Formyltetrahydrofolate synthetase
Formyltetrahydrofolate synthetase (FTHFS) is one of the enzymes participating in the transfer of one-carbon units, an essential element of various biosynthetic pathways. FTHFS catalyses the ATP-dependent activation of a formate ion via its addition to the N10 position of tetrahydrofolate. FTHFS is a highly expressed key enzyme in both the Wood-Ljungdahl pathway of autotrophic CO2 fixation (acetogenesis) and the glycine synthase/reductase pathways of purinolysis. The key physiological role of this enzyme in acetogens is to catalyze the formylation of tetrahydrofolate, an initial step in the reduction of carbon dioxide and other one-carbon precursors to acetate. In purinolytic organisms, the enzymatic reaction is reversed, liberating formate from 10-formyltetrahydrofolate with concurrent production of ATP [PMID:11087401, PMID:10747779]. In many of these processes the transfers of one-carbon units are mediated by the coenzyme tetrahydrofolate (THF). In eukaryotes the FTHFS activity is expressed by a multifunctional enzyme, C-1-tetrahydrofolate synthase (C1-THF synthase), which also catalyses the dehydrogenase and cyclohydrolase activities. Two forms of C1-THF synthases are known [PMID:2836393], one is located in the mitochondrial matrix, while the second one is cytoplasmic. In both forms the FTHFS domain consists of about 600 amino acid residues and is located in the C-terminal section of C1-THF synthase. In prokaryotes FTHFS activity is expressed by a monofunctional homotetrameric enzyme of about 560 amino acid residues [PMID:2200509].
The crystal structure of N(10)-formyltetrahydrofolate synthetase from Moorella thermoacetica shows that the subunit is composed of three domains organised around three mixed beta-sheets. There are two cavities between adjacent domains. One of them was identified as the nucleotide binding site by homology modelling. The large domain contains a seven-stranded beta-sheet surrounded by helices on both sides. The second domain contains a five-stranded beta-sheet with two alpha-helices packed on one side while the other two are a wall of the active site cavity. The third domain contains a four-stranded beta-sheet forming a half-barrel. The concave side is covered by two helices while the convex side is another wall of the large cavity. Arg 97 is likely involved in formyl phosphate binding. The tetrameric molecule is relatively flat with the shape of the letter X, and the active sites are located at the end of the subunits far from the subunit interface [PMID: 10747779].
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P21164
 (6.3.4.3)
(6.3.4.3)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Moorella thermoacetica (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1eg7
- THE CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF FORMYLTETRAHYDROFOLATE SYNTHETASE FROM MOORELLA THERMOACETICA
(2.5 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.50.300
 (see all for 1eg7)
(see all for 1eg7)
- Cofactors
- Magnesium(2+) (1)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:6.3.4.3)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
This reaction occurs via a two-step mechanism in which the production of a formylphosphate intermediate is followed by formation of the product, N10-formyltetrahydrofolate.
Formate, which is stabilised through hydrogen bonding from Arg1097 and Ala1276, attacks the γ-phosphate of Mg-ATP. Formylphosphate, the intermediate, is formed and ADP dissociates. Tetrahydrofolate, the third substrate, binds in the active site between Trp1412 and Phe1384, positioning its N10 towards the formylphosphate. Nucleophilic attack from N10 to the carbonyl of formylphosphate occurs, transferring the formyl group to tetrahydrofolate, forming the final products formyltetrahydrofolate and phosphate.
The presence of a metal cation (one not associated with ATP) enhances catalytic activity, but its binding site is too far from the active site to be implicated in the catalytic mechanism.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1eg7) | ||
| Phe384, Trp412 | Phe1384(384)A, Trp1412(410)A | Forms a pi-pi stacking sandwich with the adenine rings of both ATP, ADP and the THF substrate. These interactions serve to bind and stabilise the reactants and intermediates. | activator |
| Lys74, Lys108 | Lys1074(74)A, Lys1108(108)A | Binds and activates the formylphosphate intermediate. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Thr76 | Thr1076(76)A | Helps guide the nucleophilic attack of the THF substrate to the formylphosphate intermediate. | steric role |
| Arg97, Ala276 (main-N), Phe304 (main-N) | Arg1097(97)A, Ala1276(276)A (main-N), Phe1304(304)A (main-N) | Bind and activate the formate substrate for its initial nucleophilic activity. | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
bimolecular nucleophilic substitutionReferences
- Celeste LR et al. (2012), Protein Sci, 21, 219-228. Mechanism of N10-formyltetrahydrofolate synthetase derived from complexes with intermediates and inhibitors. DOI:10.1002/pro.2005. PMID:22109967.
- Henderson G et al. (2010), Appl Environ Microbiol, 76, 2058-2066. Presence of Novel, Potentially Homoacetogenic Bacteria in the Rumen as Determined by Analysis of Formyltetrahydrofolate Synthetase Sequences from Ruminants. DOI:10.1128/aem.02580-09. PMID:20118378.
- Vickers TJ et al. (2009), Mol Biochem Parasitol, 166, 142-152. The enzymes of the 10-formyl-tetrahydrofolate synthetic pathway are found exclusively in the cytosol of the trypanosomatid parasite Leishmania major. DOI:10.1016/j.molbiopara.2009.03.009. PMID:19450731.
- Marx CJ et al. (2003), J Bacteriol, 185, 7169-7175. Purification of the formate-tetrahydrofolate ligase from Methylobacterium extorquens AM1 and demonstration of its requirement for methylotrophic growth. PMID:14645277.
- Radfar R et al. (2000), Biochemistry, 39, 14481-14486. Cation binding and thermostability of FTHFS monovalent cation binding sites and thermostability of N10-formyltetrahydrofolate synthetase from Moorella thermoacetica. PMID:11087401.
- Radfar R et al. (2000), Biochemistry, 39, 3920-3926. The crystal structure of N(10)-formyltetrahydrofolate synthetase from Moorella thermoacetica. DOI:10.2210/pdb1eg7/pdb. PMID:10747779.
- Lovell CR et al. (1990), Biochemistry, 29, 5687-5694. Primary structure of the thermostable formyltetrahydrofolate synthetase from Clostridium thermoaceticum. PMID:2200509.
- Mejillano MR et al. (1989), Biochemistry, 28, 5136-5145. Formation and utilization of formyl phosphate by N10-formyltetrahydrofolate synthetase: evidence for formyl phosphate as an intermediate in the reaction. DOI:10.1021/bi00438a034. PMID:2548602.
- Shannon KW et al. (1988), J Biol Chem, 263, 7717-7725. Isolation and characterization of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae MIS1 gene encoding mitochondrial C1-tetrahydrofolate synthase. PMID:2836393.
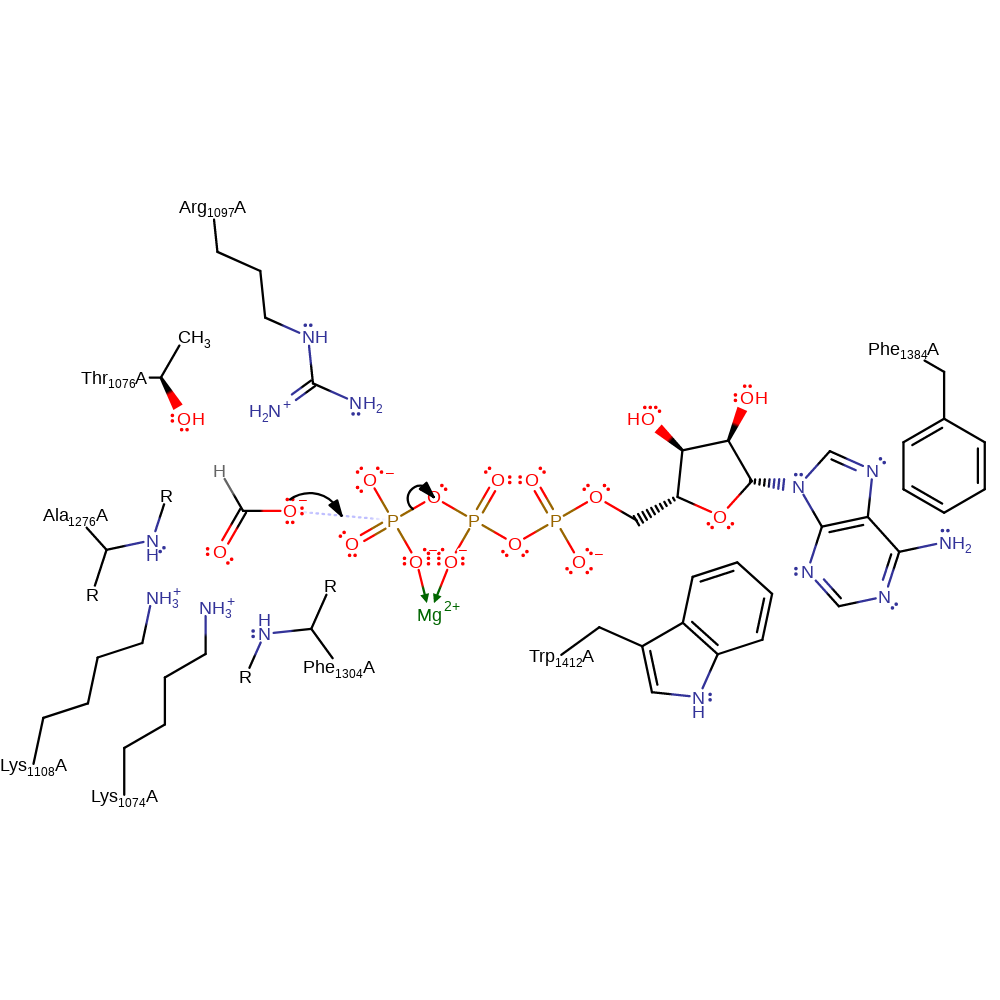
Step 1. Formate initiates a nucleophilic attack on the gamma phosphate of ATP, eliminating ADP.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Phe1304(304)A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Thr1076(76)A | steric role |
| Lys1108(108)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys1074(74)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg1097(97)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ala1276(276)A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Trp1412(410)A | activator |
| Phe1384(384)A | activator |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution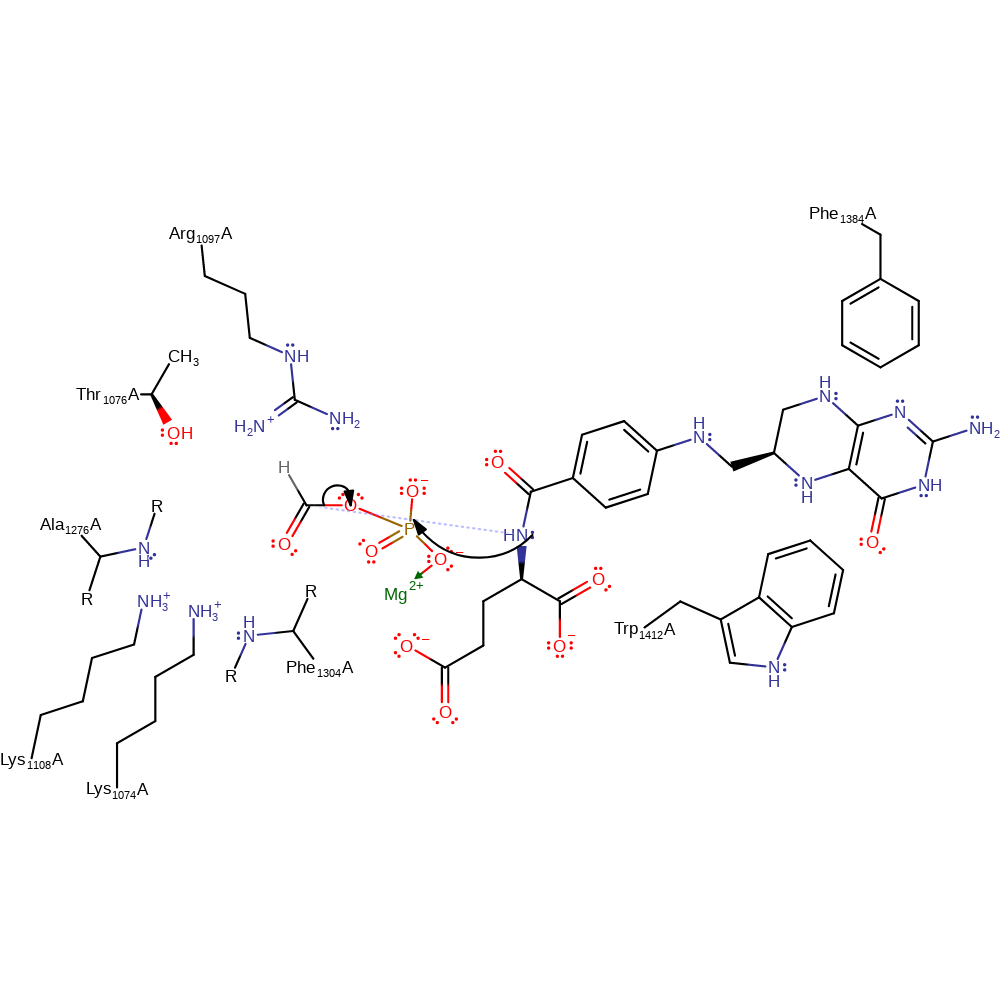
Step 2. THF initiates a nucleophilic attack carbonyl carbon of the phosphorylated formate intermediate, eliminating the phosphate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys1108(108)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Phe1304(304)A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Phe1384(384)A | activator |
| Trp1412(410)A | activator |
| Ala1276(276)A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg1097(97)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys1074(74)A | electrostatic stabiliser |






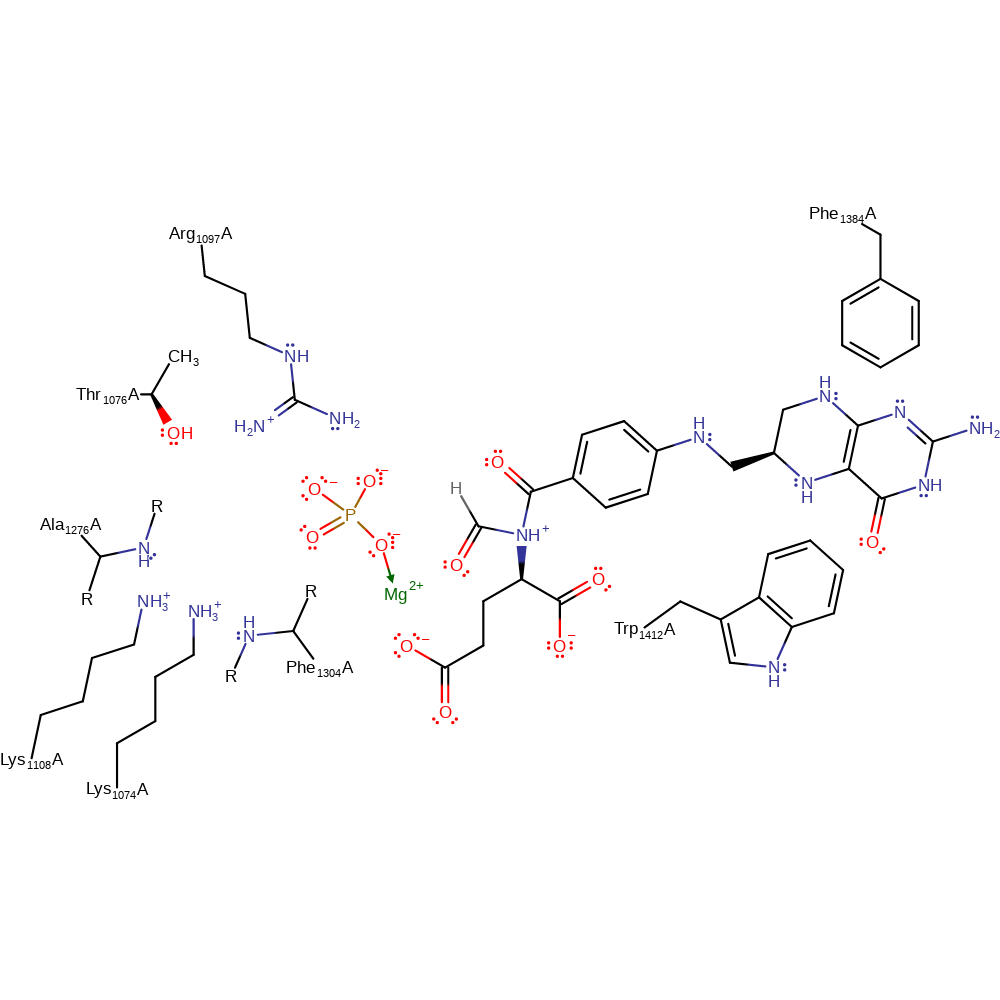 Download:
Download: