Vanadium-dependent bromoperoxidase (HOBr Formation)
V-BPO, isolated from Ascophyllum nodosum, is a vanadium-dependent haloperoxidase. It catalyses the oxidation of halides by hydrogen peroxide to form hypohalides, which can go on to react with organic substrates in halogenation reactions. In this entry, we show the primary biological reaction of V-BPO: the formation of HOBr. V-BPO has the ability to oxidise bromide and, to a lesser extent, chloride and iodide as well as chlorinate organic hydrocarbons and oxidise organic sulfides. V-BPO contains a vanadium(V) ion with a trigonal bipyramidal coordination sphere. It is coordinated to His486 and a hydroxide in the axial positions, and two oxygen atoms and a hydroxide in the equatorial positions.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P81701
 (1.11.1.18)
(1.11.1.18)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Ascophyllum nodosum (Knotted wrack)

- PDB
-
1qi9
- X-RAY SIRAS STRUCTURE DETERMINATION OF A VANADIUM-DEPENDENT HALOPEROXIDASE FROM ASCOPHYLLUM NODOSUM AT 2.0 A RESOLUTION
(2.05 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
1.10.606.10
 (see all for 1qi9)
(see all for 1qi9)
- Cofactors
- Vanadate(3-) (1)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:1.11.1.18)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
An oxygen of hydrogen peroxide attacks the vanadium centre and causes the elimination of the axial hydroxide, which then deprotonates the bound peroxide to form water. The second oxygen of the peroxide ligand then attacks the vanadium centre and causes the elimination of an equatorial oxygen, which then abstracts the second peroxide proton. This forms a side-on vanadium-peroxo species. Bromide attacks one of the oxygens of the peroxo group, causing the O-O bond to break and leading to the formation of an axial vanadium-OBr complex. In the final step, the hypobromite ligand is protonated by water and is displaced by the resulting hydroxide ligand.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1qi9) |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, dehydration, intramolecular nucleophilic substitution, bimolecular nucleophilic additionReferences
- Weyand M et al. (1999), J Mol Biol, 293, 595-611. X-ray structure determination of a vanadium-dependent haloperoxidase from Ascophyllum nodosum at 2.0 Å resolution. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.1999.3179. PMID:10543953.
- Waller MP et al. (2008), J Phys Chem B, 112, 5813-5823. 51V NMR Chemical Shifts from Quantum-Mechanical/Molecular-Mechanical Models of Vanadium Bromoperoxidase. DOI:10.1021/jp800580n. PMID:18412416.
- Raugei S et al. (2006), J Phys Chem B, 110, 3747-3758. Structure and Function of Vanadium Haloperoxidases†. DOI:10.1021/jp054901b. PMID:16494433.
- Zampella G et al. (2005), J Am Chem Soc, 127, 953-960. Reactivity of Peroxo Forms of the Vanadium Haloperoxidase Cofactor. A DFT Investigation. DOI:10.1021/ja046016x. PMID:15656634.
- Rehder D et al. (2000), J Inorg Biochem, 80, 115-121. Water and bromide in the active center of vanadate-dependent haloperoxidases. DOI:10.1016/s0162-0134(00)00047-7. PMID:10885471.
- Macedo-Ribeiro S et al. (1999), J Biol Inorg Chem, 4, 209-219. X-ray crystal structures of active site mutants of the vanadium-containing chloroperoxidase from the fungus Curvularia inaequalis. DOI:10.1007/s007750050306. PMID:10499093.

Step 1. The axial hydroxide of the vanadate cofactor deprotonates hydrogen peroxide.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His486A | metal ligand, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg349A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His411A | increase basicity |
| His418A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser416A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly417A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg480A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp490A | activator |
| Lys341A | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer
Step 2. The activated hydrogen peroxide initiates a nucleophilic attack on the vanadate in a substitution reaction, eliminating water.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His486A | metal ligand, activator |
| Arg349A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys341A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His411A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His418A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser416A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly417A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg480A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp490A | activator |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, dehydration
Step 3. One of the equatorial oxo groups deprotonates the attached hydrogen peroxide.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His486A | metal ligand, activator |
| Arg349A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys341A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His418A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser416A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly417A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg480A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp490A | activator |
Chemical Components
proton transfer
Step 4. The peroxide initiates a nucleophilic attack on the vanadate in a substitution reaction, eliminating hydroxide and forming a three membered ring.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His486A | metal ligand, activator |
| Lys341A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His418A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg349A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser416A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly417A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg480A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp490A | activator |
Chemical Components
ingold: intramolecular nucleophilic substitutionCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His418A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His486A | metal ligand, activator |
| Lys341A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg349A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser416A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly417A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg480A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp490A | activator |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition
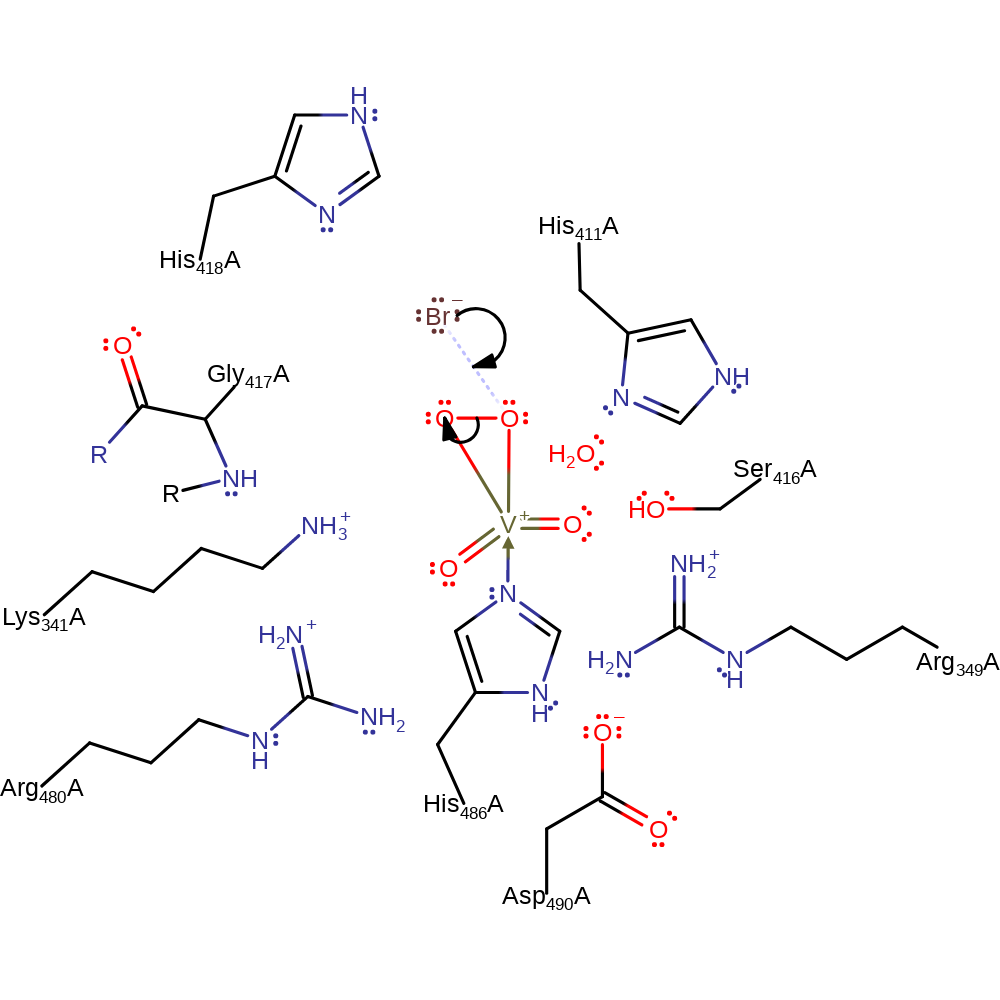
Step 6. Hypobromate is eliminated with concomitant deprotonation of water, which initiates a nucleophilic attack on the vanadate in a coordination reaction to regenerate the cofactor.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His418A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His486A | metal ligand, activator |
| Lys341A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His411A | increase acidity |
| Arg349A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser416A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly417A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg480A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp490A | activator |





 Download:
Download: