UDP-N-acetylglucosamine enolpyruvyl transferase
UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 1-carboxyvinyltransferase or UDP-N-acetylglucosamine enolpyruvyl transferase (EPT) is a key enzyme in the biosynthesis of peptidoglycan, a major component of the bacterial cell wall. The enzyme is involved in the first step of peptidoglycan biosynthesis, it catalyses the the enolpyruvyl transfer from phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) to a second substrate.
Historically, the pathway of peptidogycan biosynthesis has been an important target for antibacterial agents, such as the beta-lactams. EPT is of particular interest because it is inhibited by the naturally occurring antibiotic fosfomycin.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P33038
 (2.5.1.7)
(2.5.1.7)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Enterobacter cloacae subsp. cloacae ATCC 13047 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1dlg
- CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE C115S ENTEROBACTER CLOACAE MURA IN THE UN-LIGANDED STATE
(1.9 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.65.10.10
 (see all for 1dlg)
(see all for 1dlg)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:2.5.1.7)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
Conserved residue Asp305 deprotonates the 3-OH of UDP-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine, activating the oxygen towards nucleophilic attack at the carbonyl group of phosphoenolpyruvate with concomitant deprotonation of Cys115. in the second step, the anionic sulphur deprotonates the methyl group, reforming the alkene with elimination of phosphate. The active site is regenerated for the next round of catalysis by deprotonation of Asp305 by the departing phosphate.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1dlg) | ||
| Asn23 | Asn23B | Acts to stabilise the transition state. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys115, Asp305 | Ser115B, Asp305B | General acid/base. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor, activator |
| Arg397, Lys22, Arg120 | Arg397B, Lys22B, Arg120B | Coordinate to the phosphate moiety of the tetrahedral intermediate acting to stabilise the reactive intermediates and transition states. | hydrogen bond donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, native state of enzyme regenerated, inferred reaction step, bimolecular eliminationReferences
- Eschenburg S et al. (2003), J Biol Chem, 278, 49215-49222. A New View of the Mechanisms of UDP-N-Acetylglucosamine Enolpyruvyl Transferase (MurA) and 5-Enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate Synthase (AroA) Derived from X-ray Structures of Their Tetrahedral Reaction Intermediate States. DOI:10.1074/jbc.m309741200. PMID:13129913.
- Eschenburg S et al. (2005), J Biol Chem, 280, 3757-3763. Evidence That the Fosfomycin Target Cys115 in UDP-N-acetylglucosamine Enolpyruvyl Transferase (MurA) Is Essential for Product Release. DOI:10.1074/jbc.m411325200. PMID:15531591.
- Samland AK et al. (2001), Biochemistry, 40, 1550-1559. Asparagine 23 and Aspartate 305 Are Essential Residues in the Active Site of UDP-N-Acetylglucosamine Enolpyruvyl Transferase fromEnterobacter cloacae†. DOI:10.1021/bi001490a. PMID:11327813.
- Krekel F et al. (2000), Biochemistry, 39, 12671-12677. Determination of the pKaValue of C115 in MurA (UDP-N-Acetylglucosamine Enolpyruvyltransferase) fromEnterobacter cloacae†. DOI:10.1021/bi001310x. PMID:11027147.
- Shuttleworth WA et al. (1999), Biochemistry, 38, 296-302. Site-Directed Mutagenesis of Putative Active Site Residues of 5-Enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate Synthase†. DOI:10.1021/bi9815142. PMID:9890910.
- Skarzynski T et al. (1998), Biochemistry, 37, 2572-2577. Stereochemical Course of Enzymatic Enolpyruvyl Transfer and Catalytic Conformation of the Active Site Revealed by the Crystal Structure of the Fluorinated Analogue of the Reaction Tetrahedral Intermediate Bound to the Active Site of the C115A Mutant of MurA‡. DOI:10.1021/bi9722608. PMID:9485407.
- Schönbrunn E et al. (1996), Structure, 4, 1065-1075. Crystal structure of UDP-N-acetylglucosamine enolpyruvyltransferase, the target of the antibiotic fosfomycin. DOI:10.1016/s0969-2126(96)00113-x. PMID:8805592.
- Skarzynski T et al. (1996), Structure, 4, 1465-1474. Structure of UDP-N-acetylglucosamine enolpyruvyl transferase, an enzyme essential for the synthesis of bacterial peptidoglycan, complexed with substrate UDP-N-acetylglucosamine and the drug fosfomycin. PMID:8994972.
- Brown ED et al. (1994), Biochemistry, 33, 10638-10645. Detection and characterization of a phospholactoyl-enzyme adduct in the reaction catalyzed by UDP-N-acetylglucosamine enolpyruvoyl transferase, MurZ. PMID:8075064.
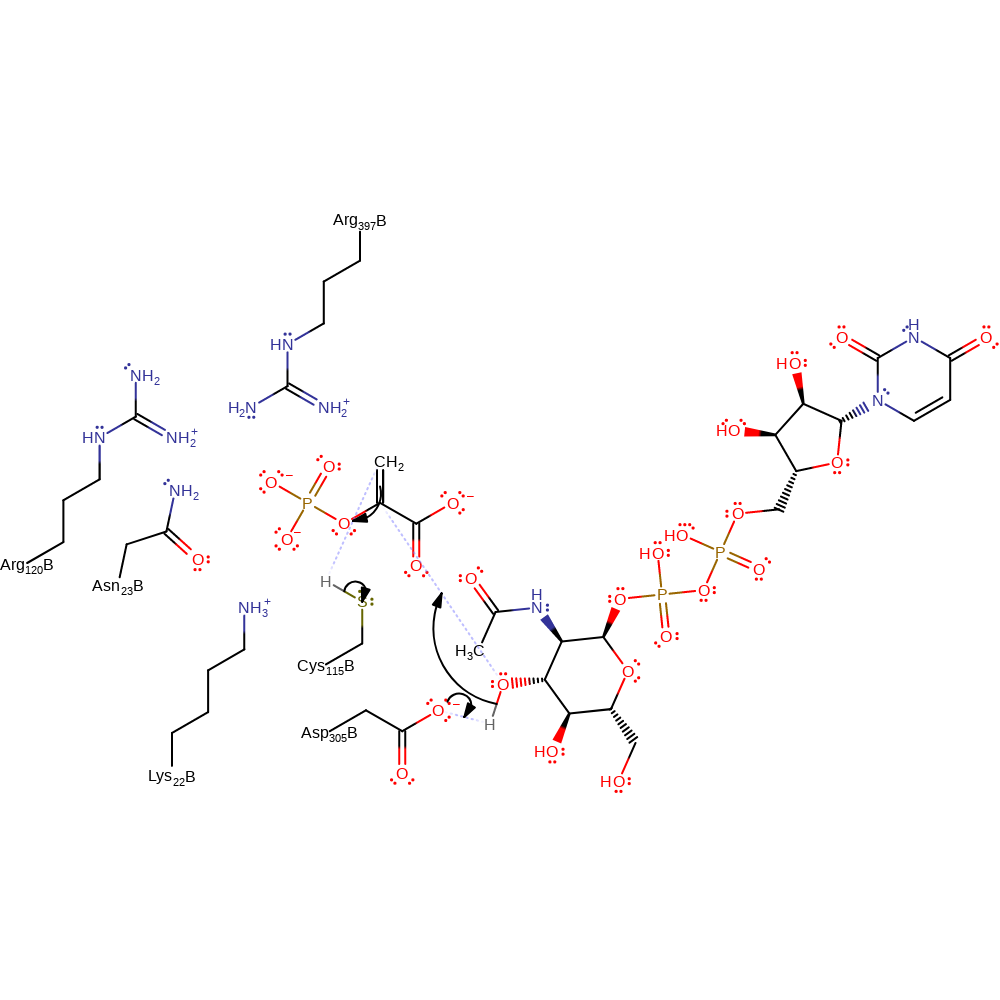
Step 1. Glu305 deprotonates the attacking hydroxyl, activating it towards nucleophilic addition at the phosphoenolpyruvate double bond, with concomitant deprotonation of Cys115, forming a quaternary centre intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg397B | hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser115B | activator, hydrogen bond donor |
| Lys22B | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asn23B | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp305B | activator, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Arg120B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser115B | proton donor |
| Asp305B | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, intermediate formation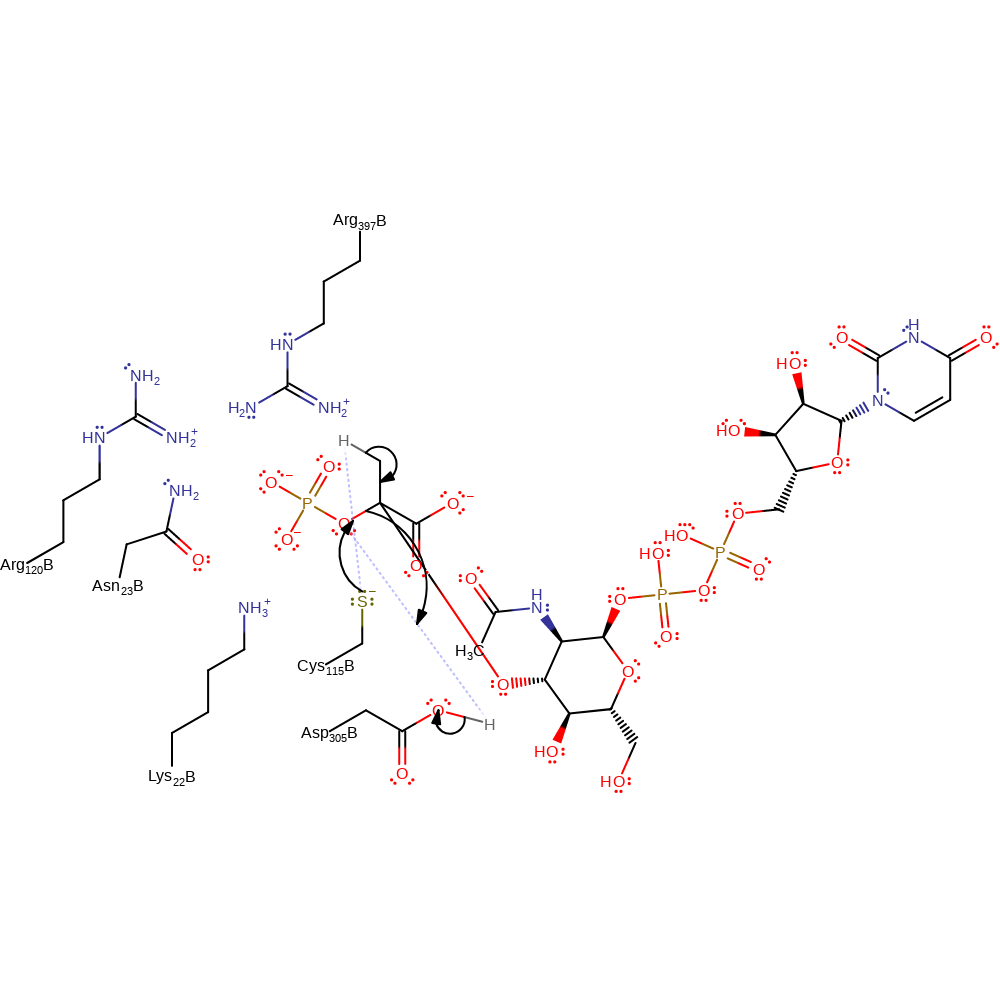
Step 2. The anionic Cys115 deprotonates the methyl group, initiating the elimination of phosphate and formation of the carboxy-vinyl glucosamine. The proton transfer from Asp305 to the departing phosphate is inferred.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg397B | hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser115B | activator, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Lys22B | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asn23B | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp305B | activator, hydrogen bond donor |
| Arg120B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp305B | proton donor |
| Ser115B | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, native state of enzyme regenerated, inferred reaction step, proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular eliminationIntroduction
Cys115 is responsible for both the binding of PEP and fosfomycin. This active cysteine residue is located in a solvent accessible highly flexible loop. The region around Cys 115 is a large flexible loop which has been postulated to undergo substantial structural changes upon catalysis. It is postulated that the binding of the first substrate - UDPGlcNAc, takes place at the cleft between the two domains, resulting in a large conformational change (mediated by the hinge region), thus allowing the movement of the active Cys 115 residue towards the the cleft. The enolpyruvyl transfer occurs through an addition-elimination mechanism that proceeds through a tetrahedral ketal intermediate.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1dlg) | ||
| Asn23 | Asn23B | Acts to stabilise the transition state. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys115 | Ser115B | Ascts as i) a nucleophile towards a known inhibitor and ii) a general acid/base residue, | nucleofuge, nucleophile, proton acceptor, proton donor, proton relay |
| Asp305, Arg397, Lys22, Arg120 | Asp305B, Arg397B, Lys22B, Arg120B | General acid/base | proton acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, bimolecular nucleophilic substitutionReferences
- Zhu JY et al. (2012), J Biol Chem, 287, 12657-12667. Functional Consequence of Covalent Reaction of Phosphoenolpyruvate with UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 1-Carboxyvinyltransferase (MurA). DOI:10.1074/jbc.m112.342725. PMID:22378791.
- Samland AK et al. (2001), Biochemistry, 40, 1550-1559. Asparagine 23 and Aspartate 305 Are Essential Residues in the Active Site of UDP-N-Acetylglucosamine Enolpyruvyl Transferase fromEnterobacter cloacae†. DOI:10.1021/bi001490a. PMID:11327813.
- Schönbrunn E et al. (2000), Biochemistry, 39, 2164-2173. Role of the loop containing residue 115 in the induced-fit mechanism of the bacterial cell wall biosynthetic enzyme MurA. PMID:10694381.
- Krekel F et al. (2000), Biochemistry, 39, 12671-12677. Determination of the pKaValue of C115 in MurA (UDP-N-Acetylglucosamine Enolpyruvyltransferase) fromEnterobacter cloacae†. DOI:10.1021/bi001310x. PMID:11027147.
- Shuttleworth WA et al. (1999), Biochemistry, 38, 296-302. Site-Directed Mutagenesis of Putative Active Site Residues of 5-Enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate Synthase†. DOI:10.1021/bi9815142. PMID:9890910.
- Skarzynski T et al. (1998), Biochemistry, 37, 2572-2577. Stereochemical Course of Enzymatic Enolpyruvyl Transfer and Catalytic Conformation of the Active Site Revealed by the Crystal Structure of the Fluorinated Analogue of the Reaction Tetrahedral Intermediate Bound to the Active Site of the C115A Mutant of MurA‡. DOI:10.1021/bi9722608. PMID:9485407.
- Kim DH et al. (1996), Biochemistry, 35, 4923-4928. Characterization of a Cys115 to Asp Substitution in theEscherichia coliCell Wall Biosynthetic Enzyme UDP-GlcNAc Enolpyruvyl Transferase (MurA) That Confers Resistance to Inactivation by the Antibiotic Fosfomycin†. DOI:10.1021/bi952937w. PMID:8664284.
- Schönbrunn E et al. (1996), Structure, 4, 1065-1075. Crystal structure of UDP-N-acetylglucosamine enolpyruvyltransferase, the target of the antibiotic fosfomycin. DOI:10.1016/s0969-2126(96)00113-x. PMID:8805592.
- Wanke C et al. (1993), Eur J Biochem, 218, 861-870. Evidence that the reaction of the UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 1-carboxyvinyltransferase proceeds through the O-phosphothioketal of pyruvic acid bound to Cys115 of the enzyme. PMID:8281938.
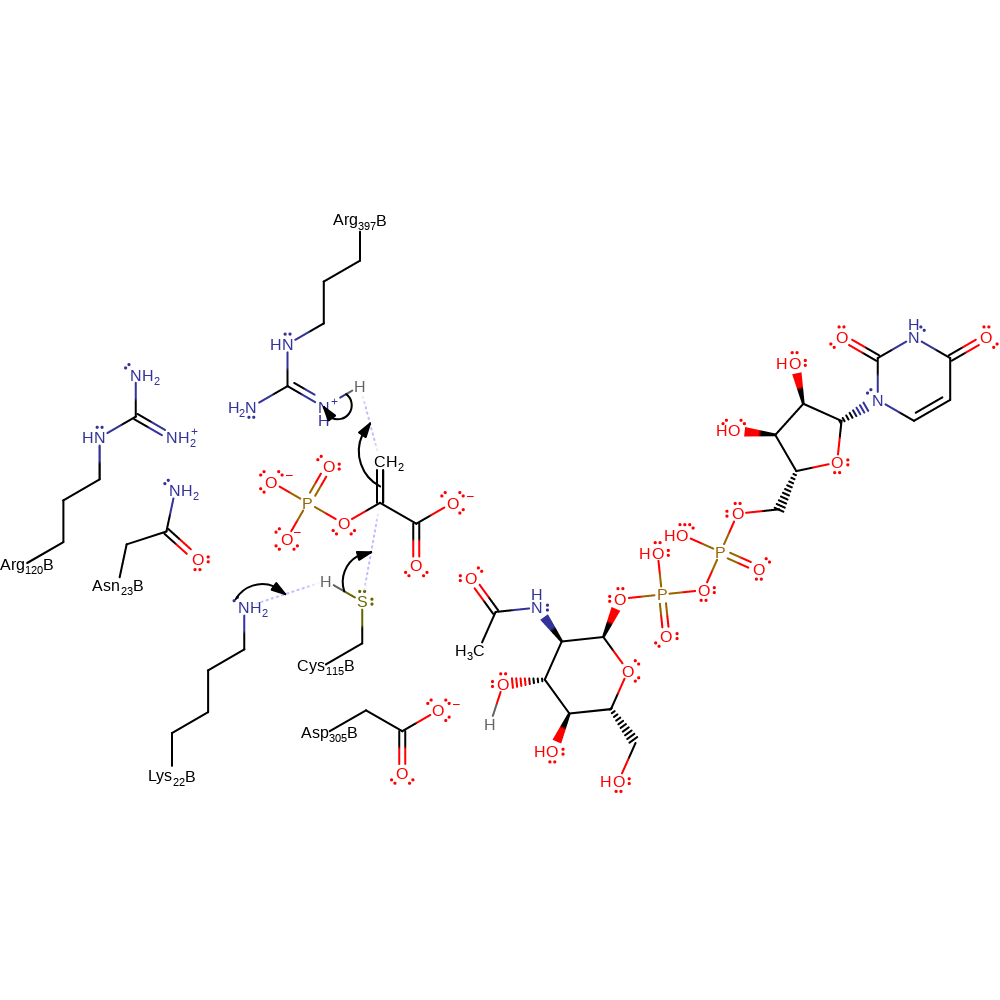
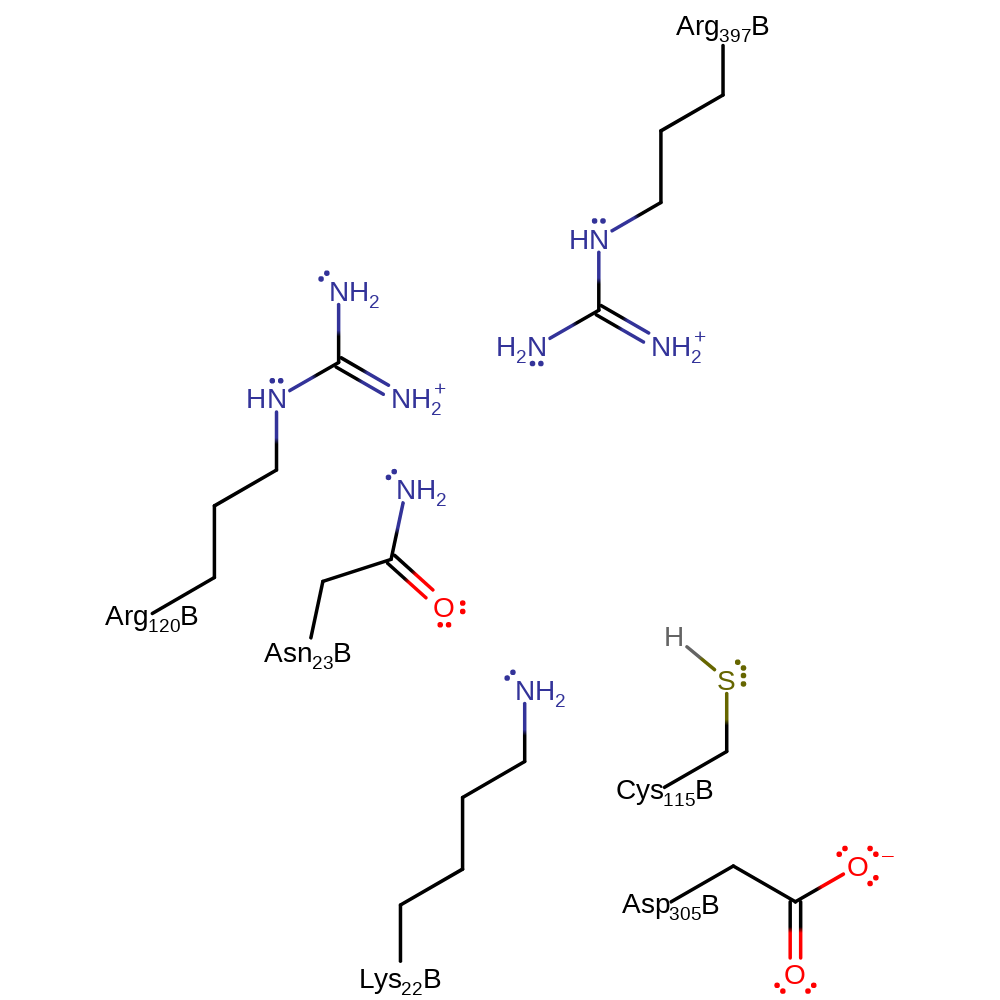
Step 1. A base, possibly Lys22, deprotonates Cys115 which initiates a nucleophilic attack on PEP which deprotonates a general acid, possible Arg397.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asn23B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg120B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys22B | proton acceptor |
| Ser115B | proton donor, nucleophile |
| Arg397B | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition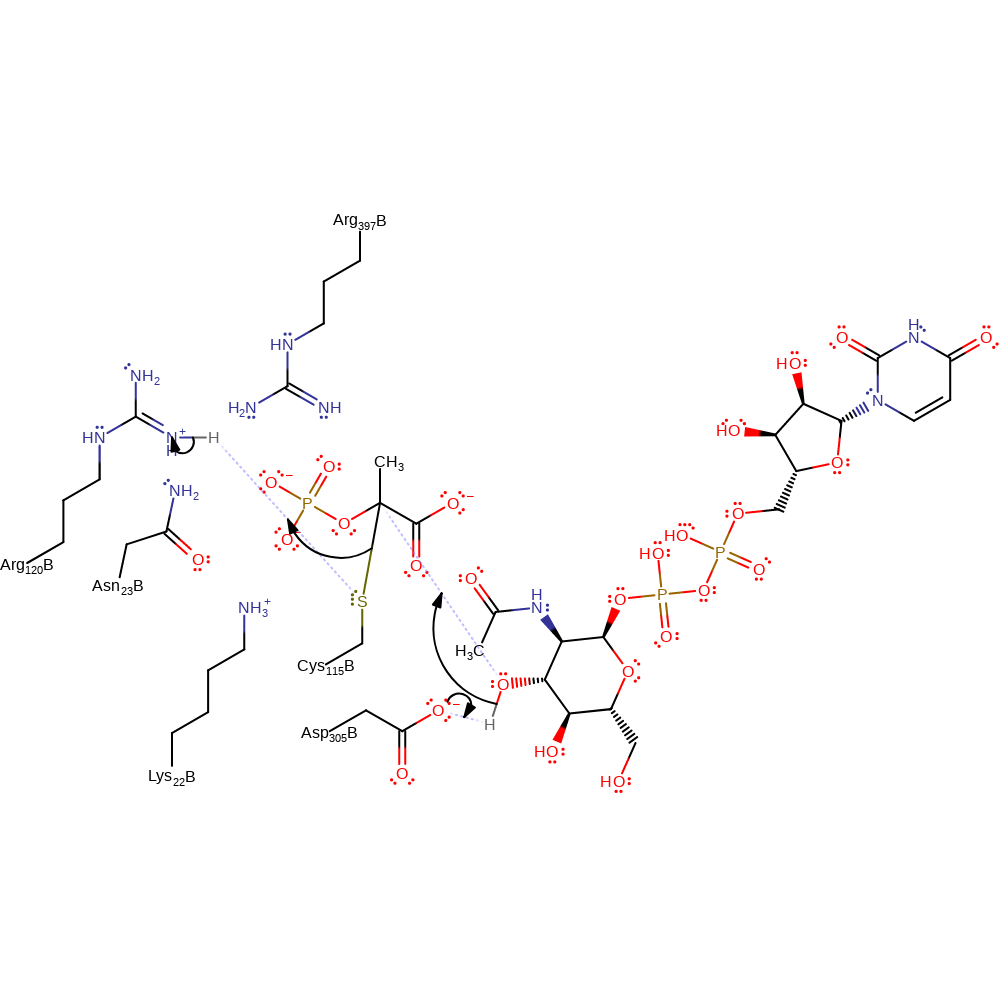
Step 2. Asp305 deprotonates the UAG substrate, which initiates a nucleophilic attack on the PEP-Cys enzyme-substrate complex. Eliminating Cys115 with concomittant deprotonation of a general acid, thought to be Arg120.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asn23B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg397B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys22B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp305B | proton acceptor |
| Ser115B | nucleofuge, proton acceptor |
| Arg120B | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitutionCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg397B | proton acceptor |
| Ser115B | proton acceptor |
| Lys22B | proton donor |
| Arg120B | proton acceptor |
| Ser115B | proton donor |
| Asp305B | proton donor |
| Ser115B | proton relay |




 Download:
Download: 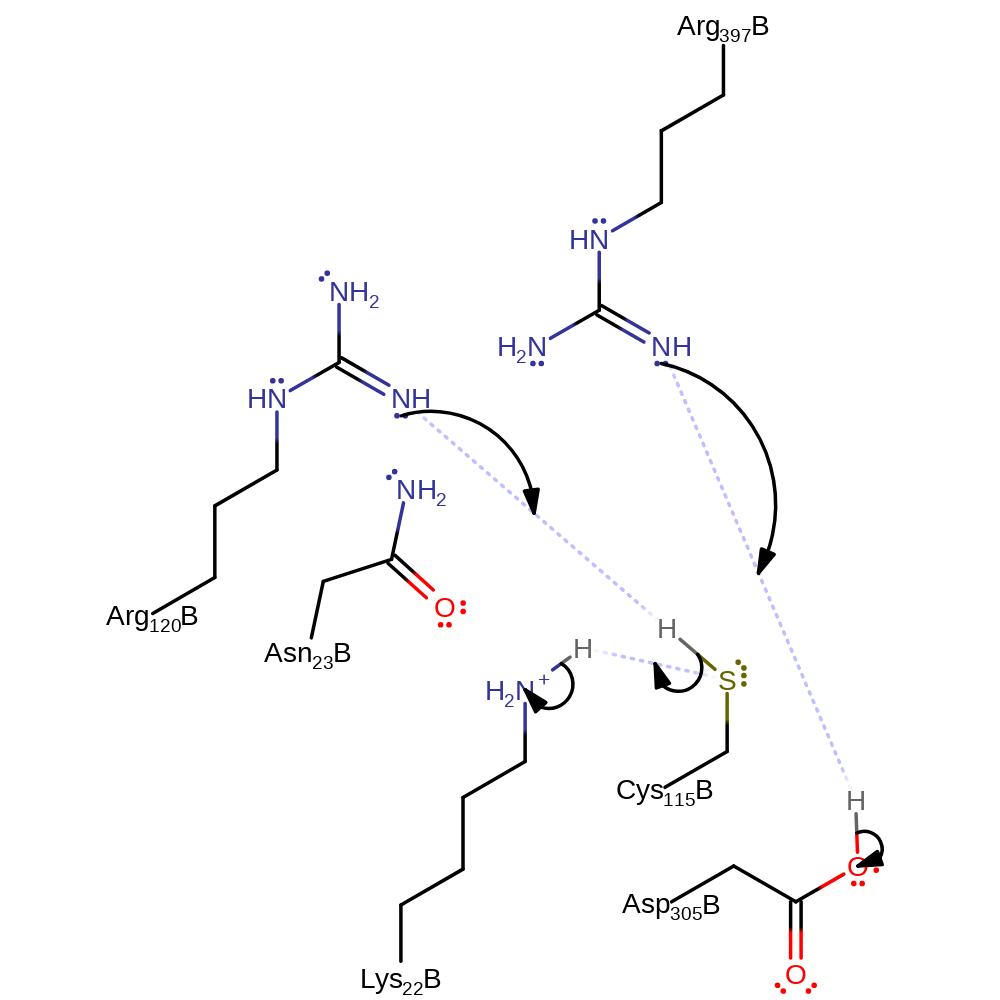
 Download:
Download: