Phosphoglucomutase
Phosphoglucomutase catalyses the transfer of a phosphate fragment between the 1- and 6-O atoms of glucose. As suggested by the enzyme's name, in its stable form it exists esterified, at the gamma-hydroxyl group of Ser116. The enzyme is involved in the glycogenolysis pathway. Once a 1-phosphate glucose molecule is released from glycogen by glycogen phosphorylase, phosphoglucomutase catalyses the interconversion of this relatively useless metabolic intermediate into 6-phosphate glucose. This metabolite can then be utilised in multiple cellular pathways including the glycolytic, pentose phosphate or biosynthetic pathways. When glucose levels are high, phosphoglucomutase can act in the opposite fashion, converting 6-phosphate glucose to 1-phosphate glucose. In combination with UDP-glucose-pyrophosphorylase and glycogen synthase, this change in equilibrium will result in the reformation of the 1-phosphate glucose monomer with a glycogen polymer.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P00949
 (5.4.2.2)
(5.4.2.2)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit)

- PDB
-
3pmg
- STRUCTURE OF RABBIT MUSCLE PHOSPHOGLUCOMUTASE AT 2.4 ANGSTROMS RESOLUTION. USE OF FREEZING POINT DEPRESSANT AND REDUCED TEMPERATURE TO ENHANCE DIFFRACTIVITY
(2.4 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.120.10
 (see all for 3pmg)
(see all for 3pmg)
- Cofactors
- Magnesium(2+) (1)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:5.4.2.2)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
This mechanism involves the di-phosphate intermediate flipping in the active site. Such a conformational rearrangement has been identified by phosphorous and fluorine NMR studies, indicating that two glucose-phosphate binding sites are present within the active site. The final product is shown with undefined stereochemistry at the anomeric carbon, even though no direct substitution has occurred at this positions in the reaction. This stereochemistry has been inferred from similar mechanisms, where water molecules within the active site are known to racemise the stereochemistry at this position, resulting in rapid stereochemical interconversion. Since the stereochemistry does not remain defined at this position in the product, it has been annotated as interchangeable. In the first step, the phosphate group is transferred from Ser116 to the 6-oxygen group of mono-glucose to give a diphosphate intermediate. Diffusion led reorientation of the intermediate in the active site allows to re-phosphorylation of the serine from the 1-phosphate group, and formation of the 6-phosphate glucose. This step is fast compared to the first and no intermediate has ever been isolated. The mechanism requires a divalent cation, which spectrometry has shown to be bound directly to the phosphate group.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (3pmg) | ||
| Ser117 | Sep116B | Ser116 exists in an esterified form in the ground state of the enzyme. In the first step, the phosphate group is transferred from Ser116 to the 6-oxygen group of mono-glucose to give a diphosphate intermediate. Ser116 then abstracts the phosphate from the C1 position. Also forms part of the magnesium binding site (through the phosphate group). | covalently attached, nucleofuge, nucleophile, metal ligand, proton donor, proton acceptor, activator |
| His118, Lys389 | His117B, Lys388B | Act as general acid/base catalysts. | proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Arg293 | Arg292B | stabilizes the phosphate group | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp288, Asp290, Asp292 | Asp287B, Asp289B, Asp291B | Form part of the magnesium binding site. | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, proton transfer, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, inferred reaction step, rate-determining step, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, overall product formed, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Percival MD et al. (1992), Biochemistry, 31, 505-512. Fluorine-19 NMR investigations of the catalytic mechanism of phosphoglucomutase using fluorinated substrates and inhibitors. DOI:10.1021/bi00117a029. PMID:1531026.
- Brás NF et al. (2018), Chemistry, 24, 1978-1987. Mechanistic Insights on Human Phosphoglucomutase Revealed by Transition Path Sampling and Molecular Dynamics Calculations. DOI:10.1002/chem.201705090. PMID:29131453.
- Kvam C et al. (1997), Biochem J, 326, 197-203. Studies on recombinant Acetobacter xylinum α-phosphoglucomutase. DOI:10.1042/bj3260197. PMID:9337869.
- Dai JB et al. (1992), J Biol Chem, 267, 6322-6337. The crystal structure of muscle phosphoglucomutase refined at 2.7-angstrom resolution. DOI:10.2210/pdb2pmg/pdb. PMID:1532581.
- Wålinder O et al. (1974), J Biol Chem, 249, 3166-3169. Mechanism of action of rabbit muscle phosphoglucomutase. Rate of enzyme phosphate turnover studied with a rapid mixing technique. PMID:4830239.
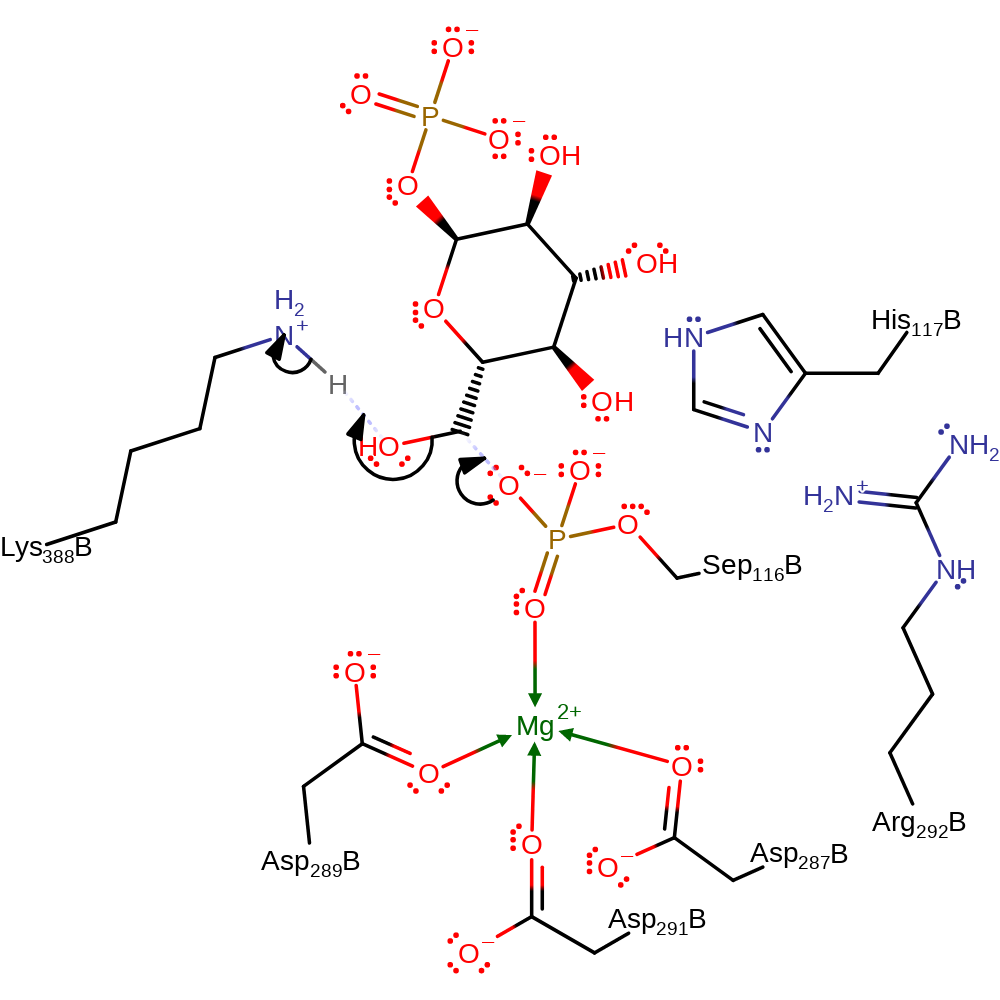
Step 1. The phosphorylated Ser116 attacks at the O6 position, forming a phospho-enzyme-substrate intermediate. This is assisted by Lys389 acting as a general acid, protonating the water molecule- the leaving group from C6.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Sep116B | metal ligand |
| Asp287B | metal ligand |
| Asp291B | metal ligand |
| Asp289B | metal ligand |
| Sep116B | covalently attached, activator |
| Arg292B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys388B | proton donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, proton transfer, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, inferred reaction step, rate-determining step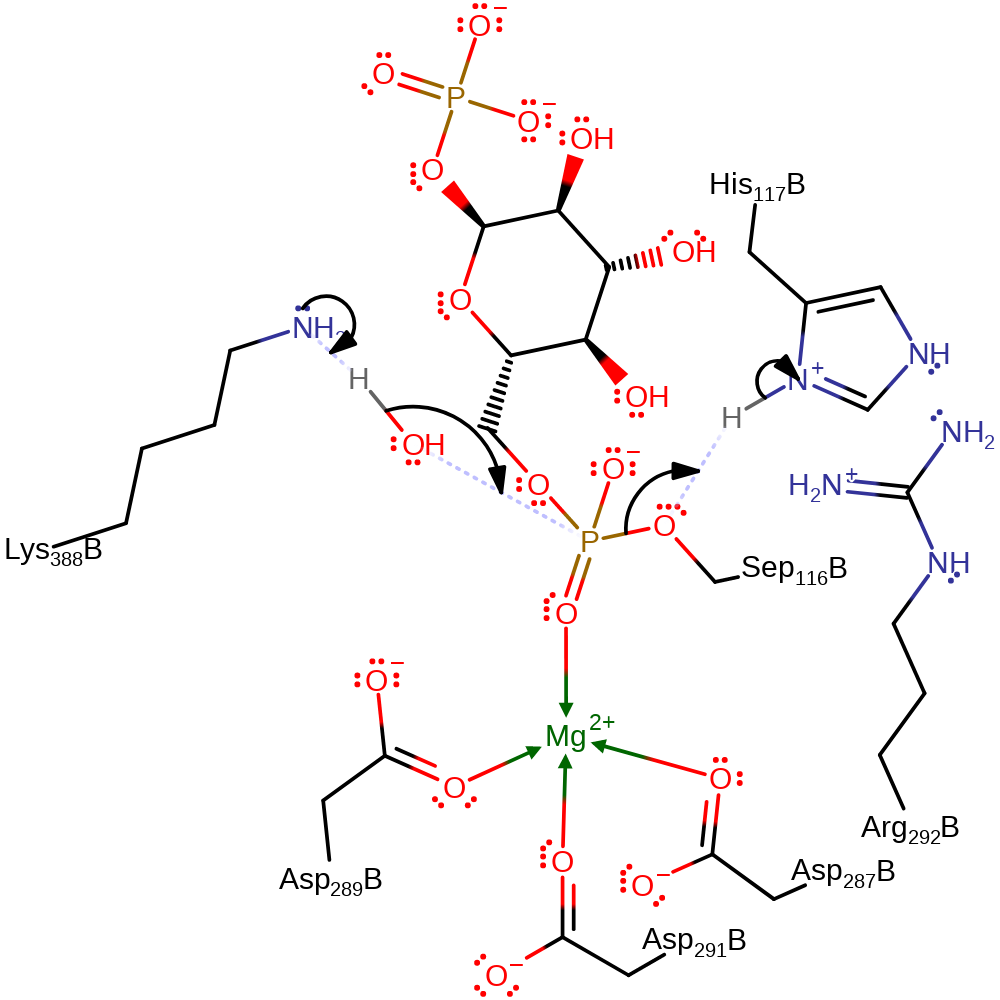
Step 2. Ser116 is displaced by a water molecule which is activated by Lys398. The intermediate retains the phosphate group. Ser116 accepts a proton from His118 upon displacement.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Sep116B | metal ligand |
| Asp287B | metal ligand |
| Asp291B | metal ligand |
| Asp289B | metal ligand |
| Arg292B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys388B | proton acceptor |
| His117B | proton donor |
| Sep116B | proton acceptor, nucleofuge |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, proton transfer, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, intermediate formation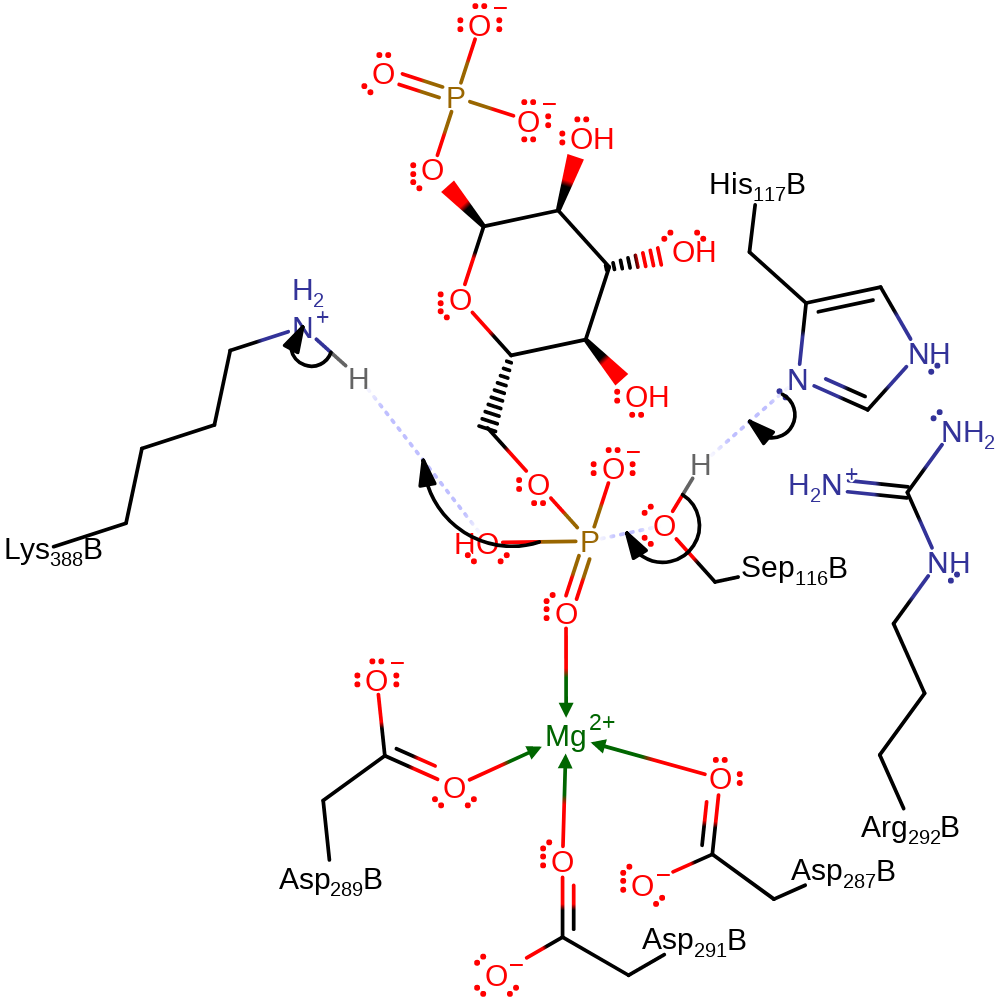
Step 3. Ser166 is re-phosphorylated, regenerating the active site and forming the 6-phosphate glucose product. Ser116 is activated by His118. Lys389 donates a proton to the water which is displaced from the phosphate group.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp287B | metal ligand |
| Asp291B | metal ligand |
| Asp289B | metal ligand |
| Arg292B | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Sep116B | proton donor |
| His117B | proton acceptor |
| Lys388B | proton donor |
| Sep116B | nucleophile |


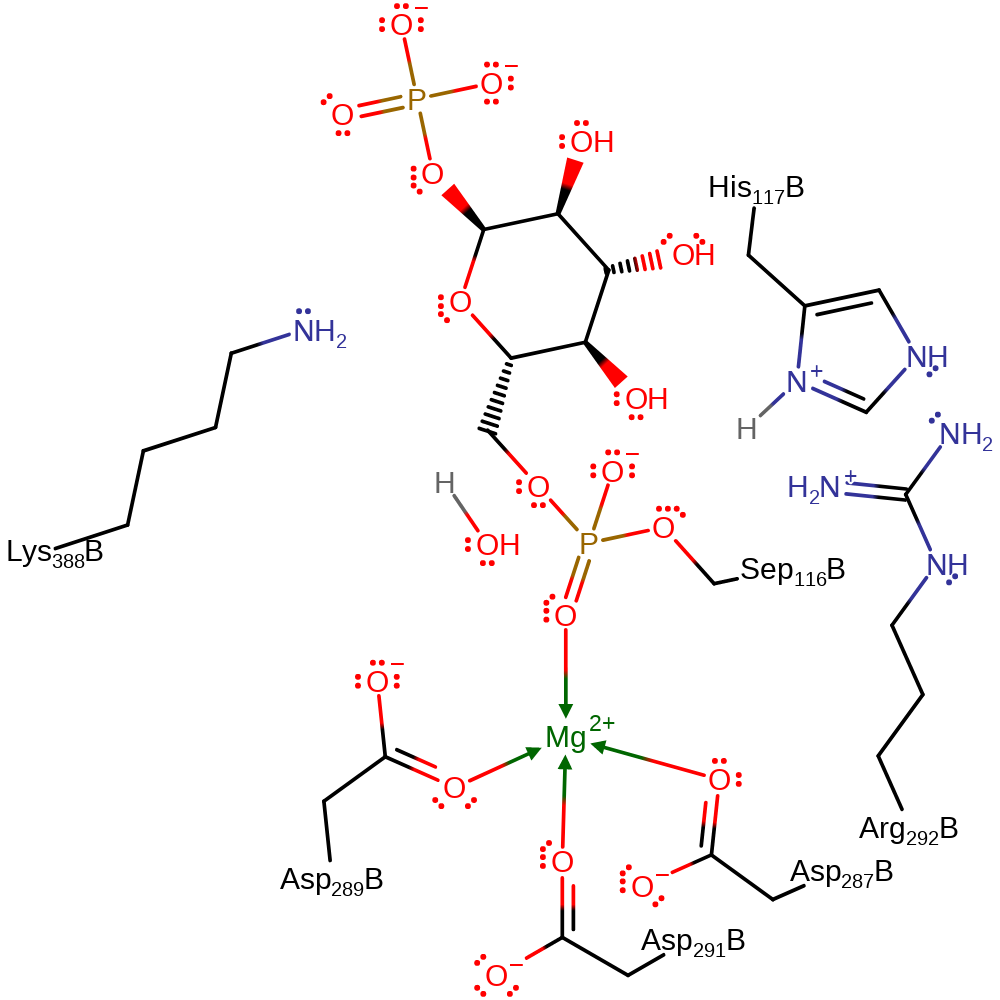 Download:
Download: