Protein-glutamate methylesterase (CheB)
Protein-glutamate methyl-esterase, also known as chemotaxis-specific methylesterase, is involved in regulating the signalling activity of bacterial chemotaxis transmembrane receptors through chemical modification of specific glutamate residues. The protein consists of two main domains, an N-terminal regulatory domain and a C-terminal effector domain. Phosphorylation of the N-terminal domain influences the reactivity of the catalytic C-terminus, although the truncated, C-terminus only protein retains full catalytic activity and substrate specificity [PMID:7608974].
The bacterial chemotaxis receptors are dimeric transmembrane proteins with periplasmic ligand-binding domains that detect specific chemoeffector molecules, and cytoplasmic domains that control the activities of intracellular signalling proteins. Like many of the response regulator proteins, it is a multi-domain protein consisting of an N-terminal regulatory domain and a C-terminal effector domain. Regulation of CheB involves both inter- and intramolecular interactions. The bacterial chemotaxis receptors control the activity of the first cytoplasmic component of the signal transduction pathway, the histidine protein kinase, CheA. The autophosphorylation activity of the CheA kinase is influenced by both the ligand occupancy of the receptors and the level of receptor methylation. Bacterial chemotaxis serves as a useful tool/model for the study of molecular strategies of signal transduction.
Methylester hydrolysis depends both on the conformation of the receptor and on phosphorylation of the Protein-glutamate methylesterase regulatory domain. Phosphorylation of the regulatory domain activates the effector function. The methylesterase active site is identified as a cleft at the C-terminal edge of the beta-sheet containing residues SER 164, HIS 190 and ASP 286. The three-dimensional fold, and the arrangement of residues within the catalytic triad distinguishes the CheB methyltransferase from any previously described serine protease or serine hydrolase. The three-dimensional arrangement of the catalytic triad in the CheB methyl transferase is different from that of previously characterised serine hydrolases and serine proteases due to the opposite orientation of the histidine residue - similar orientations are observed in thiol proteases papain and actinidin.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P04042
 (3.1.1.61, 3.5.1.44)
(3.1.1.61, 3.5.1.44)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Typhimurium str. LT2 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1chd
- CHEB METHYLESTERASE DOMAIN
(1.75 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.50.180
 (see all for 1chd)
(see all for 1chd)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:3.1.1.61)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The hydrolysis of carboxyl methyl groups and amide groups catalysed by the CheB methylesterase is expected to involve a catalytic mechanism similar to that of the serine proteases and other hydrolases. The active site proposed is consistent with a proton relay mechanism proposed for hydrolysis by a serine nucleophile within a catalytic triad. For the hydrolysis catalysed by CheB, the proposed reaction mechanism would involve the hydroxyl group of Ser 164 as the nucleophile and the imidazole ring of His 190 as the proton donor to the leaving group, methanol. A potential oxyanion hole for stabilisation of the tetrahedral intermediate would be provided by the backbone amide groups of Met 283 and Thr165.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1chd) | ||
| Asp286 | Asp286(140)A | The residue hydrogen bonds to the (E)N of the His190 imidazole ring, directing and stabilising the catalytic general base within the active site. | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His190 | His190(44)A | The residue acts as a proton acceptor from the nucleophilic Ser164 and as a proton donor to the departing methanol. Hydrogen bonding interactions with Asp 286 orientates the residue for interaction with Ser164, and also modifies the pKa of the general acid imidazole nitrogen towards proton donation. | hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor, activator, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser164 | Ser164(18)A | The residue acts as a nucleophile towards the carbonyl functionality of the carboxyl-methylglutamate residues of the receptor substrate, resulting in an anionic tetrahedral intermediate. The hydroxyl proton of the residue is relayed to His 190, and then to the methanol leaving group. | covalently attached, hydrogen bond donor, nucleophile, nucleofuge, proton donor, proton acceptor, activator |
| Met283 (main-N), Thr165 (main-N) | Met283(137)A (main-N), Thr165(19)A (main-N) | The residue's backbone forms an oxyanion hole which stabilises the anionic tetrahedral intermediate. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
bimolecular nucleophilic addition, proton transfer, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, enzyme-substrate complex formation, inferred reaction step, elimination (not covered by the Ingold mechanisms), intermediate collapse, overall product formedReferences
- West AH et al. (1995), J Mol Biol, 250, 276-290. Crystal Structure of the Catalytic Domain of the Chemotaxis Receptor Methylesterase, CheB. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.1995.0376. PMID:7608974.
- Jurica MS et al. (1998), Structure, 6, 809-813. Mind your B's and R's: bacterial chemotaxis, signal transduction and protein recognition. DOI:10.1016/s0969-2126(98)00082-3.
- Djordjevic S et al. (1997), Structure, 5, 545-558. Crystal structure of the chemotaxis receptor methyltransferase CheR suggests a conserved structural motif for binding S-adenosylmethionine. DOI:10.1016/s0969-2126(97)00210-4.
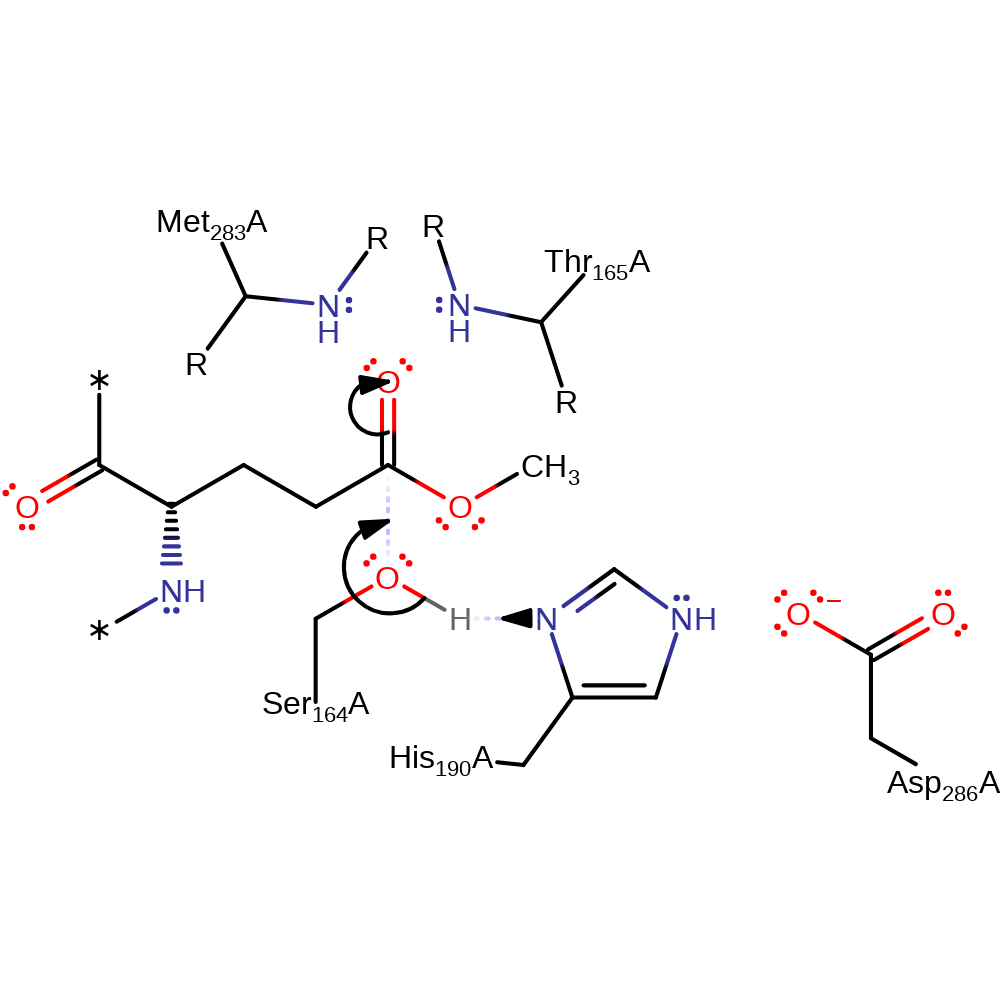
Step 1. Ser164 acts as a nucleophile towards the glutamine methyl-ester, activated by His190 and Asp283, the two other residues involved in forming the hydrolase triad. It has been inferred that the proton originally from Ser164 is relayed to His190, since no alternative proton acceptors have been identified.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser164(18)A | activator, hydrogen bond donor |
| His190(44)A | activator, hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp286(140)A | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Met283(137)A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Thr165(19)A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser164(18)A | nucleophile |
| His190(44)A | proton acceptor |
| Ser164(18)A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, proton transfer, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, enzyme-substrate complex formation, inferred reaction step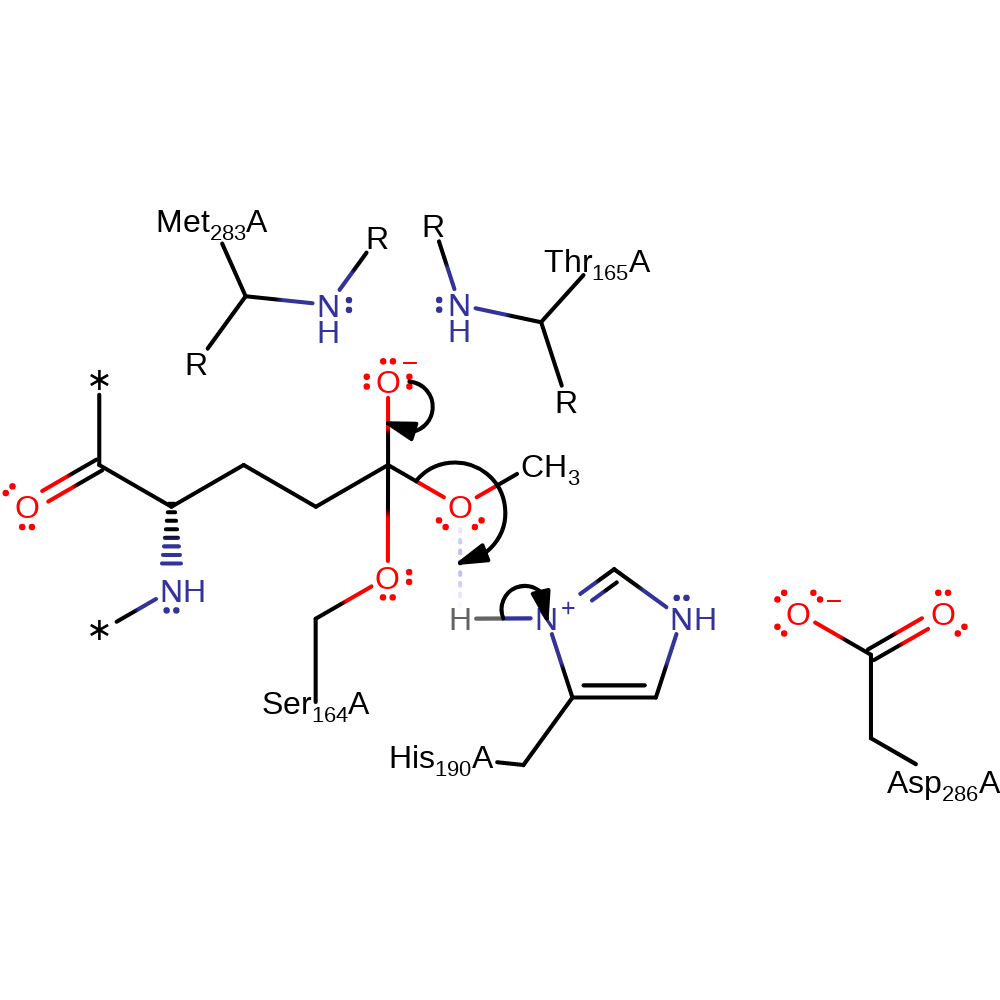
Step 2. The tetrahedral oxyanion intermediate collapses, releasing methanol with concomitant protonation of the leaving group, methanol.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser164(18)A | activator, covalently attached, hydrogen bond donor |
| His190(44)A | activator, hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp286(140)A | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Met283(137)A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Thr165(19)A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His190(44)A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
elimination (not covered by the Ingold mechanisms), proton transfer, intermediate formation, intermediate collapse, overall product formed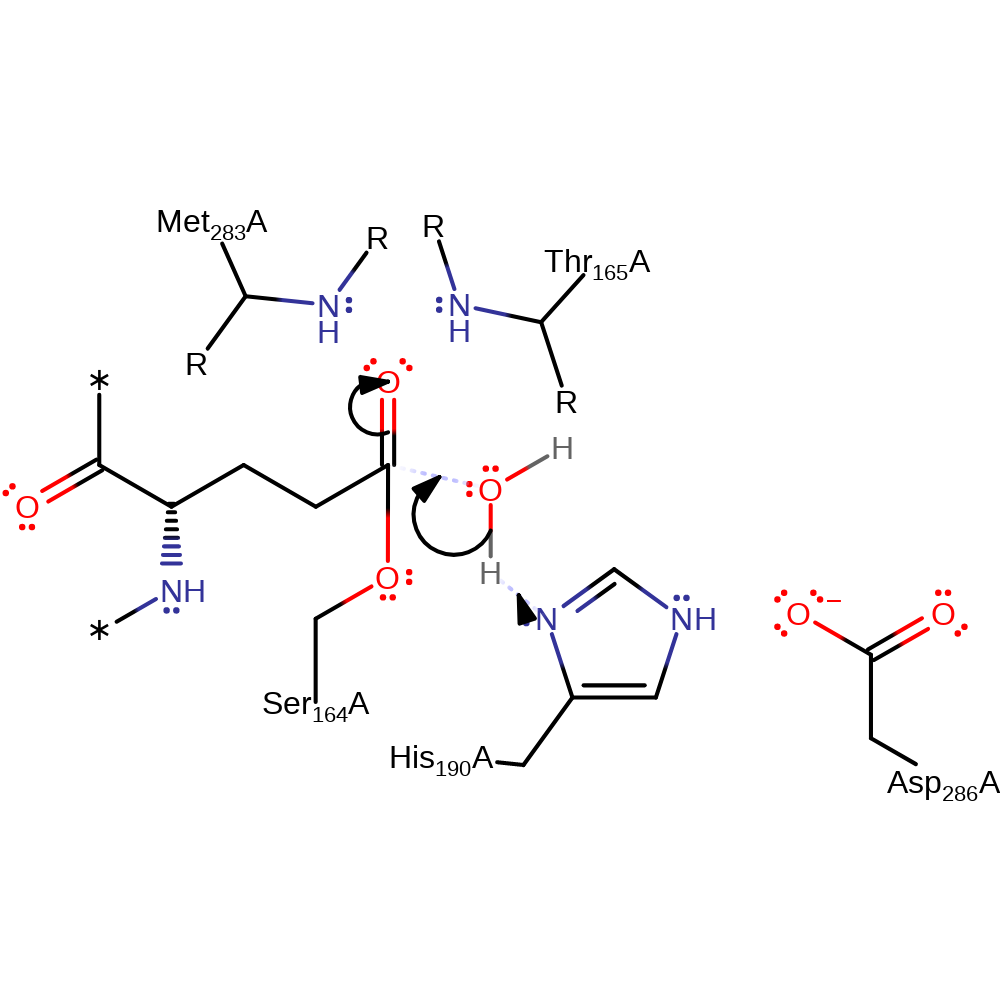
Step 3. Water, activated by His190, attacks the enzyme-glutamine carbonyl bond, forming a second tetrahedral intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser164(18)A | activator, covalently attached |
| His190(44)A | activator, hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp286(140)A | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Met283(137)A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Thr165(19)A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His190(44)A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, proton transfer, intermediate formation, overall reactant used
Step 4. The tetrahedral intermediate collapses, eliminating the protein glutamine residue and regenerating the active site protonation state.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser164(18)A | activator, covalently attached |
| His190(44)A | activator, hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp286(140)A | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Met283(137)A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Thr165(19)A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser164(18)A | nucleofuge, proton acceptor |
| His190(44)A | proton donor |





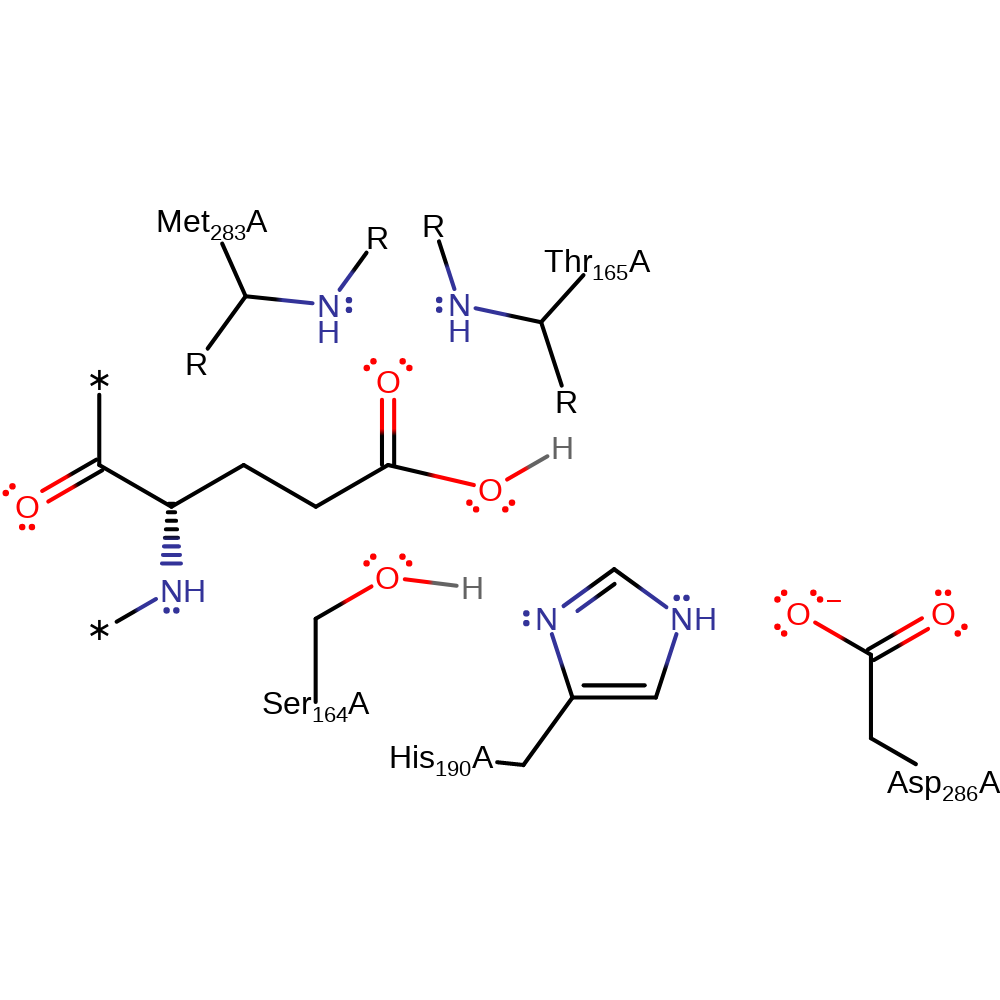 Download:
Download: