Methylmalonyl-CoA epimerase
Methylmalonyl-CoA epimerase is essential for the breakdown of odd-numbered fatty acids and the amino acids valine, isoleucine and methionine. It is present in many species of bacteria and animals. Defective activity in humans can result in severe acidosis and damage to the central nervous system.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
Q8VQN0
 (5.1.99.1)
(5.1.99.1)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Propionibacterium freudenreichii subsp. shermanii (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1jc5
- Crystal Structure of Native Methylmalonyl-CoA Epimerase
(2.2 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.10.180.10
 (see all for 1jc5)
(see all for 1jc5)
- Cofactors
- Cobalt(3+) (1), Cobalt(2+) (1) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Reaction (EC:5.1.99.1)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
Although there is no Co(II) present in the crystal structure, it has been determined that the ion is necessary and the most likely to bind well [PMID:11470438].
Glu48 deprotonates the chiral centre of methylmalonyl-CoA, forming an enol intermediate. Glu141 then deprotonates Glu48. The oxyanion intermediate collapses, reforming the ketone while the chiral centre is reformed by proton transfer from Glu141.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1jc5) | ||
| Glu48, Glu141 | Glu48A, Glu141A | Acts as a general acid/base. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Glu141, His12, Gln65, His91 | Glu141A, His12A, Gln65A, His91A | Binds the Co(II) ion. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, metal ligand, proton acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, atom stereo change, decoordination from a metal ion, coordination to a metal ion, overall product formed, native state of enzyme regenerated, intermediate terminatedReferences
- McCarthy AA et al. (2001), Structure, 9, 637-646. Crystal structure of methylmalonyl-coenzyme A epimerase from P. shermanii: a novel enzymatic function on an ancient metal binding scaffold. PMID:11470438.
- Shi L et al. (2009), Proteins, 77, 994-999. Crystal structure of a putative methylmalonyl-coenzyme a epimerase fromThermoanaerobacter tengcongensisat 2.0 Å resolution. DOI:10.1002/prot.22528. PMID:19731367.
- Armstrong RN (2000), Biochemistry, 39, 13625-13632. Mechanistic Diversity in a Metalloenzyme Superfamily†. DOI:10.1021/bi001814v. PMID:11076500.
- Cameron AD et al. (1999), Biochemistry, 38, 13480-13490. Reaction Mechanism of Glyoxalase I Explored by an X-ray Crystallographic Analysis of the Human Enzyme in Complex with a Transition State Analogue†. DOI:10.1021/bi990696c. PMID:10521255.
- Stabler SP et al. (1985), Arch Biochem Biophys, 241, 252-264. Isolation and characterization of dl-methylmalonyl-coenzyme A racemase from rat liver. DOI:10.1016/0003-9861(85)90381-9.
- Leadlay PF (1981), Biochem J, 197, 413-419. Purification and characterization of methylmalonyl-CoA epimerase fromPropionibacterium shermanii. DOI:10.1042/bj1970413.
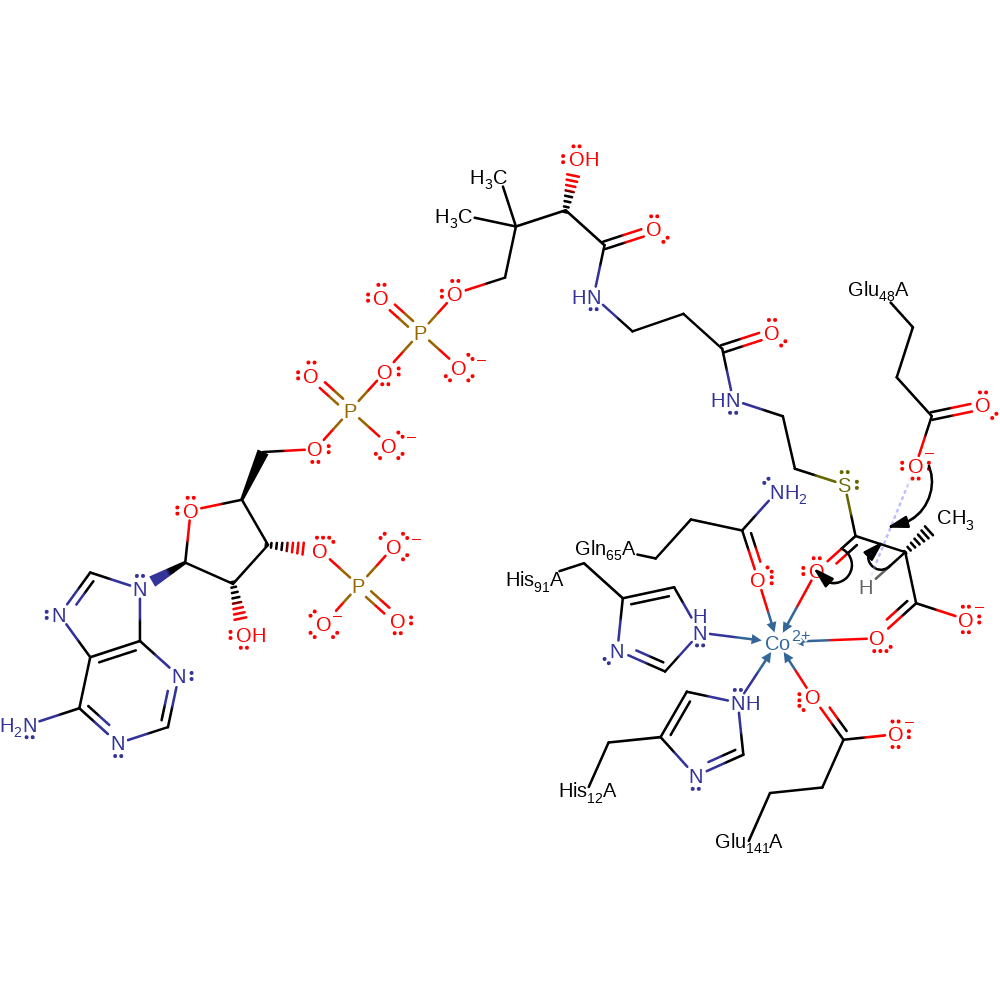
Step 1. Glu48 deprotonates the chiral centre of methylmalonyl-CoA, resulting in formation of an enol intermediate that is stabilised by the Co(II) centre.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu141A | metal ligand |
| Glu48A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| His12A | metal ligand |
| His91A | metal ligand |
| Gln65A | metal ligand |
| Glu48A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, assisted keto-enol tautomerisation, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, atom stereo change, decoordination from a metal ion, coordination to a metal ionCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu141A | hydrogen bond acceptor, metal ligand |
| Glu48A | hydrogen bond donor |
| His12A | metal ligand |
| His91A | metal ligand |
| Gln65A | metal ligand |
| Glu48A | proton donor |
| Glu141A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, decoordination from a metal ion, coordination to a metal ion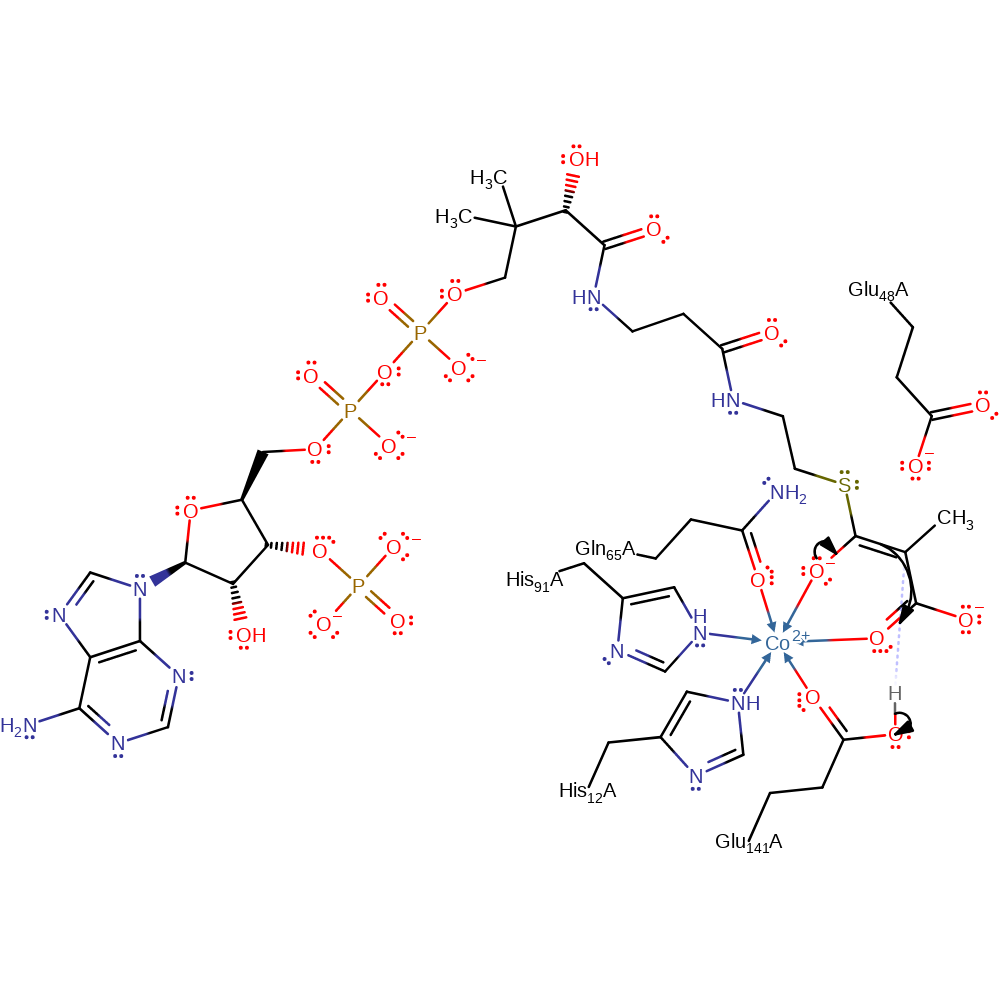
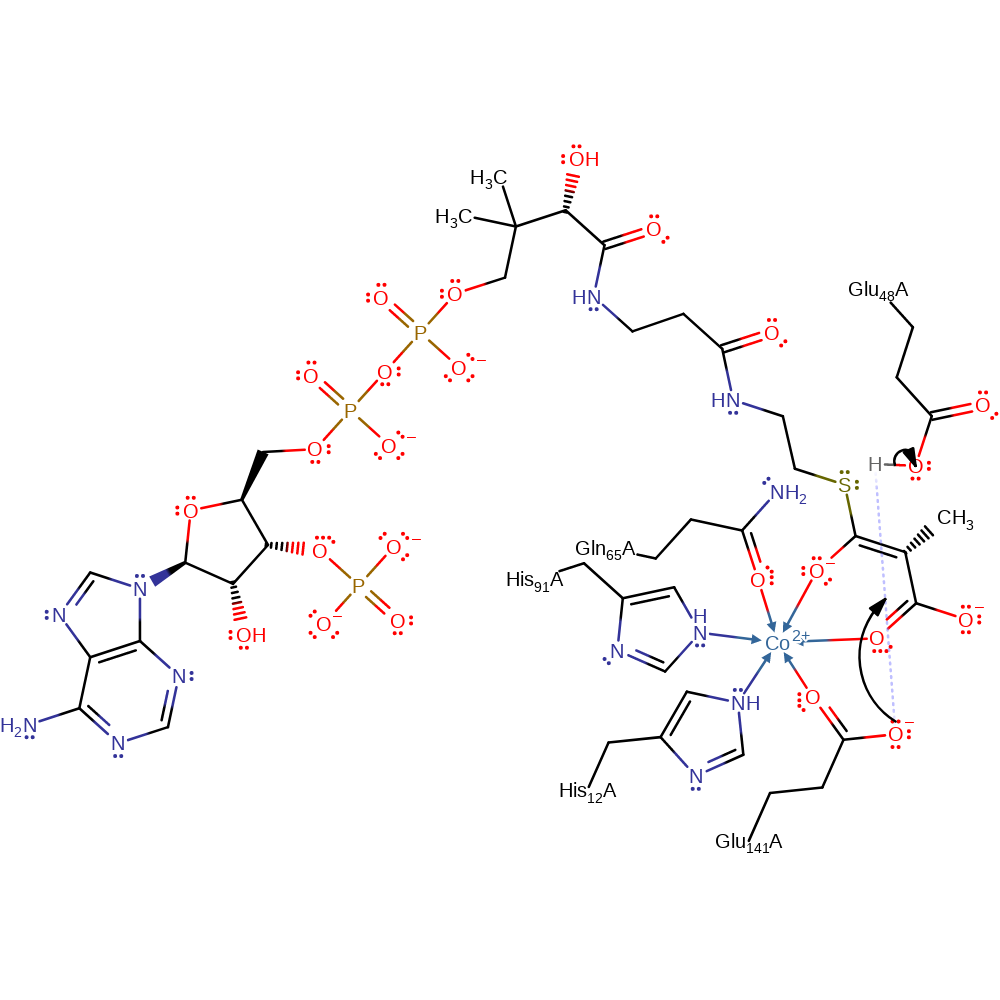
Step 3. The oxyanion collapses back to re-form the keto-form, the chiral centre is re-formed by proton transfer from Glu141.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu141A | metal ligand, hydrogen bond donor |
| His12A | metal ligand |
| Gln65A | metal ligand |
| His91A | metal ligand |
| Glu141A | proton donor |


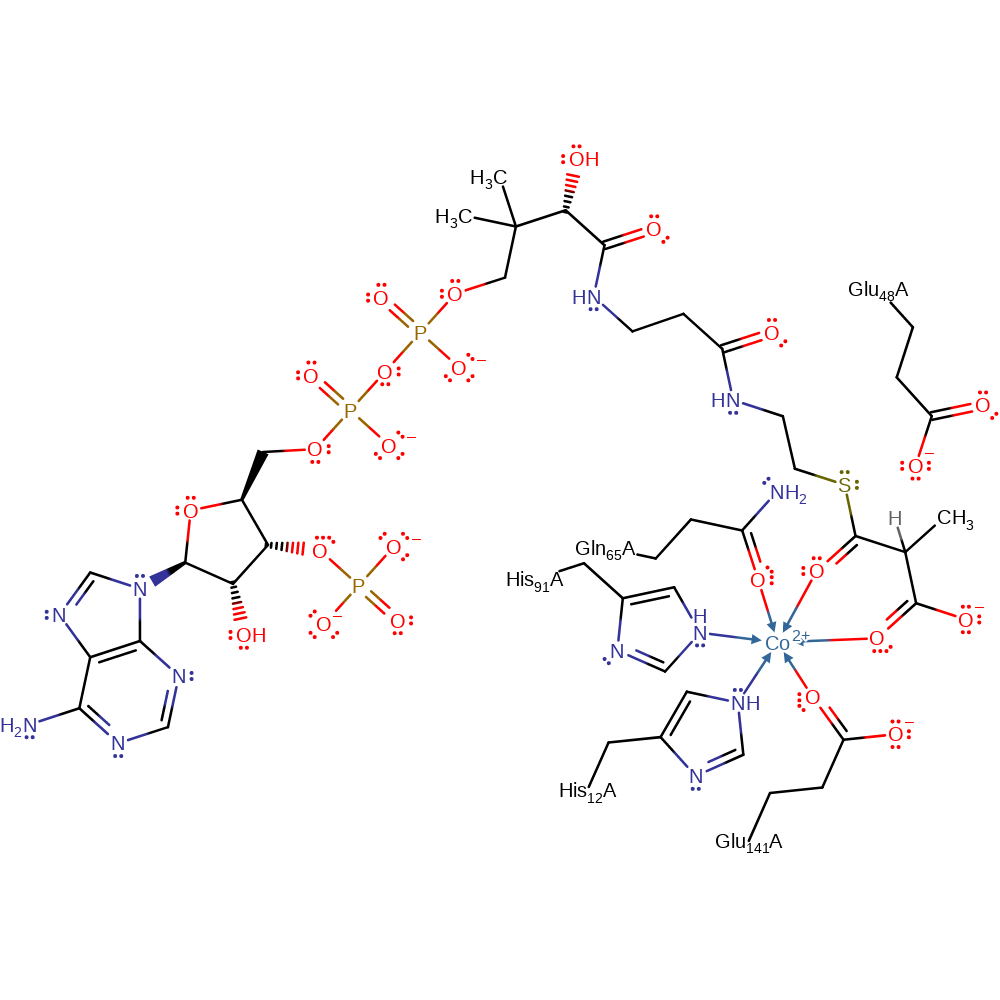 Download:
Download: