L-rhamnose isomerase
This enzyme interconverts L-rhamnose and L-rhamnulose. In some species, including Escherichia coli, this is the first step in rhamnose catabolism.
The enzyme contains two divalent metal ions located at different metal-binding sites within the active site. The enzyme binds the closed ring form of the substrate and catalyses ring opening to generate a form of open-chain conformation that is coordinated to one of the metal sites.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P32170
 (5.3.1.14)
(5.3.1.14)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Escherichia coli K-12 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1de6
- L-RHAMNOSE ISOMERASE
(2.1 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.20.20.150
 (see all for 1de6)
(see all for 1de6)
- Cofactors
- Zinc(2+) (1), Manganese(2+) (1)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:5.3.1.14)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
Isomerization proceeds via a hydride-shift mechanism. In this mechanism, Asp334 acts as an acid-base catalyst in ring opening, helping to transfer a proton from O2 to O5. After the ring has been opened, the catalytic water molecule (W4) mediates the transfer of a proton from O1 to O2, and a hydride (H1A), shielded by Trp193 from solvent access, attacks C2, producing an aldose with a hydroxyl group (O2) .
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1de6) | ||
| Asp296 | Asp304(303)A | Forms part of the manganese binding site, although thought to be responsible for the proton abstraction from the catalytic water that initiates the O1 to O2 proton transfer. | metal ligand, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Glu226, His286, Asp259 | Glu234(233)A, His294(293)A, Asp267(266)A | Forms the zinc binding site. | metal ligand |
| Asp294, Asp259 | Asp302(301)A, Asp267(266)A | Forms manganese binding site. | metal ligand |
| Asp326 | Asp334(333)A | Forms part of the zinc binding site, also thought to be responsible for the initial abstraction of a hydrogen from a catalytic water for the ring opening step of the reaction. | metal ligand, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| His262, Lys228, Trp185 | His270(269)A, Lys236(235)A, Trp193(192)A | Activate the substrate to make hydride transfer favourable. | activator, metal ligand |
Chemical Components
overall reactant used, decyclisation, proton transfer, hydride transfer, overall product formedReferences
- Korndörfer IP et al. (2000), J Mol Biol, 300, 917-933. The Structure of Rhamnose Isomerase from Escherichia coli and its Relation with Xylose Isomerase Illustrates a Change Between Inter and Intra-subunit Complementation During Evolution. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.2000.3896. PMID:10891278.
- Prabhu P et al. (2014), FEBS J, 281, 3446-3459. Structure-based studies on the metal binding of two-metal-dependent sugar isomerases. DOI:10.1111/febs.12872. PMID:24925069.
- Yoshida H et al. (2013), FEBS Open Bio, 3, 35-40. Structure ofl-rhamnose isomerase in complex withl-rhamnopyranose demonstrates the sugar-ring opening mechanism and the role of a substrate sub-binding site. DOI:10.1016/j.fob.2012.11.008. PMID:23772372.
- Yoshida H et al. (2010), FEBS J, 277, 1045-1057. Catalytic reaction mechanism of Pseudomonas stutzeri l-rhamnose isomerase deduced from X-ray structures. DOI:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2009.07548.x. PMID:20088877.
- Yoshida H et al. (2007), J Mol Biol, 365, 1505-1516. The Structures of l-Rhamnose Isomerase from Pseudomonas stutzeri in Complexes with l-Rhamnose and d-Allose Provide Insights into Broad Substrate Specificity. DOI:10.1016/j.jmb.2006.11.004. PMID:17141803.
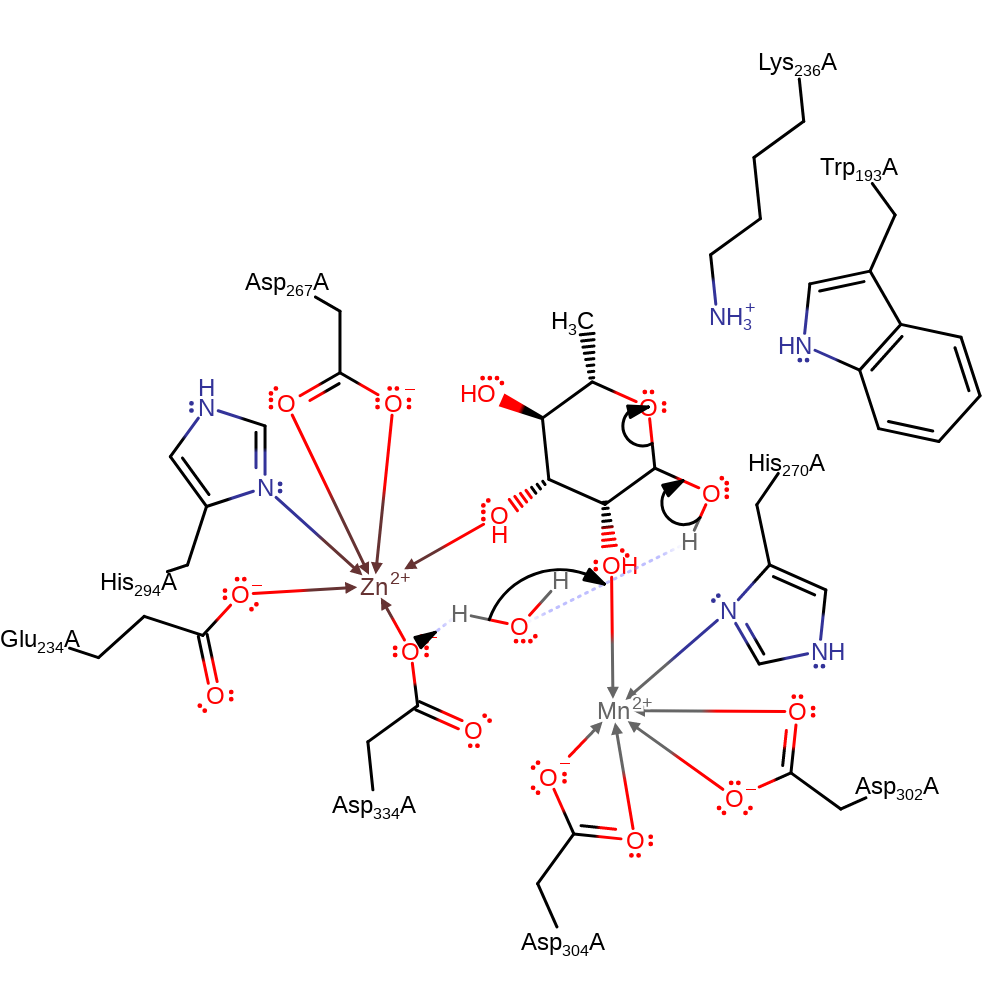
Step 1. Asp334 acts as a base via a water molecule to deprotonate O2 this causes the ring to open.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu234(233)A | metal ligand |
| Asp267(266)A | metal ligand |
| His294(293)A | metal ligand |
| Asp302(301)A | metal ligand |
| Asp304(303)A | metal ligand |
| Asp334(333)A | metal ligand |
| His270(269)A | metal ligand |
| Asp334(333)A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
overall reactant used, decyclisation, proton transferCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu234(233)A | metal ligand |
| Asp267(266)A | metal ligand |
| His270(269)A | metal ligand |
| His294(293)A | metal ligand |
| Asp302(301)A | metal ligand |
| Asp304(303)A | metal ligand |
| Asp334(333)A | metal ligand, proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer
Step 3. Asp304 deprotonates O2 via another water molecule. This causes a hydride shift from C2 to C1.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu234(233)A | metal ligand |
| Asp267(266)A | metal ligand |
| His270(269)A | metal ligand |
| His294(293)A | metal ligand |
| Asp302(301)A | metal ligand |
| Asp304(303)A | metal ligand |
| Asp334(333)A | metal ligand |
| Trp193(192)A | activator |
| Lys236(235)A | activator |
| His270(269)A | activator |
| Asp304(303)A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, hydride transferCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu234(233)A | metal ligand |
| Asp267(266)A | metal ligand |
| His270(269)A | metal ligand |
| His294(293)A | metal ligand |
| Asp302(301)A | metal ligand |
| Asp304(303)A | metal ligand |
| Asp334(333)A | metal ligand |
| Asp304(303)A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, overall product formedIntroduction
The ene-diol mechanism. In this mechanism two bases transfer a proton from O2 to O1 (thought to be water), and a proton from C1 to C2 (no base identified as yet), respectively, producing ketose from aldose. During the reaction, the ene-diol intermediate is stabilized by the metal ion(s).
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1de6) | ||
| Asp294, Asp296, Asp259 | Asp302(301)A, Asp304(303)A, Asp267(266)A | Forms manganese binding site. | metal ligand |
| Glu226, His286, Asp259, Asp326 | Glu234(233)A, His294(293)A, Asp267(266)A, Asp334(333)A | Forms zinc binding site. | metal ligand |
| His262, Lys228, Trp185 | His270(269)A, Lys236(235)A, Trp193(192)A | Act to stabilise the substrate and transition states. | activator, metal ligand |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, decyclisation, overall reactant used, assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, overall product formedReferences
- Carrell HL et al. (1989), Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 86, 4440-4444. X-ray analysis of D-xylose isomerase at 1.9 A: native enzyme in complex with substrate and with a mechanism-designed inactivator. PMID:2734296.
- Yoshida H et al. (2010), FEBS J, 277, 1045-1057. Catalytic reaction mechanism of Pseudomonas stutzeri l-rhamnose isomerase deduced from X-ray structures. DOI:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2009.07548.x. PMID:20088877.
- Kovalevsky AY et al. (2008), Biochemistry, 47, 7595-7597. Hydrogen Location in Stages of an Enzyme-Catalyzed Reaction: Time-of-Flight Neutron Structure ofd-Xylose Isomerase with Boundd-Xylulose†‡. DOI:10.1021/bi8005434. PMID:18578508.
- Katz AK et al. (2006), Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 103, 8342-8347. Locating active-site hydrogen atoms in D-xylose isomerase: Time-of-flight neutron diffraction. DOI:10.1073/pnas.0602598103. PMID:16707576.

Step 1. Asp334 acts as a base via a water molecule to deprotonate O2 this causes the ring to open.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His270(269)A | metal ligand |
| Asp334(333)A | metal ligand |
| Asp304(303)A | metal ligand |
| Asp302(301)A | metal ligand |
| His294(293)A | metal ligand |
| Asp267(266)A | metal ligand |
| Glu234(233)A | metal ligand |
| Asp334(333)A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, decyclisation, overall reactant usedCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp334(333)A | metal ligand |
| Asp304(303)A | metal ligand |
| Asp302(301)A | metal ligand |
| His294(293)A | metal ligand |
| His270(269)A | metal ligand |
| Asp267(266)A | metal ligand |
| Glu234(233)A | metal ligand |
| Asp334(333)A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transferCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu234(233)A | metal ligand |
| Asp267(266)A | metal ligand |
| His270(269)A | metal ligand |
| His294(293)A | metal ligand |
| Asp302(301)A | metal ligand |
| Asp304(303)A | metal ligand |
| Asp334(333)A | metal ligand |
| Trp193(192)A | activator |
| Lys236(235)A | activator |
| His270(269)A | activator |
| Asp304(303)A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, assisted keto-enol tautomerisation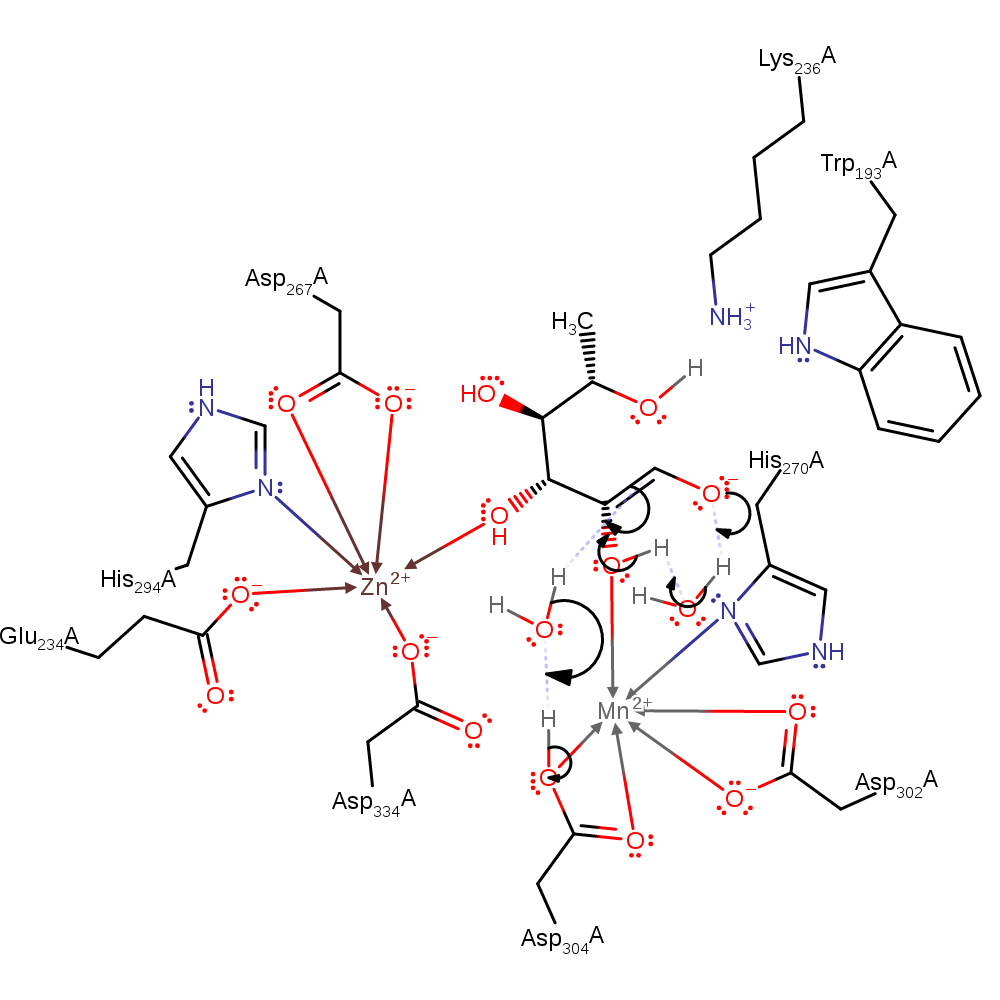
Step 4. A proton is transferred from O2 to O1 via a water molecule and the enolate collapses into the product.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu234(233)A | metal ligand |
| Asp267(266)A | metal ligand |
| His270(269)A | metal ligand |
| His294(293)A | metal ligand |
| Asp302(301)A | metal ligand |
| Asp304(303)A | metal ligand |
| Asp334(333)A | metal ligand |
| Trp193(192)A | activator |
| Lys236(235)A | activator |
| His270(269)A | activator |
| Asp304(303)A | proton donor |



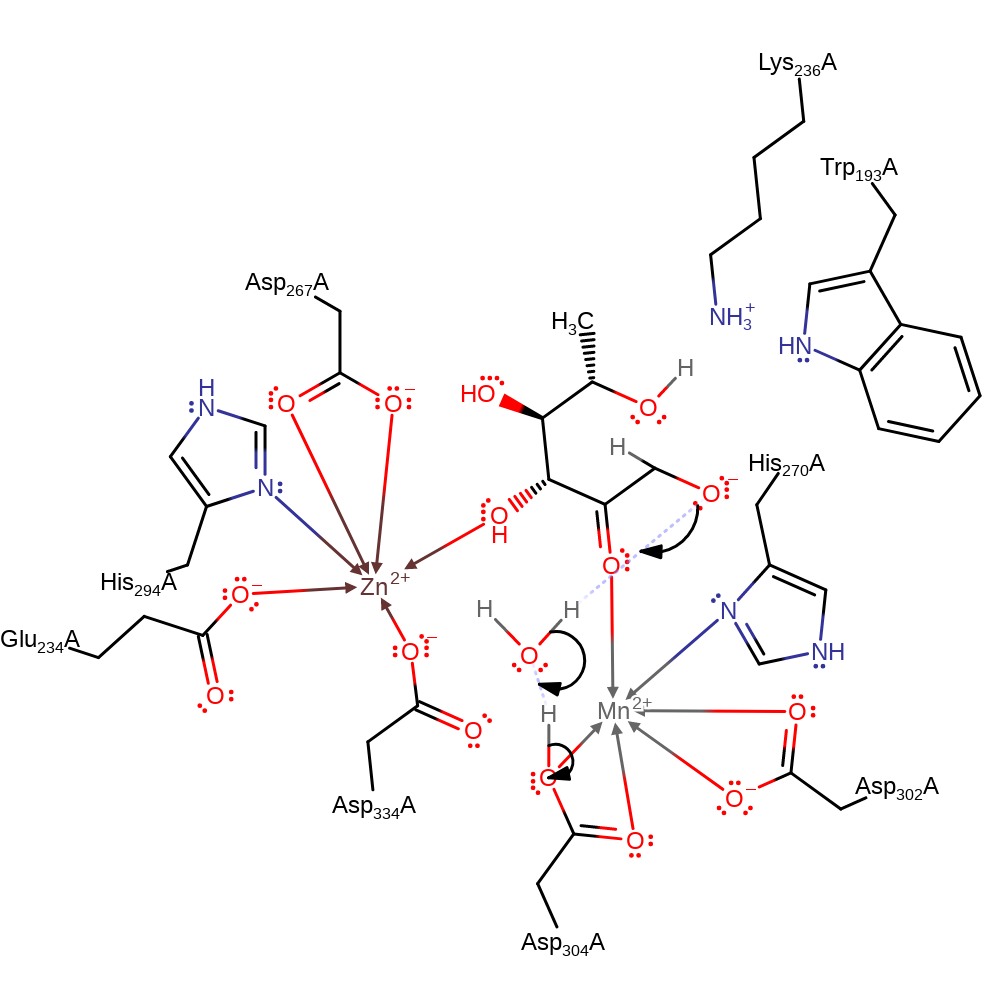
 Download:
Download: 
 Download:
Download: