Aspartate 1-decarboxylase
This enzyme catalyses the formation of beta-alanine from L-aspartate. This is a step in the biosynthetic pathway of pantothenate, the precursor to phosphopantothenate, the acyl carrier found in coenzyme A and acyl carrier proteins. The enzyme requires a main chain rearrangement of the pro-protein to active enzyme. Autocatalytic post-translational modification which cleaves the Gly24-Ser25 peptide bond and converts Ser25 to a pyruvoyl group yield the active enzyme.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P0A790
 (4.1.1.11)
(4.1.1.11)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Escherichia coli K-12 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1aw8
- PYRUVOYL DEPENDENT ASPARTATE DECARBOXYLASE
(2.2 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
2.40.40.20
 (see all for 1aw8)
(see all for 1aw8)
- Cofactors
- Pyruvic acid (1)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:4.1.1.11)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The mechanism involves formation of an imine between the amino group of aspartate and an integral pyruvoyl group. The pyruvol group is formed by an autocatalytic post-translational modification which cleaves the Gly24-Ser25 bond and converts Ser25 into the pyruvoyl group.
Aspartate firstly forms an imine-linkage to the pyruvoyl group of the enzyme, followed by the decarboxylation of the aspartate, forming the extended enolate intermediate. The enolate is then reprotonated by Tyr58 to form an imine intermediate of the product, beta-alanine, which is finally released by hydrolysis to regenerate the pyruvoyl group. Lys9 may play a role in keeping the alpha-carboxyl group of the substrate deprotonated by forming an ion pair.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1aw8) | ||
| Tyr58 | Tyr58(34)B | Acts as a general acid/base, protonates the enolate intermediate to form an imine intermediate of the product beta-alanine. | activator, increase nucleophilicity, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Ser25 (ptm) | Pyr25(1)B (ptm) | Ser25 is post-translationally modified to form the pyruvyl cofactor. Acts as the electrofuge in the nucleophilic addition of the aspartate substrate. | covalently attached, electrofuge, electrophile |
| Lys9 | Lys9D(CA) | Keeps the alpha-carboxyl group of aspartate deprotonated by forming an ion pair. | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
overall reactant used, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, heterolysis, proton transfer, decarboxylation, electron transfer, keto-enol tautomerisation, hydrolysis, intermediate terminated, native state of enzyme regenerated, overall product formedReferences
- Lee BI et al. (2004), J Mol Biol, 340, 1-7. Crystal Structure of the Schiff Base Intermediate Prior to Decarboxylation in the Catalytic Cycle of Aspartate α-Decarboxylase. DOI:10.1016/j.jmb.2004.04.049. PMID:15184017.
- Saldanha SA et al. (2001), Chem Commun (Camb), 1760-1761. Identification of Tyr58 as the proton donor in the aspartate-α-decarboxylase reaction. DOI:10.1039/b106090m. PMID:12240302.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys9D(CA) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Pyr25(1)B (ptm) | electrophile, covalently attached |
Chemical Components
overall reactant used, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formationCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Pyr25(1)B (ptm) | covalently attached |
| Lys9D(CA) | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
heterolysis, proton transfer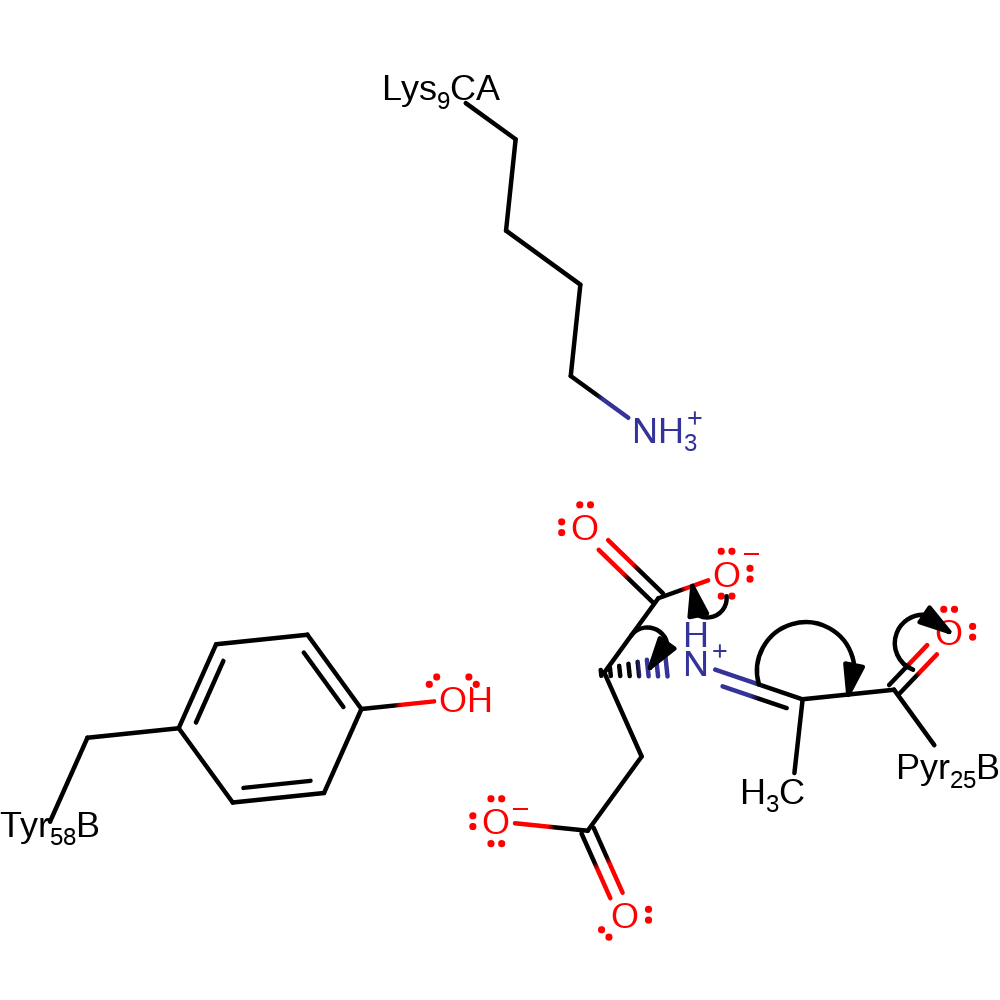
Step 3. The iminium intermediate is decarboxylated with the carbonyl of the pyruvoyl group acting as an electron sink causing it to tautomerise into an enolate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys9D(CA) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Pyr25(1)B (ptm) | covalently attached |
Chemical Components
decarboxylation, electron transfer, keto-enol tautomerisation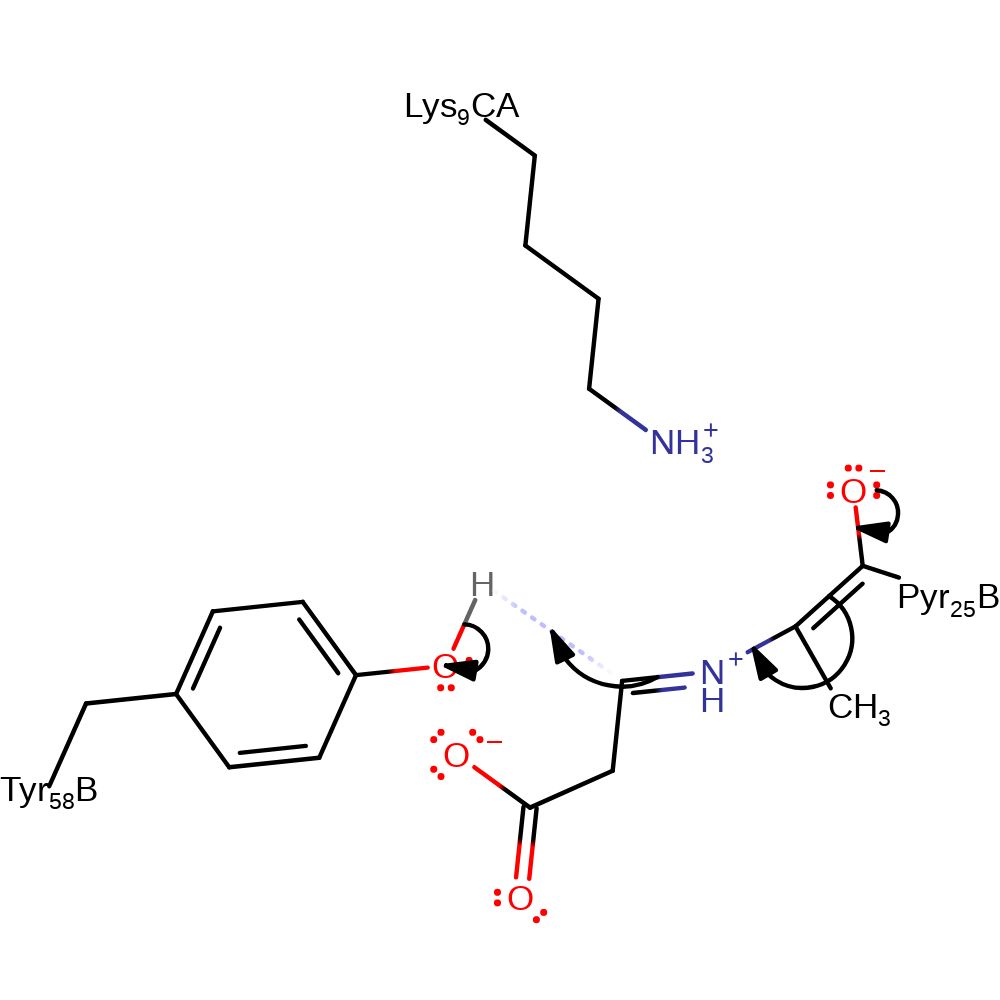
Step 4. The enolate tautomerises back into a keto group. This causes the iminium ion to accept a proton from Tyr58.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Pyr25(1)B (ptm) | covalently attached |
| Lys9D(CA) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr58(34)B | proton donor |
Chemical Components
keto-enol tautomerisation, electron transfer, proton transfer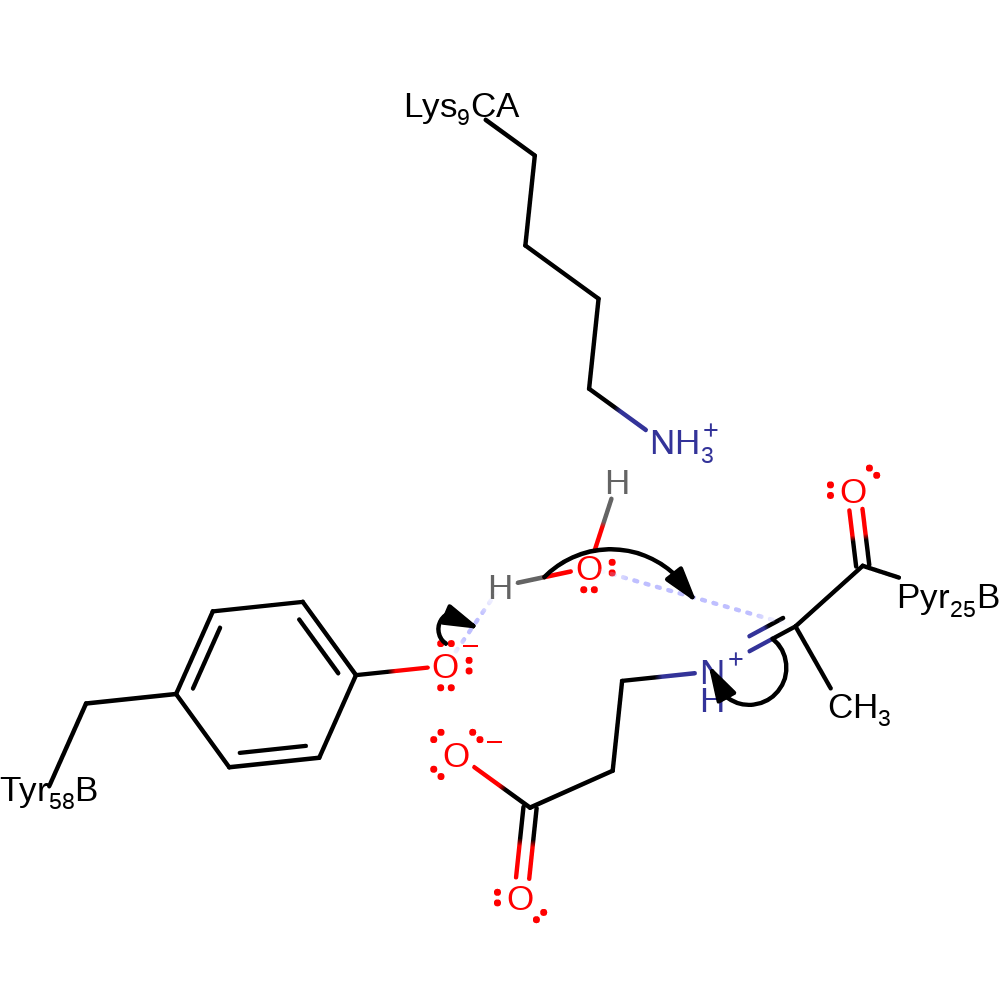
Step 5. Tyr58 now acts as a base to activate a water molecule to begin the hydrolysis of the iminium ion.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Pyr25(1)B (ptm) | covalently attached |
| Tyr58(34)B | activator, increase nucleophilicity |
| Lys9D(CA) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr58(34)B | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, hydrolysisCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Pyr25(1)B (ptm) | electrofuge |
| Lys9D(CA) | electrostatic stabiliser |
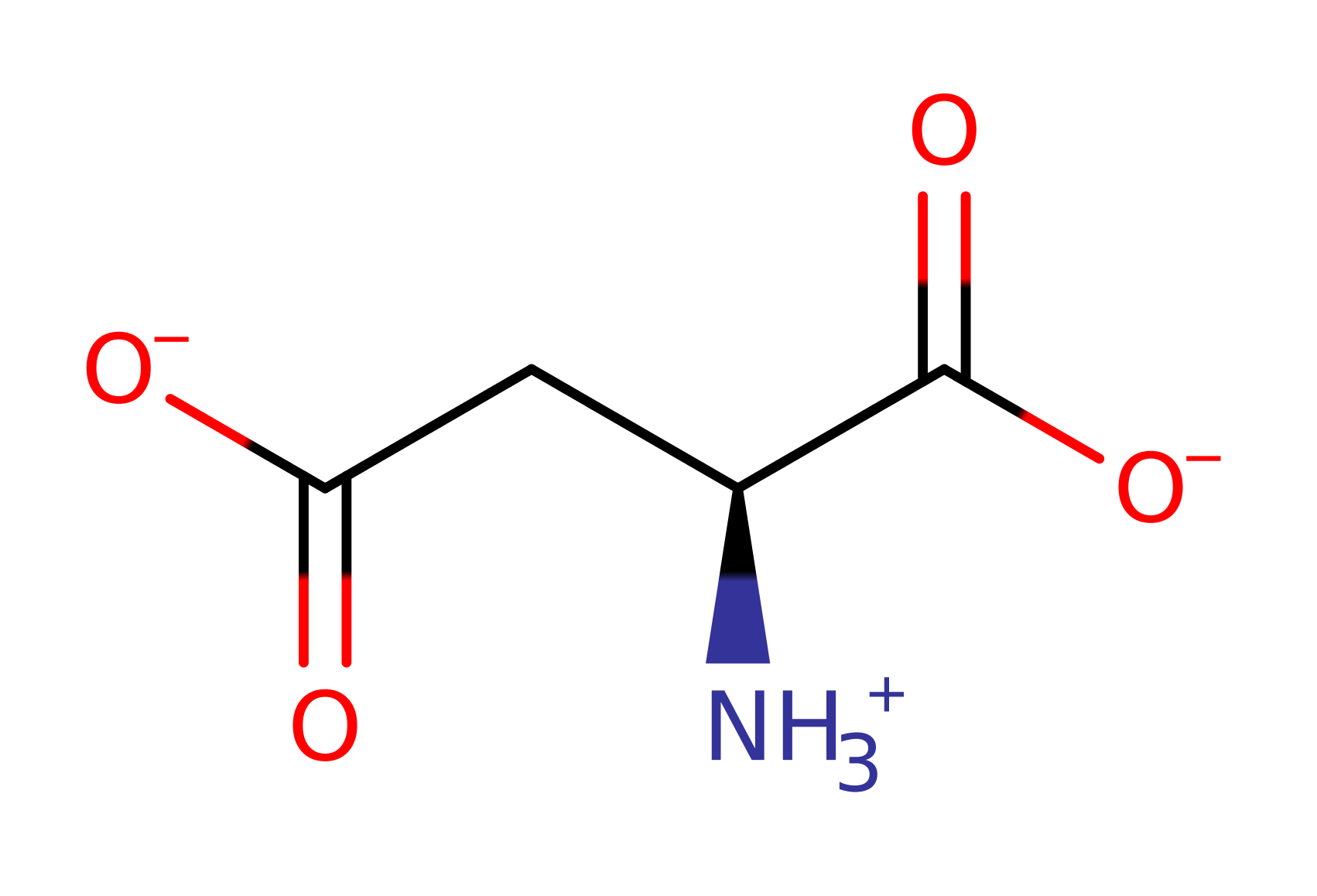



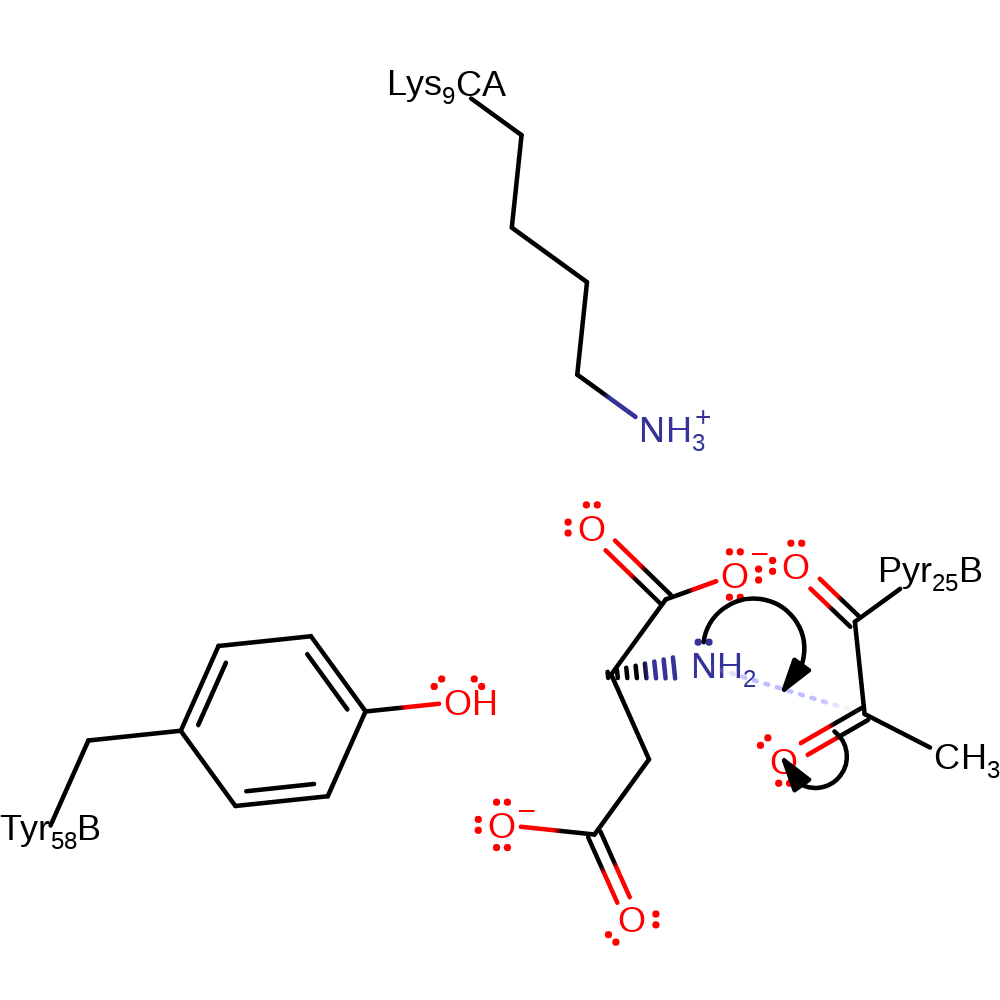
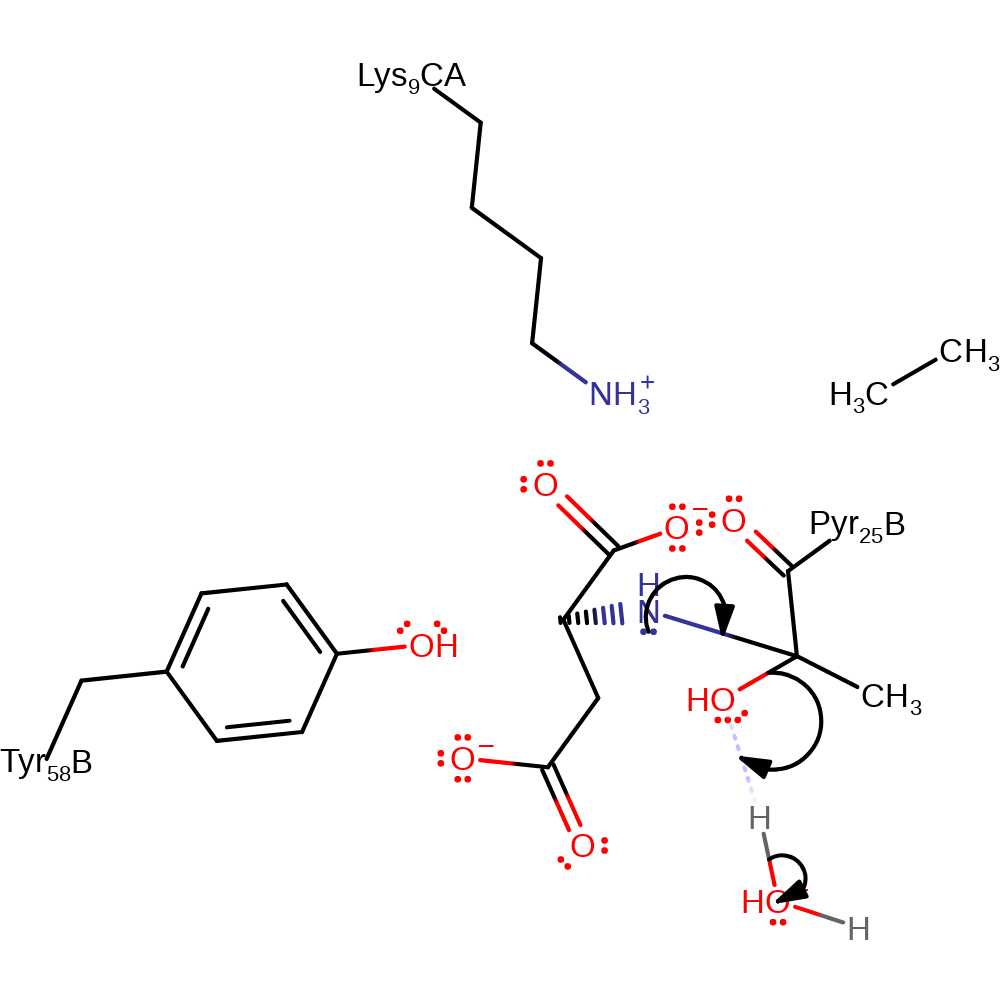

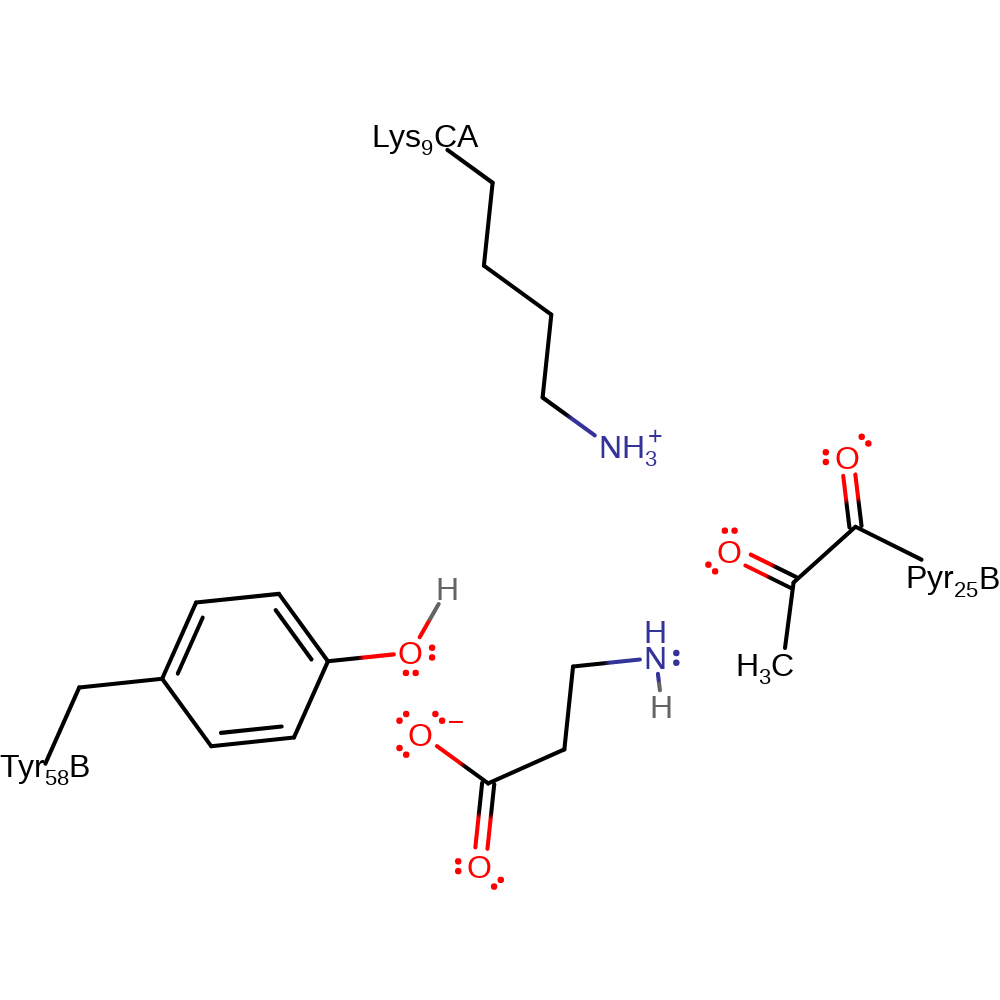 Download:
Download: