Glycerol dehydrogenase
Glycerol dehydrogenase catalyses the NAD-dependent oxidation of glycerol to dihydroxyacetone (glycerone). This reaction allows microorganisms to utilise glycerol as a source of carbon under anaerobic conditions.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
Q9WYQ4
 (1.1.1.6)
(1.1.1.6)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Thermotoga maritima MSB8 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1kq3
- CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF A GLYCEROL DEHYDROGENASE (TM0423) FROM THERMOTOGA MARITIMA AT 1.5 A RESOLUTION
(1.5 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
1.20.1090.10
 (see all for 1kq3)
(see all for 1kq3)
- Cofactors
- Zinc(2+) (1) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Reaction (EC:1.1.1.6)
+
→
+
+
Alternative enzyme names: NAD-linked glycerol dehydrogenase, Glycerin dehydrogenase,
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
A bound water molecule (activated by His255) abstracts a proton from the zinc-boud hydroxyl group of the substrate. This eliminates a hydride ion that is transferred to NAD.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1kq3) | ||
| His255 | His255(267)A | Increases the basicity of a water molecule. Although it has been suggested that the water molecule may be part of a proton relay chain, there is no direct evidence (other than the crystal structure) that His255 actually acts as a general acid/base. | increase basicity, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp169, His252, His269 | Asp169(181)A, His252(264)A, His269(281)A | Forms part of the catalytic zinc binding site. | metal ligand |
*PDB label guide - RESx(y)B(C) - RES: Residue Name; x: Residue ID in PDB file;
y: Residue ID in PDB sequence if different from PDB file; B: PDB Chain;
C: Biological Assembly Chain if different from PDB. If label is "Not Found" it means this residue is not found in the reference PDB.
Chemical Components
proton transfer, hydride transfer, bimolecular elimination, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, overall product formedReferences
- Ruzheinikov SN et al. (2001), Structure, 9, 789-802. Glycerol dehydrogenase. structure, specificity, and mechanism of a family III polyol dehydrogenase. PMID:11566129.
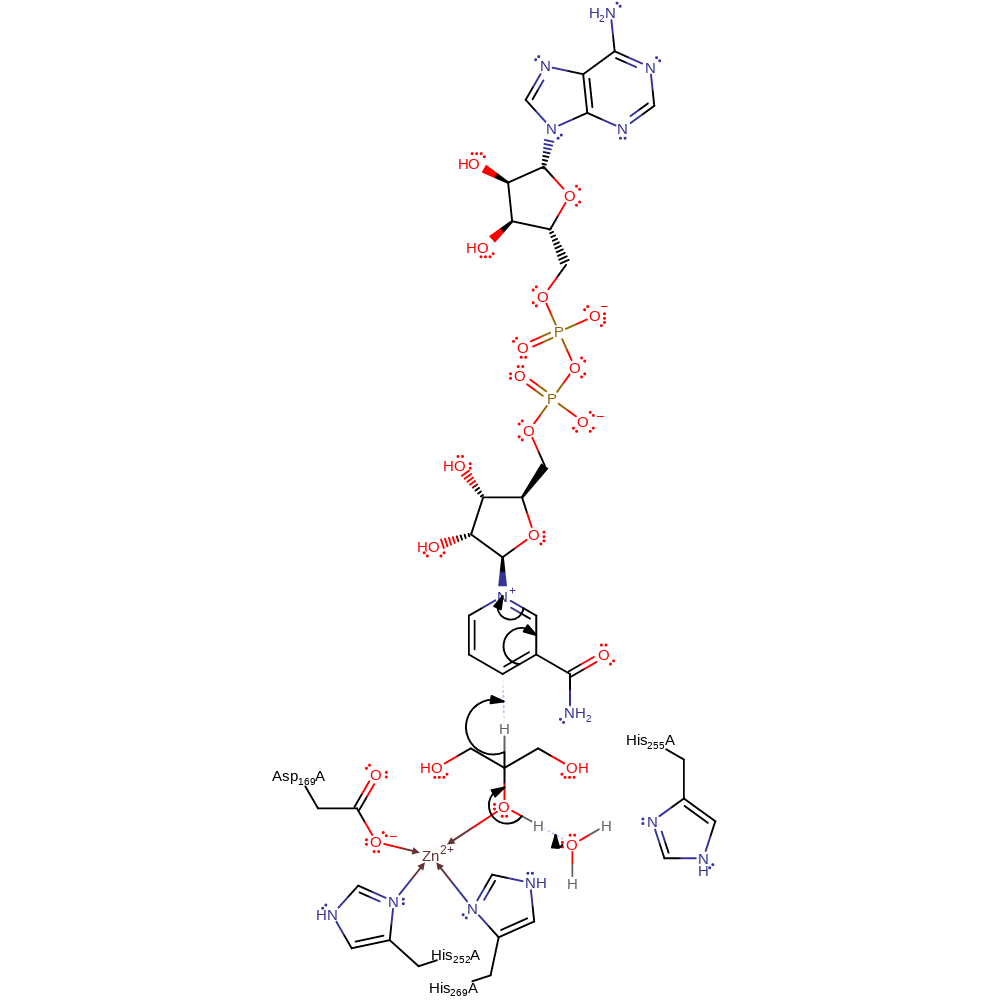
Step 1. Water deprotonates the zinc-activated hydroxyl group resulting in the elimination of a hydride ion onto NAD
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His255(267)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, increase basicity |
| Asp169(181)A | metal ligand |
| His252(264)A | metal ligand |
| His269(281)A | metal ligand |





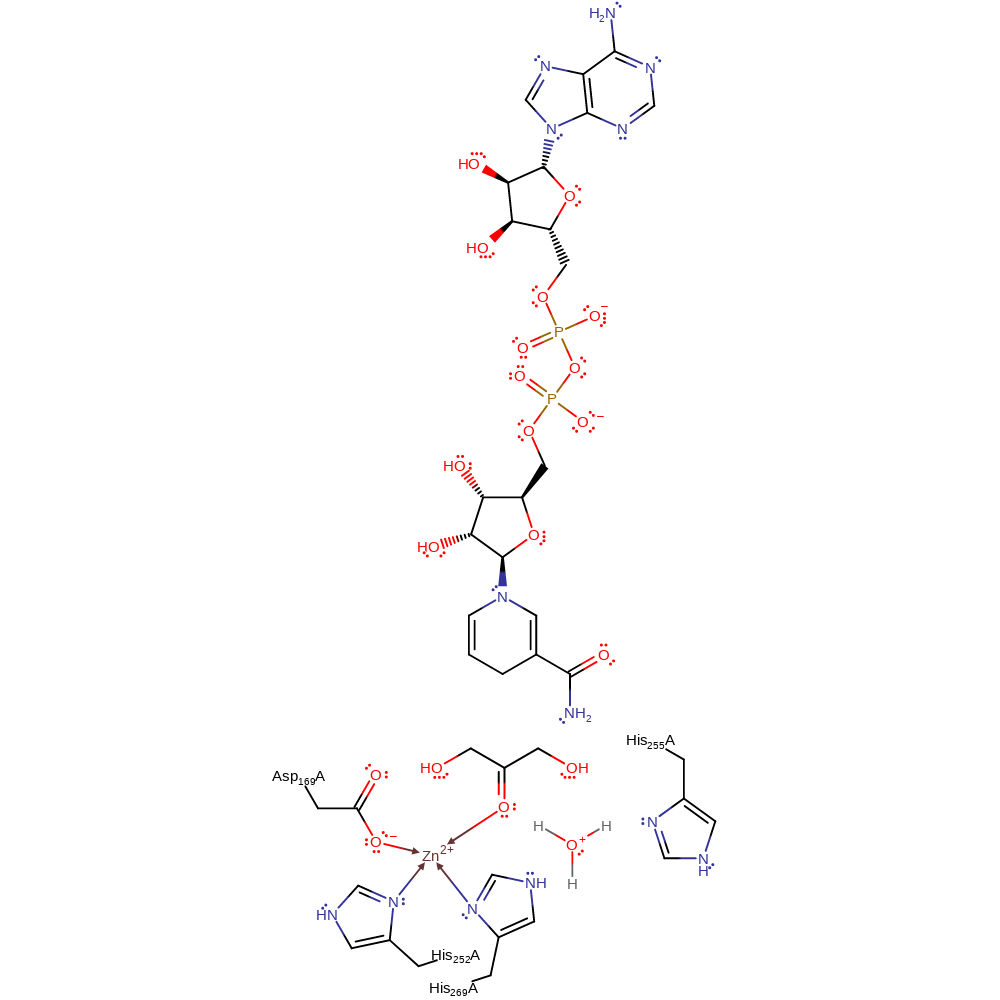 Download:
Download: