Phosphoinositide phospholipase C
Mammalian phospholipase C catalyses the hydrolysis of inositol lipid to inositol 1,4,5 trisphosphate and diacyl glycerol, both of which are important second messengers in Ca(II) signalling pathways. It possesses a Triose phosphate isomerase-like catalytic domain, indicating some homology with triosephosphate isomerase, but catalyses a different reaction by a mechanism more similar to the T1 RNAases.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P10688
 (3.1.4.11)
(3.1.4.11)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Rattus norvegicus (Norway rat)

- PDB
-
1djx
- PHOSPHOINOSITIDE-SPECIFIC PHOSPHOLIPASE C-DELTA1 FROM RAT COMPLEXED WITH INOSITOL-1,4,5-TRISPHOSPHATE
(2.3 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.20.20.190
 (see all for 1djx)
(see all for 1djx)
- Cofactors
- Calcium(2+) (1) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Reaction (EC:3.1.4.11)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The OH group on C2 acts as a nucleophile, activated by the general base Glu 341, and forms a cyclic phosphate intermediate, with the release of DAG facilitated by the general acid His 356. The intermediate, stabilised by Ca2+ and His 311, is then hydrolysed by a water molecule activated by His 356 to give 1,4,5,inositol trisphosphate and complete the reaction cycle.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1djx) | ||
| Glu390 | Glu390(258)A | Acts as general base to deprotonate the C2 OH of the inositol so that it can act as a nucleophile and attack the phosphate to form the cyclic intermediate, releasing DAG. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, metal ligand, proton acceptor, proton donor, increase acidity |
| His356 | His356(224)A | Activates water by deprotonation to allow it to act as a nucleophile and hydrolyse the cyclic phosphate intermediate. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Glu341 | Glu341(209)A | Could also act as the general acid/base in this reaction. | hydrogen bond acceptor, metal ligand, electrostatic stabiliser, increase acidity |
| His311 | His311(179)A | Forms hydrogen bonds to stabilise the cyclic intermediate structure which then collapses to release the products. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn312, Asp343 | Asn312(180)A, Asp343(211)A | Binds Ca(II) ion. | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
intramolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall reactant used, overall product formed, cyclisation, intermediate formation, proton transfer, bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, decyclisation, intermediate terminated, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Essen LO et al. (1997), Biochemistry, 36, 1704-1718. Structural Mapping of the Catalytic Mechanism for a Mammalian Phosphoinositide-Specific Phospholipase C†,‡. DOI:10.1021/bi962512p. PMID:9048554.
- Apiyo D et al. (2005), Biochemistry, 44, 9980-9989. X-ray Structure of the R69D Phosphatidylinositol-Specific Phospholipase C Enzyme: Insight into the Role of Calcium and Surrounding Amino Acids in Active Site Geometry and Catalysis. DOI:10.1021/bi047896v. PMID:16042375.
- Heinz DW et al. (1998), J Mol Biol, 275, 635-650. Structural and mechanistic comparison of prokaryotic and eukaryotic phosphoinositide-specific phospholipases C. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.1997.1490. PMID:9466937.
- Ellis MV et al. (1998), J Biol Chem, 273, 11650-11659. Catalytic Domain of Phosphoinositide-specific Phospholipase C (PLC). MUTATIONAL ANALYSIS OF RESIDUES WITHIN THE ACTIVE SITE AND HYDROPHOBIC RIDGE OF PLCdelta 1. DOI:10.1074/jbc.273.19.11650. PMID:9565585.
- Essen LO et al. (1996), Nature, 380, 595-602. Crystal structure of a mammalian phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase Cδ. DOI:10.1038/380595a0. PMID:8602259.
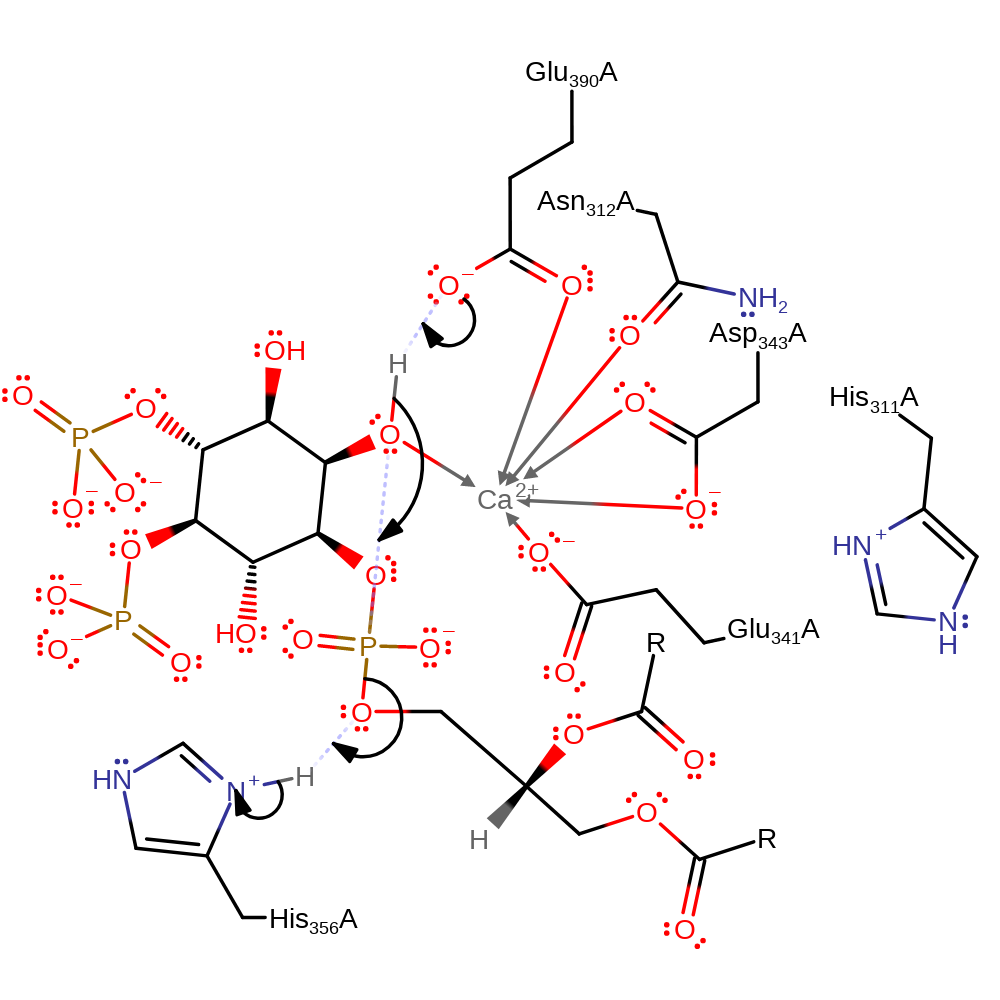
Step 1. Glu390 deprotonates the hydroxyl group adjacent to the phosphate, which initiates a nucleophilic attack on the phosphorus in a substitution reaction that eliminates diacylglycerol which deprotonates His356.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu341(209)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, increase acidity, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His356(224)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu390(258)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, increase acidity |
| His311(179)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu390(258)A | metal ligand |
| Asp343(211)A | metal ligand |
| Glu341(209)A | metal ligand |
| Asn312(180)A | metal ligand |
| Glu390(258)A | proton acceptor |
| His356(224)A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: intramolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall reactant used, overall product formed, cyclisation, intermediate formation, proton transfer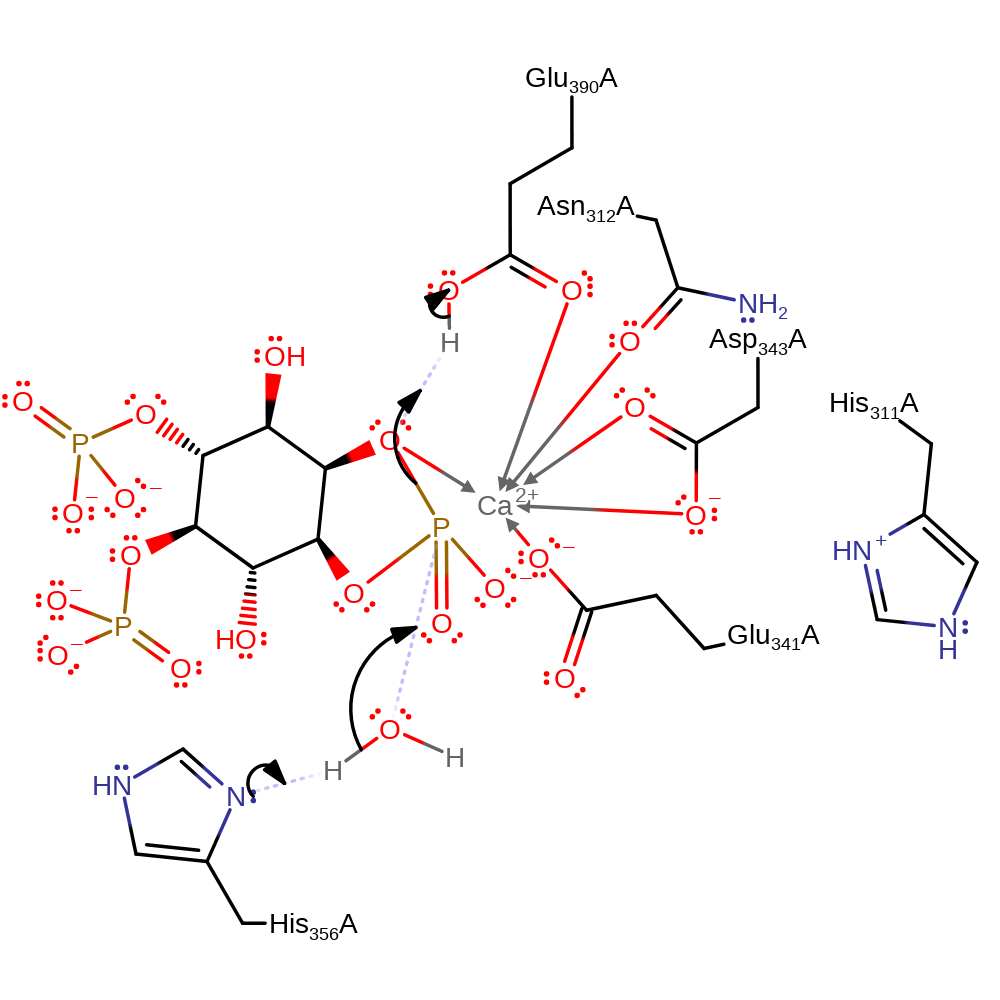
Step 2. His356 deprotonates water, which initiates a nucleophilic attack upon the phosphorus in a substitution reaction. The initial attacking hydroxyl is regenerated and deprotonates Glu390.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu341(209)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His356(224)A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Glu390(258)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| His311(179)A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu390(258)A | metal ligand |
| Asp343(211)A | metal ligand |
| Glu341(209)A | metal ligand |
| Asn312(180)A | metal ligand |
| His356(224)A | proton acceptor |
| Glu390(258)A | proton donor |





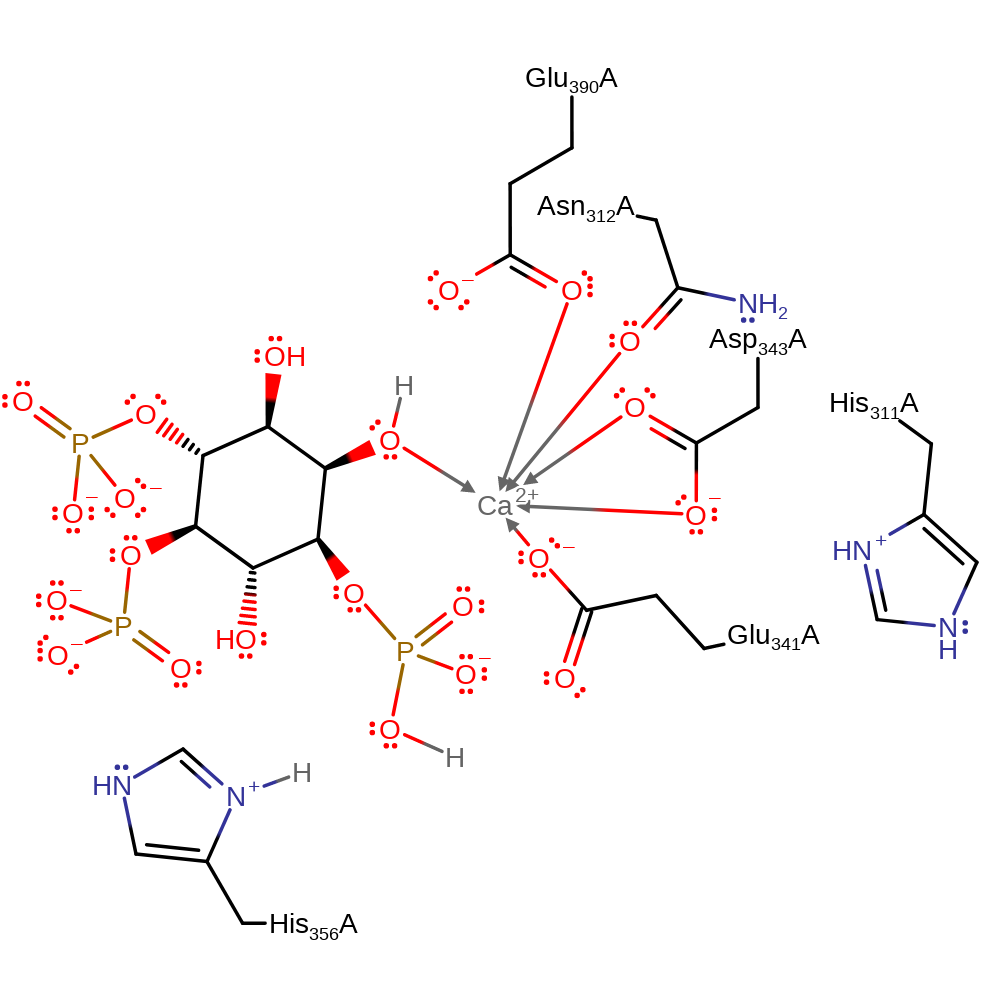 Download:
Download: