Pantetheine-phosphate adenylyltransferase
Phosphopantetheine adenylyltransferase (PPAT), isolated from Escherichia coli, catalyses the magnesium-dependent adenylyl transfer from ATP to 4'-phosphopantetheine (Ppant or PhP) to form dephospho-CoA (dPCoA). This reaction is the penultimate step in the synthesis of CoA. PPAT belongs to the nucleotidyltransferase alpha/beta phosphodiesterase superfamily, whose members catalyse the transfer of a nucleotide monophosphate to a substrate by stabilising the transition state of the reaction.
PPAT is a hexamer consisting of two trimers. While each subunit possesses an active site, it appears that only the subunits of one trimer will catalyse the reaction at a given time. The reaction proceeds via a random bi-bi mechanism in that the order of the binding of ATP and Ppant is not fixed, nor is the release of dPCoA and pyrophosphate. CoA can regulate the activity of PPAT by binding to the PPAT.PPi complex, thus preventing the binding of a new Ppant substrate molecule.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P0A6I6
 (2.7.7.3)
(2.7.7.3)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Escherichia coli K-12 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1b6t
- PHOSPHOPANTETHEINE ADENYLYLTRANSFERASE IN COMPLEX WITH 3'-DEPHOSPHO-COA FROM ESCHERICHIA COLI
(1.8 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.50.620
 (see all for 1b6t)
(see all for 1b6t)
- Cofactors
- Magnesium(2+) (1) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Reaction (EC:2.7.7.3)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
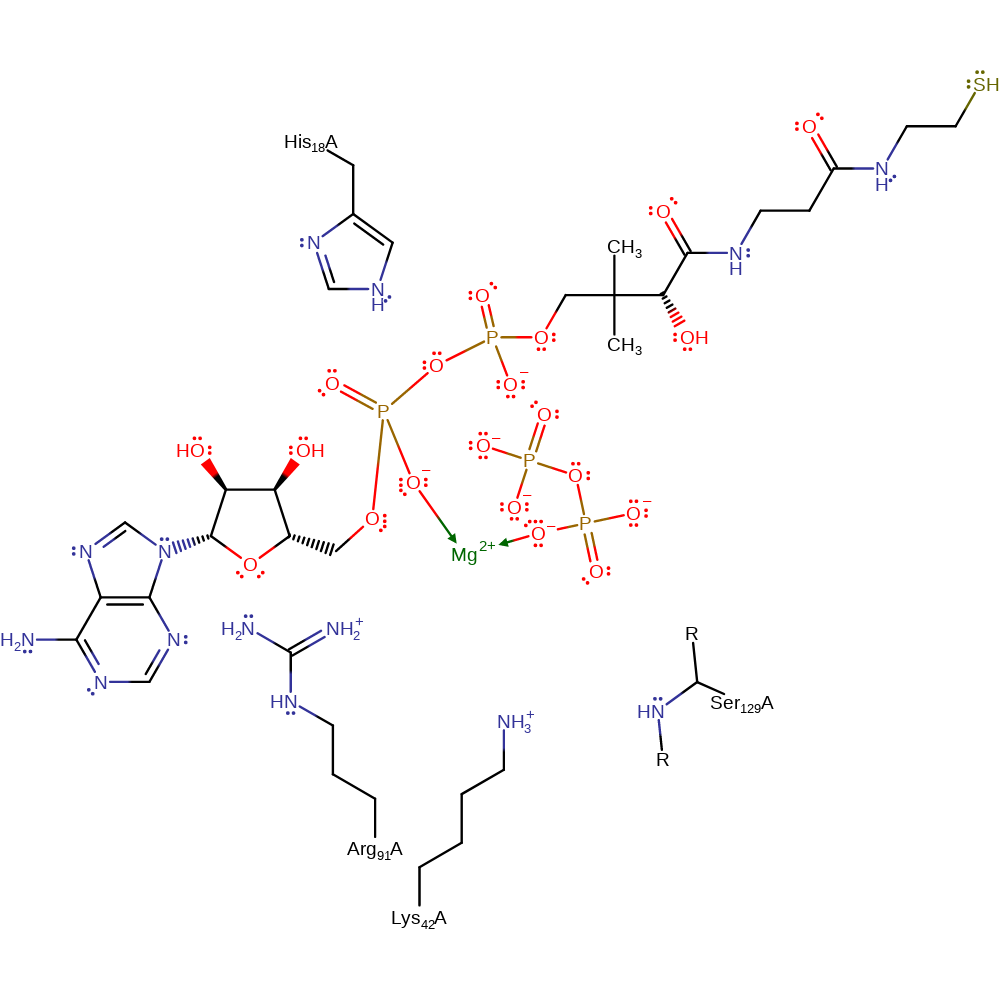
One of the 4'-phosphate oxygen's of Ppant undergoes nucleophilic attack on the alpha-phosphate group of ATP with pyrophosphate as the leaving group. The pentacovalent transition state is stabilised by His18 while the leaving group is stabilised by Arg91, Ser129 and the magnesium ion.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1b6t) | ||
| His18 | His18A | Stabilises the pentacovalent transition state by forming a hydrogen bond to the non-ester oxygens of P(alpha). | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser129 (main-N), Lys42, Arg91 | Ser129A (main-N), Lys42A, Arg91A | Stabilises the beta-phosphate, making pyrophosphate a better leaving group. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall reactant used, overall product formed, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Izard T et al. (1999), EMBO J, 18, 2021-2030. The crystal structure of a novel bacterial adenylyltransferase reveals half of sites reactivity. DOI:10.1093/emboj/18.8.2021. PMID:10205156.
- Izard T (2002), J Mol Biol, 315, 487-495. The crystal structures of phosphopantetheine adenylyltransferase with bound substrates reveal the enzyme’s catalytic mechanism. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.2001.5272. PMID:11812124.
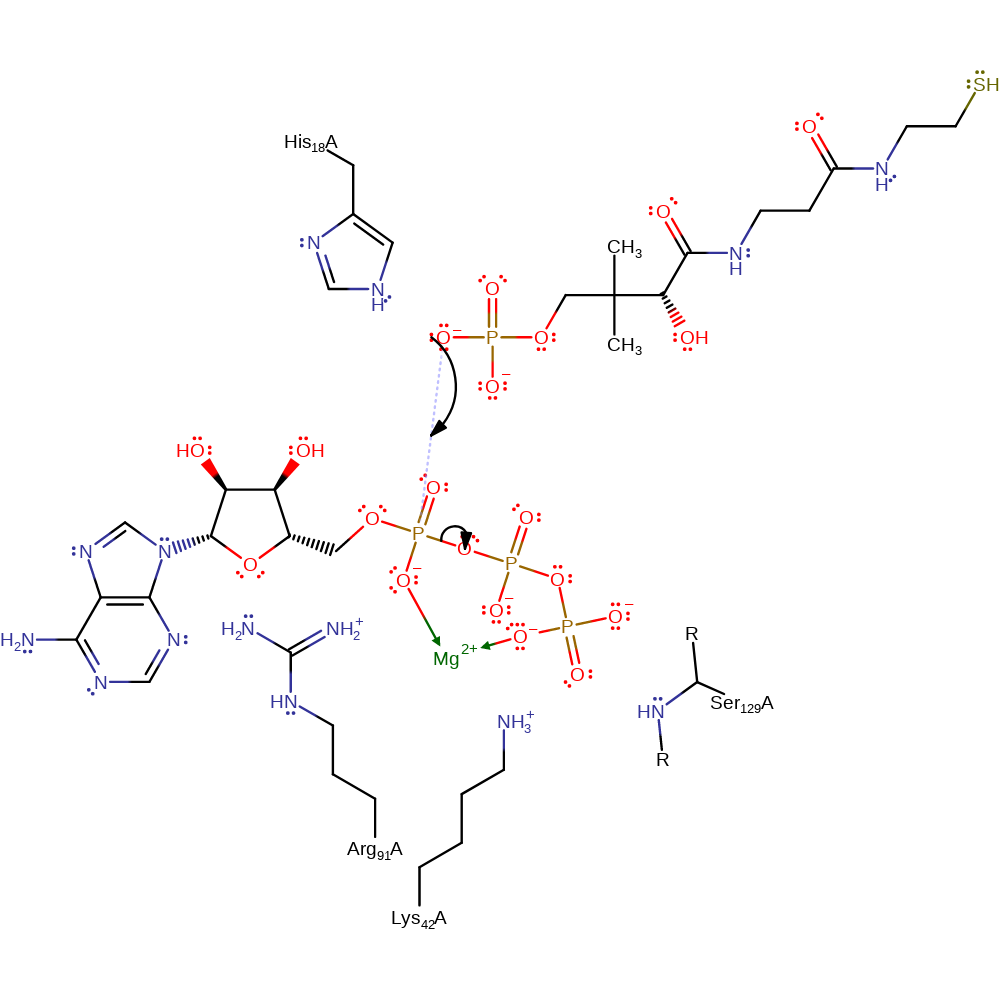
Step 1. The ATP adopts a strained conformation, as seen in the active sites of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase enzymes. This raises the energy of the ground state towards that of the transition state, lowering the overall activation energy required for the reaction [PMID:10205156]. The phosphate group of pantetheine 4'-phosphate initiates a nucleophilic attack on the alpha phosphate group of ATP in a substitution reaction.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg91A | attractive charge-charge interaction, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys42A | attractive charge-charge interaction, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His18A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser129A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |





 Download:
Download: