UDP-galactopyranose mutase
UDP-galactopyranose mutase catalyses the ring contraction of a non-reducing sugar via a redox-reaction, transforming UDP-D-galactopyranose to UDP-D-galacto-1,4-furanose. This product (UDP-Galf) is the precursor of the D-galactofuranose (Galf) residues found in bacterial and parasitic cell walls, including those of many pathogens such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Trypanosoma cruzi. The mutase enzyme is essential for the viability of mycobacteria and is not found in humans, making it a potential therapeutic target. A novel mechanism involving reduced FAD acting as a nucleophile has been proposed.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P37747
 (5.4.99.9)
(5.4.99.9)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Escherichia coli K-12 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1i8t
- STRCUTURE OF UDP-GALACTOPYRANOSE MUTASE FROM E.COLI
(2.4 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.50.720
 (see all for 1i8t)
(see all for 1i8t)
- Cofactors
- Fadh2(2-) (1)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:5.4.99.9)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
Nucleophilic attack by N5 of reduced FAD on C1 of UDP-Galp via an SN2 type mechanism that results in the loss of UDP. The charged leaving group is stabilised by electrostatic and hydrogen bonding interactions with Arg170 and Arg278. The imminium intermediate is formed by a second attack of FAD N5 lone pair on C1 of the sugar. This results in the opening of the ring at the OH6 position. The negative charge at N1 is required to increase the nucleophilicity of N5.
The intramolecular nucleophilic attack by OH4 on the imminium group forms a new galactofuranose ring still bound to N5 of the reduced FAD. To release the sugar from the enzyme cofactor, UDP attacks the C1 position leading to lysis of the C1-N5 bond and release of UDP-Galf.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1i8t) | ||
| Asp348, Glu298 | Asp348A(B), Glu298A(B) | Charge stabilisation. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr346 | Tyr346B | Acts to hold substrate in the correct position for the correct reaction to occur. | hydrogen bond donor, steric role |
| Arg174, Arg247 | Arg174A(B), Arg247B | Essential for catalytic activity, proposed to be involved in hydrogen bonding interactions with the substrate. | hydrogen bond donor |
| Arg278, Arg170 | Arg278A(B), Arg170A(B) | Electrostatic stabilisation of the UDP leaving group. | hydrogen bond donor |
Chemical Components
bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, cofactor used, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, proton transfer, inferred reaction step, native state of cofactor regeneratedReferences
- Mehra-Chaudhary R et al. (2016), Biochemistry, 55, 833-836. In Crystallo Capture of a Covalent Intermediate in the UDP-Galactopyranose Mutase Reaction. DOI:10.1021/acs.biochem.6b00035. PMID:26836146.
- Lin GM et al. (2016), Org Lett, 18, 3438-3441. Study of Uridine 5'-Diphosphate (UDP)-Galactopyranose Mutase Using UDP-5-Fluorogalactopyranose as a Probe: Incubation Results and Mechanistic Implications. DOI:10.1021/acs.orglett.6b01618. PMID:27384425.
- Pierdominici-Sottile G et al. (2014), PLoS One, 9, e109559-. QM/MM molecular dynamics study of the galactopyranose → galactofuranose reaction catalysed by Trypanosoma cruzi UDP-galactopyranose mutase. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0109559. PMID:25299056.
- Da Fonseca I et al. (2014), Biochemistry, 53, 7794-7804. Contributions of unique active site residues of eukaryotic UDP-galactopyranose mutases to substrate recognition and active site dynamics. DOI:10.1021/bi501008z. PMID:25412209.
- Tanner JJ et al. (2014), Arch Biochem Biophys, 544, 128-141. Structure, mechanism, and dynamics of UDP-galactopyranose mutase. DOI:10.1016/j.abb.2013.09.017. PMID:24096172.
- Oppenheimer M et al. (2012), PLoS One, 7, e32918-. Chemical mechanism of UDP-galactopyranose mutase from Trypanosoma cruzi: a potential drug target against Chagas' disease. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0032918. PMID:22448231.
- van Straaten KE et al. (2012), J Biol Chem, 287, 10780-10790. Structural insight into the unique substrate binding mechanism and flavin redox state of UDP-galactopyranose mutase from Aspergillus fumigatus. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M111.322974. PMID:22334662.
- Sun HG et al. (2012), J Biol Chem, 287, 4602-4608. Nucleophilic participation of reduced flavin coenzyme in mechanism of UDP-galactopyranose mutase. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M111.312538. PMID:22187430.
- Gruber TD et al. (2009), Biochemistry, 48, 9171-9173. X-ray crystallography reveals a reduced substrate complex of UDP-galactopyranose mutase poised for covalent catalysis by flavin. DOI:10.1021/bi901437v. PMID:19719175.
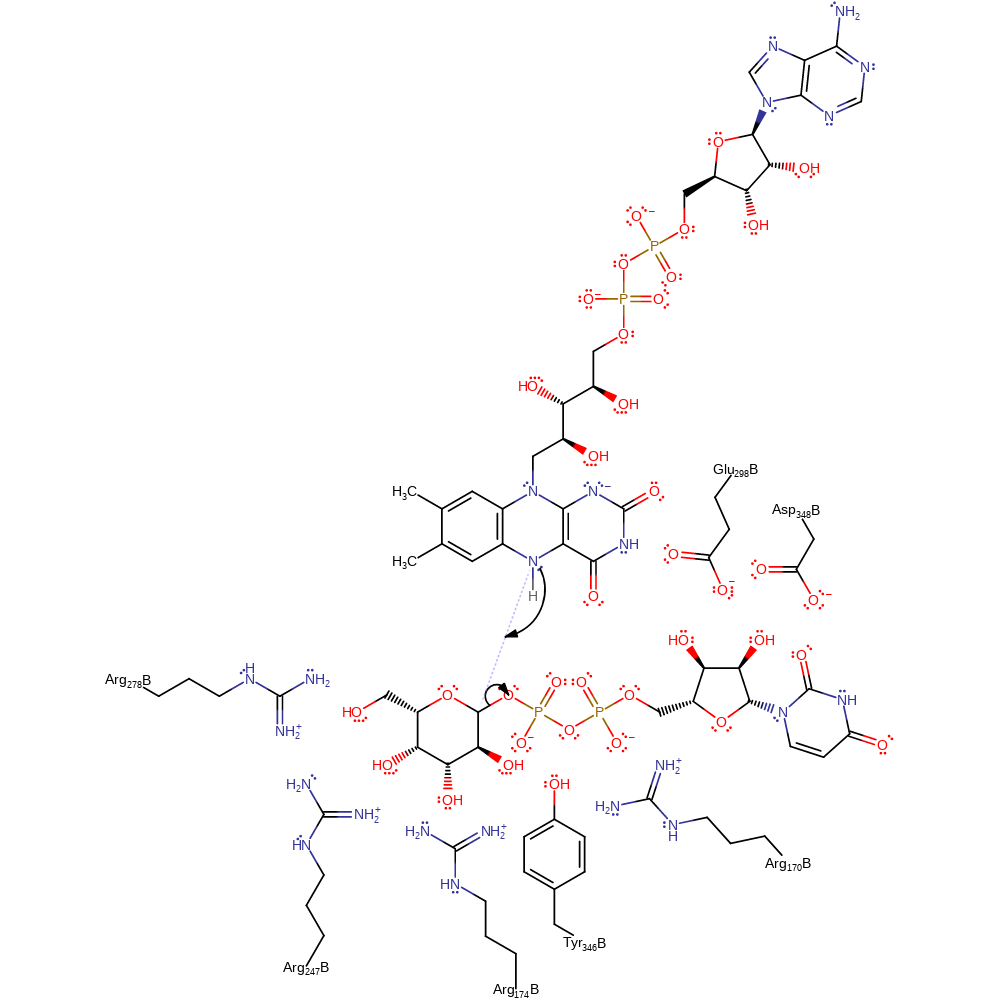
Step 1. The lone pair of electrons present on the reduced FAD attack the anomeric carbon, forming a substrate-cofactor covalent complex.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp348A(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg170A(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg278A(B) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Tyr346B | steric role, hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu298A(B) | steric role, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Arg174A(B) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Arg247B | hydrogen bond donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, cofactor used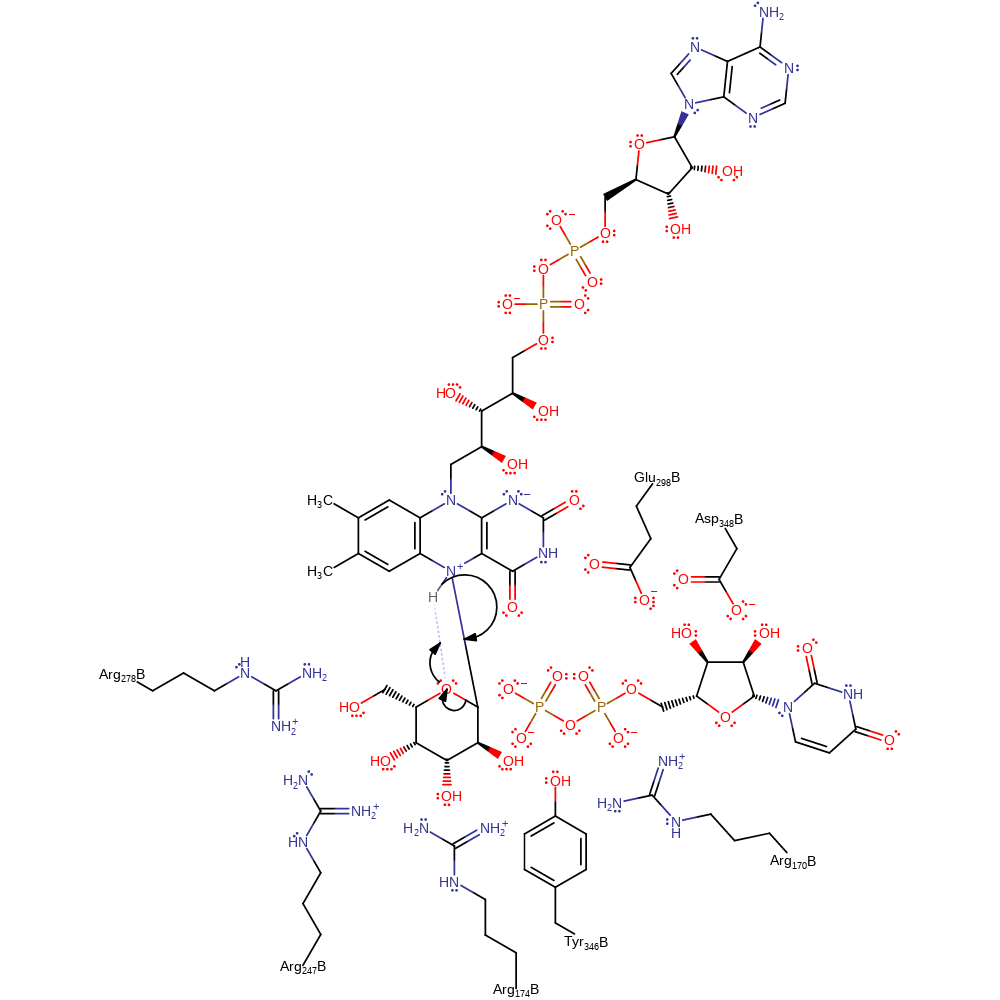
Step 2. The FAD N5 atom uses electron density accumulating from the cleavage of the N-H bond to initiate an internal elimination reaction, resulting in the cleavage of the sugar ring while covalently attached to the cofactor. The rearrangements of protonation states have been inferred.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp348A(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg170A(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg278A(B) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Tyr346B | steric role, hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu298A(B) | steric role, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Arg174A(B) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Arg247B | hydrogen bond donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, proton transfer, intermediate formation, cofactor used, inferred reaction step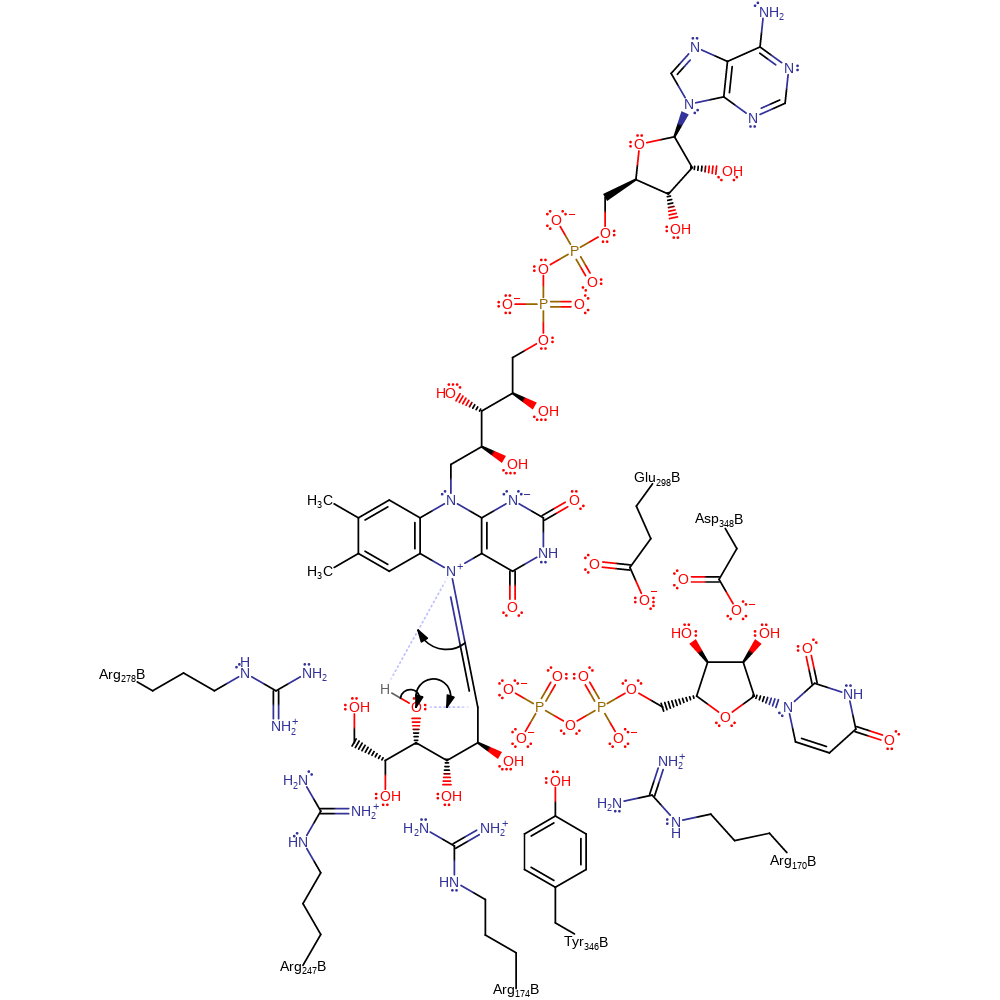
Step 3. The opened ring now undergoes a five exo-tet cyclisation reaction with the C4-OH, which is enthalpically more favourable to the six exo-tet attack, which would give the original six-membered ring. The rearrangements of protonation states have been inferred.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp348A(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg170A(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg278A(B) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Tyr346B | steric role, hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu298A(B) | steric role, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Arg174A(B) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Arg247B | hydrogen bond donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, proton transfer, intermediate formation, cofactor used, inferred reaction step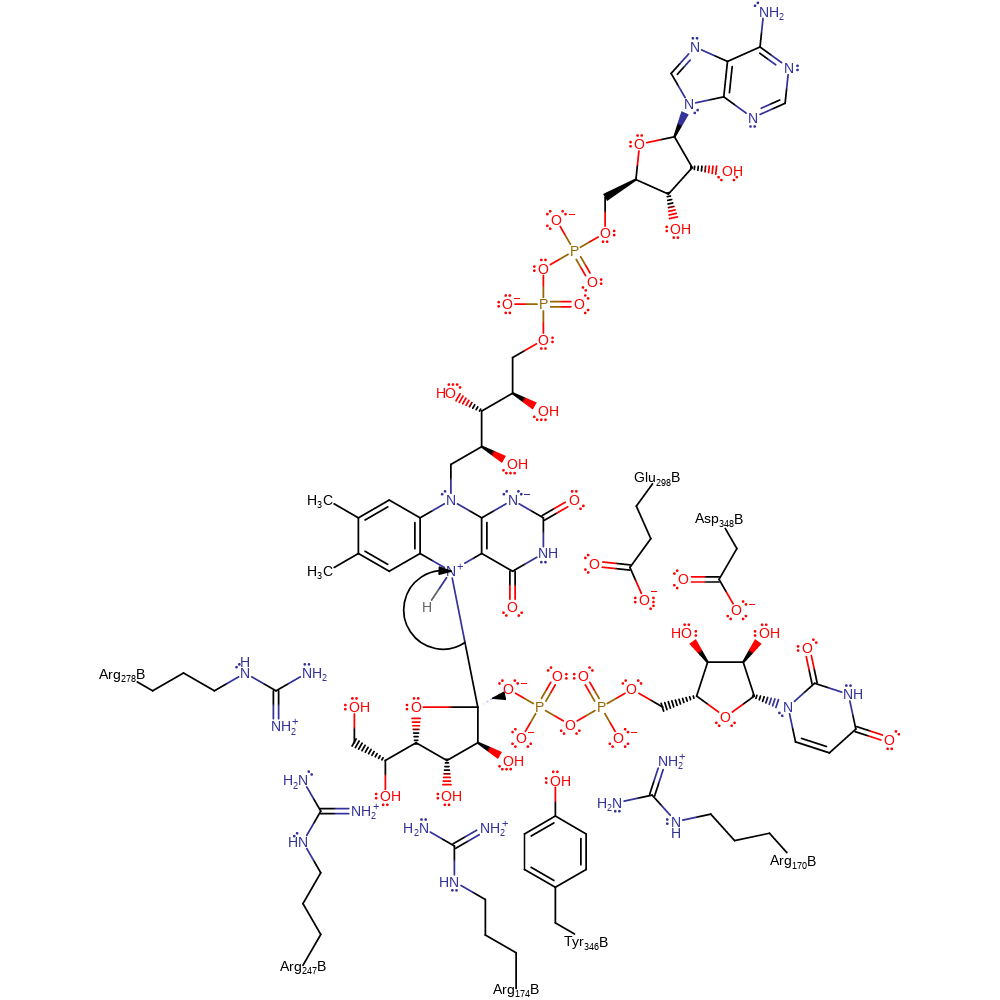
Step 4. The phosphate group then attacks the intermediate anomeric carbon to eliminate the FAD cofactor and generate the final product.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp348A(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg170A(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg278A(B) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Tyr346B | steric role, hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu298A(B) | steric role, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Arg174A(B) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Arg247B | hydrogen bond donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate formation, native state of cofactor regeneratedIntroduction
Nucleophilic attack by N5 of reduced FAD on C1 of UDP-Galp via an SN1 or SN2 type mechanism results in the loss of UDP. This proposal represents the SN1 mechanism.
The charged leaving group is stabilised by electrostatic and hydrogen bonding interactions with Arg170 and Arg278. The imminium intermediate is formed by a second attack of FAD N5 lone pair on C1 of the sugar. This results in the opening of the ring at the OH6 position. The negative charge at N1 is required to increase the nucleophilicity of N5.
The intramolecular nucleophilic attack by OH4 on the imminium group forms a new galactofuranose ring still bound to N5 of the reduced FAD. To release the sugar from the enzyme cofactor, UDP attacks the C1 position leading to lysis of the C1-N5 bond and release of UDP-Galf.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1i8t) | ||
| Asp348, Glu298 | Asp348A(B), Glu298A(B) | Charge stabilisation. | electrostatic stabiliser, steric role |
| Tyr346 | Tyr346B | Acts to hold substrate in the correct position for the correct reaction to occur. | hydrogen bond donor, steric role, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg174, Arg247 | Arg174A(B), Arg247B | Essential for catalytic activity, proposed to be involved in hydrogen bonding interactions with the substrate. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg278, Arg170 | Arg278A(B), Arg170A(B) | Electrostatic stabilisation of the UDP leaving group. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, rate-determining step, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, cofactor used, proton transfer, inferred reaction step, native state of cofactor regenerated, overall product formedReferences
- Sanders DA et al. (2001), Nat Struct Biol, 8, 858-863. UDP-galactopyranose mutase has a novel structure and mechanism. DOI:10.1038/nsb1001-858. PMID:11573090.
- Mehra-Chaudhary R et al. (2016), Biochemistry, 55, 833-836. In Crystallo Capture of a Covalent Intermediate in the UDP-Galactopyranose Mutase Reaction. DOI:10.1021/acs.biochem.6b00035. PMID:26836146.
- Sun HG et al. (2012), J Biol Chem, 287, 4602-4608. Nucleophilic participation of reduced flavin coenzyme in mechanism of UDP-galactopyranose mutase. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M111.312538. PMID:22187430.
- van Straaten KE et al. (2012), J Biol Chem, 287, 10780-10790. Structural insight into the unique substrate binding mechanism and flavin redox state of UDP-galactopyranose mutase from Aspergillus fumigatus. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M111.322974. PMID:22334662.
- Gruber TD et al. (2009), Biochemistry, 48, 9171-9173. X-ray crystallography reveals a reduced substrate complex of UDP-galactopyranose mutase poised for covalent catalysis by flavin. DOI:10.1021/bi901437v. PMID:19719175.
- Friedland N et al. (2007), Biochemistry, 46, 6733-6743. Domain Orientation in the Inactive Response RegulatorMycobacterium tuberculosisMtrA Provides a Barrier to Activation†,‡. DOI:10.1021/bi602546q. PMID:17511470.
- Chad JM et al. (2007), Biochemistry, 46, 6723-6732. Site-Directed Mutagenesis of UDP-Galactopyranose Mutase Reveals a Critical Role for the Active-Site, Conserved Arginine Residues†. DOI:10.1021/bi7002795. PMID:17511471.
- Itoh K et al. (2007), Org Lett, 9, 879-882. Synthesis and analysis of substrate analogues for UDP-galactopyranose mutase: implication for an oxocarbenium ion intermediate in the catalytic mechanism. DOI:10.1021/ol0631408. PMID:17266324.
- Soltero-Higgin M et al. (2004), Nat Struct Mol Biol, 11, 539-543. A unique catalytic mechanism for UDP-galactopyranose mutase. DOI:10.1038/nsmb772. PMID:15133501.
- Barlow JN et al. (1999), J Am Chem Soc, 121, 6968-6969. Positional Isotope Exchange Catalyzed by UDP-Galactopyranose Mutase. DOI:10.1021/ja991582r.
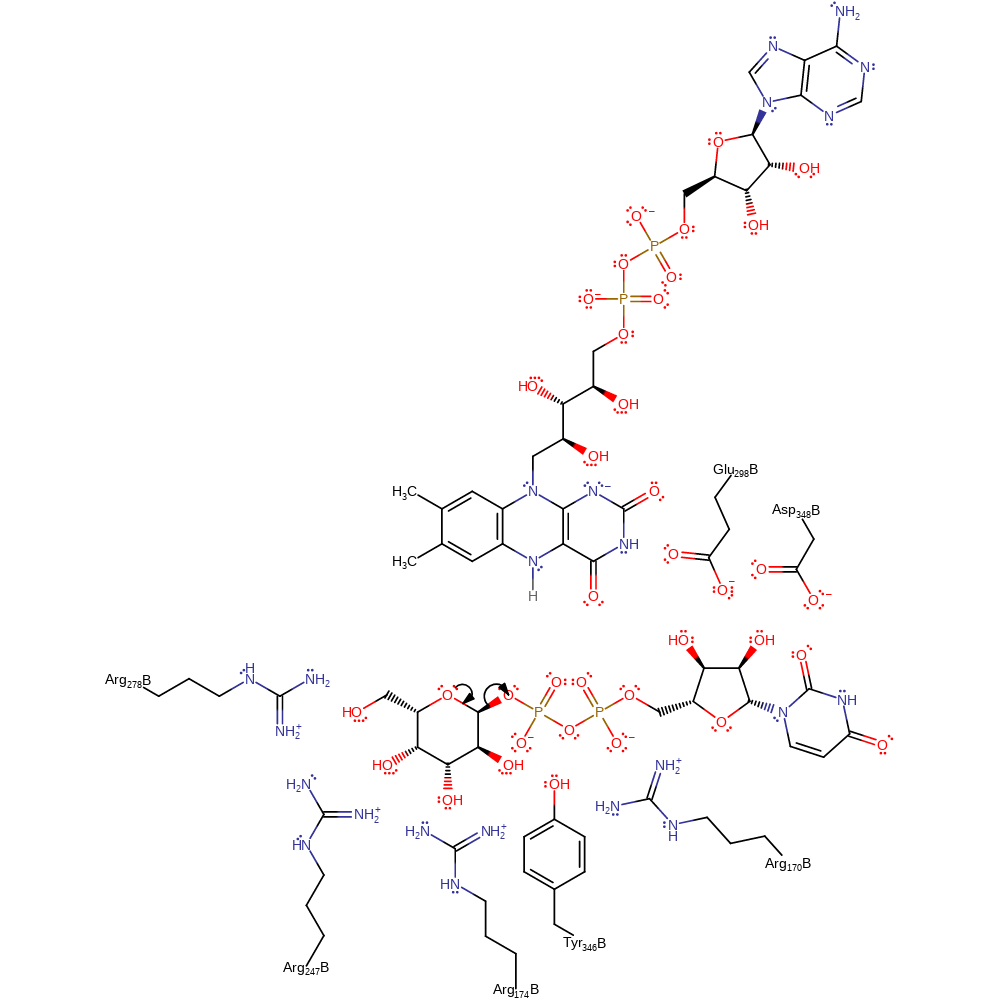
Step 1. Chemical modification of the substrate suggests the departure of UDP to occur by an SN1 type mechanism, with the ring oxygen eliminating UDP and forming an oxonium intermediate [PMID:17266324]. Evidence from mutagenesis studies of homologous proteins from other species suggests the main role of the active site amino acids is to anchor the substrate, intermediates and cofactor into a reactive conformation and also to stabilise the cationic intermediate [PMID:17266324, PMID:19719175]. Electrostatic interactions between Glu298A and Arg174 are thought to peturb the attraction of the product to the active site, and therefore facilitate the removal of product from the active site [PMID:17511471].
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg247B | hydrogen bond donor |
| Arg174A(B) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu298A(B) | hydrogen bond acceptor, steric role |
| Tyr346B | hydrogen bond donor, steric role |
| Arg278A(B) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Arg170A(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp348A(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, rate-determining step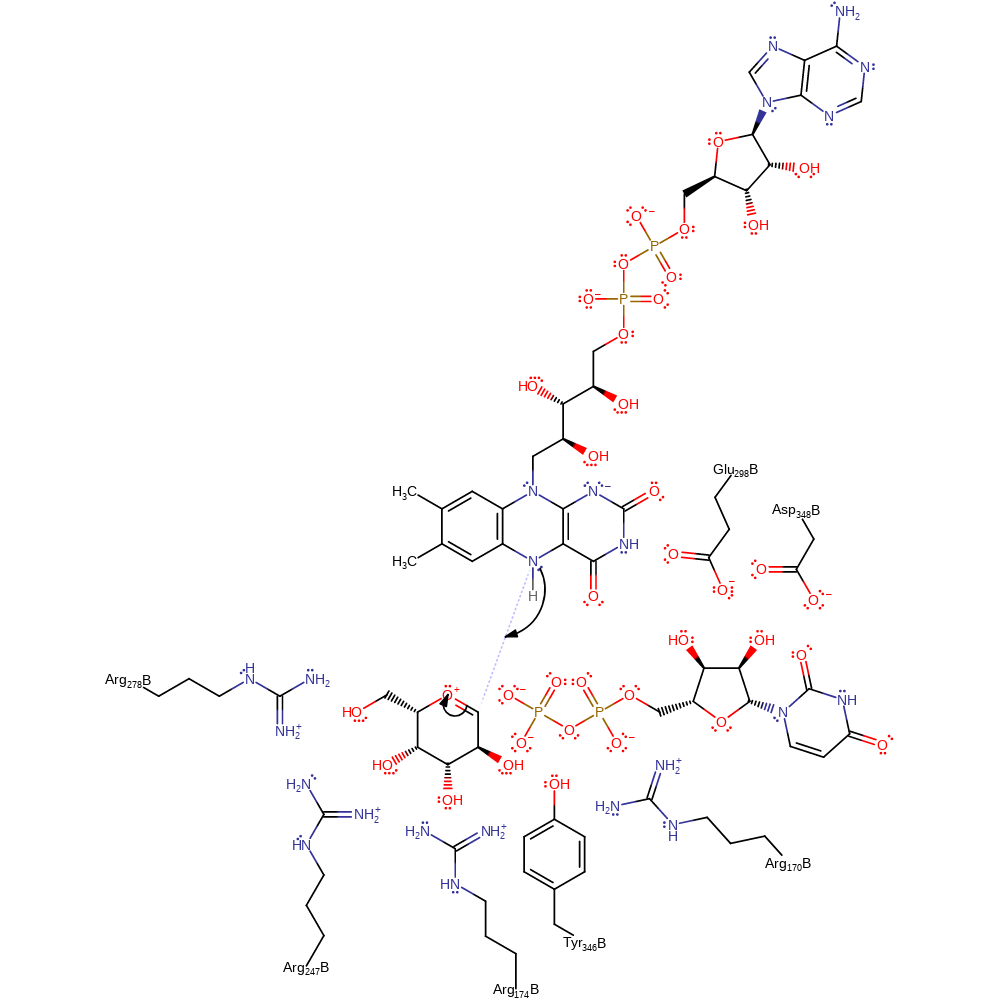
Step 2. The lone pair of electrons present on the reduced FAD attack the oxonium intermediate, forming a substrate-cofactor covalent complex.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg247B | hydrogen bond donor |
| Arg174A(B) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu298A(B) | hydrogen bond acceptor, steric role |
| Tyr346B | hydrogen bond donor, steric role |
| Arg278A(B) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Arg170A(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp348A(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate formation, cofactor used
Step 3. The FAD N5 atom uses electron density accumulating from the cleavage of the N-H bond to initiate an internal elimination reaction, resulting in the cleavage of the sugar ring while covalently attached to the cofactor. The rearrangements of protonation states have been inferred.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg247B | hydrogen bond donor |
| Arg174A(B) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu298A(B) | hydrogen bond acceptor, steric role |
| Tyr346B | hydrogen bond donor, steric role |
| Arg278A(B) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Arg170A(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp348A(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, proton transfer, intermediate formation, cofactor used, inferred reaction step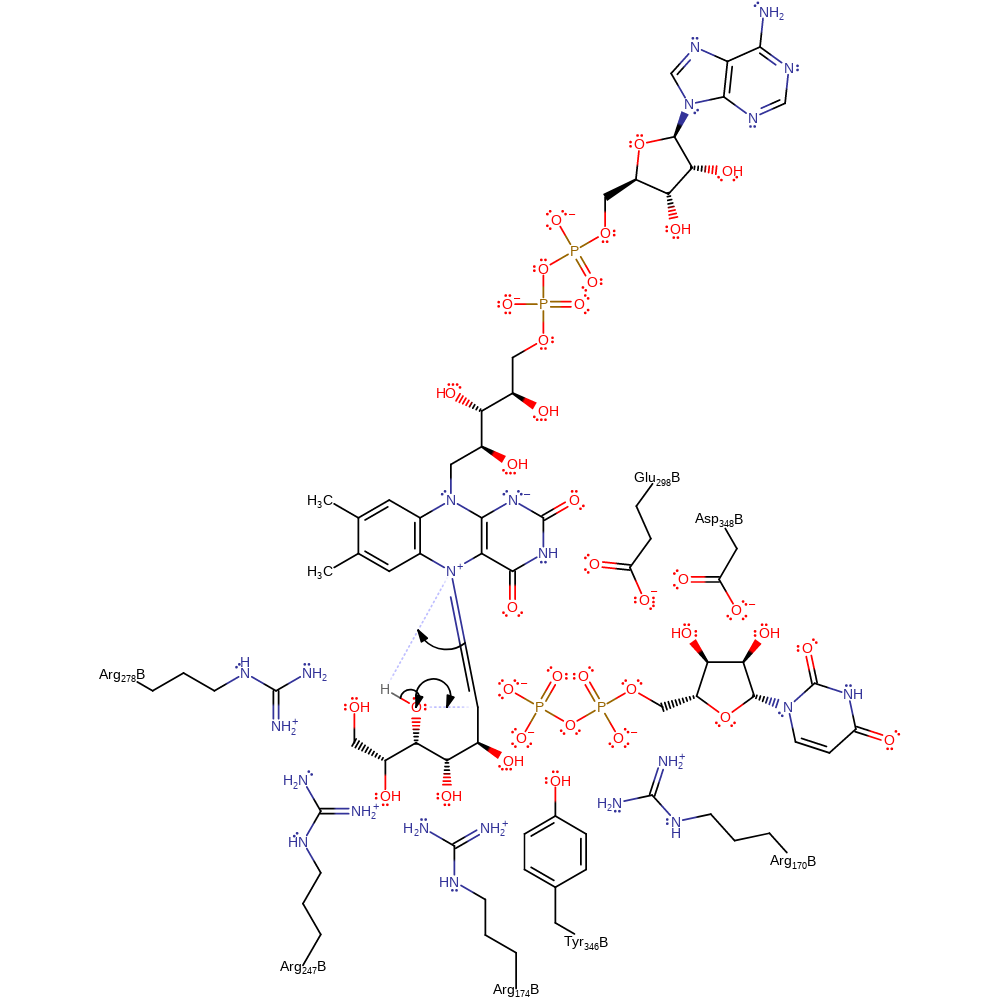
Step 4. The opened ring now undergoes a five exo-tet cyclisation reaction with the C4-OH, which is enthalpically more favourable to the six exo-tet attack, which would give the original six-membered ring. The rearrangements of protonation states have been inferred.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg247B | hydrogen bond donor |
| Arg174A(B) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu298A(B) | hydrogen bond acceptor, steric role |
| Tyr346B | hydrogen bond donor, steric role |
| Arg278A(B) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Arg170A(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp348A(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, proton transfer, intermediate formation, cofactor used, inferred reaction step
Step 5. The oxygen lone pair kicks out the FAD N5, regenerating the reduced form of the cofactor.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg247B | hydrogen bond donor |
| Arg174A(B) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu298A(B) | hydrogen bond acceptor, steric role |
| Tyr346B | hydrogen bond donor, steric role |
| Arg278A(B) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Arg170A(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp348A(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate formation, native state of cofactor regenerated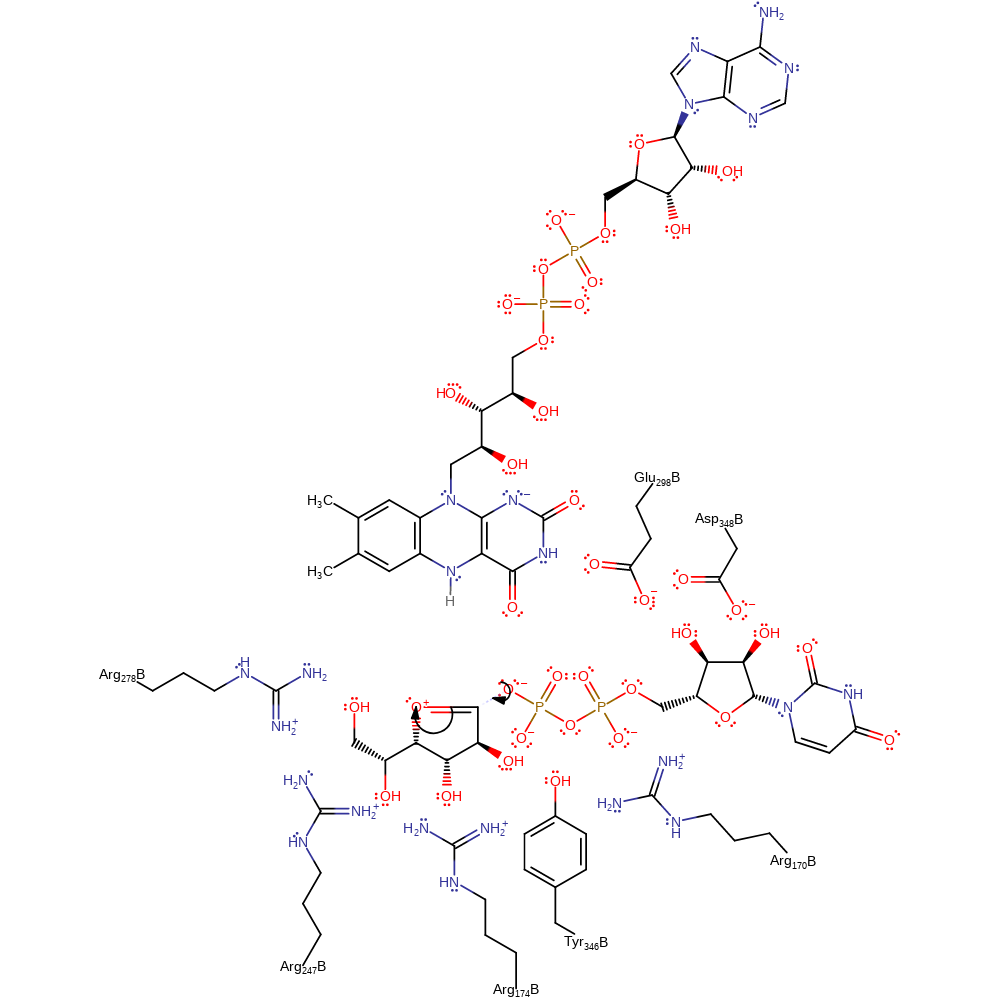
Step 6. In the reverse of the first step, the phosphate group reattaches to the UDP-furanose.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg170A(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg174A(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg247B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg278A(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu298A(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr346B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp348A(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu298A(B) | steric role |
| Tyr346B | steric role |
| Asp348A(B) | steric role |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall product formedIntroduction
In the first step, the anomeric C1−O bond is broken in a reaction drawn here to involve the direct nucleophilic attack of the axial 4‘-hydroxyl group on C1, displacing UDP and generating a bicyclo acetal. The β-phosphorus atom of enzyme-bound UDP is torsionally unrestricted, and the oxygen atoms are torsiosymmetric and scramble. In the second step, bond cleavage between the ring oxygen O-5 and C1 must take place since the α-anomer is formed as the sole product, and direct nucleophilic attack by UDP on the anomeric center of the bicyclo acetal would generate β-UDPgalf. This step is shown to proceeding via anchimeric assistance. In the third step, nucleophilic attack by UDP on the anomeric C1 position generates the product α-UDP-galf.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1i8t) | ||
| Arg174 | Arg174A(B) | Essential for catalytic activity, proposed to be involved in hydrogen bonding interactions with the substrate. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp348, Glu298 | Asp348A(B), Glu298A(B) | Charge stabilisation. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr346 | Tyr346B | Acts to hold substrate in the correct position for the correct reaction to occur. | hydrogen bond donor, steric role |
| Arg247 | Arg247B | Essential for catalytic activity, proposed to be involved in hydrogen bonding interactions with the substrate. Proposed as the general acid/base for this mechanism (based solely on proximity to the relevant hydroxyl group). | proton acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, proton donor |
| Arg278, Arg170 | Arg278A(B), Arg170A(B) | Electrostatic stabilisation of the UDP leaving group. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
intermediate formation, overall reactant used, proton transfer, intramolecular elimination, inferred reaction step, decyclisation, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall product formed, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Barlow JN et al. (1999), J Am Chem Soc, 121, 6968-6969. Positional Isotope Exchange Catalyzed by UDP-Galactopyranose Mutase. DOI:10.1021/ja991582r.
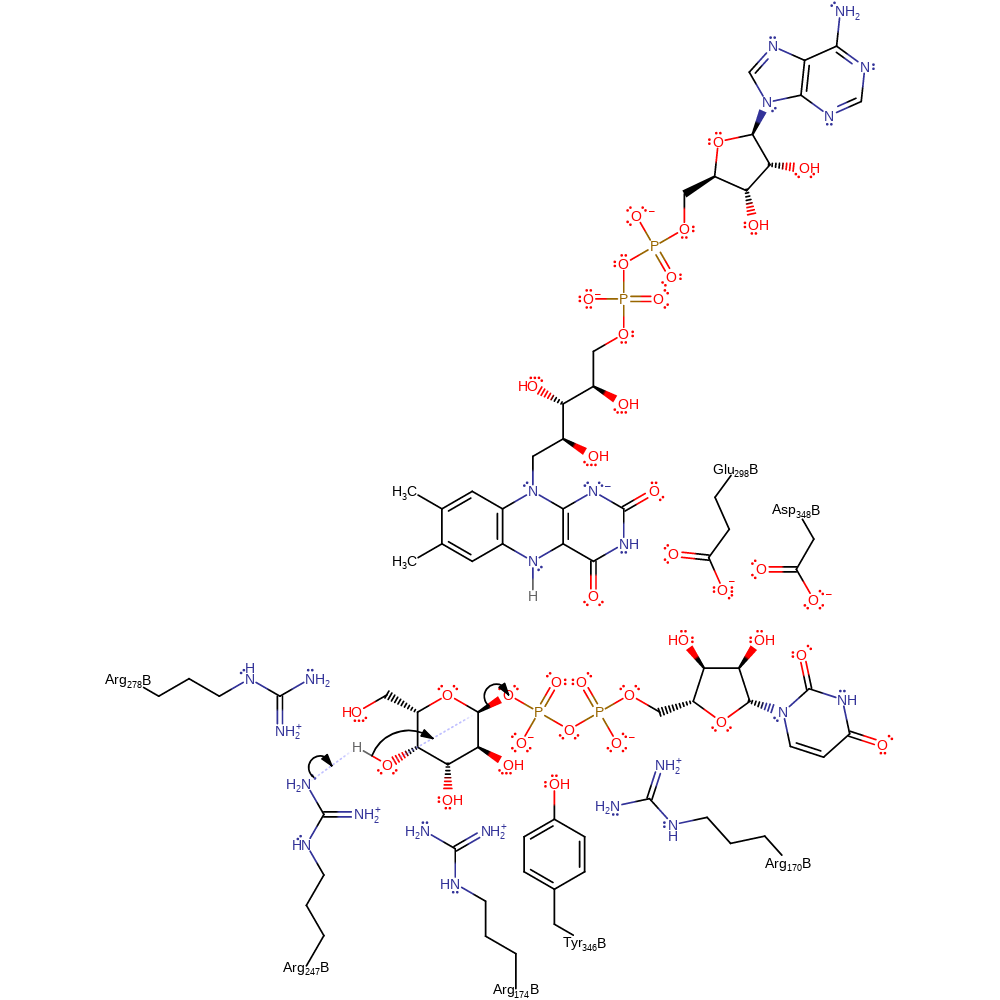
Step 1. A base (inferred to be Arg247 due to proximity) abstracts a proton from the substrate, initiating a nucleophilic attack of the deprotonated hydroxyl group on the anomeric carbon, displacing the diphosphate group.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp348A(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg170A(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg278A(B) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Tyr346B | steric role, hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu298A(B) | steric role, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Arg174A(B) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Arg247B | hydrogen bond donor |
| Arg247B | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
intermediate formation, overall reactant used, proton transfer, ingold: intramolecular elimination, inferred reaction stepCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg170A(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg174A(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg278A(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp348A(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu298A(B) | steric role |
| Tyr346B | steric role |
| Arg247B | proton donor |
Chemical Components
inferred reaction step, decyclisation, proton transfer, ingold: intramolecular elimination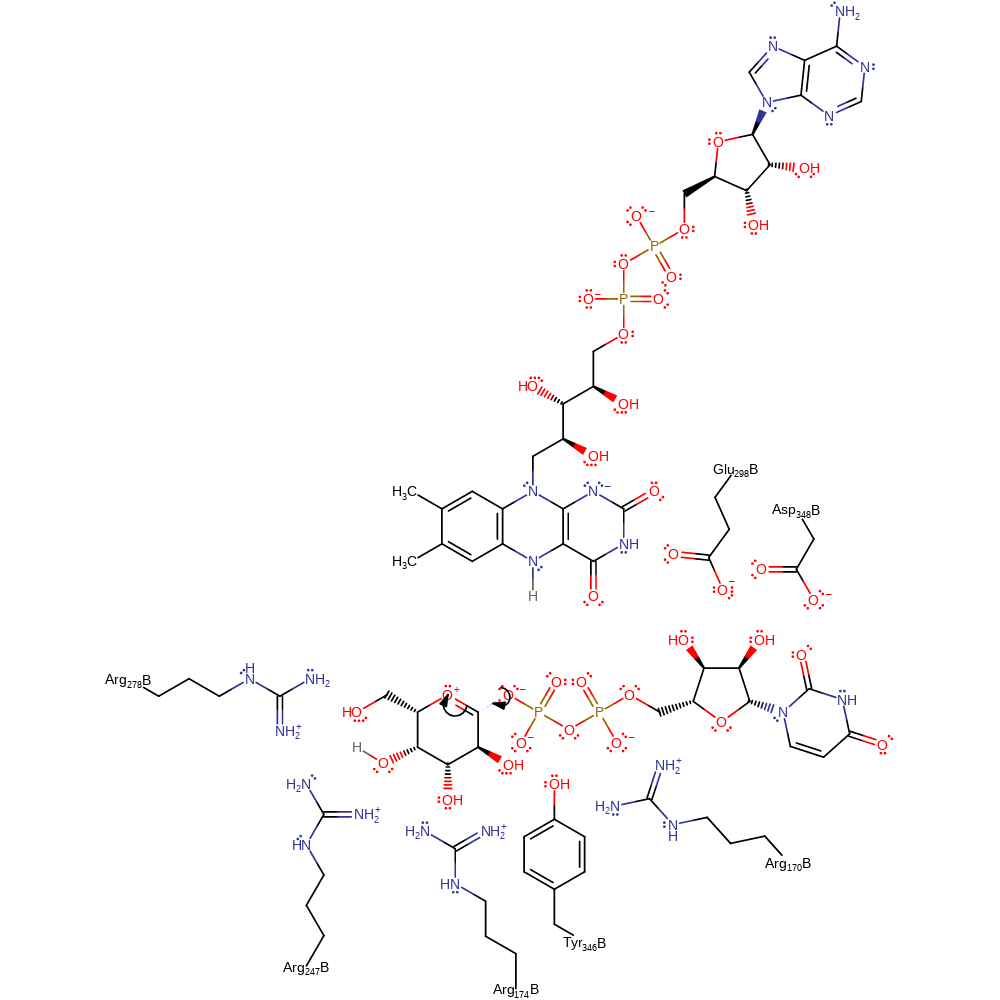
Step 3. The eliminated phosphate attacks the anomeric carbon to form the final product.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg170A(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg174A(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg247B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg278A(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp348A(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu298A(B) | steric role |
| Tyr346B | steric role |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall product formed, native state of enzyme regeneratedIntroduction
Nucleophilic attack by N5 of reduced FAD on C1 of UDP-Galp via an SN1 type mechanism results in the loss of UDP. The charged leaving group is stabilised by electrostatic and hydrogen bonding interactions with Arg170 and Arg278. The imminium intermediate is formed by a single electron transfer type reaction and a covalent intermediate is formed bwteeen the FAD N5 and C1 of the sugar. This results in the opening of the ring at the OH6 position. The negative charge at N1 is required to increase the nucleophilicity of N5. The intramolecular nucleophilic attack by OH4 on the imminium group forms a new galactofuranose ring still bound to N5 of the reduced FAD. To release the sugar from the enzyme cofactor, UDP attacks the C1 position leading to lysis of the C1-N5 bond and release of UDP-Galf.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1i8t) | ||
| Asp348, Glu298 | Asp348A(B), Glu298A(B) | Charge stabilisation. | electrostatic stabiliser, steric role |
| Tyr346 | Tyr346B | Acts to hold substrate in the correct position for the correct reaction to occur | hydrogen bond donor, steric role, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg174, Arg247 | Arg174A(B), Arg247B | Essential for catalytic activity, proposed to be involved in hydrogen bonding interactions with the substrate. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg278, Arg170 | Arg278A(B), Arg170A(B) | Electrostatic stabilisation of the UDP leaving group. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
rate-determining step, unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, electron transfer, colligation, proton transfer, cofactor used, inferred reaction step, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, native state of cofactor regenerated, overall product formedReferences
- Sun HG et al. (2012), J Biol Chem, 287, 4602-4608. Nucleophilic participation of reduced flavin coenzyme in mechanism of UDP-galactopyranose mutase. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M111.312538. PMID:22187430.
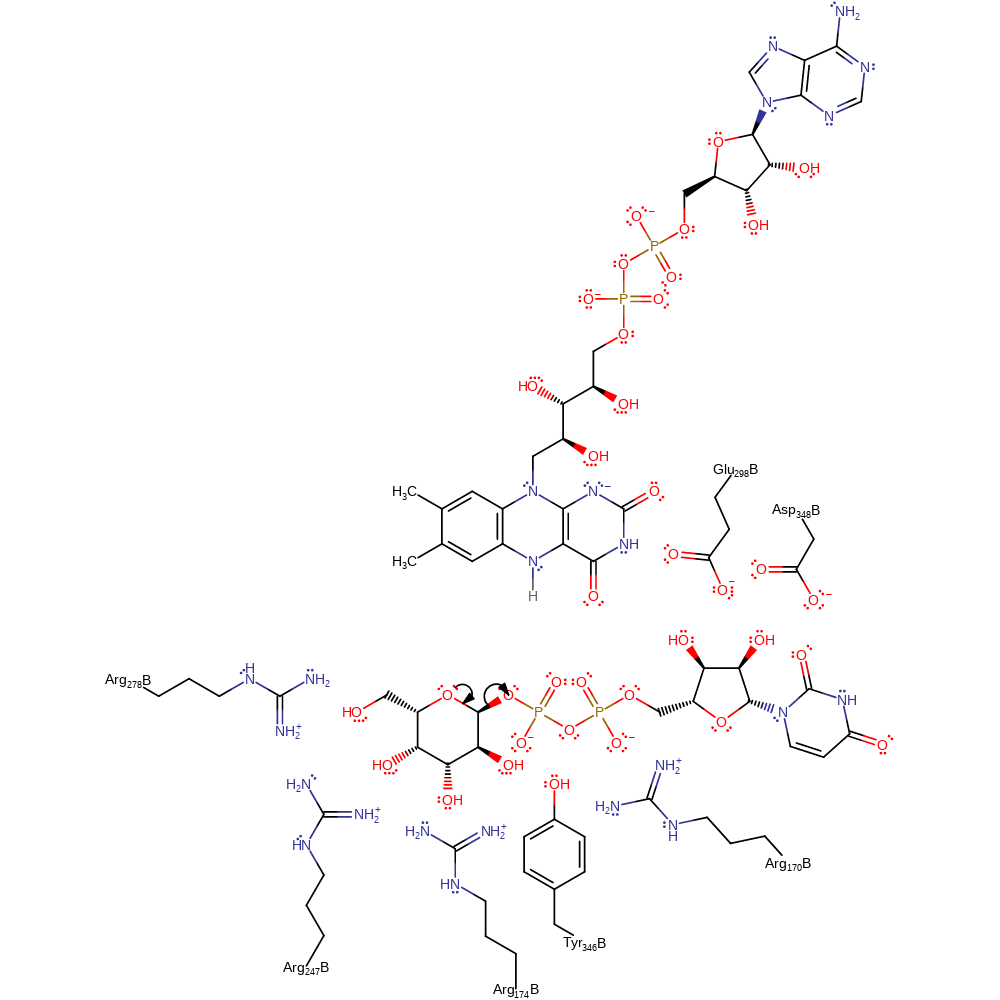
Step 1. Chemical modification of the substrate suggests the departure of UDP to occur by an SN1 type mechanism, with the ring oxygen eliminating UDP and forming an oxonium intermediate [PMID:17266324]. Evidence from mutagenesis studies of homologous proteins from other species suggests the main role of the active site amino acids is to anchor the substrate, intermediates and cofactor into a reactive conformation and also to stabilise the cationic intermediate [PMID:17266324, PMID:19719175]. Electrostatic interactions between Glu298A and Arg174 are thought to peturb the attraction of the product to the active site, and therefore facilitate the removal of product from the active site [PMID:17511471].
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp348A(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg170A(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg278A(B) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Tyr346B | steric role, hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu298A(B) | steric role, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Arg174A(B) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Arg247B | hydrogen bond donor |
Chemical Components
rate-determining step, ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate formation, overall reactant used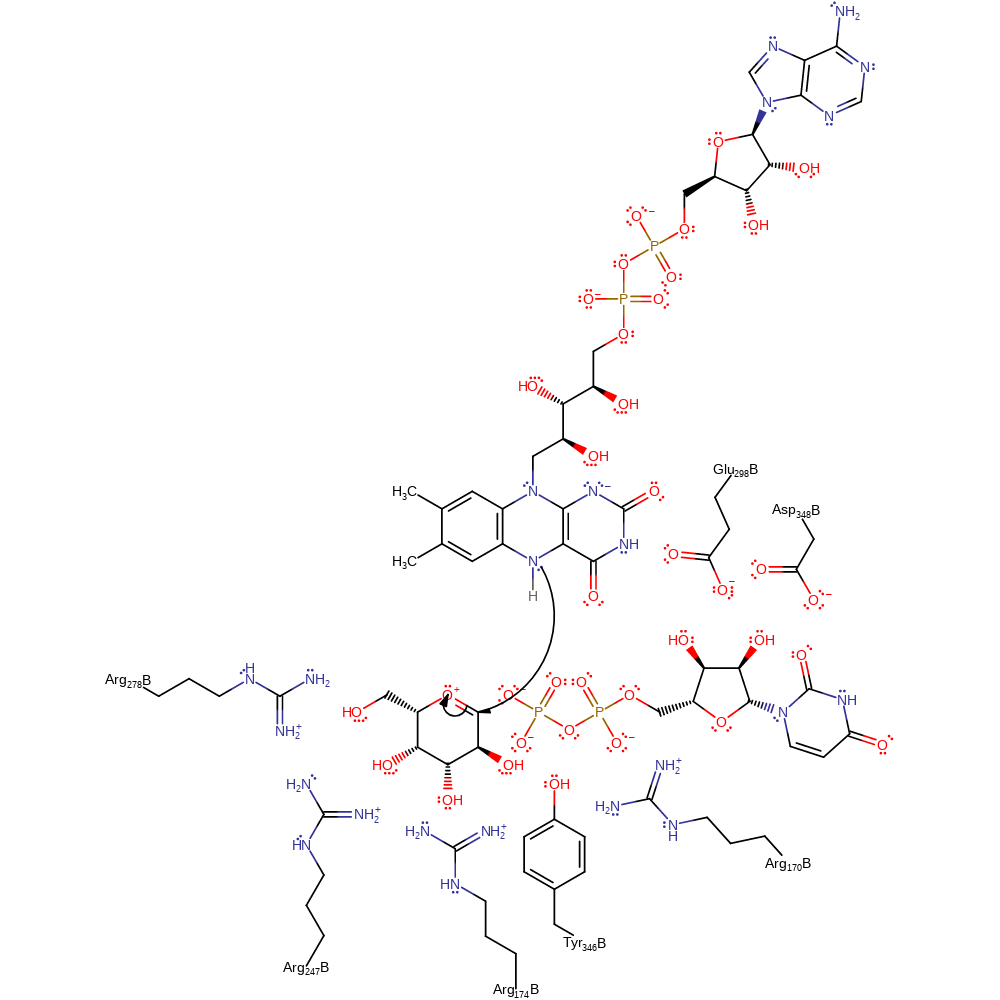
Step 2. A single electron is transferred from the FAD cofactor to the intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg170A(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg174A(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg247B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg278A(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu298A(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr346B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp348A(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr346B | steric role |
Chemical Components
electron transfer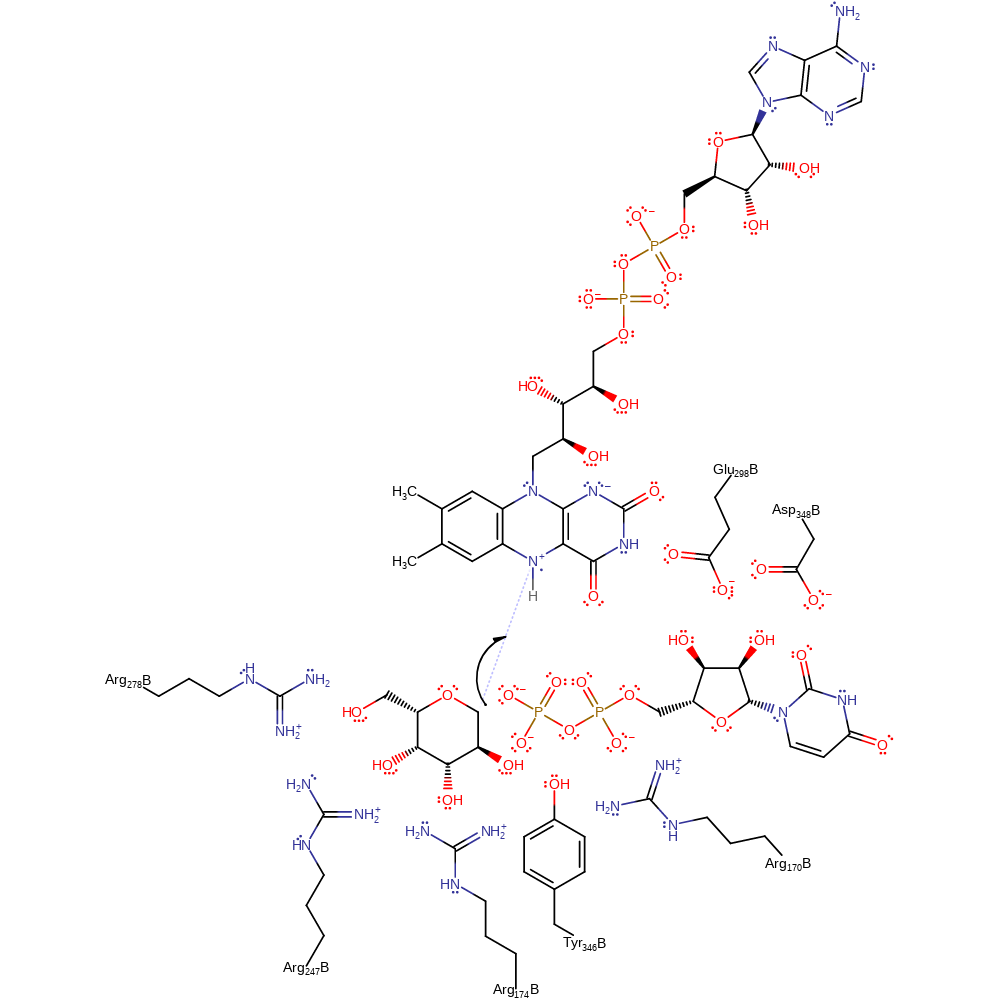
Step 3. A coligation reaction occurs to form the covalent intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg170A(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg174A(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg247B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg278A(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu298A(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp348A(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr346B | steric role |
Chemical Components
colligation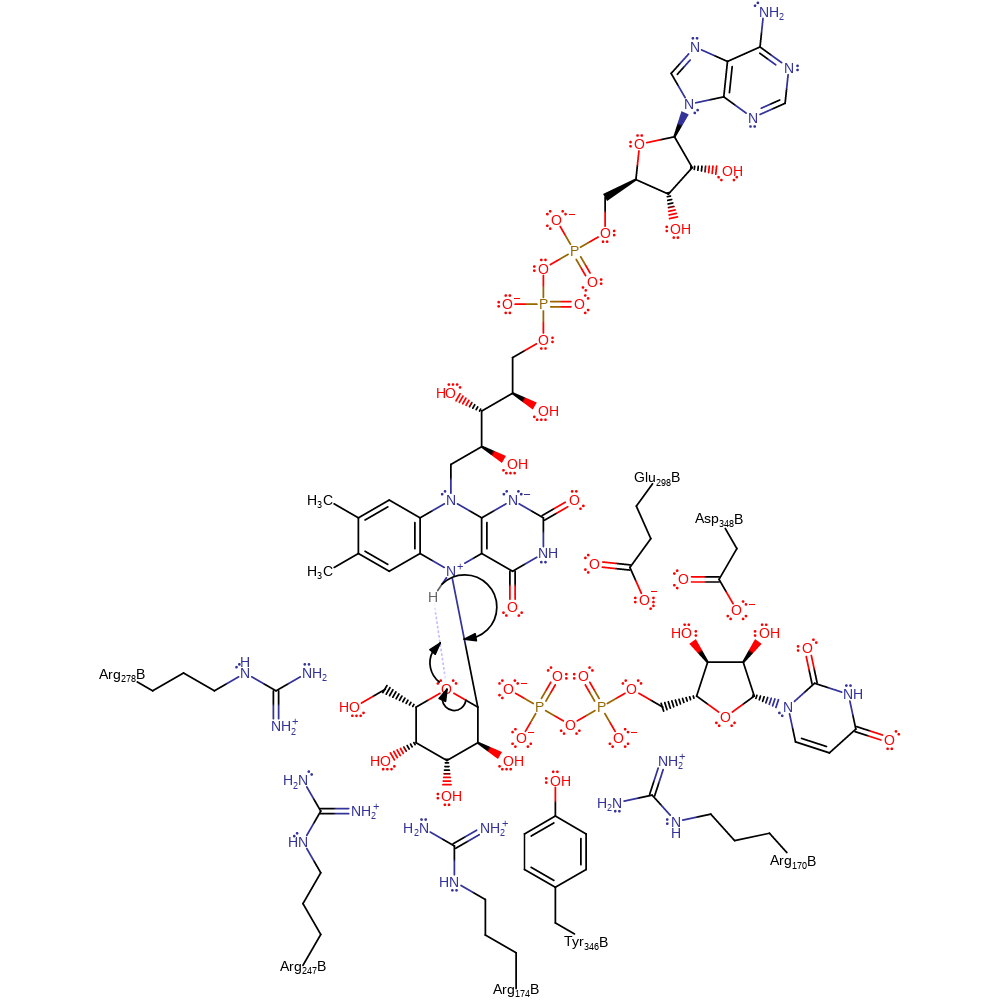
Step 4. The FAD N5 atom uses electron density accumulating from the cleavage of the N-H bond to initiate an internal elimination reaction, resulting in the cleavage of the sugar ring while covalently attached to the cofactor. The rearrangements of protonation states have been inferred.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp348A(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg170A(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg278A(B) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Tyr346B | steric role, hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu298A(B) | steric role, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Arg174A(B) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Arg247B | hydrogen bond donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, proton transfer, intermediate formation, cofactor used, inferred reaction step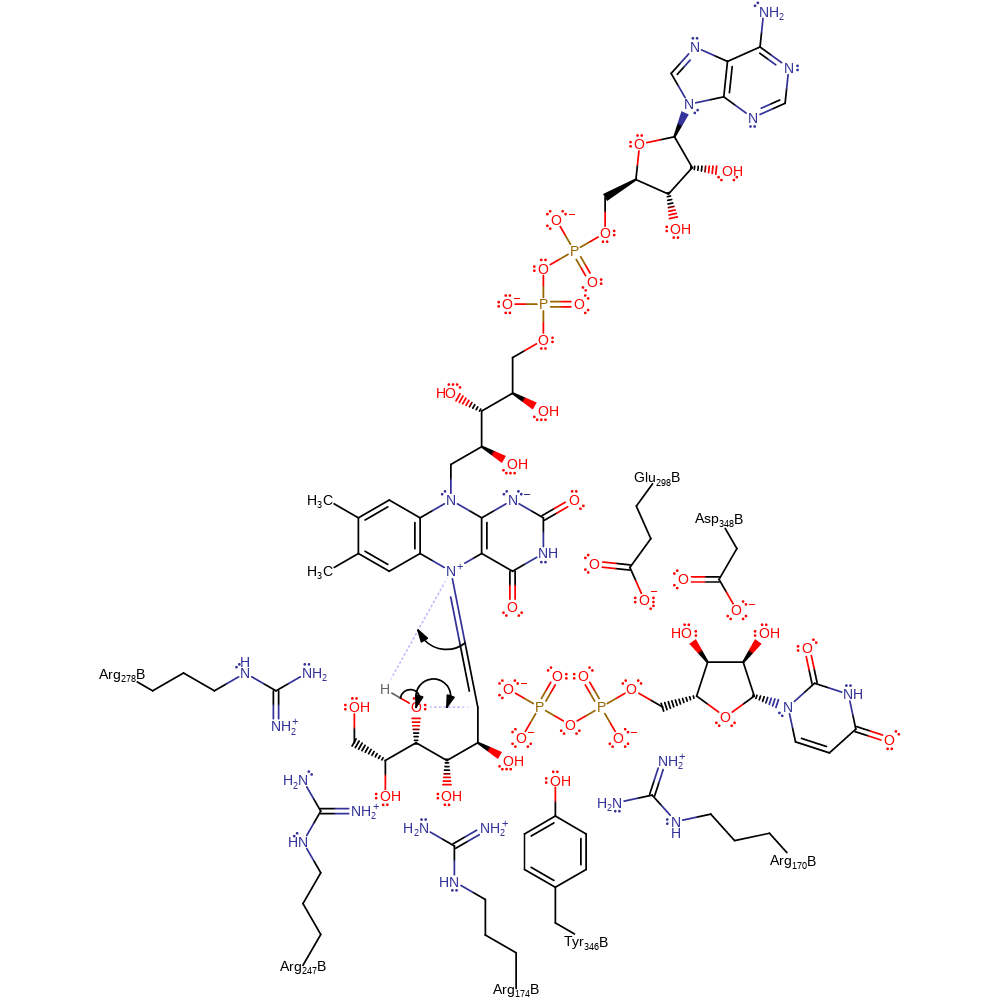
Step 5. The opened ring now undergoes a five exo-tet cyclisation reaction with the C4-OH, which is enthalpically more favourable to the six exo-tet attack, which would give the original six-membered ring. The rearrangements of protonation states have been inferred.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp348A(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg170A(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg278A(B) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Tyr346B | steric role, hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu298A(B) | steric role, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Arg174A(B) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Arg247B | hydrogen bond donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, proton transfer, intermediate formation, cofactor used, inferred reaction step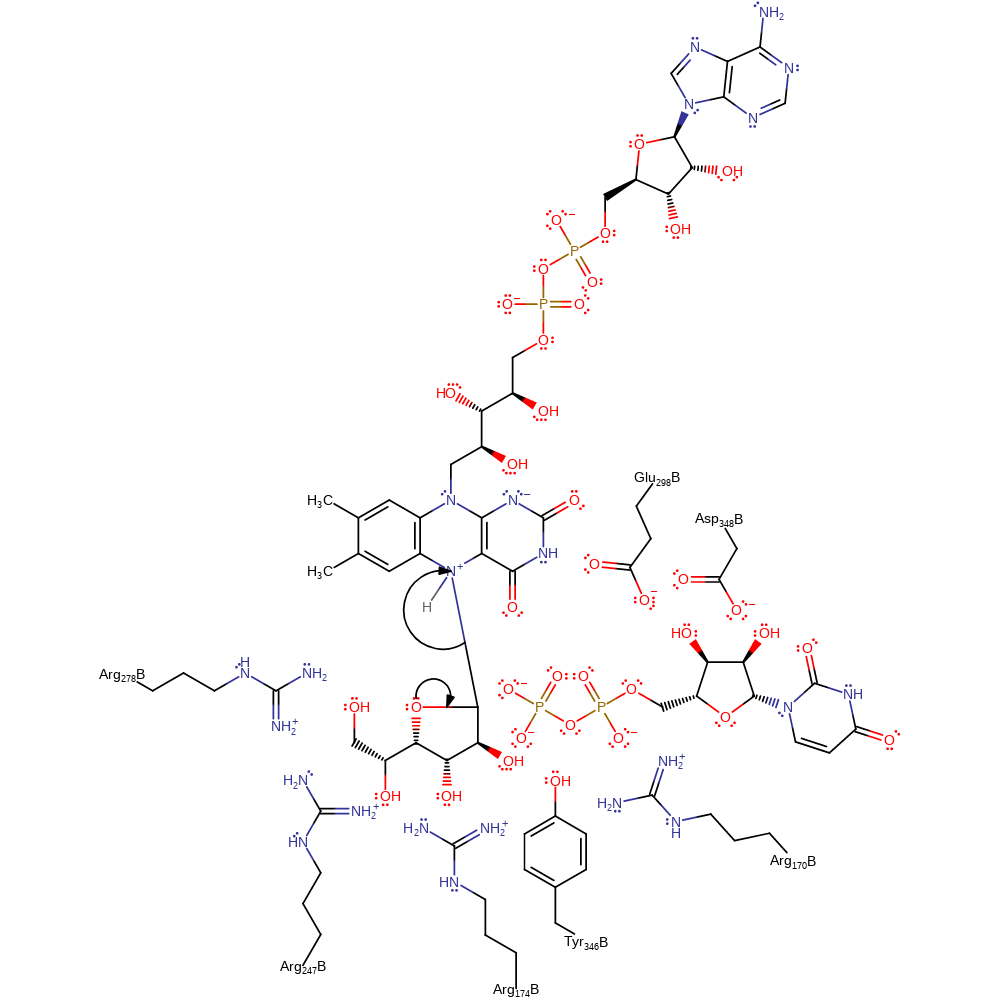
Step 6. The oxygen lone pair kicks out the FAD N5, regenerating the reduced form of the cofactor.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp348A(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg170A(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg278A(B) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Tyr346B | steric role, hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu298A(B) | steric role, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Arg174A(B) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Arg247B | hydrogen bond donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, intermediate formation, native state of cofactor regenerated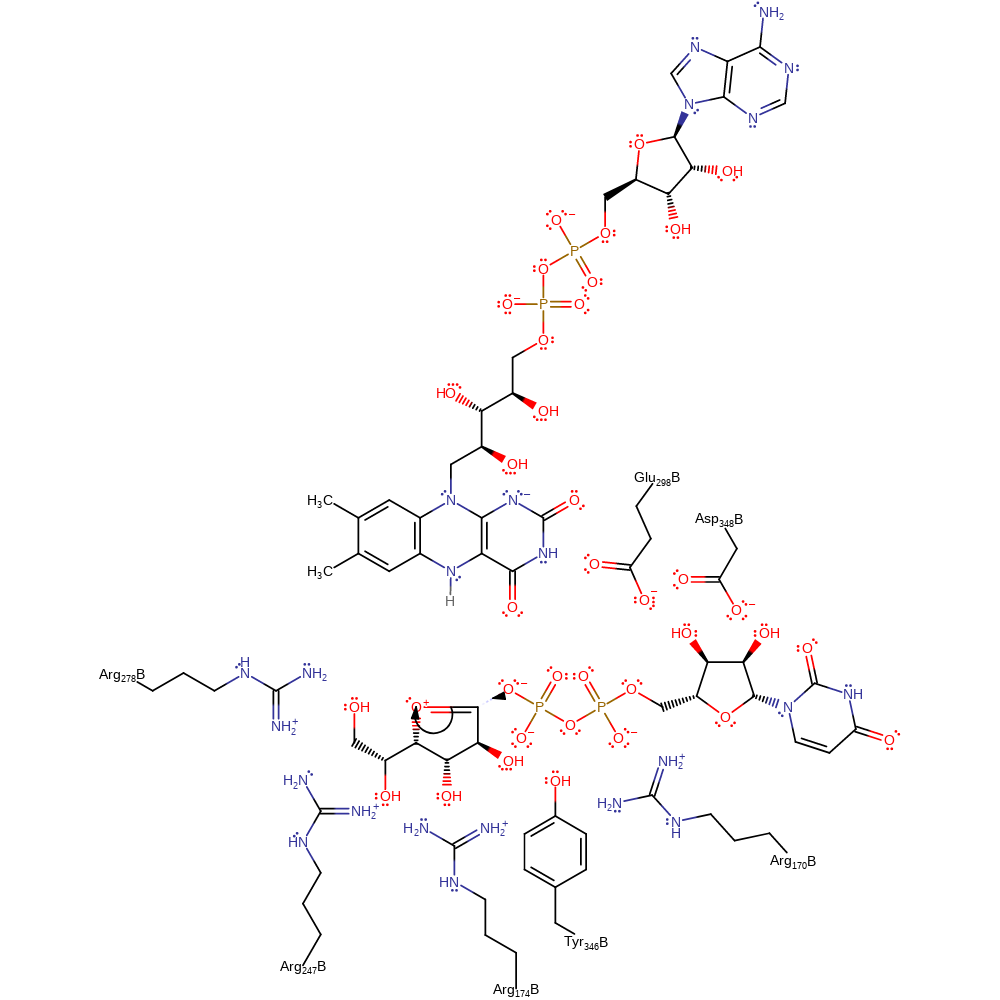
Step 7. In the reverse of the first step, the phosphate group reattaches to the UDP-furanose.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp348A(B) | steric role |
| Tyr346B | steric role |
| Glu298A(B) | steric role |
| Asp348A(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr346B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu298A(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg278A(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg247B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg174A(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg170A(B) | electrostatic stabiliser |


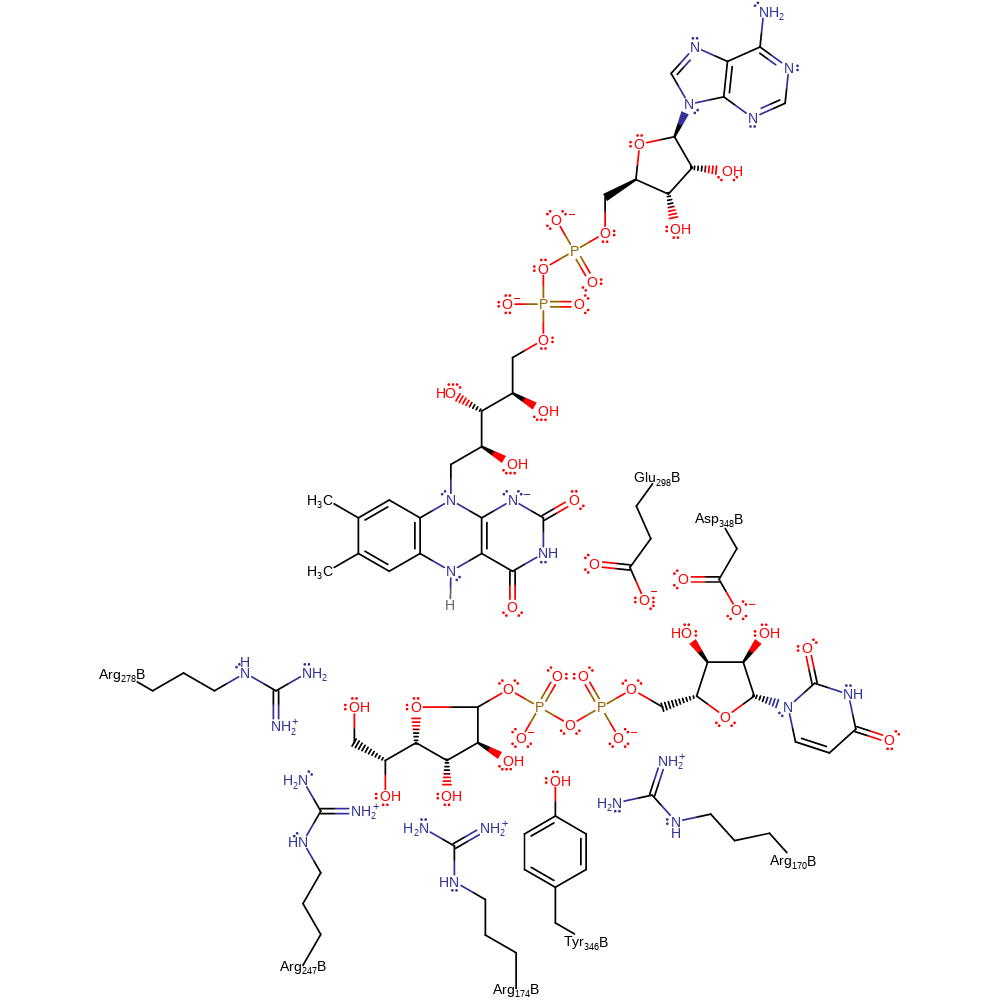 Download:
Download:  Download:
Download: 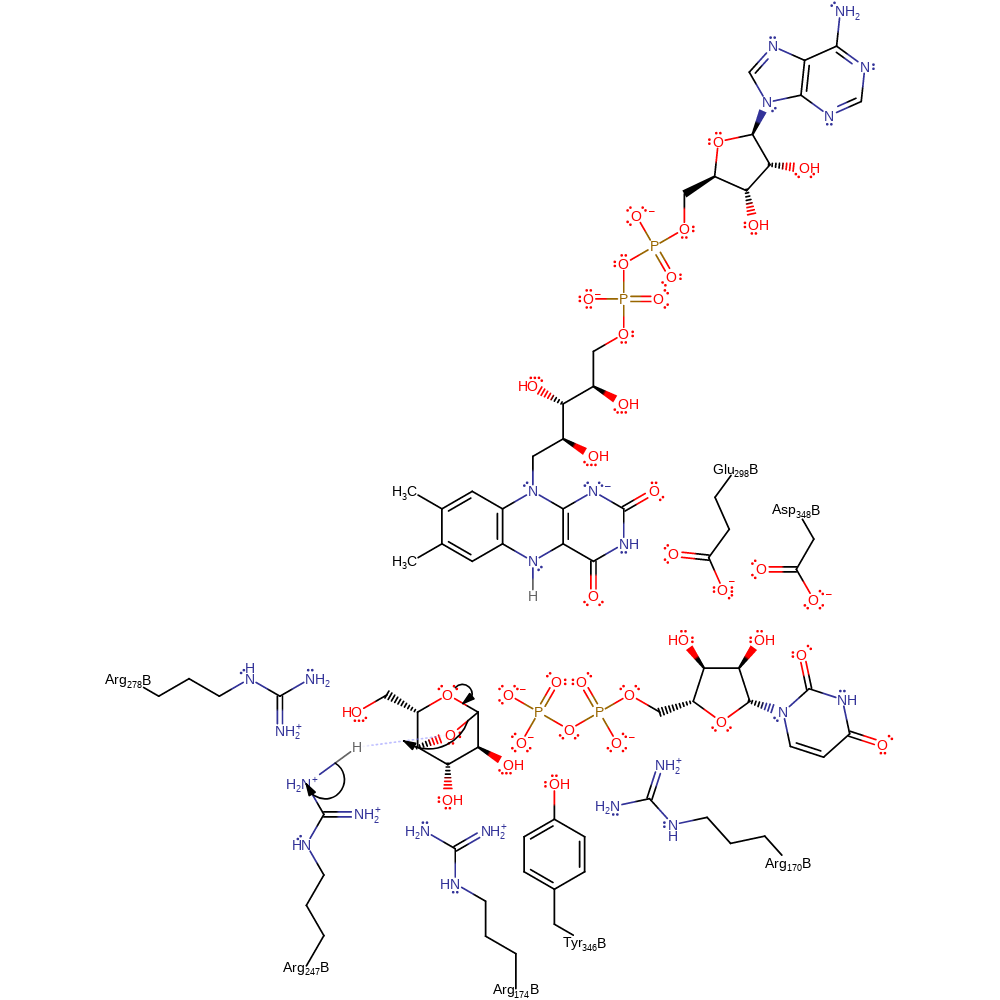
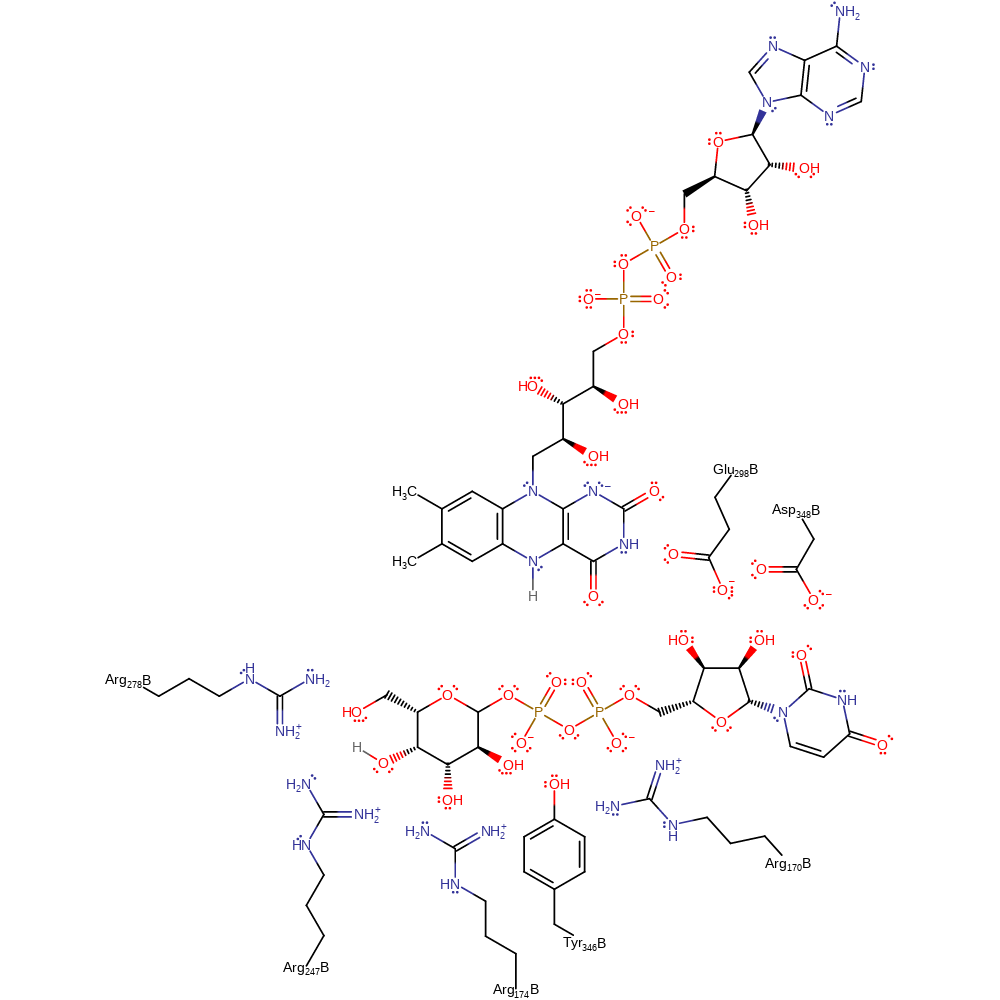 Download:
Download: 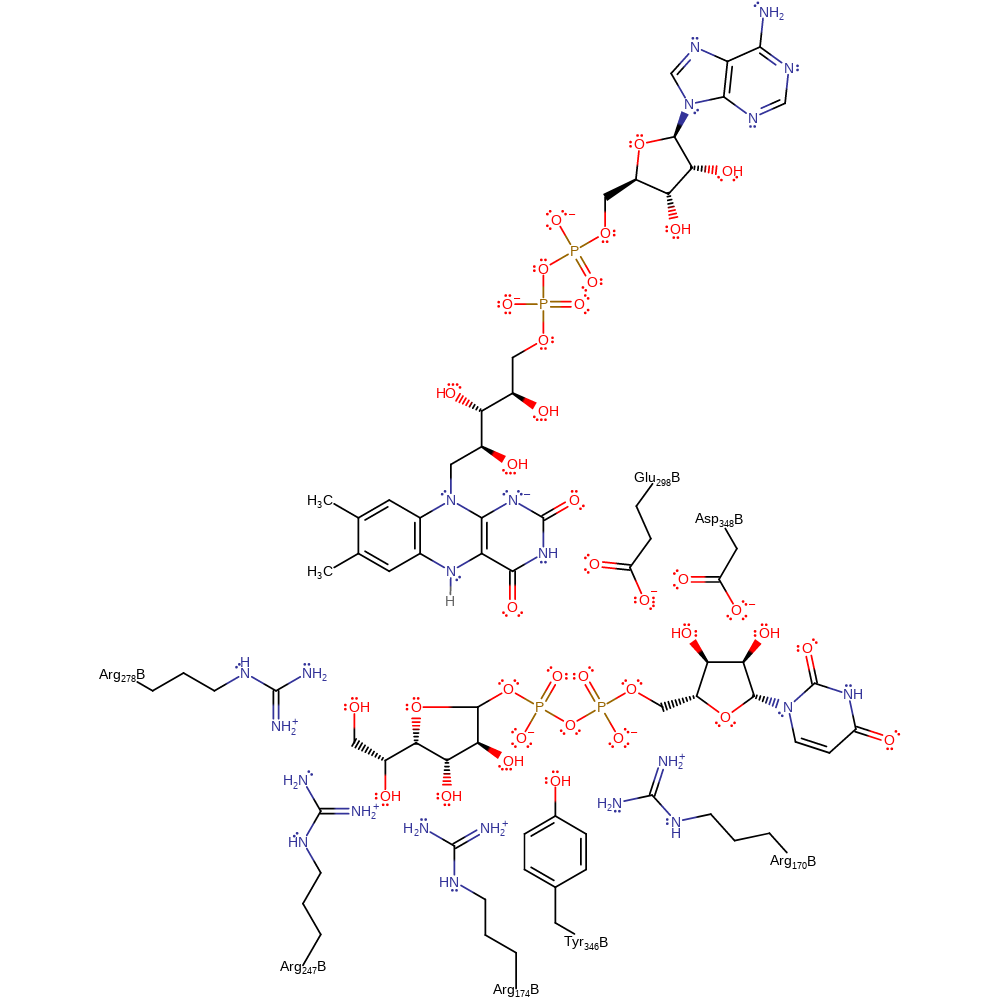 Download:
Download: