Electron-transferring-flavoprotein dehydrogenase
Electron transfer flavoprotein-ubiquinone oxidoreductase is oxidised by the diffusible ubiquinone. The ubiquinol product relays electrons onto complex III. The enzyme links electrons from the oxidations of fatty acids to the mitochondrial respiratory chain.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P55931
 (1.5.5.1)
(1.5.5.1)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Sus scrofa (pig)

- PDB
-
2gmh
- Structure of Porcine Electron Transfer Flavoprotein-Ubiquinone Oxidoreductase in Complexed with Ubiquinone
(2.5 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.50.50.60
 3.30.70.20
3.30.70.20  3.30.9.90
3.30.9.90  (see all for 2gmh)
(see all for 2gmh)
- Cofactors
- Fadh2(2-) (1), Tetra-mu3-sulfido-tetrairon (1) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Reaction (EC:1.5.5.1)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The reduced electron transfer flavoprotein delivers electron to the FAD cofactor via the iron sulfur cluster. The oxidised electron transfer flavoprotein donates a proton to the FAD cofactor. The one electron oxidised electron transfer flavoprotein donates a second electron to the iron sulfur cluster, reducing its overall charge from +2 to +1. The semiquinone FAD intermediate reduces the bound ubiquinone substrate. The electron held by the iron sulfur cluster is now transferred to the FAD cofactor. The oxidised electron transfer flavoprotein donates a proton to the FAD cofactor. FAD now donates a second reducing equivalent to the ubiquinone, forming the quinol product and regenerating the cofactor.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (2gmh) | ||
| Cys589 (main-C) | Cys556A (main-C) | Forms part of the electron relay chain from the electron transfer protein to the FAD of the active site. | single electron relay, single electron acceptor, single electron donor |
| Thr400, Ser115 | Thr367A, Ser82A | Help stabilise the reactive intermediates formed during the course of the reaction. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg364 | Arg331A | Forms part of the electron relay from the electron transfer protein to the FAD in the active site. | single electron relay, hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, activator, single electron acceptor, single electron donor |
| Cys586, Cys592, Cys561, Cys589 | Cys553A, Cys559A, Cys528A, Cys556A | Binds the iron-sulfur cluster. | attractive charge-charge interaction, activator, metal ligand, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
electron transfer, redox reaction, overall reactant used, cofactor used, intermediate formation, electron relay, proton transfer, native state of cofactor regenerated, intermediate terminated, overall product formed, inferred reaction step, intermediate collapse, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Zhang J et al. (2006), Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 103, 16212-16217. Structure of electron transfer flavoprotein-ubiquinone oxidoreductase and electron transfer to the mitochondrial ubiquinone pool. DOI:10.1073/pnas.0604567103. PMID:17050691.
- Swanson MA et al. (2008), Biochemistry, 47, 8894-8901. The Iron−Sulfur Cluster of Electron Transfer Flavoprotein−Ubiquinone Oxidoreductase Is the Electron Acceptor for Electron Transfer Flavoprotein†. DOI:10.1021/bi800507p. PMID:18672901.
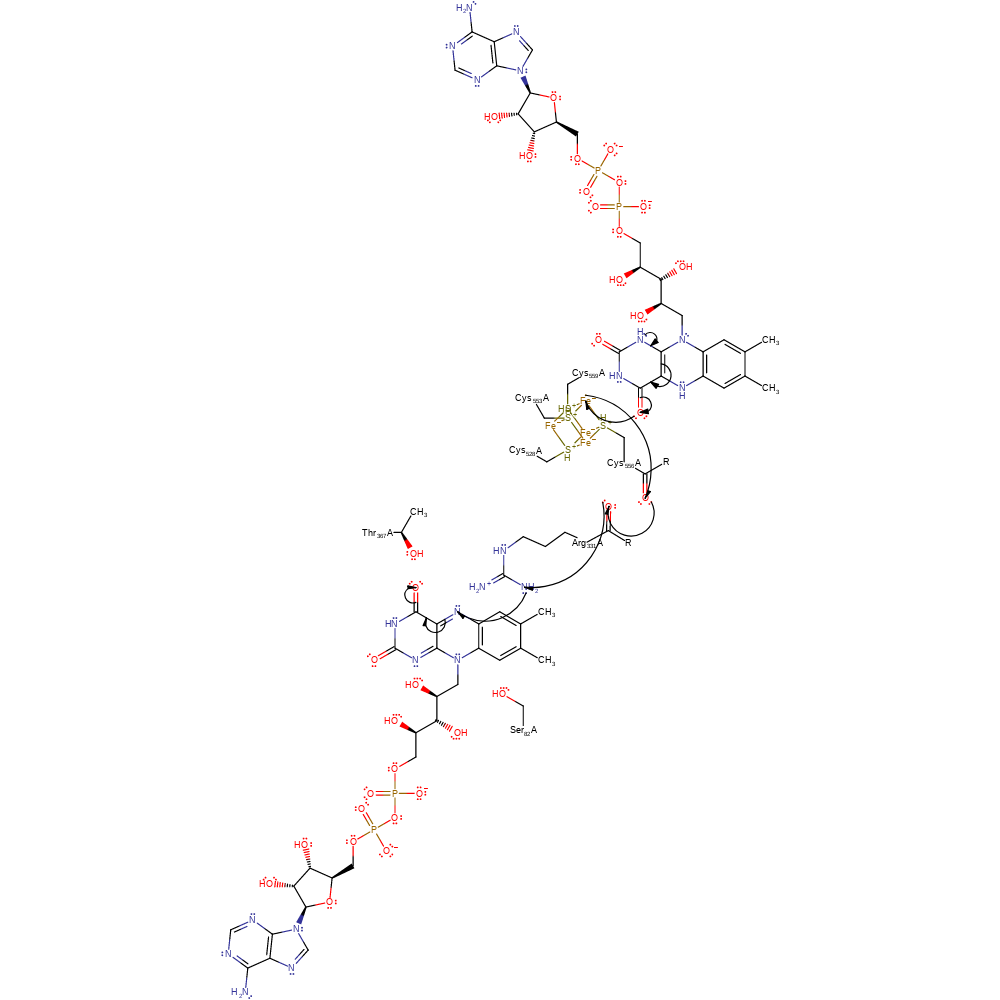
Step 1. The reduced electron transfer flavoprotein delivers electron to the FAD cofactor via the iron sulfur cluster. Mutagenesis and kinetic calculations have shown the electron to relay through the Fe4S4 cluster before reaching the FAD cofactor, rather than being directly donated to the flavin [PMID:18672901]. The electron is relayed to FAD from the iron sulfur cluster through interactions between the close proximity cabronyl of the metal ligand Cys556 and the carbonyl of Arg331 [PMID:17050691].
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg331A | activator, hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys556A | activator, attractive charge-charge interaction, metal ligand, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys528A | activator, attractive charge-charge interaction, metal ligand |
| Cys559A | activator, attractive charge-charge interaction, metal ligand |
| Cys553A | activator, attractive charge-charge interaction, metal ligand |
| Ser82A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg331A | single electron acceptor |
| Thr367A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg331A | single electron relay |
| Cys556A (main-C) | single electron relay, single electron donor, single electron acceptor |
| Arg331A | single electron donor |
Chemical Components
electron transfer, redox reaction, overall reactant used, cofactor used, intermediate formation, electron relay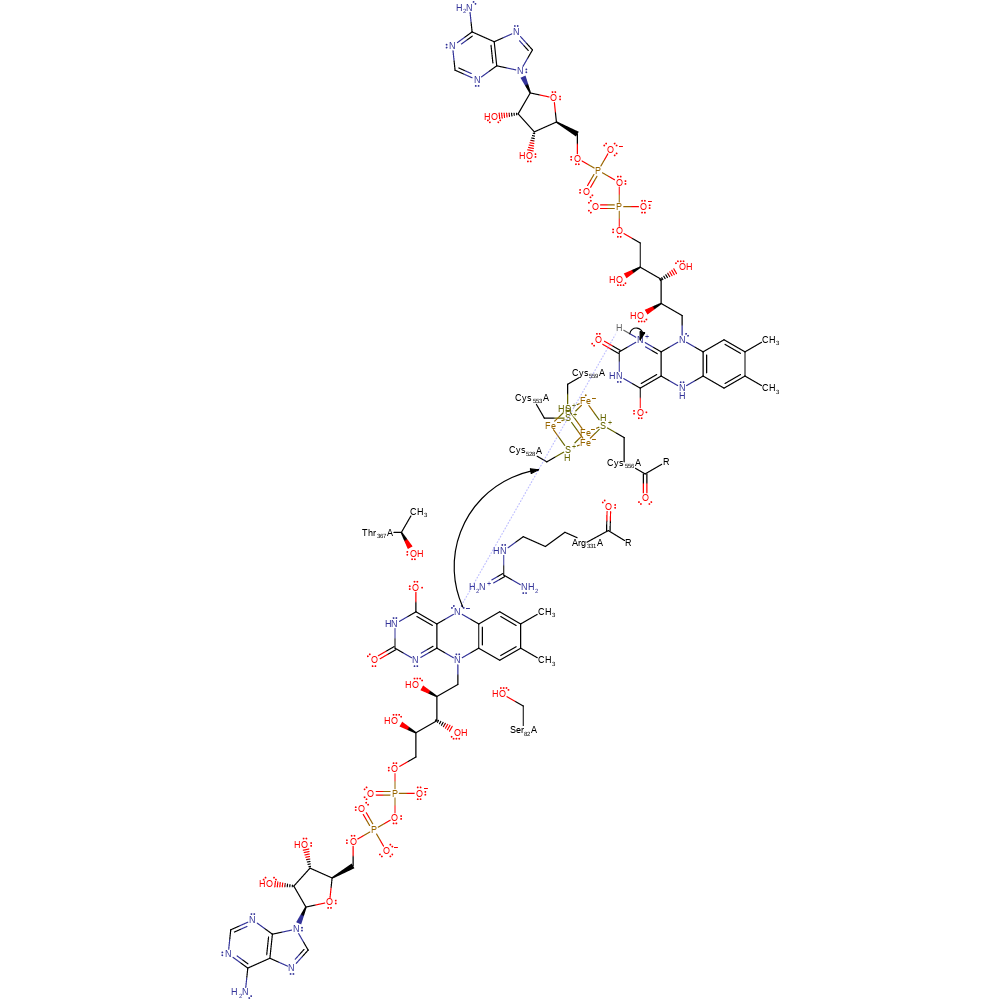
Step 2. The oxidised electron transfer flavoprotein donates a proton to the FAD cofactor
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg331A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys556A | activator, attractive charge-charge interaction, metal ligand, electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys528A | activator, attractive charge-charge interaction, metal ligand, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys559A | activator, attractive charge-charge interaction, metal ligand, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys553A | activator, attractive charge-charge interaction, metal ligand, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser82A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Thr367A | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, cofactor used, overall reactant used, intermediate formation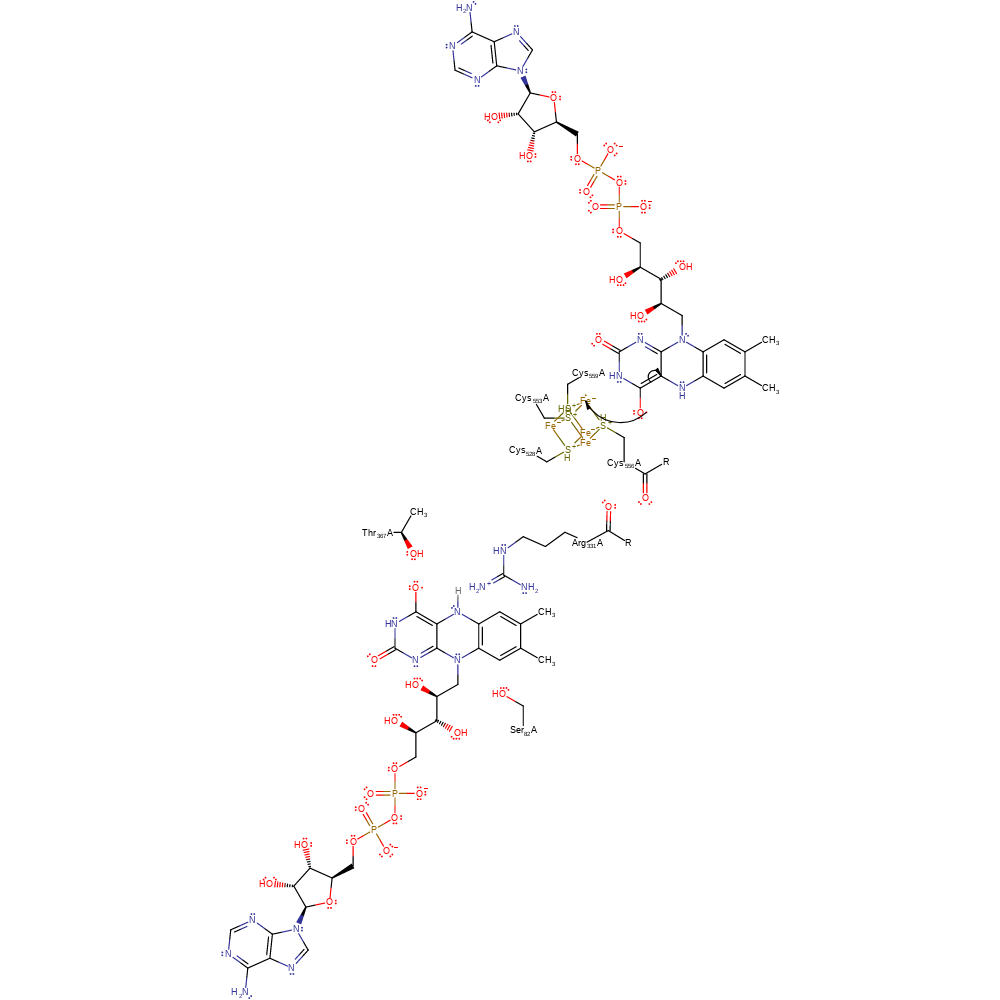
Step 3. The one electron oxidised electron transfer flavoprotein donates a second electron to the iron sulfur cluster. On the addition of a second electron from the ET-transport flavin, both the flavin cofactor and Fe-S cluster are in a single electron reduced states, i.e a semi-quinone and +1 state, respecitively [PMID:17050691].
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg331A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys556A | activator, attractive charge-charge interaction, metal ligand, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys528A | activator, attractive charge-charge interaction, metal ligand, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys559A | activator, attractive charge-charge interaction, metal ligand, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys553A | activator, attractive charge-charge interaction, metal ligand, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser82A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Thr367A | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
electron transfer, redox reaction, cofactor used, intermediate formation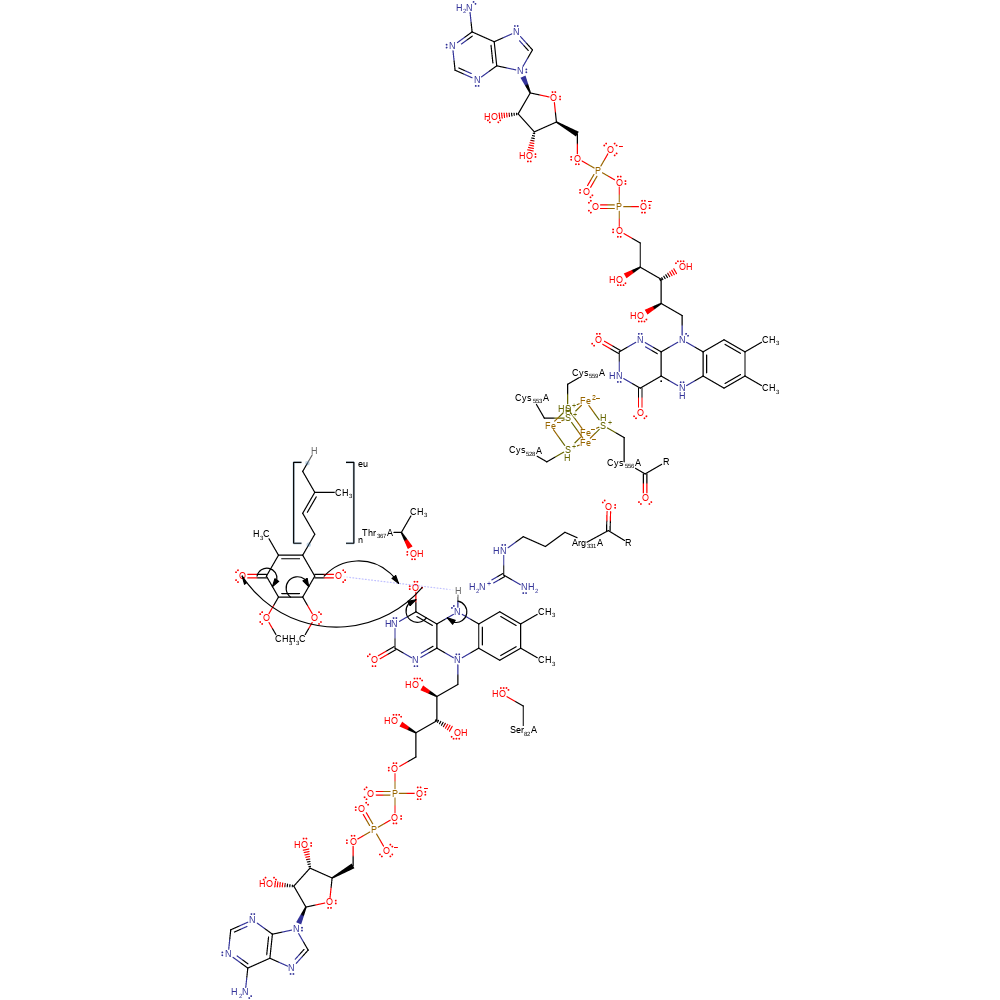
Step 4. The semiquinone FAD intermediate reduces the bound ubiquinone substrate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg331A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys556A | activator, metal ligand, attractive charge-charge interaction, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys528A | activator, metal ligand, attractive charge-charge interaction, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys559A | activator, metal ligand, attractive charge-charge interaction, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys553A | activator, metal ligand, attractive charge-charge interaction, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser82A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Thr367A | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
electron transfer, proton transfer, redox reaction, overall reactant used, native state of cofactor regenerated, intermediate formation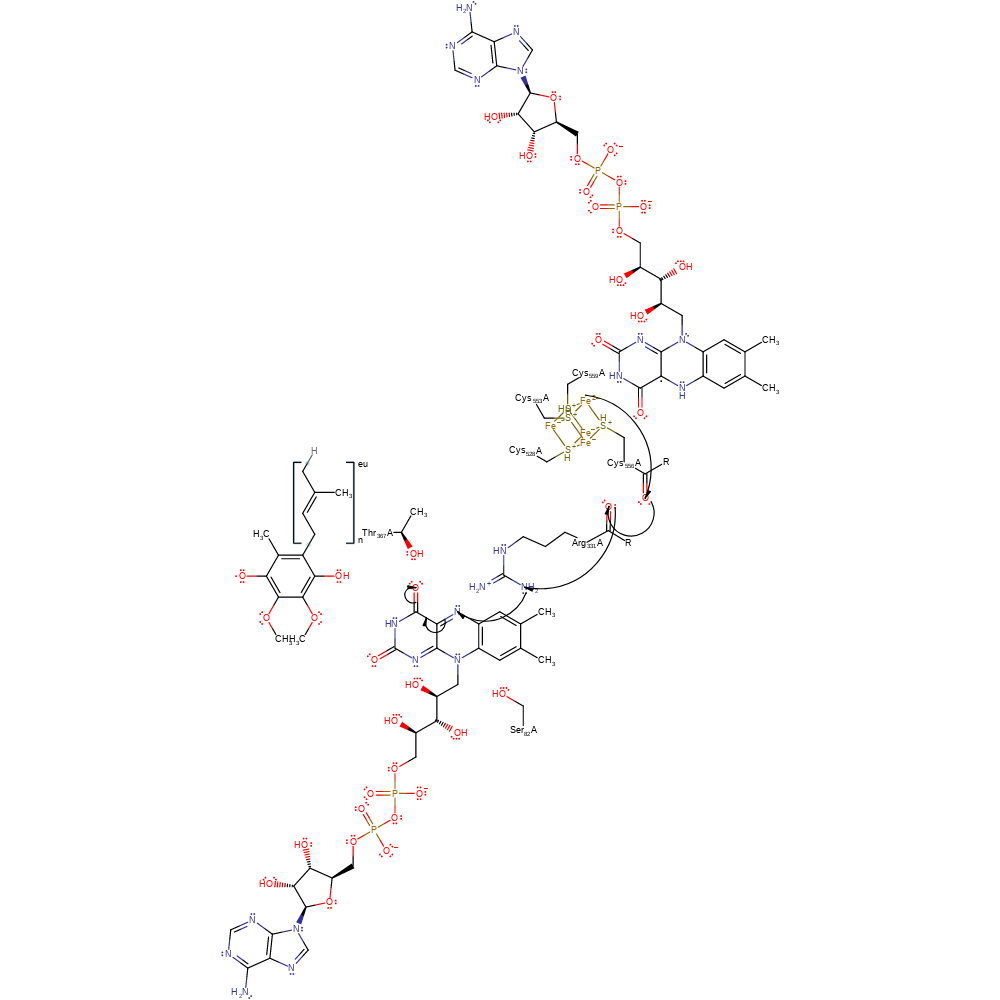
Step 5. A second electron is donated from the Fe4S4 cluster to the FAD. The centres are coupled by the interaction between the Cys556 carbonyl and Arg331 [PMID:18672901].
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg331A | activator, hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys556A | activator, attractive charge-charge interaction, metal ligand, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys528A | activator, attractive charge-charge interaction, metal ligand, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys559A | activator, attractive charge-charge interaction, metal ligand, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys553A | activator, electrostatic stabiliser, attractive charge-charge interaction, metal ligand |
| Ser82A | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Arg331A | single electron acceptor |
| Thr367A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg331A | single electron relay |
| Cys556A (main-C) | single electron donor, single electron relay, single electron acceptor |
| Arg331A | single electron donor |
Chemical Components
electron transfer, cofactor used, intermediate terminated, electron relay, native state of cofactor regenerated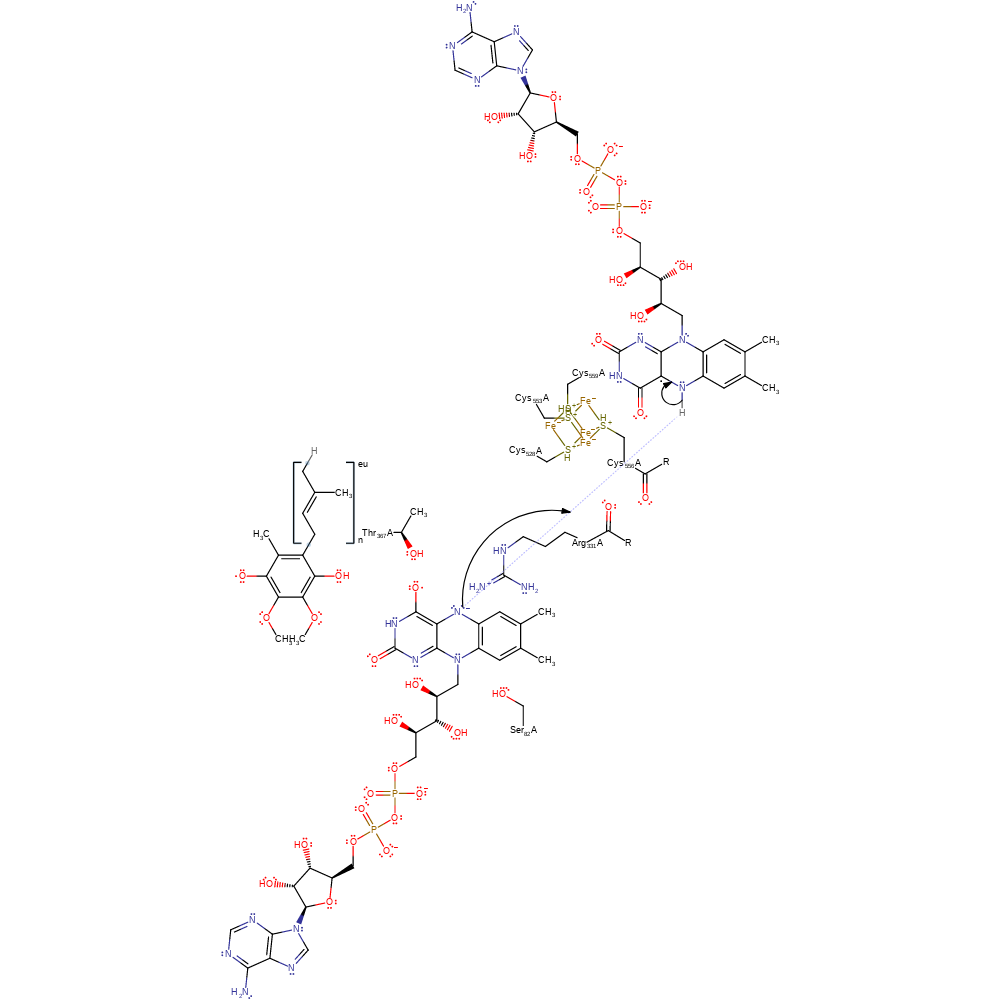
Step 6. The oxidised electron transfer flavoprotein donates a proton to the FAD cofactor
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg331A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys556A | activator, attractive charge-charge interaction, metal ligand, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys528A | activator, attractive charge-charge interaction, metal ligand, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys559A | activator, attractive charge-charge interaction, metal ligand, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys553A | activator, attractive charge-charge interaction, metal ligand, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser82A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Thr367A | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, cofactor used, overall reactant used, intermediate formation, overall product formed, inferred reaction step
Step 7. FAD now donates a second reducing equivalent to the ubiquinone, forming the quinol product and regenerating the cofactor.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg331A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys556A | activator, attractive charge-charge interaction, metal ligand, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys528A | activator, attractive charge-charge interaction, metal ligand, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys559A | activator, attractive charge-charge interaction, metal ligand, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys553A | activator, attractive charge-charge interaction, metal ligand, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser82A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Thr367A | electrostatic stabiliser |





 Download:
Download: