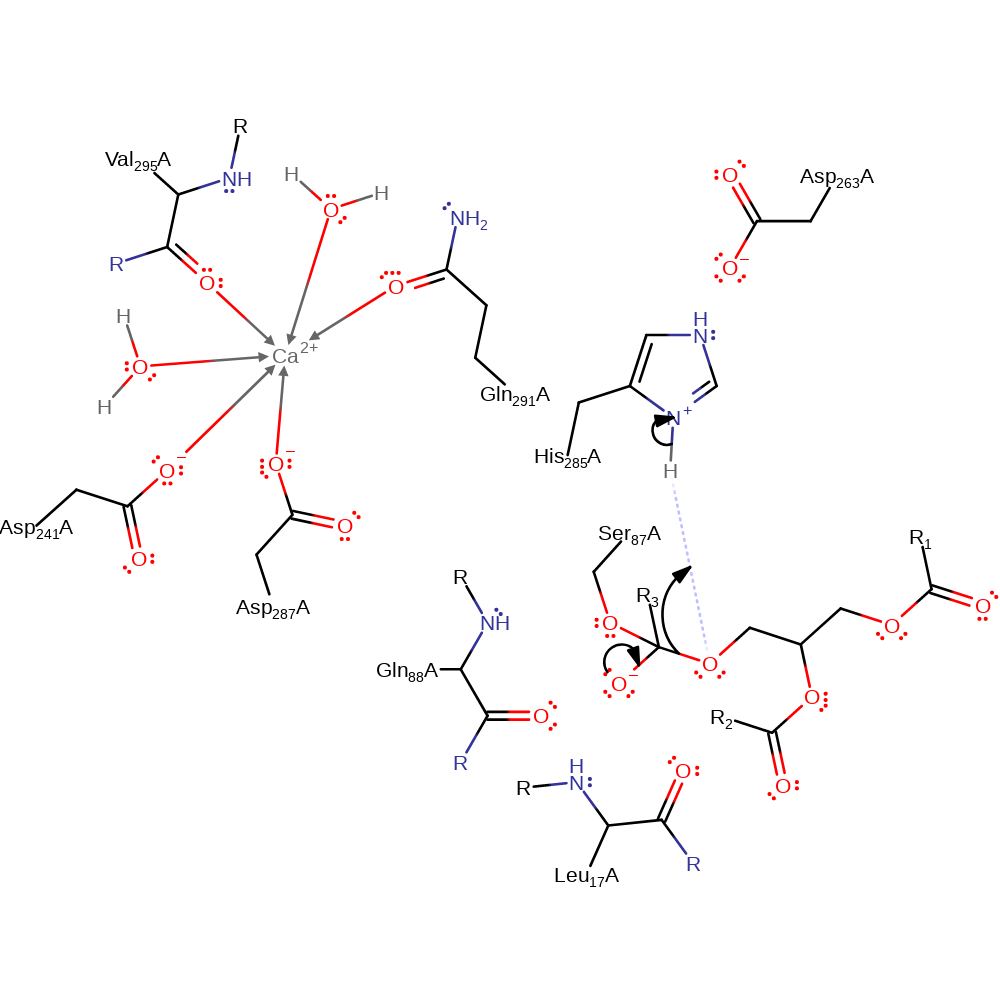
Step 2. The tetrahedral intermediate collapses and diacylglycerol is eliminated.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser87(86)B(A) | covalently attached |
| Leu17(16)B(A) (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gln88(87)B(A) (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp263(262)B(A) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp241(240)B(A) | metal ligand |
| Asp287(286)B(A) | metal ligand |
| Gln291(290)B(A) | metal ligand |
| Val295(294)B(A) (main-C) | metal ligand |
| His285(284)B(A) | proton donor |
Chemical Components
overall product formed, proton transfer, ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base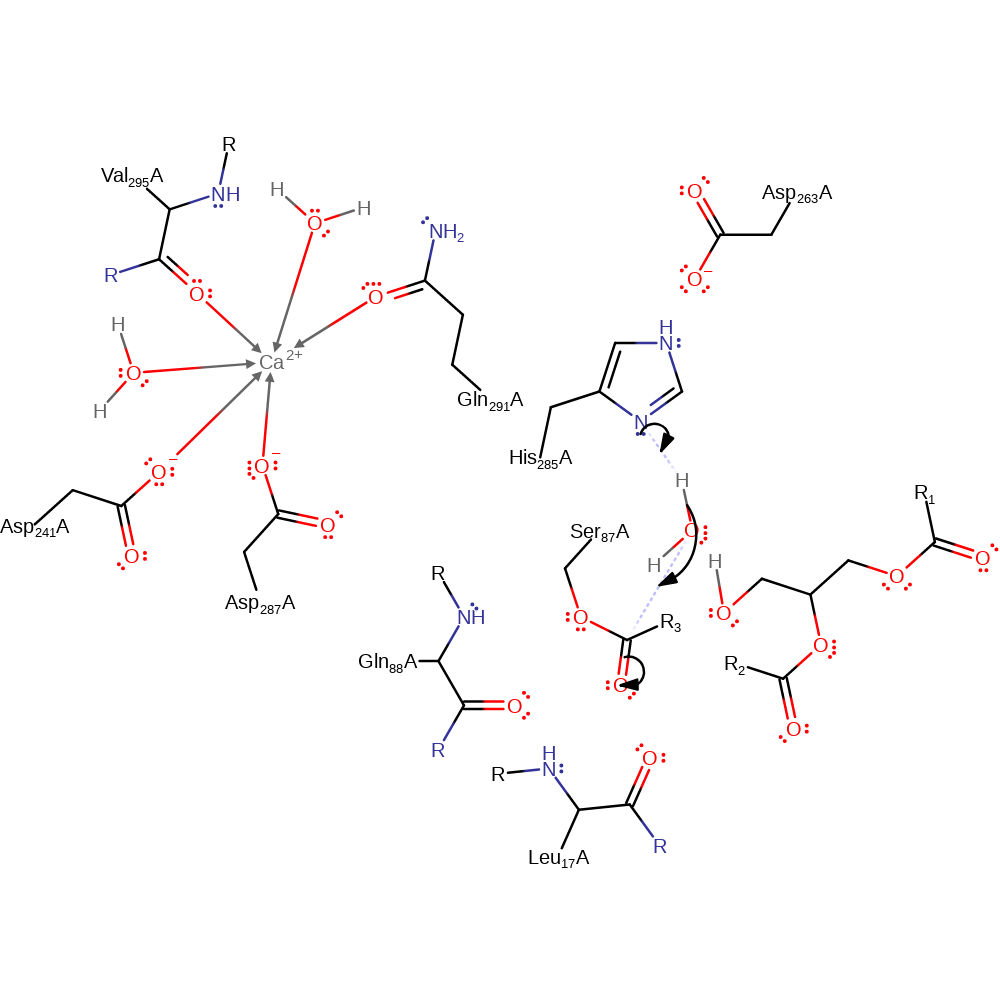
Step 3. His285 activates water for nucleophilic attack and another oxyanion intermediate is formed.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser87(86)B(A) | covalently attached |
| Leu17(16)B(A) (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gln88(87)B(A) (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp263(262)B(A) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp263(262)B(A) | increase basicity, modifies pKa |
| Asp241(240)B(A) | metal ligand |
| Asp287(286)B(A) | metal ligand |
| Gln291(290)B(A) | metal ligand |
| Val295(294)B(A) (main-C) | metal ligand |
| His285(284)B(A) | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition
Step 4. The tetrahedral intermediate collapses and Ser87 is eliminated.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Leu17(16)B(A) (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gln88(87)B(A) (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp263(262)B(A) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp241(240)B(A) | metal ligand |
| Asp287(286)B(A) | metal ligand |
| Gln291(290)B(A) | metal ligand |
| Val295(294)B(A) (main-C) | metal ligand |
| Ser87(86)B(A) | nucleofuge |
| His285(284)B(A) | proton donor |
| Ser87(86)B(A) | proton acceptor |





 Download:
Download: