Diaminopimelate epimerase
Diaminopimelate epimerase catalyses the isomerisation of L,L-dimaminopimelate to meso-DAP in the biosynthetic pathway leading from aspartate to lysine. It is a member of the broader family of PLP-independent amino acid racemases. Diaminopimelic acid is an essential component of bacterial cell wall biosynthesis. Diaminopimelate epimerase utilises a pair of cysteine residues in catalysis, as seen in other non-PLP dependent alpha-amino acid racemases. However, its specificity for a substrate with two stereo-centres separates the kinetic from data that presented by functionally related enzymes [PMID:16723397, PMID:10194362].
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P44859
 (5.1.1.7)
(5.1.1.7)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Haemophilus influenzae Rd KW20 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1bwz
- DIAMINOPIMELATE EPIMERASE FROM HEMOPHILUS INFLUENZAE
(2.72 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.10.310.10
 (see all for 1bwz)
(see all for 1bwz)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:5.1.1.7)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
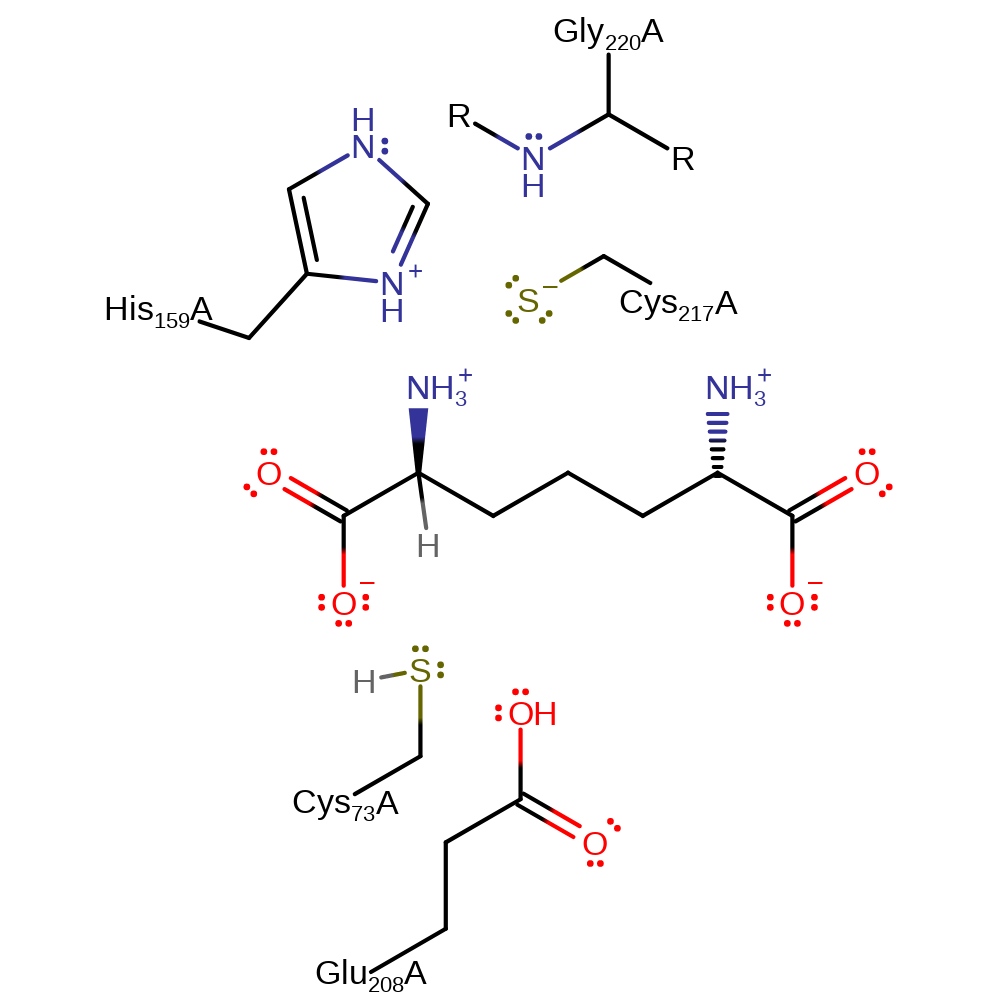
The Cys73 thiolate abstracts the substrate's alpha position proton, generating a carbanion transition state which rapidly abstracts a proton from Cys217. This residue is positioned on the alternative face of the molecule Cys73 and therefore, on reprotonation the stereochemistry at this centre is inverted. The enzyme is able to catalyse the interconversion of either S or R stereochemistry, creating an equilibrium between the diastereoisomer and the meso-product.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1bwz) | ||
| Cys217, Cys73 | Cys217A, Cys73A | Act as a general acid/base. In the 2S,6S to 2R,6S direction Cys73 is negatively charged in the ground state, acting to abstract a proton from the substrate. Cys217 is neutral and donates a proton to the transition state to form the product. In the reverse reaction direction, the roles of the cysteine residues are reversed. | hydrogen bond donor, proton donor |
| Gly220 (main-N), His159 | Gly220A (main-N), His159A | Activates and stabilises Cys217 | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu208 | Glu208A | Stabilises and activates Cys73. | activator, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, isomerisation reaction (not covered by named reactions), overall reactant used, overall product formed, native state of enzyme is not regenerated, rate-determining stepReferences
- Koo CW et al. (1999), Biochemistry, 38, 4416-4422. Chemical Mechanism ofHaemophilus influenzaeDiaminopimelate Epimerase†. DOI:10.1021/bi982911f. PMID:10194362.
- Stenta M et al. (2009), J Chem Theory Comput, 5, 1915-1930. Catalytic Mechanism of Diaminopimelate Epimerase: A QM/MM Investigation. DOI:10.1021/ct900004x. PMID:26610016.
- Pillai B et al. (2006), Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 103, 8668-8673. Structural insights into stereochemical inversion by diaminopimelate epimerase: An antibacterial drug target. DOI:10.1073/pnas.0602537103. PMID:16723397.
- Diaper CM et al. (2005), Org Biomol Chem, 3, 4402-4411. The stereoselective synthesis of aziridine analogues of diaminopimelic acid (DAP) and their interaction with dap epimerase. DOI:10.1039/b513409a. PMID:16327902.
- Cirilli M et al. (1998), Biochemistry, 37, 16452-16458. Structural Symmetry: The Three-Dimensional Structure ofHaemophilus InfluenzaeDiaminopimelate Epimerase†,‡. DOI:10.1021/bi982138o. PMID:9843410.

Step 1. The Cys73 thiolate abstracts the substrate's alpha position proton, generating a carbanion transition state which rapidly abstracts a proton from Cys217. This residue is positioned on the alternative face of the molecule Cys73 and therefore, on reprotonation the stereochemistry at this centre is inverted. The stereochemsitry of the bound substrate interconverts until it dissociates from the active site. The enzyme is therefore not regenerated, per say, before a second round of catalysis occurs [PMID:16723397, PMID:10194362].
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Gly220A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys217A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Cys73A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| His159A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu208A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His159A | activator |
| Glu208A | activator |
| Cys217A | proton donor |
| Cys73A | proton acceptor |


 Download:
Download: