3-methyl-2-oxobutanoate dehydrogenase (2-methylpropanoyl-transferring)
The branched-chain alpha-keto dehydrogenase complex catalyzes the overall conversion of alpha-keto acids to acyl-CoA and CO2. It is a multienzyme complex composed of 3 functional components: (E1) branched-chain alpha-keto acid decarboxylase or 2-oxoisovalerate dehydrogenase; (E2) lipoamide acyltransferase; (E3) lipoamide dehydrogenase. This entry represents E2, the lipoamide acyltransferase function, which is a thiamine diphposphate dependent reaction.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequences
-
P12694
 (1.2.4.4)
(1.2.4.4)
P21953 (1.2.4.4)
(1.2.4.4)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Homo sapiens (Human)

- PDB
-
1dtw
- HUMAN BRANCHED-CHAIN ALPHA-KETO ACID DEHYDROGENASE
(2.7 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.50.970
 (see all for 1dtw)
(see all for 1dtw)
- Cofactors
- Thiamine(1+) diphosphate(3-) (1), Magnesium(2+) (1), Potassium(1+) (1) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Reaction (EC:1.2.4.4)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
Glu76' abstracts a proton from the N(1)a position of the thiamine diphosphate cofactor, inducing a proton transfer which activates the cofactor. The cofactor anion attacks at the substrate carbonyl, forming a tetrahedral intermediate. The tetrahedral anion intermediate removes the N(1) proton from the imine ring. This results in the deprotonation of Glu76'. His291 induces decarboxylation from the cofactor-substrate intermediate by abstracting a proton. The disulfide bridge of lipoamide E is broken by nucleophilic attack. His291 initiates the collapse of the intermediate with concomitant product formation. The thiamine diphosphate cofactor is regenerated by abstracting a proton from the positively charged imidazole ring of His291.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1dtw) | ||
| His336 | His291A | Acts as a general acid/base. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor, activator |
| Ser337 | Ser292A | Helps stabilise the reactive intermediates formed. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser207 (main-C) | Ser162A (main-C) | The 'V' conformation of thiamine diphosphate, maintained though interactions with Ser162. | hydrogen bond acceptor, steric role |
| Glu121 | Glu76A(BA) | Acts as a general acid/base in the activation of the thiamine diphosphate cofactor. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor, activator, steric role |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, cofactor used, intermediate formation, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, bimolecular elimination, decarboxylation, overall product formed, intermediate collapse, bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, intermediate terminated, native state of enzyme regenerated, native state of cofactor regeneratedReferences
- Aevarsson A et al. (1999), Nat Struct Biol, 6, 785-792. Crystal structure of 2-oxoisovalerate and dehydrogenase and the architecture of 2-oxo acid dehydrogenase multienzyme complexes. DOI:10.1038/11563. PMID:10426958.
- AEvarsson A et al. (2000), Structure, 8, 277-291. Crystal structure of human branched-chain α-ketoacid dehydrogenase and the molecular basis of multienzyme complex deficiency in maple syrup urine disease. DOI:10.1016/s0969-2126(00)00105-2. PMID:10745006.
- Hawes JW et al. (1995), J Biol Chem, 270, 31071-31076. Roles of Amino Acid Residues Surrounding Phosphorylation Site 1 of Branched-chain -Ketoacid Dehydrogenase (BCKDH) in Catalysis and Phosphorylation Site Recognition by BCKDH Kinase. DOI:10.1074/jbc.270.52.31071. PMID:8537366.
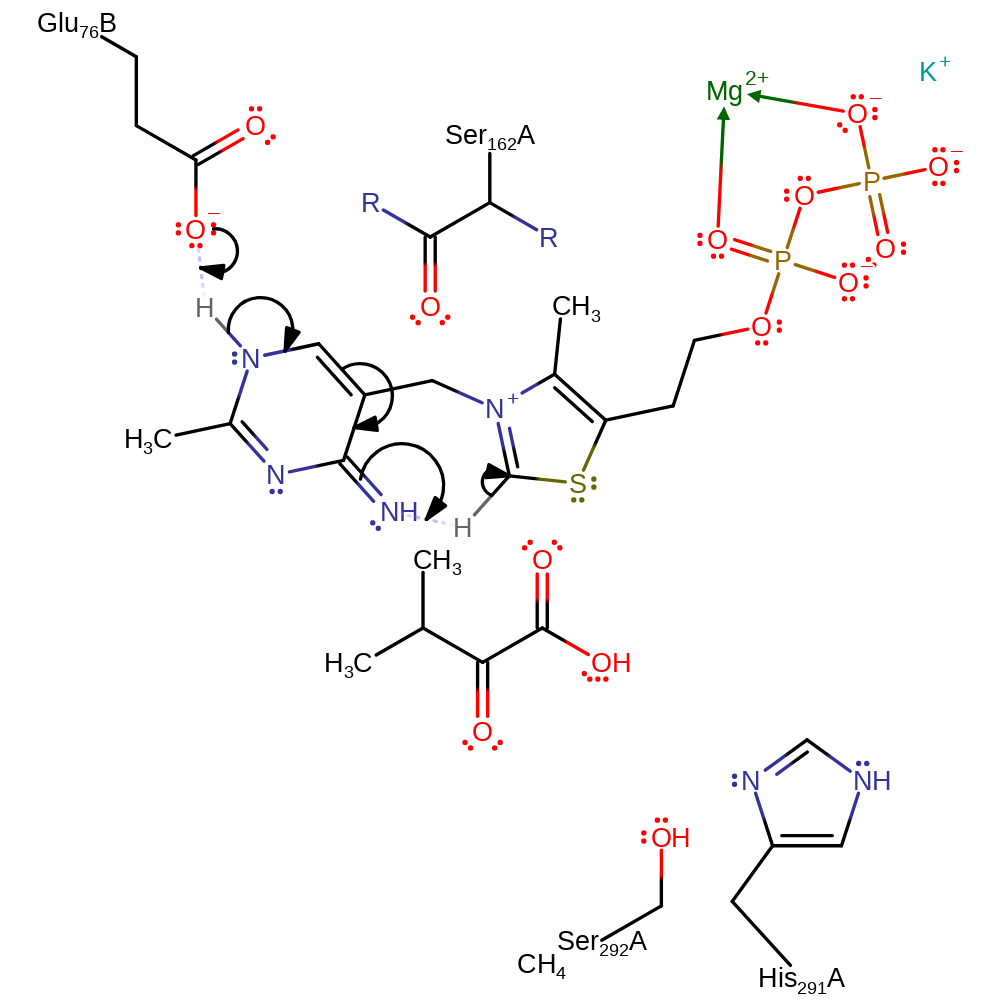
Step 1. Glu76' abstracts a proton from the N(1)a position of the thiamine diphosphate cofactor, inducing a proton transfer which activates the cofactor.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His291A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu76A(BA) | activator, hydrogen bond acceptor, steric role |
| Ser292A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser162A (main-C) | hydrogen bond acceptor, steric role |
| Glu76A(BA) | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, cofactor used, intermediate formation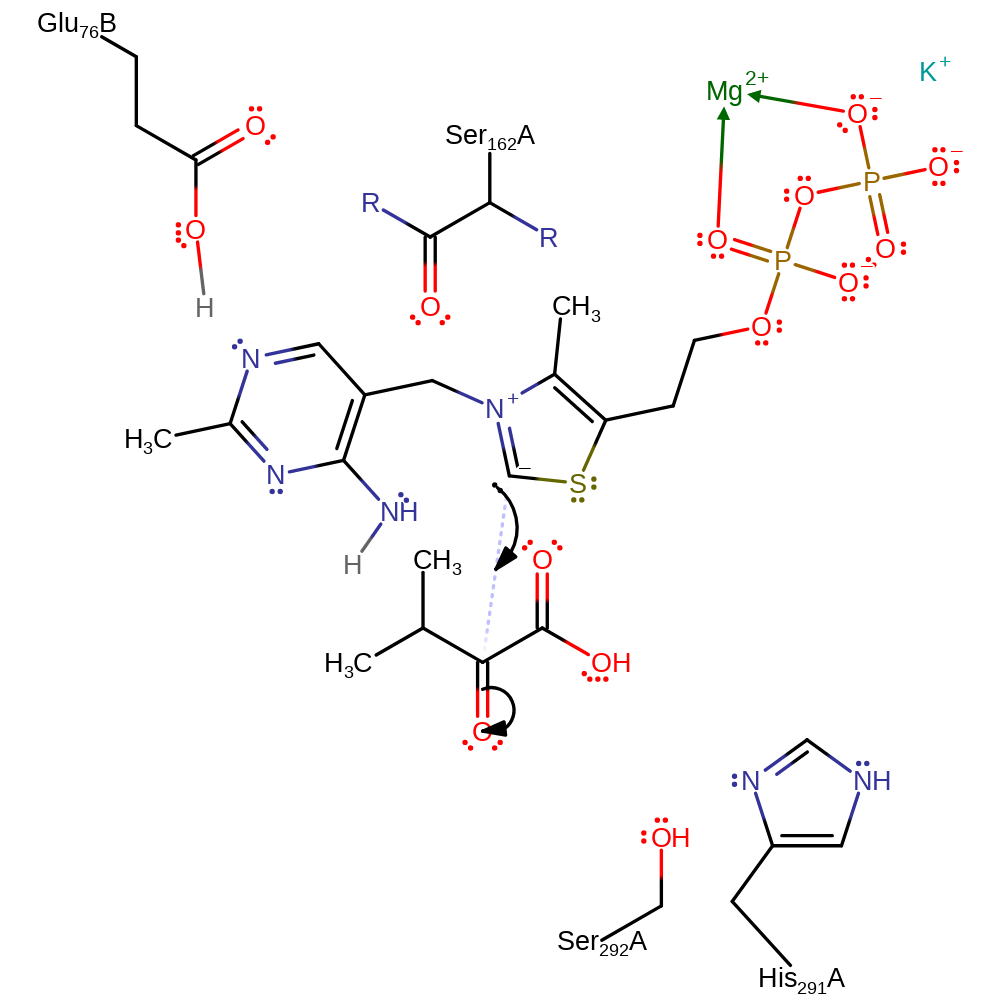
Step 2. The thiamine cofactor polarises the substrate carbonyl, increasing its reactivity towards the carbanion [PMID:10426958]. The cofactor anion attacks at the substrate carbonyl, forming a tetrahedral intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His291A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu76A(BA) | hydrogen bond donor, steric role |
| Ser292A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Ser162A (main-C) | hydrogen bond acceptor, steric role |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, intermediate formation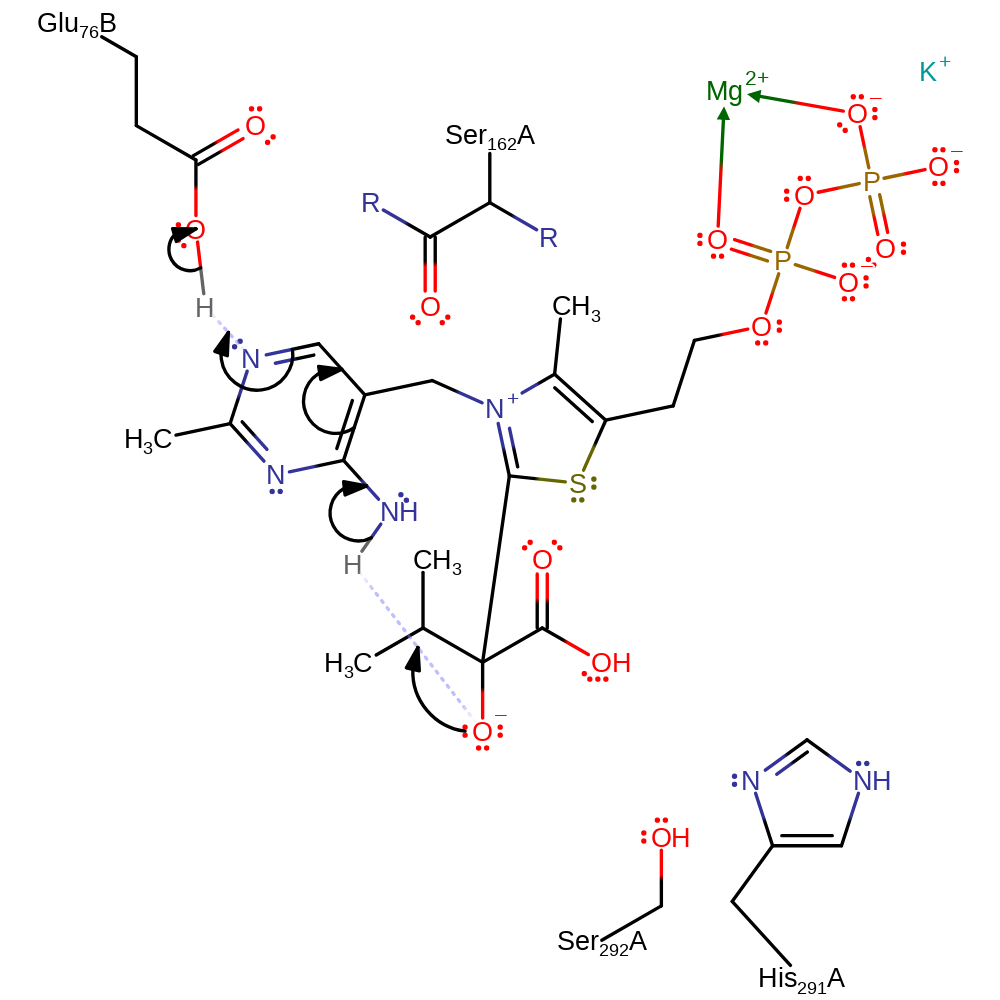
Step 3. The tetrahedral anion intermediate removes the N(1) proton from the imine ring. This results in the deprotonation of Glu76'.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His291A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu76A(BA) | activator, steric role, hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser292A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser162A (main-C) | hydrogen bond acceptor, steric role |
| Glu76A(BA) | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, intermediate formation
Step 4. His291 induces decarboxylation from the cofactor-substrate intermediate by abstracting a proton. The presence of a proton acceptor close to the departing carboxyl group lowers the activation barrier associated with decarboxylation [PMID:10426958].
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His291A | activator, hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu76A(BA) | hydrogen bond acceptor, steric role |
| Ser292A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser162A (main-C) | hydrogen bond acceptor, steric role |
| His291A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular elimination, decarboxylation, overall product formed, intermediate collapse, intermediate formation
Step 5. The disulfide bridge of lipoamide E is broken by nucleophilic attack.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His291A | activator, hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu76A(BA) | hydrogen bond acceptor, steric role |
| Ser292A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser162A (main-C) | hydrogen bond acceptor, steric role |
| His291A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, proton transfer, intermediate formation, overall reactant used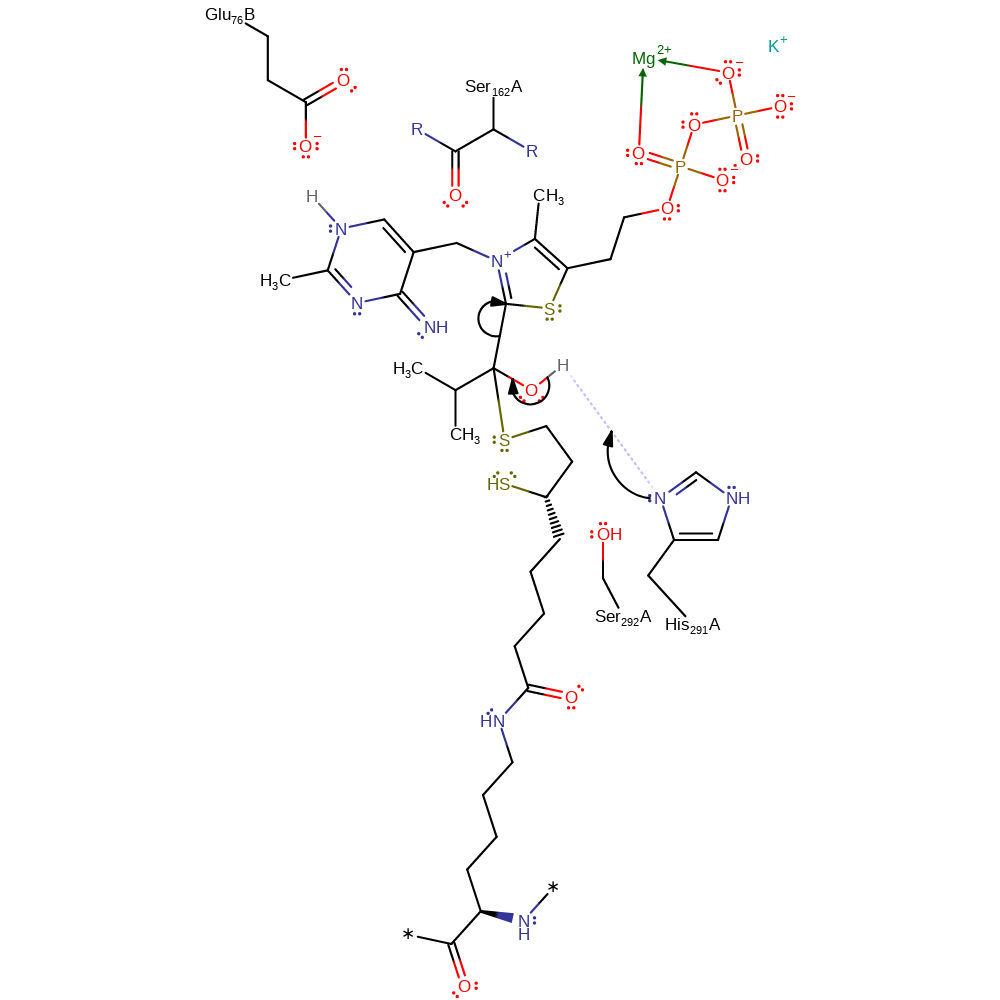
Step 6. His291 initiates the collapse of the intermediate with concomitant product formation.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His291A | activator, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu76A(BA) | hydrogen bond acceptor, steric role |
| Ser292A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser162A (main-C) | hydrogen bond acceptor, steric role |
| His291A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular elimination, intermediate collapse, overall product formed, intermediate formation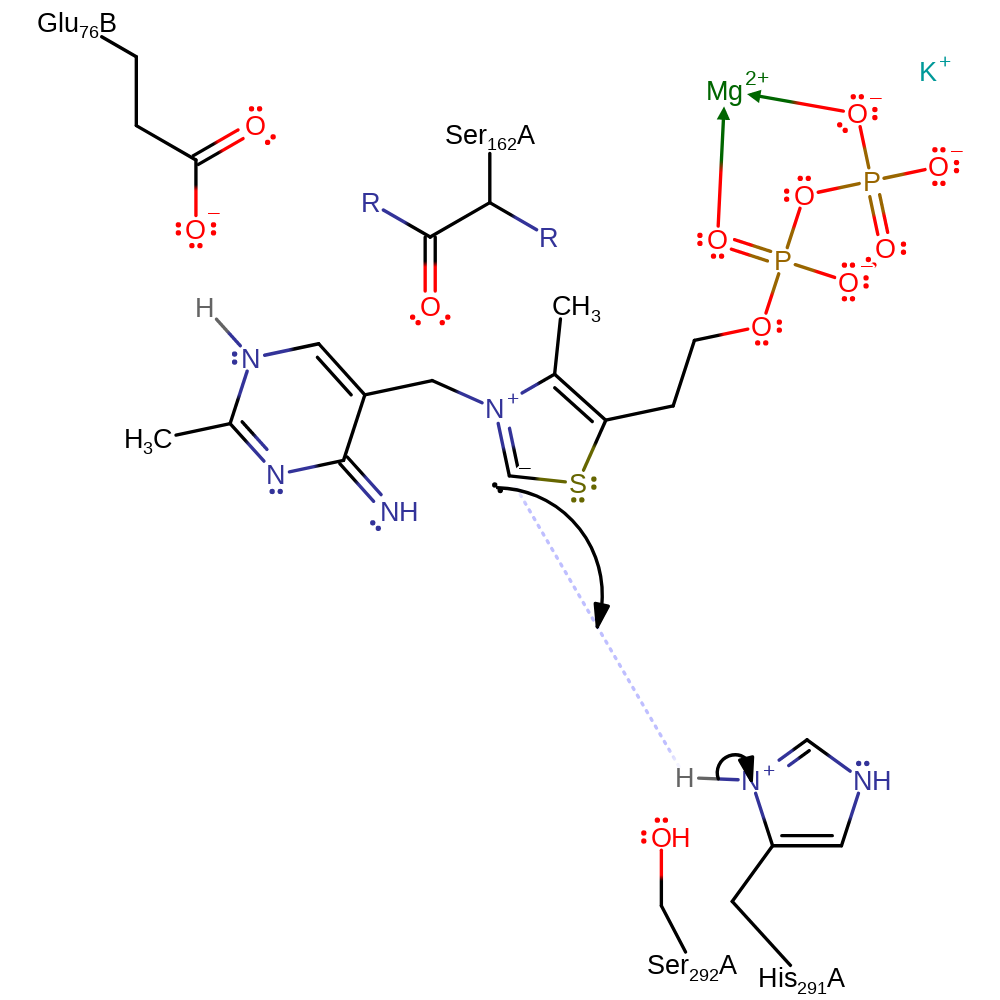
Step 7. The thiamine diphosphate cofactor is regenerated by abstracting a proton from the positively charged imidazole ring of His291.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| His291A | activator, hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu76A(BA) | hydrogen bond acceptor, steric role |
| Ser292A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser162A (main-C) | hydrogen bond acceptor, steric role |
| His291A | proton donor |





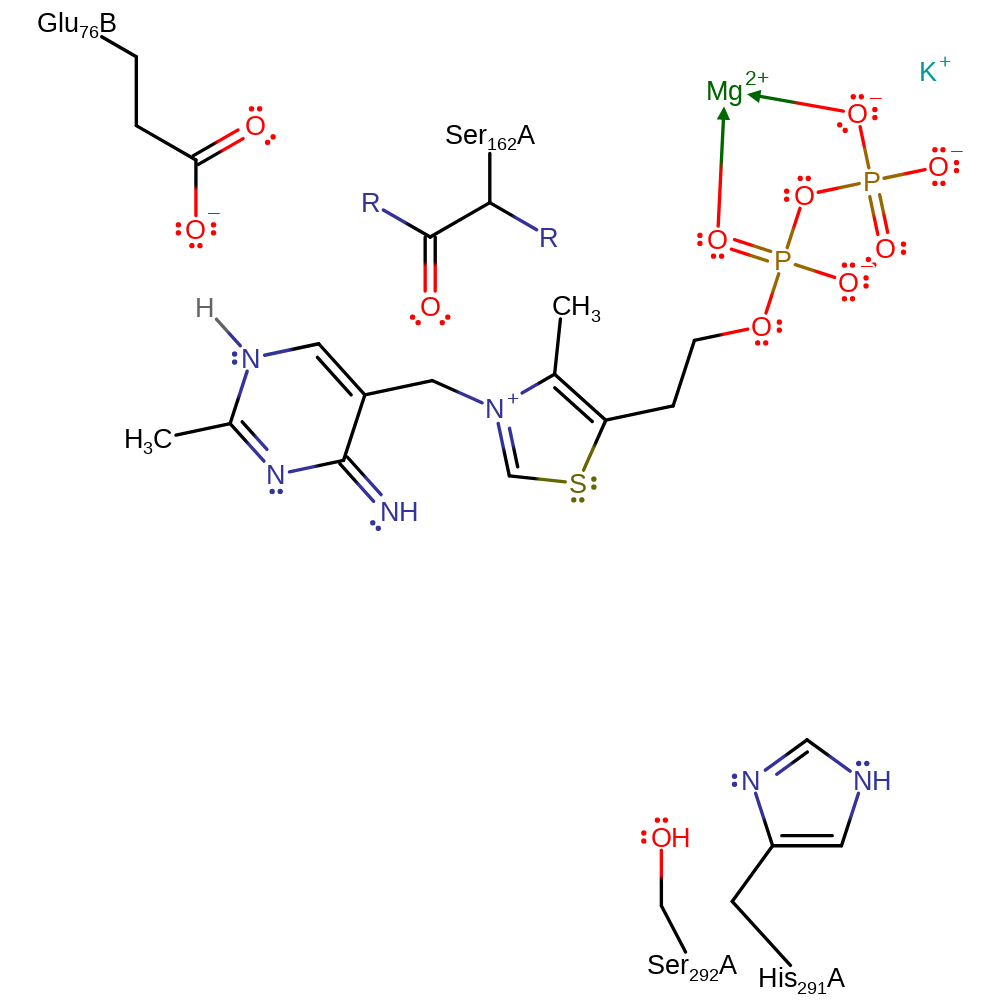 Download:
Download: