Glutamin-(asparagin-)ase
Glutaminase-asparaginase catalyses the hydrolysis of D and L isomers of glutamine and asparagine.
Glutaminase-asparaginase belongs to a family of related amidohydrolases, in a less specific class that catalyses the hydrolysis of glutamine to glutamic acid and asparagine to aspartic acid with similar efficiency. They are mechanistically similar to trypsin.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P10182
 (3.5.1.38)
(3.5.1.38)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Pseudomonas sp. ATCC29598 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1djo
- Crystal structure of Pseudomonas 7A Glutaminase-asparaginase with the inhibitor donv covalently bound in the active site
(2.0 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.50.40
 3.40.50.1170
3.40.50.1170  (see all for 1djo)
(see all for 1djo)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:3.5.1.38)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
Tyr 1034 is polarised by Glu 3294 B and facilitates proton abstraction from Thr 1020 and its transfer to the substrate. Nucleophilic attack by Thr 1020 proceeds on the carbonyl carbon and this forms a tetrahedral intermediate, which collapses using Tyr 1034 as a general acid/base catalyst, and activation by Glu 3294 B with release of ammonia as a by-product. Hydrolysis occurs using Thr 1100 to activate water as a nucleophile to attack the carbonyl carbon, which is activated by Tyr 1034. By general acid/base catalysis of Tyr 1034 and activation by Glu 3294 B the tetrahedral intermediate again collapses to break the acyl-enzyme linkage and release the product.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1djo) | ||
| Glu294 | Glu3294(287)B | Activates the substrate and Tyr 1034 | proton relay, hydrogen bond acceptor, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Thr20 | Thr1020(13)A | Acts as a nucleophile to attack the substrate and form an acyl-enzyme intermediate. | covalently attached, hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, nucleophile, nucleofuge, proton donor, proton acceptor |
| Tyr34 | Tyr1034(27)A | Acts as a general acid/base catalyst in activating Thr 1020 and the substrate. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor, proton relay |
| Thr100 | Thr1100(93)A | Activates water for nucleophilic attack on the substrate. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp101, Lys173 | Asp1101(94)A, Lys1173(166)A | Part of the charge relay system that activates Thr1100 | hydrogen bond acceptor |
Chemical Components
bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, enzyme-substrate complex formation, proton relay, intermediate formation, proton transfer, bimolecular elimination, overall product formed, deamination, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, intermediate collapse, native state of enzyme regenerated, intermediate terminatedReferences
- Sanches M et al. (2007), Curr Chem Biol, 1, 75-86. Structure, Substrate Complexation and Reaction Mechanism of Bacterial Asparaginases. DOI:10.2174/2212796810701010075.
- Ortlund E et al. (2000), Biochemistry, 39, 1199-1204. Reactions ofPseudomonas7A Glutaminase-Asparaginase with Diazo Analogues of Glutamine and Asparagine Result in Unexpected Covalent Inhibitions and Suggests an Unusual Catalytic Triad Thr-Tyr-Glu†,‡. DOI:10.1021/bi991797d. PMID:10684596.

Step 1. Glu3294B deprotonates Tyr1034, which in turn deprotonates Thr1020. Thr1020 then initiates a nucleophilic attack upon the amide carbon of L-asparagine in an addition reaction. The oxyanion formed deprotonates Glu3294B.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr1034(27)A | proton relay, hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Lys1173(166)A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu3294(287)B | hydrogen bond acceptor, proton relay |
| Asp1101(94)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Thr1100(93)A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Thr1020(13)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Thr1020(13)A | proton donor |
| Glu3294(287)B | proton acceptor |
| Tyr1034(27)A | proton acceptor |
| Glu3294(287)B | proton donor |
| Thr1020(13)A | nucleophile |
| Tyr1034(27)A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, enzyme-substrate complex formation, proton relay, intermediate formation, proton transfer
Step 2. Glu1294B deprotonates the hydroxyl formed from the oxyanion, initiating the elimination of ammonia, which gains a proton from Glu1294B.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr1034(27)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Lys1173(166)A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu3294(287)B | hydrogen bond acceptor, proton relay |
| Asp1101(94)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Thr1100(93)A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Thr1020(13)A | covalently attached, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu3294(287)B | proton donor, proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular elimination, overall product formed, proton relay, deamination, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, intermediate collapse, intermediate formation
Step 3. The Asp-Lys-Thr triad activates water, which initiates a nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl carbon of the covalently attached intermediate. The formed oxyanion deprotonates the water which attacked.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr1034(27)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Lys1173(166)A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu3294(287)B | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp1101(94)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Thr1100(93)A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Thr1020(13)A | covalently attached, hydrogen bond acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation
Step 4. Glu1294B deprotonates the hydroxyl formed from the oxyanion, initiating the elimination of Thr1020, which in turn deprotonates Tyr1034, which then deprotonates Glu1294B.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr1034(27)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton relay |
| Lys1173(166)A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu3294(287)B | hydrogen bond acceptor, proton relay |
| Asp1101(94)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Thr1100(93)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Thr1020(13)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu3294(287)B | proton donor, proton acceptor |
| Tyr1034(27)A | proton acceptor |
| Thr1020(13)A | nucleofuge, proton acceptor |
| Tyr1034(27)A | proton donor |


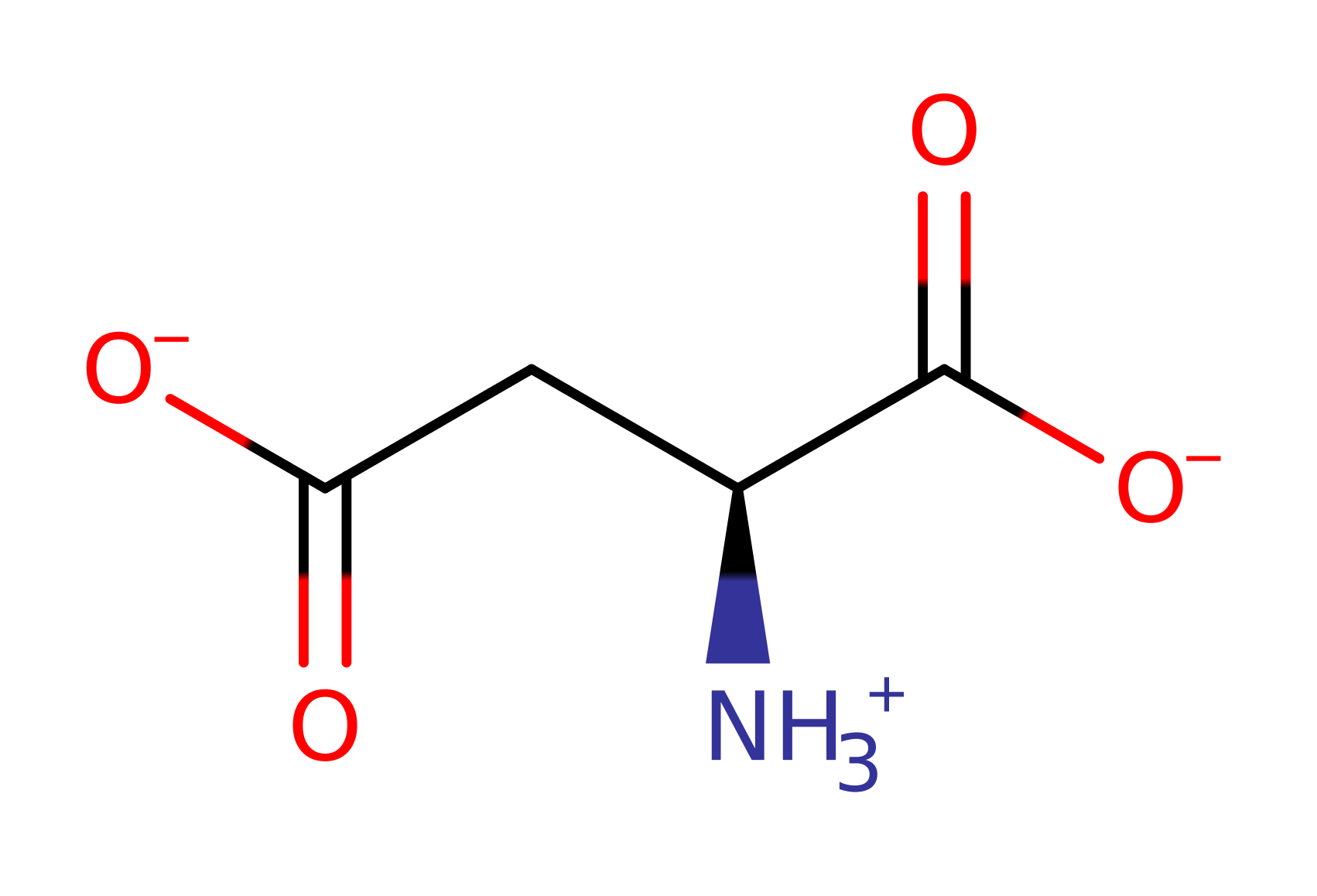

 Download:
Download: