Mercury(II) reductase
Mercuric reductase is responsible for detoxifying and volatilising mercury as Hg0. The catalytic centre is activated when in the diol form, rather than the disulfide. This preliminary, activating reduction step is proposed to involve another NADPH molecule. Both forms are present under physiological conditions and have been identified by structural data [PMID:16114877, PMID:2067577].
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P00392
 (1.16.1.1)
(1.16.1.1)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Pseudomonas aeruginosa (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1zk7
- Crystal Structure of Tn501 MerA
(1.6 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.30.390.30
 3.50.50.60
3.50.50.60  (see all for 1zk7)
(see all for 1zk7)
- Cofactors
- Fadh2(2-) (1) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Reaction (EC:1.16.1.1)
Enzyme Mechanism
- Summary
- Step 1
- Step 2
- Step 3
- Step 4
- Step 5
- Step 6
- Step 7
- Step 8
- Step 9
- Step 10
- Step 11
- Step 12
- Step 13
- Step 14
- Step 15
- Products
- All Steps
Introduction
The first steps of this mechanism are responsible for moving the Hg(II) ion from the N-terminus of the protein to where the FAD is bound. The NADPH substrate transfers a hydride to the FAD cofactor. The FAD cofactor now attacks the mercury centre, eliminating Cys136 and forming a carbon-mercury intermediate. Cys136 abstracts a proton from the flavin-mercury adduct, initiating a reductive elimination of the mercury metal and thiolate Cys141. The active site is regenerated when Cys558' is reprotonated.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1zk7) | ||
| Tyr62, Met9 | Not found, Not found | Help stabilise and hold in place the reactive intermediates formed during the course of the reaction. | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys11, Cys141, Cys14, Cys136, Cys558, Cys559 | Not found, Cys47A, Not found, Cys42A, Cys464A(AA), Cys465A(AA) | The cysteine "pairs" act as nucleophiles to reduce the Hg(II) to Hg(0). The two N terminal Cys residues (Cys11/Cys14) form part of the soft-metal binding domain. | covalently attached, nucleofuge, nucleophile, metal ligand, proton donor, proton acceptor, activator, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall reactant used, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation, proton transfer, coordination to a metal ion, decoordination from a metal ion, overall product formed, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, hydride transfer, cofactor used, elimination (not covered by the Ingold mechanisms), native state of cofactor regenerated, native state of enzyme regenerated, inferred reaction stepReferences
- Ledwidge R et al. (2005), Biochemistry, 44, 11402-11416. NmerA, the Metal Binding Domain of Mercuric Ion Reductase, Removes Hg2+from Proteins, Delivers It to the Catalytic Core, and Protects Cells under Glutathione-Depleted Conditions†,‡. DOI:10.1021/bi050519d. PMID:16114877.
- Ledwidge R et al. (2010), Biochemistry, 49, 8988-8998. NmerA of Tn501Mercuric Ion Reductase: Structural Modulation of the pKaValues of the Metal Binding Cysteine Thiols,. DOI:10.1021/bi100537f. PMID:20828160.
- Schue M et al. (2008), Biometals, 21, 107-116. Evidence for direct interactions between the mercuric ion transporter (MerT) and mercuric reductase (MerA) from the Tn501 mer operon. DOI:10.1007/s10534-007-9097-4. PMID:17457514.
- Cummings RT et al. (1992), Biochemistry, 31, 1020-1030. Interaction of Tn501 mercuric reductase and dihydroflavin adenine dinucleotide anion with metal ions: implications for the mechanism of mercuric reductase mediated mercury(II) reduction. DOI:10.1021/bi00119a010. PMID:1310417.
- Schiering N et al. (1991), Nature, 352, 168-172. Structure of the detoxification catalyst mercuric ion reductase from Bacillus sp. strain RC607. DOI:10.1038/352168a0. PMID:2067577.
- Moore MJ et al. (1990), Acc Chem Res, 23, 301-308. Organomercurial lyase and mercuric ion reductase: nature's mercury detoxification catalysts. DOI:10.1021/ar00177a006.
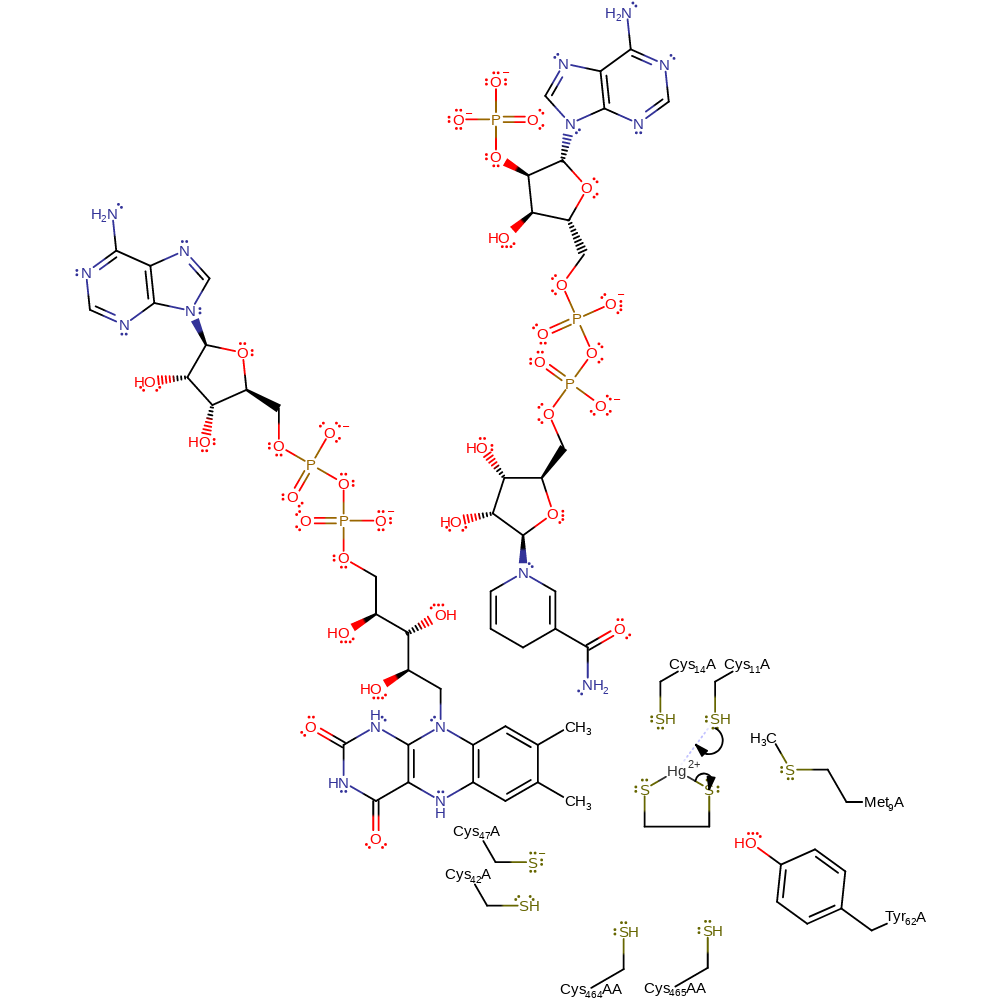
Step 1. The catalytic centre is activated towards its function in the presence of NADPH. The group reduces a disulfide bond between Cys141 and Cys136, forming the dithiol species which is necessary for catalysis to occur. A charge transfer complex exists between the FAD cofactor and Cys141 [DOI:10.1021/ar00177a006]. The two N terminal Cys residues (Cys11/Cys14) form part of a soft-metal binding domain. The positive charge of the N terminus, as well as the presence of specific interactions with surrounding residues lowers the pKa of these cysteine thiols relative to unstructured peptide analogues, enhancing their nucleophilic character and therefore their reactivity with Hg over other peptide sequences. Thus, in this step the distal sulfur of Cys11 acts as a nucleophile towards the Hg(II) complex.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Met9 | steric role, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr62 | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys14 | electrostatic stabiliser, increase nucleophilicity |
| Cys11 | activator, metal ligand |
| Cys11 | nucleophile |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall reactant used, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation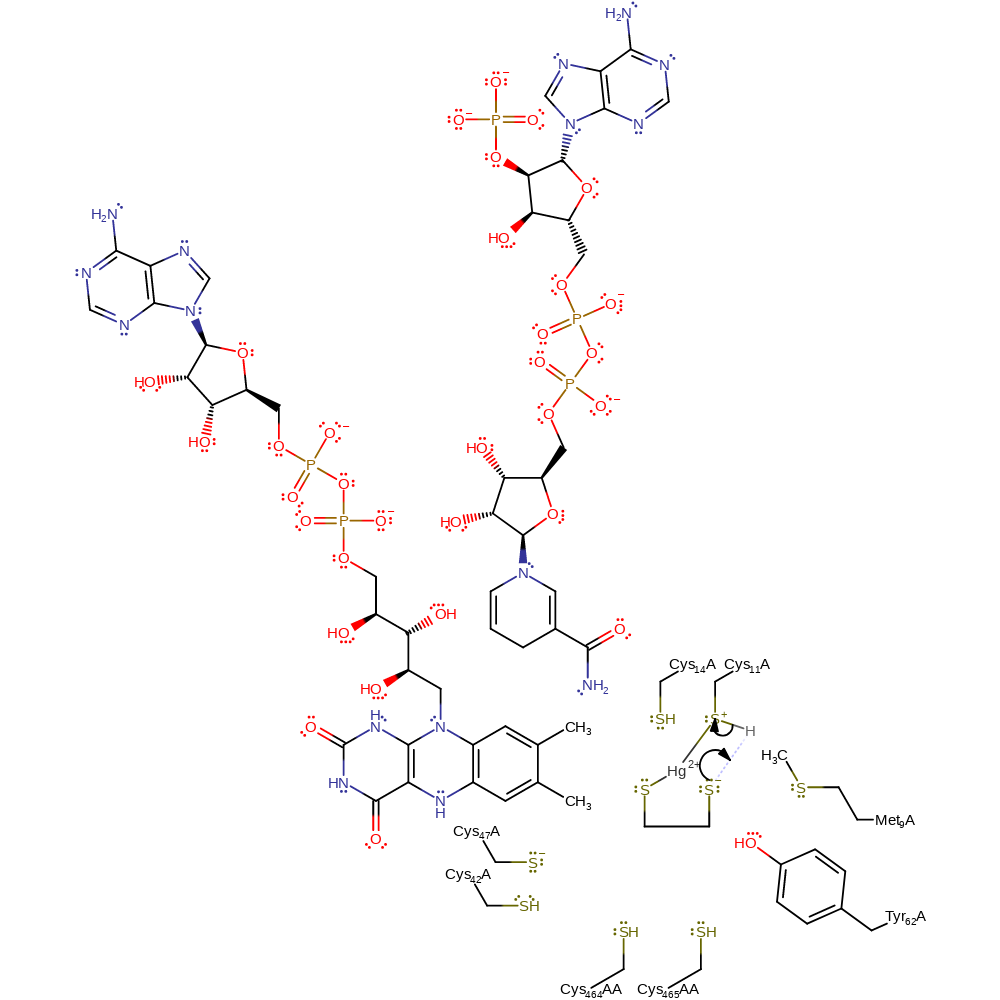
Step 2. The thiolate anion formed on the substrate acts as a base towards the protonated Cys11.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Met9 | steric role, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr62 | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys14 | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys11 | activator, covalently attached, metal ligand |
| Cys11 | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, intermediate formation
Step 3. The adjacent sulfur of Cys14 acts as a nucleophile towards the mercury-enzyme adduct. This releases the mercury free thiol-thiolate molecule with concomitant formation of a bridged thio-mercury enzyme complex.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Met9 | steric role, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr62 | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys14 | activator |
| Cys11 | activator, metal ligand |
| Cys14 | nucleophile |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, intermediate formation, coordination to a metal ion, decoordination from a metal ion, enzyme-substrate complex formation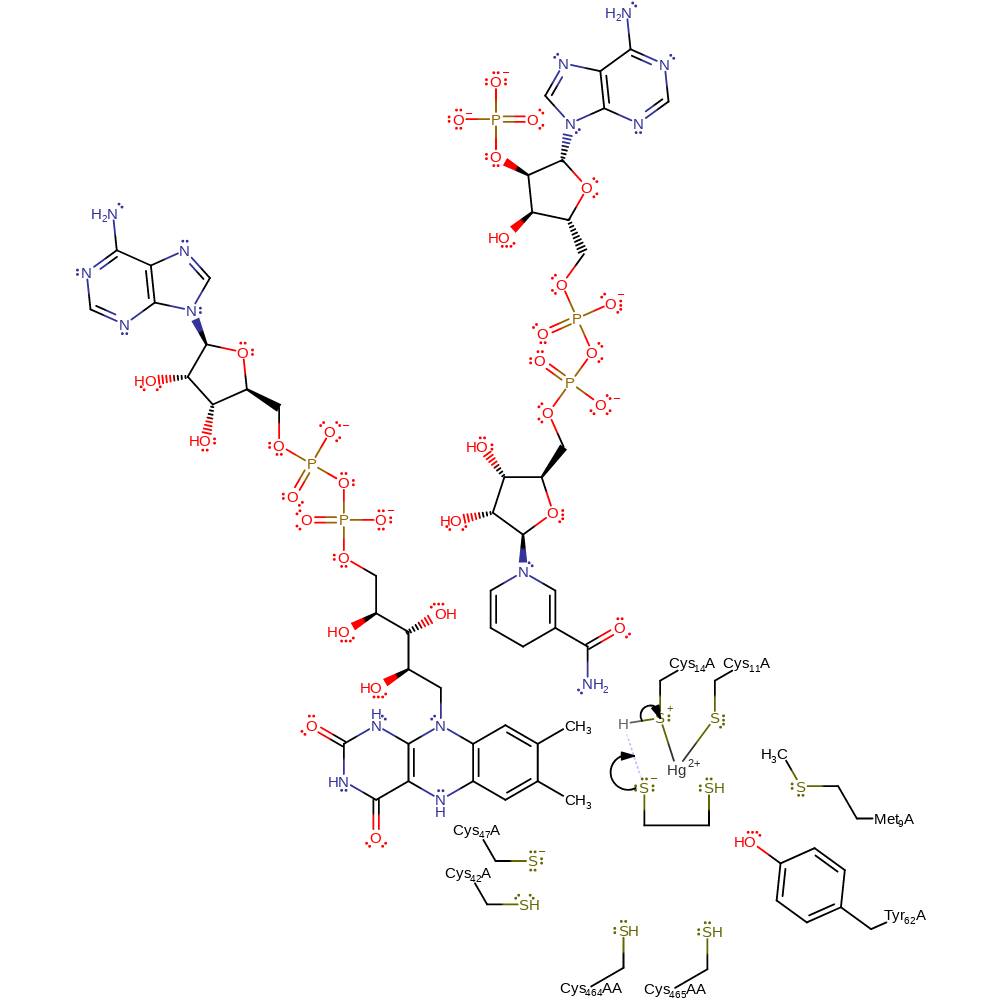
Step 4. The charged sulfur of the eliminated group removes a proton from the positively charged mercury-cysteine adduct. The dithiol equivalent of the substrate is released.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Met9 | steric role, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr62 | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys465A(AA) | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys14 | metal ligand, covalently attached |
| Cys11 | metal ligand, covalently attached |
| Cys47A | polar interaction |
| Cys14 | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, overall product formed, intermediate formation
Step 5. The mercury metal is transferred from the N terminal binding site to a thiol pair situated more closely within the active site [PMID:16114877]. Cys559AA acts as a nucleophile towards the Hg(II) metal, displacing it from the metal binding motif.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Met9 | steric role, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr62 | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys465A(AA) | metal ligand |
| Cys14 | activator, covalently attached |
| Cys11 | activator, covalently attached, metal ligand |
| Cys11 | nucleofuge |
| Cys465A(AA) | nucleophile |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation
Step 6. The Cys11 thiolate now acts as a base towards the positively charged Cys559AA, regenerating one of the soft-metal binding motif thiols.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Met9 | electrostatic stabiliser, steric role |
| Tyr62 | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys465A(AA) | metal ligand, covalently attached |
| Cys14 | activator, covalently attached, metal ligand, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys11 | activator |
| Cys11 | proton acceptor |
| Cys465A(AA) | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, intermediate formation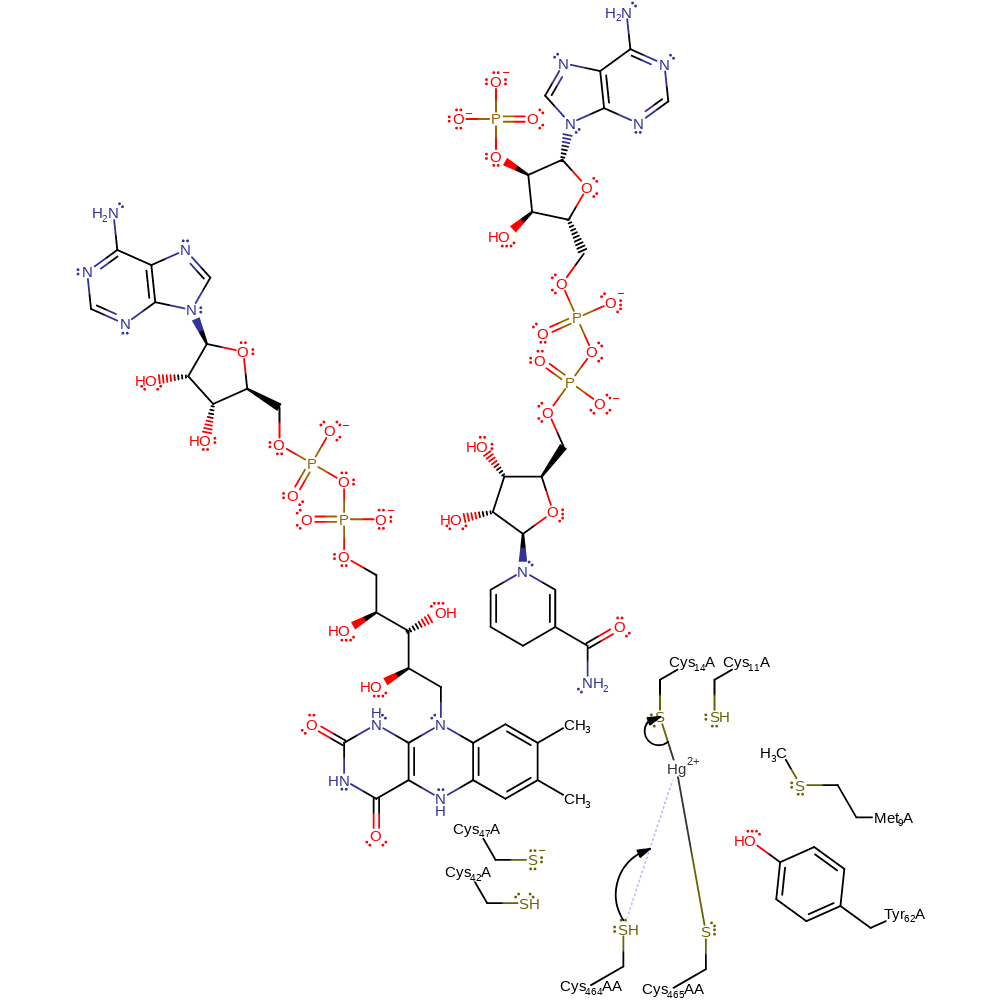
Step 7. Cys558AA now attacks the mercury, forming a sulfide-mercury link while eliminating the Cys14 thiolate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys464A(AA) | activator |
| Met9 | steric role, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr62 | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys465A(AA) | covalently attached, electrostatic stabiliser, metal ligand |
| Cys14 | activator |
| Cys11 | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys42A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys14 | nucleofuge |
| Cys464A(AA) | nucleophile |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation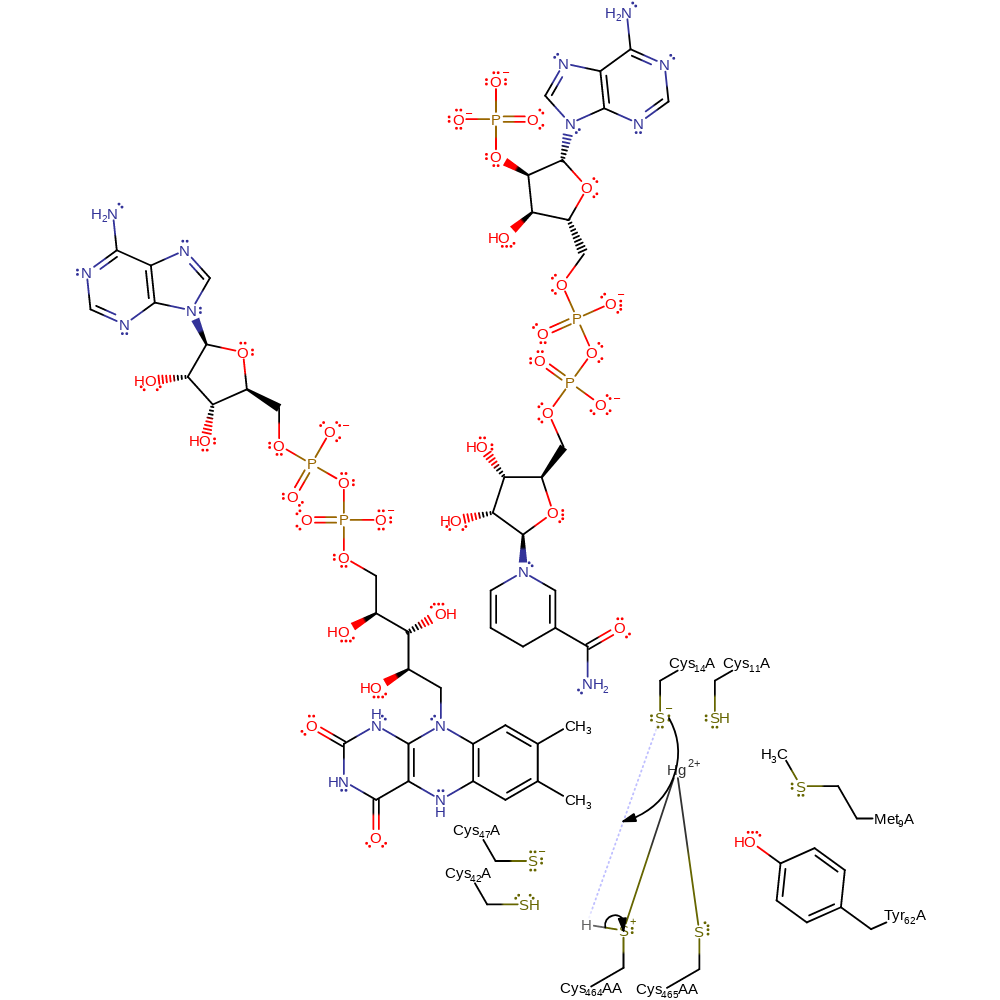
Step 8. The thiolate form of Cys14 abstracts a proton from the positively charged sulfur of Cys558AA.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys464A(AA) | activator, metal ligand |
| Met9 | steric role, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr62 | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys465A(AA) | activator, covalently attached, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys14 | activator |
| Cys11 | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys42A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys14 | proton acceptor |
| Cys464A(AA) | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, intermediate formation
Step 9. Cys136 acts as a nucleophile towards the close proximity mercury-thiol adduct, forming another metal-ligand bridging intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys464A(AA) | activator, metal ligand, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Met9 | steric role, increase nucleophilicity |
| Tyr62 | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys465A(AA) | activator |
| Cys42A | activator |
| Cys465A(AA) | nucleofuge |
| Cys42A | nucleophile |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, intermediate formation, enzyme-substrate complex formation, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage
Step 10. The resulting positively charged sulfur is deprotonated by Cys559AA
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys464A(AA) | activator, metal ligand, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Met9 | steric role, increase nucleophilicity |
| Tyr62 | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys465A(AA) | activator |
| Cys42A | activator |
| Cys465A(AA) | proton acceptor |
| Cys42A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, intermediate formation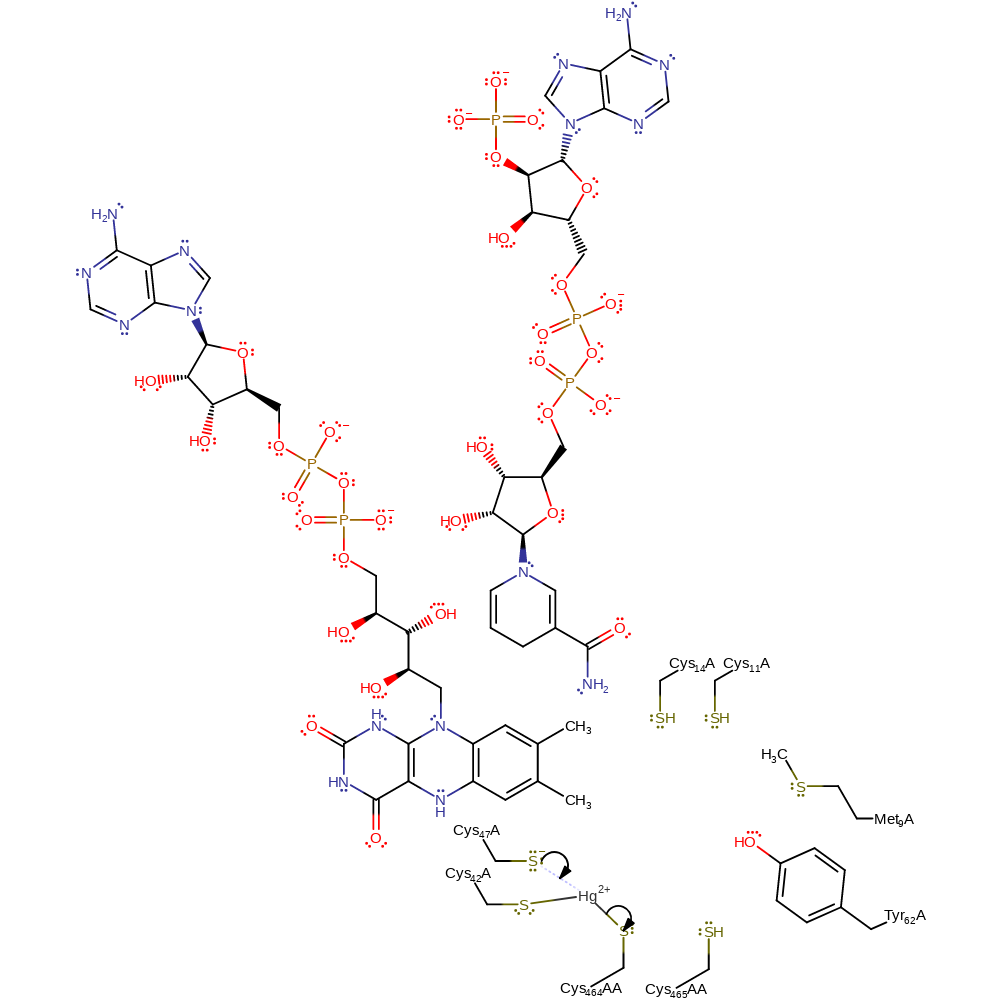
Step 11. Cys141 displaces Cys558AA within the metal coordination sphere.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys464A(AA) | activator |
| Met9 | steric role |
| Tyr62 | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys47A | activator |
| Cys42A | covalently attached |
| Cys464A(AA) | nucleofuge |
| Cys47A | nucleophile |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, coordination to a metal ion, decoordination from a metal ion, enzyme-substrate complex formation, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, intermediate formationCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Met9 | steric role |
| Tyr62 | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys47A | metal ligand |
| Cys42A | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
hydride transfer, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, overall product formed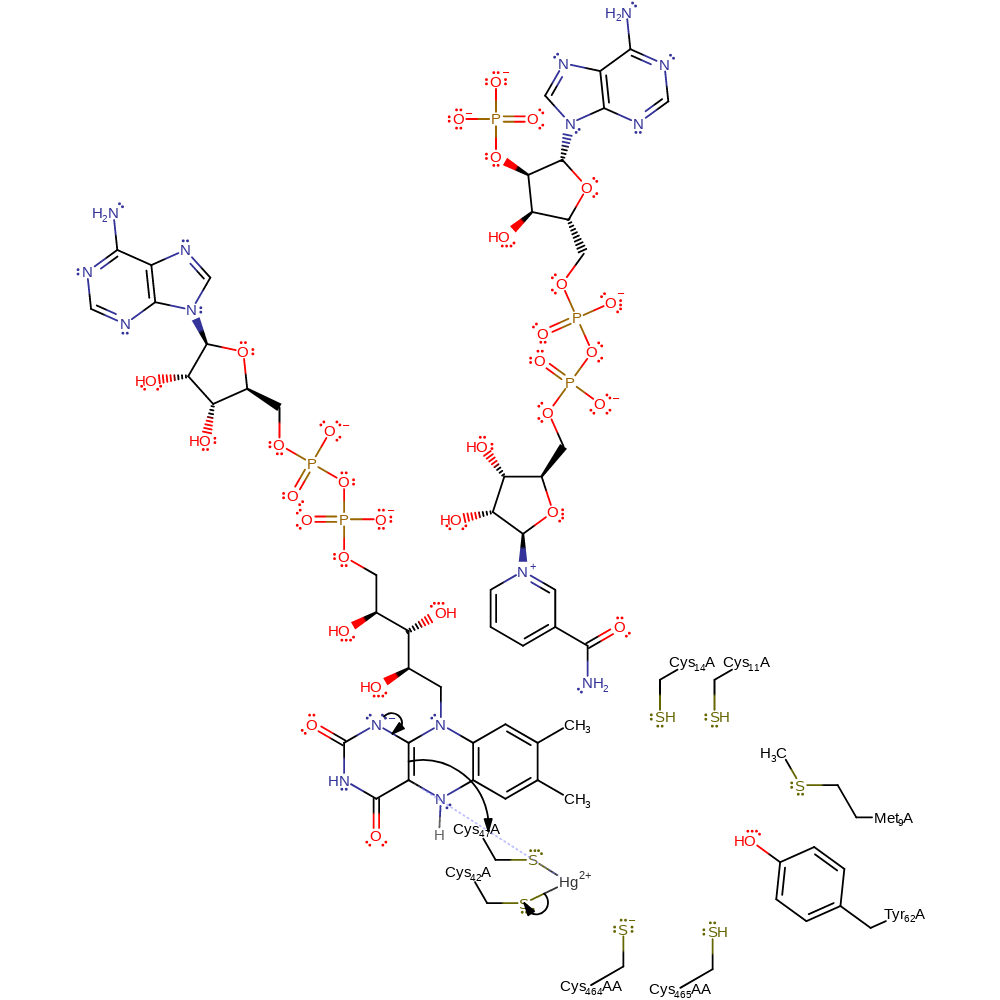
Step 13. The FAD cofactor now attacks the mercury centre, eliminating Cys136 and forming a carbon-mercury intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Met9 | steric role |
| Tyr62 | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys47A | activator, metal ligand |
| Cys42A | activator |
| Cys42A | nucleofuge |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, intermediate formation, cofactor used, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage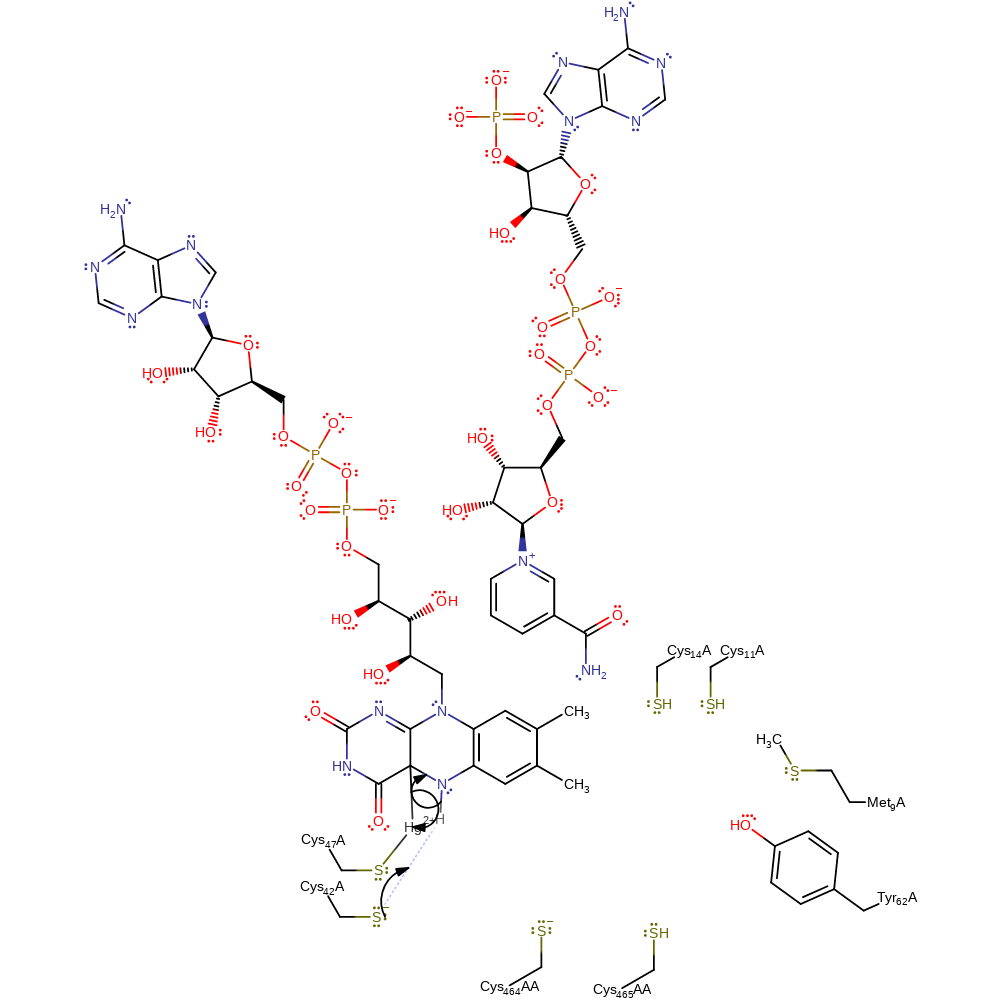
Step 14. Cys136 abstracts a proton from the flavin-mercury adduct, initiating a reductive elimination of the mercury metal and thiolate Cys141.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Met9 | steric role |
| Tyr62 | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys47A | activator |
| Cys42A | activator |
| Cys42A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, elimination (not covered by the Ingold mechanisms), native state of cofactor regenerated, overall product formed, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage
Step 15. The active site is regenerated when Cys558AA is reprotonated. In this inferred return step, the identiy of the proton donor is not clear.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys464A(AA) | activator |
| Met9 | steric role |
| Tyr62 | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys464A(AA) | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, native state of enzyme regenerated, overall reactant used, inferred reaction step- Summary
- Step 1
- Step 2
- Step 3
- Step 4
- Step 5
- Step 6
- Step 7
- Step 8
- Step 9
- Step 10
- Step 11
- Step 12
- Step 13
- Step 14
- Step 15
- Products
- All Steps
Introduction
The first steps of this mechanism are responsible for moving the Hg(II) ion from the N-terminus of the protein to where the FAD is bound. The NADPH substrate transfers a hydride to the FAD cofactor. The FAD cofactor now attacks Cys141, forming an enzyme-FAD complex with loss of Hg(0). Reductive elimination initiated by the thiolate of Cys136 regenerates the cofactor. The active site is regenerated when Cys558' is reprotonated.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1zk7) | ||
| Tyr62, Met9 | Not found, Not found | Help stabilise and hold in place the reactive intermediates formed during the course of the reaction. | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys11, Cys141, Cys14, Cys136, Cys558, Cys559 | Not found, Cys47A, Not found, Cys42A, Cys464A(AA), Cys465A(AA) | The cysteine "pairs" act as nucleophiles to reduce the Hg(II) to Hg(0). The two N terminal Cys residues (Cys11/Cys14) form part of the soft-metal binding domain. | covalently attached, nucleofuge, nucleophile, metal ligand, proton donor, proton acceptor, activator, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall reactant used, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation, proton transfer, coordination to a metal ion, decoordination from a metal ion, overall product formed, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, hydride transfer, cofactor used, elimination (not covered by the Ingold mechanisms), native state of cofactor regenerated, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Ledwidge R et al. (2005), Biochemistry, 44, 11402-11416. NmerA, the Metal Binding Domain of Mercuric Ion Reductase, Removes Hg2+from Proteins, Delivers It to the Catalytic Core, and Protects Cells under Glutathione-Depleted Conditions†,‡. DOI:10.1021/bi050519d. PMID:16114877.
- Schue M et al. (2008), Biometals, 21, 107-116. Evidence for direct interactions between the mercuric ion transporter (MerT) and mercuric reductase (MerA) from the Tn501 mer operon. DOI:10.1007/s10534-007-9097-4. PMID:17457514.
- Cummings RT et al. (1992), Biochemistry, 31, 1020-1030. Interaction of Tn501 mercuric reductase and dihydroflavin adenine dinucleotide anion with metal ions: implications for the mechanism of mercuric reductase mediated mercury(II) reduction. DOI:10.1021/bi00119a010. PMID:1310417.
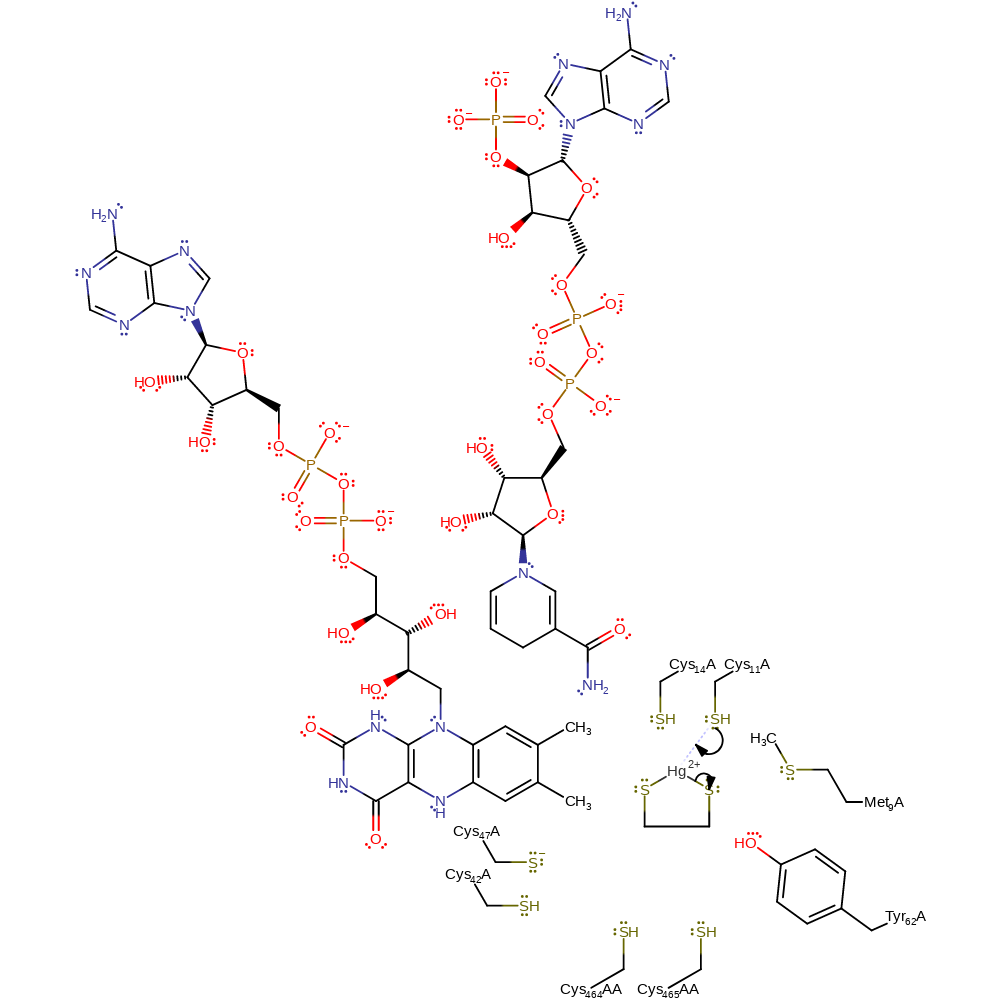
Step 1. The catalytic centre is activated towards its function in the presence of NADPH. The group reduces a disulfide bond between Cys141 and Cys136, forming the dithiol species which is necessary for catalysis to occur. A charge transfer complex exists between the FAD cofactor and Cys141 [DOI:10.1021/ar00177a006]. The two N terminal Cys residues (Cys11/Cys14) form part of a soft-metal binding domain. The positive charge of the N terminus, as well as the presence of specific interactions with surrounding residues lowers the pKa of these cysteine thiols relative to unstructured peptide analogues, enhancing their nucleophilic character and therefore their reactivity with Hg over other peptide sequences. Thus, in this step the distal sulfur of Cys11 acts as a nucleophile towards the Hg(II) complex.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Met9 | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys14 | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr62 | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Met9 | steric role |
| Tyr62 | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys14 | increase nucleophilicity |
| Cys11 | activator, metal ligand, nucleophile |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall reactant used, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation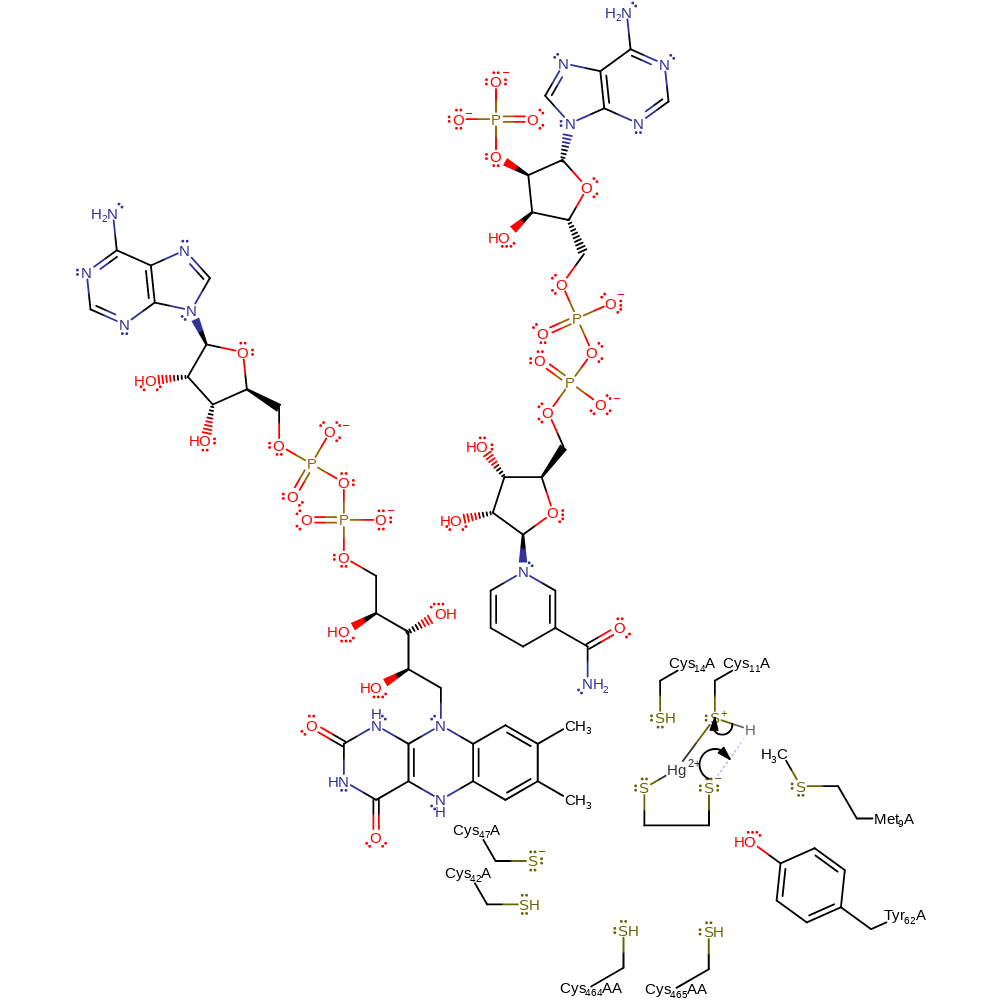
Step 2. The thiolate anion formed on the substrate acts as a base towards the protonated Cys11.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Met9 | steric role, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr62 | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys14 | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond donor |
| Cys11 | activator, covalently attached, metal ligand, proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, intermediate formation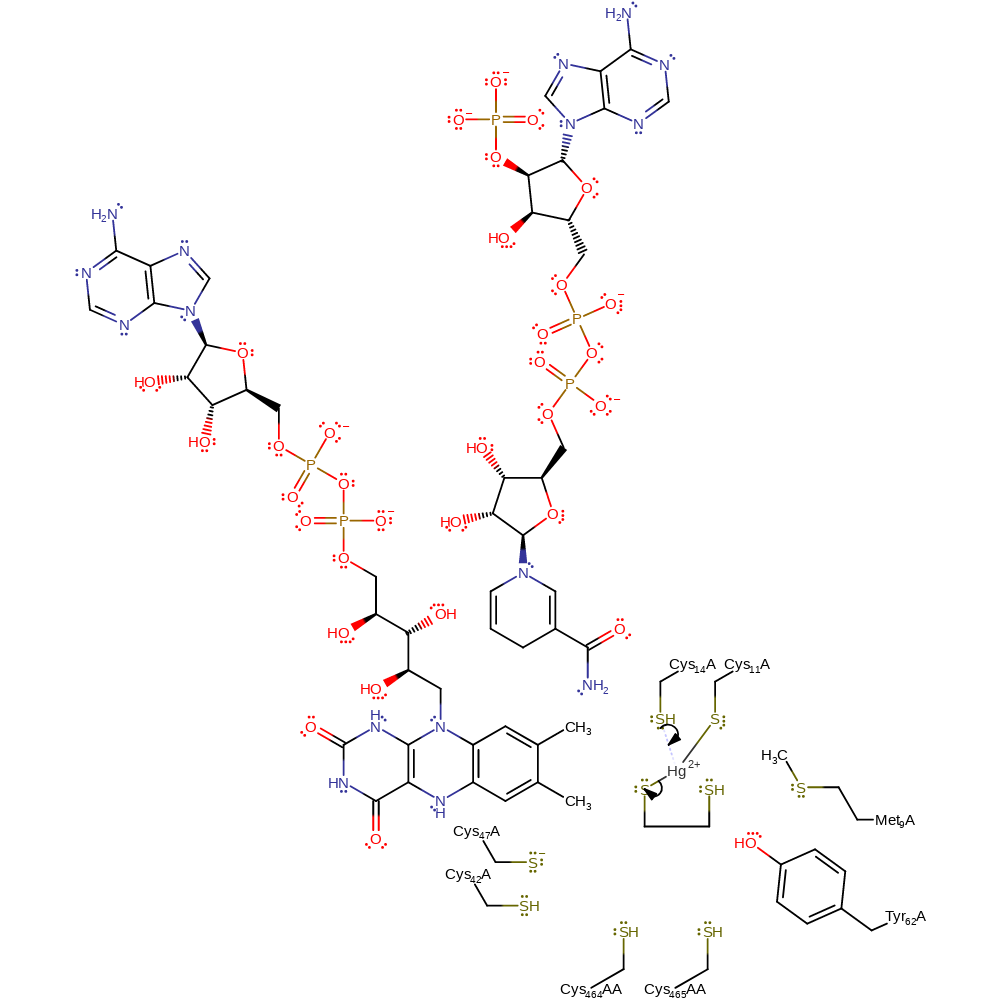
Step 3. The adjacent sulfur of Cys14 acts as a nucleophile towards the mercury-enzyme adduct. This releases the mercury free thiol-thiolate molecule with concomitant formation of a bridged thio-mercury enzyme complex.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Met9 | steric role, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr62 | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys14 | activator |
| Cys11 | activator, metal ligand |
| Cys14 | nucleophile |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, intermediate formation, coordination to a metal ion, decoordination from a metal ion, enzyme-substrate complex formation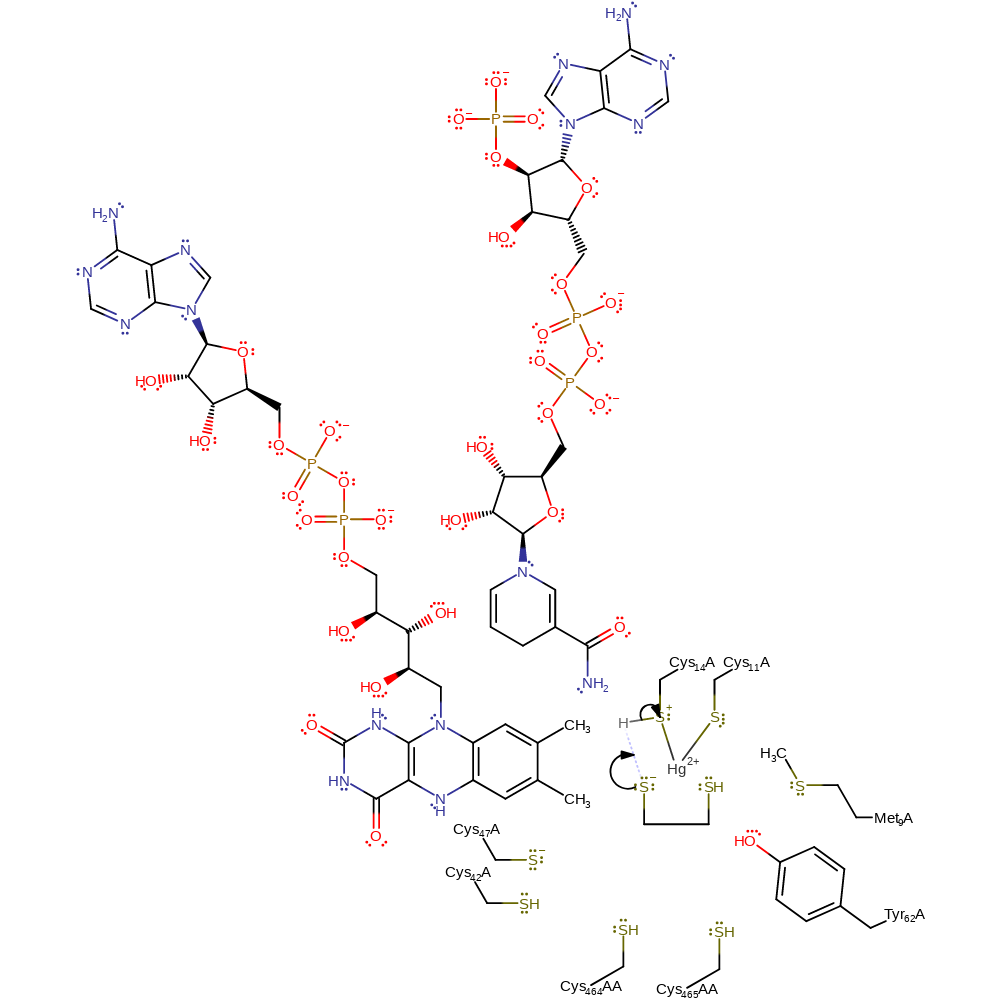
Step 4. The charged sulfur of the eliminated group removes a proton from the positively charged mercury-cysteine adduct. The dithiol equivalent of the substrate is released.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Met9 | steric role, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr62 | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys465A(AA) | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys14 | metal ligand, covalently attached |
| Cys11 | metal ligand, covalently attached |
| Cys47A | polar interaction |
| Cys14 | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, overall product formed, intermediate formation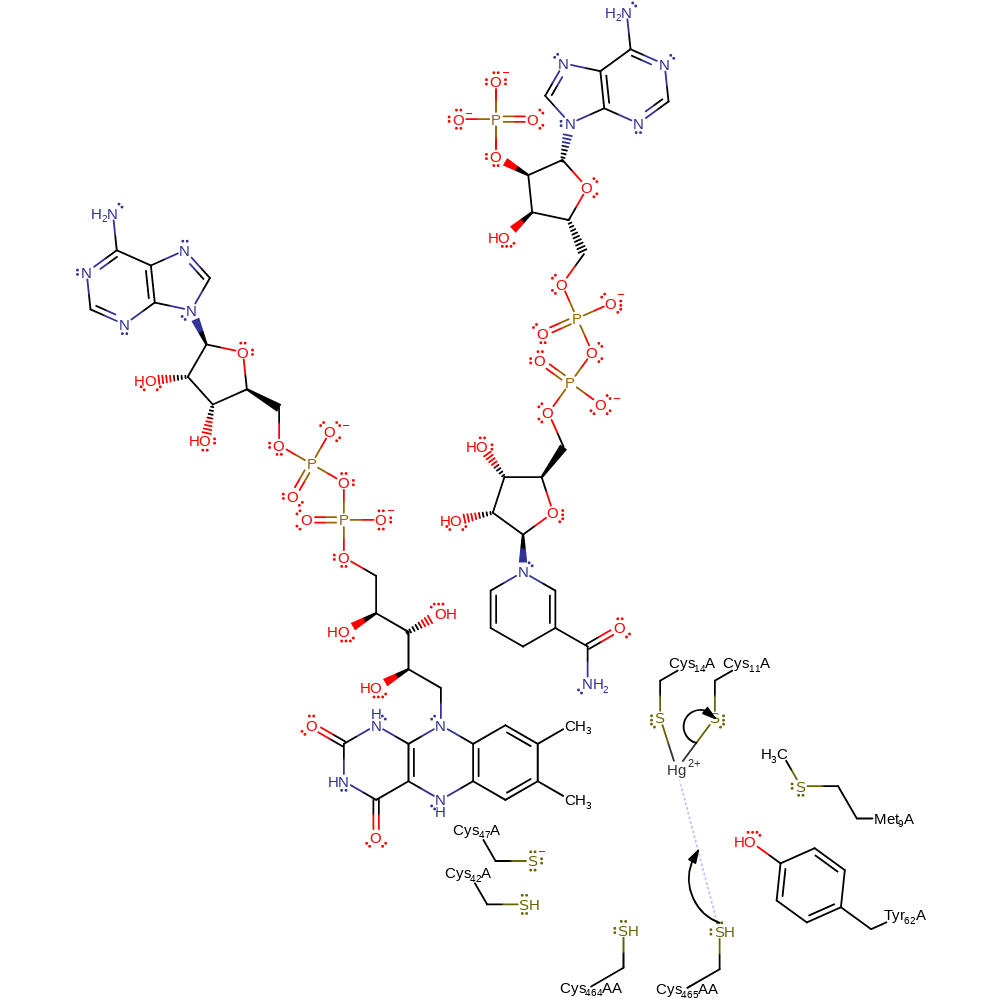
Step 5. The mercury metal is transferred from the N terminal binding site to a thiol pair situated more closely within the active site [PMID:16114877]. Cys559AA acts as a nucleophile towards the Hg(II) metal, displacing it from the metal binding motif.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Met9 | steric role, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr62 | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys465A(AA) | metal ligand |
| Cys14 | activator, covalently attached |
| Cys11 | activator, covalently attached, metal ligand |
| Cys465A(AA) | nucleophile |
| Cys11 | nucleofuge |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation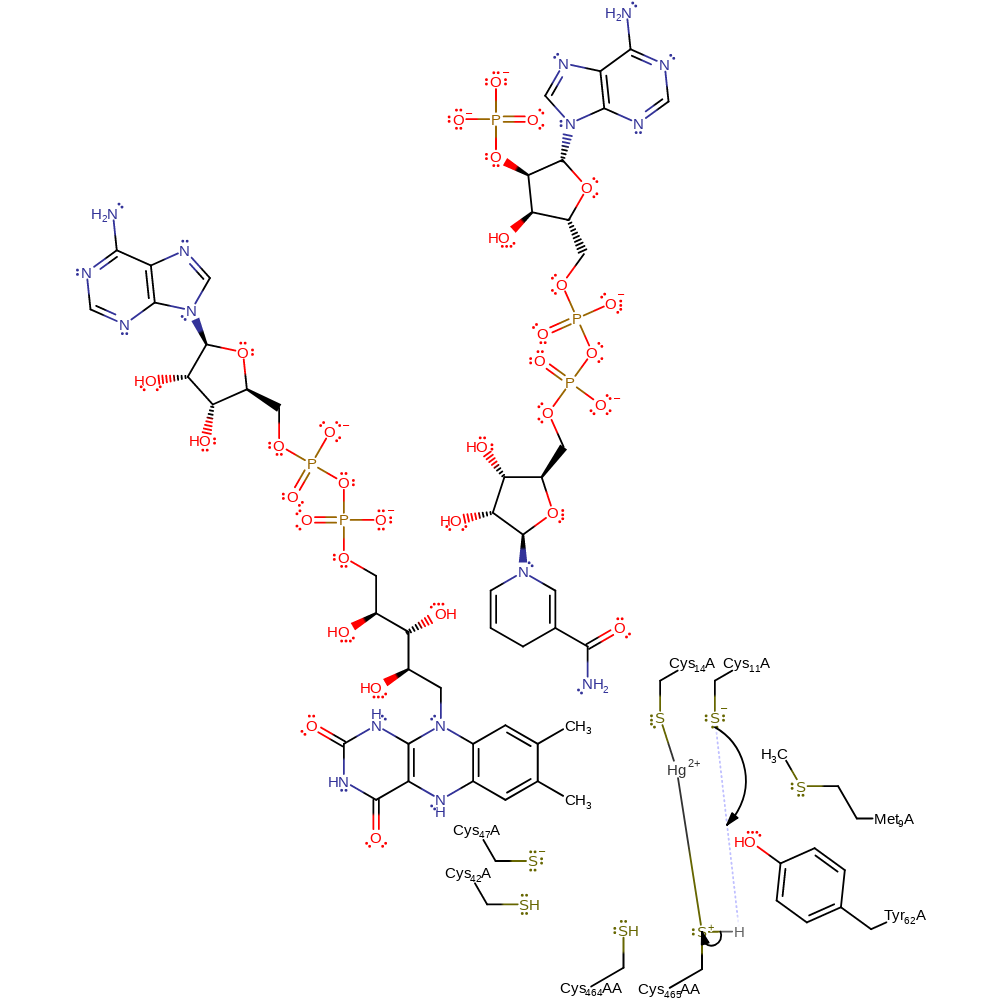
Step 6. The Cys11 thiolate now acts as a base towards the positively charged Cys559AA, regenerating one of the soft-metal binding motif thiols.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Met9 | electrostatic stabiliser, steric role |
| Tyr62 | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys465A(AA) | metal ligand, covalently attached |
| Cys14 | activator, covalently attached, metal ligand, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys11 | activator |
| Cys465A(AA) | proton donor |
| Cys11 | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, intermediate formation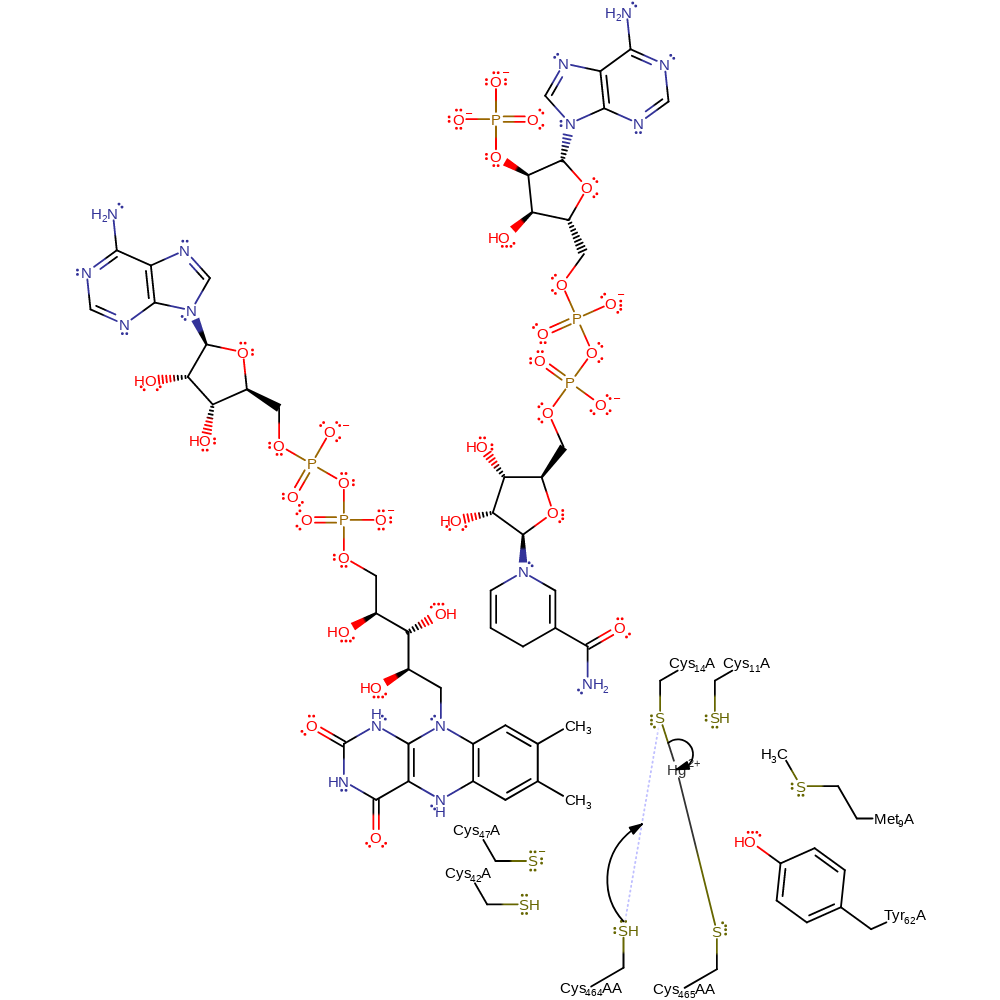
Step 7. Cys558AA now attacks the mercury, forming a sulfide-mercury link while eliminating the Cys14 thiolate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys464A(AA) | activator |
| Met9 | steric role, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr62 | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys465A(AA) | covalently attached, electrostatic stabiliser, metal ligand |
| Cys14 | activator |
| Cys11 | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys42A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys464A(AA) | nucleophile |
| Cys14 | electrofuge, electrophile |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, enzyme-substrate complex formation, intermediate formation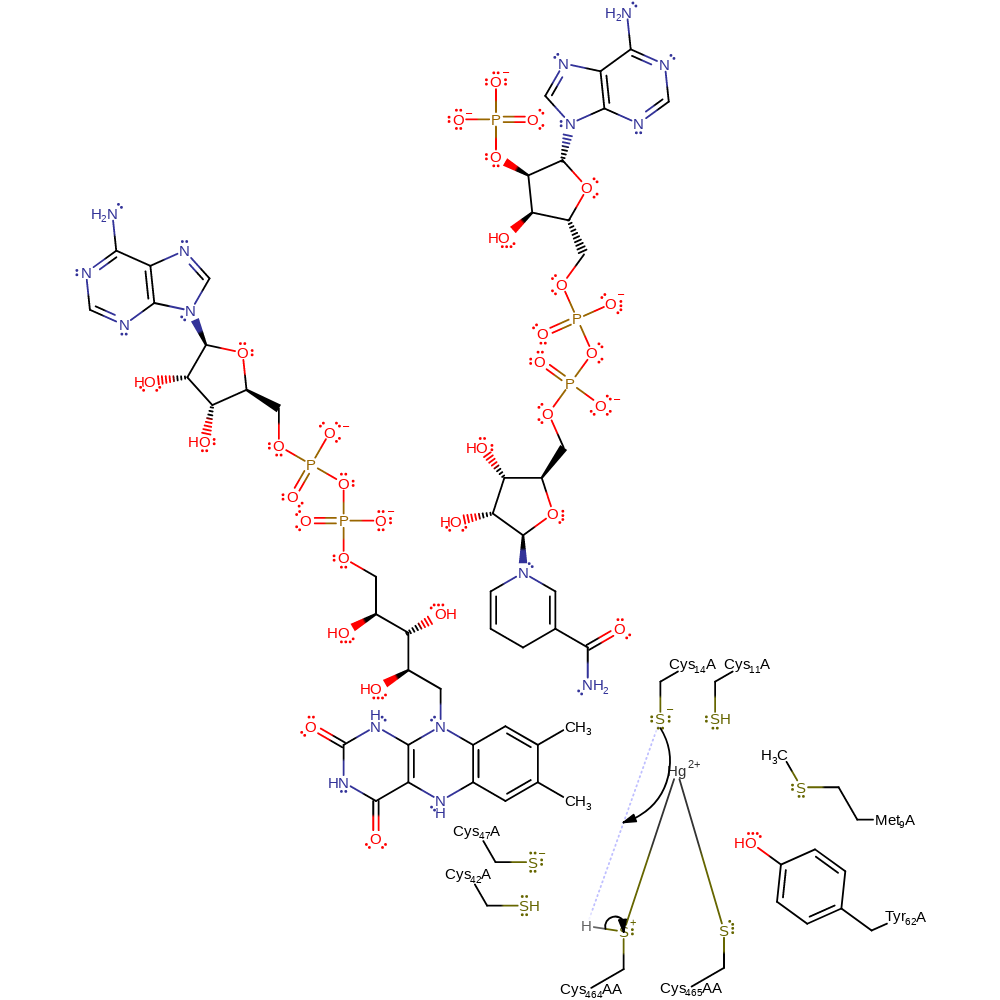
Step 8. The thiolate form of Cys14 abstracts a proton from the positively charged sulfur of Cys558AA.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys464A(AA) | activator, metal ligand |
| Met9 | steric role, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr62 | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys465A(AA) | activator, covalently attached, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys14 | activator |
| Cys11 | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Cys42A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys14 | proton acceptor |
| Cys464A(AA) | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, intermediate formation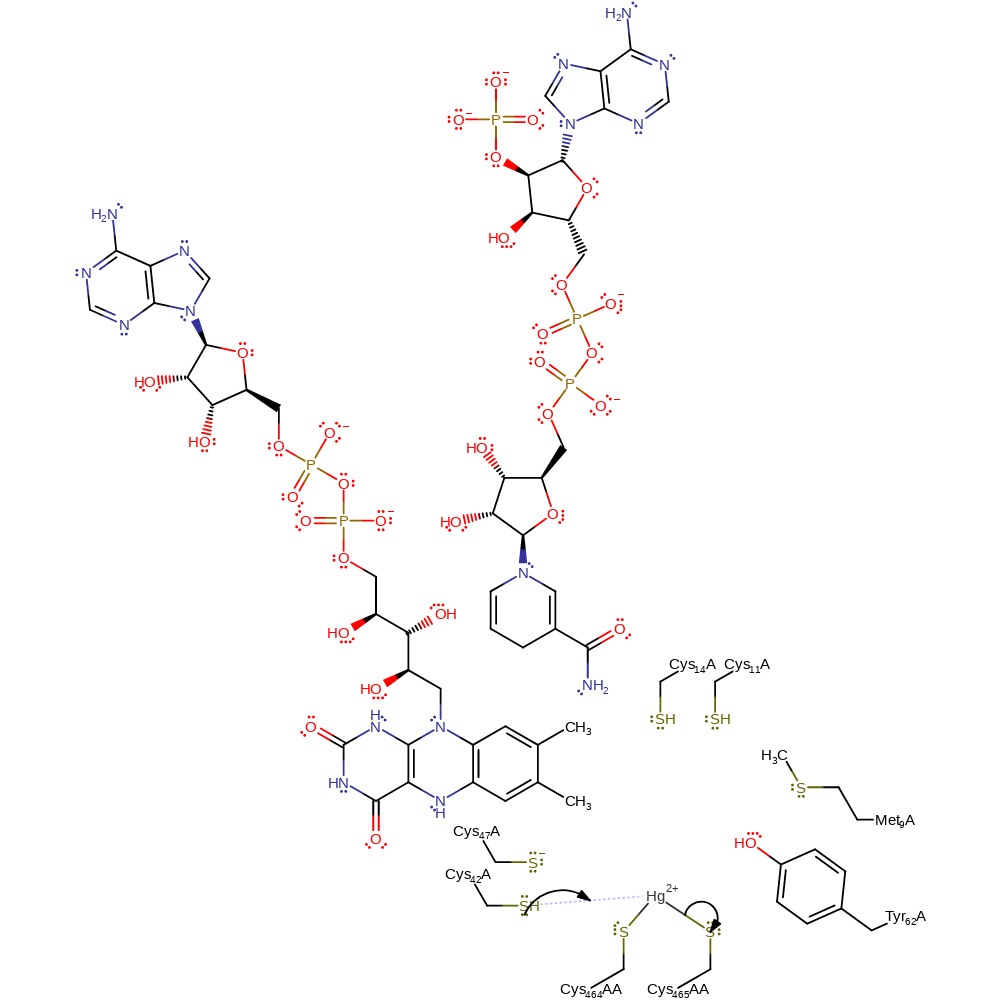
Step 9. Cys136 acts as a nucleophile towards the close proximity mercury-thiol adduct, forming another metal-ligand bridging intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys464A(AA) | activator, metal ligand, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Met9 | steric role, increase nucleophilicity |
| Tyr62 | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys465A(AA) | activator, nucleofuge |
| Cys42A | nucleophile |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, intermediate formation, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, enzyme-substrate complex formation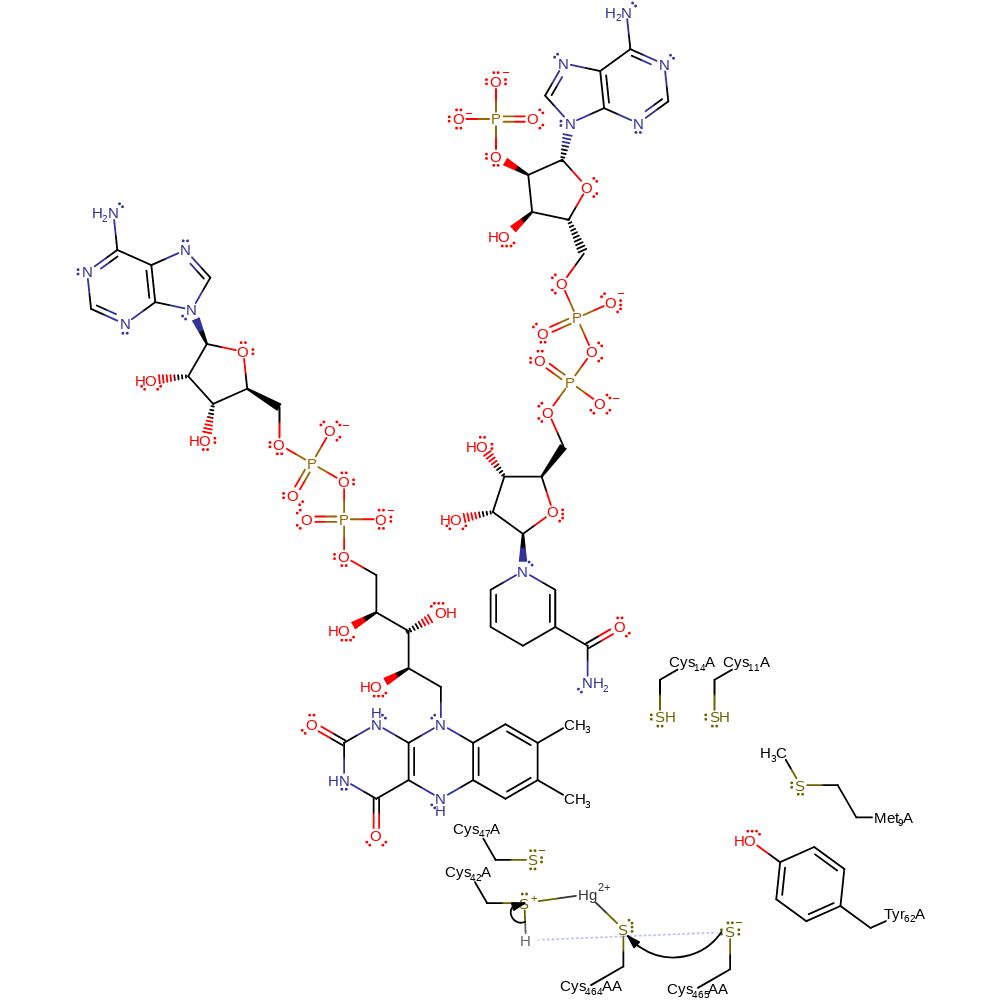
Step 10. The resulting positively charged sulfur is deprotonated by Cys559AA
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys464A(AA) | activator, metal ligand, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Met9 | steric role, increase nucleophilicity |
| Tyr62 | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys465A(AA) | activator |
| Cys42A | activator, proton donor |
| Cys465A(AA) | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, intermediate formation
Step 11. Cys141 displaces Cys558AA within the metal coordination sphere.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys464A(AA) | activator |
| Met9 | steric role |
| Tyr62 | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys47A | activator |
| Cys42A | covalently attached |
| Cys464A(AA) | nucleofuge |
| Cys47A | nucleophile |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, coordination to a metal ion, decoordination from a metal ion, enzyme-substrate complex formation, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage, intermediate formationCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Met9 | steric role |
| Tyr62 | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys47A | metal ligand |
| Cys42A | metal ligand |
Chemical Components
hydride transfer, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, overall product formed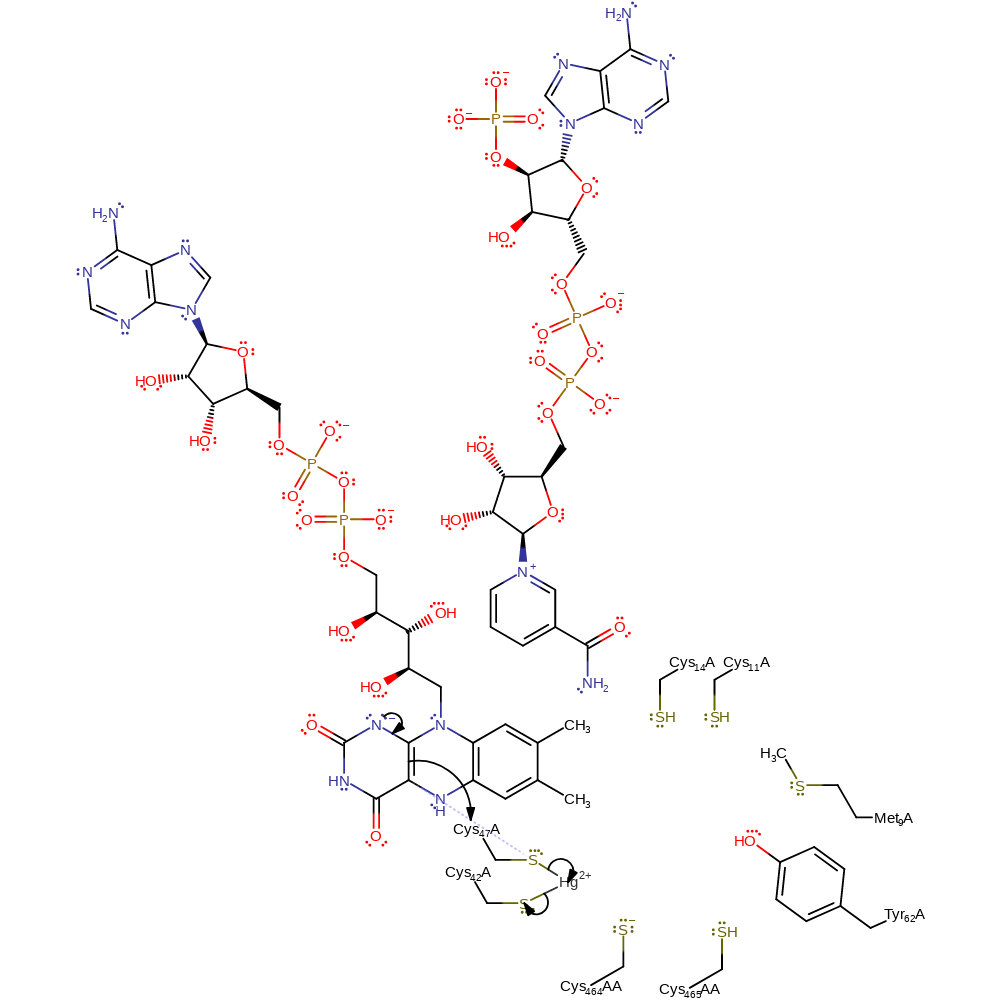
Step 13. The FAD cofactor attacks Cys141, forming an enzyme-FAD complex with loss of Hg(0).
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Met9 | steric role |
| Tyr62 | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys47A | electrophile |
| Cys42A | nucleofuge |
| Cys47A | electrofuge |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, intermediate formation, cofactor used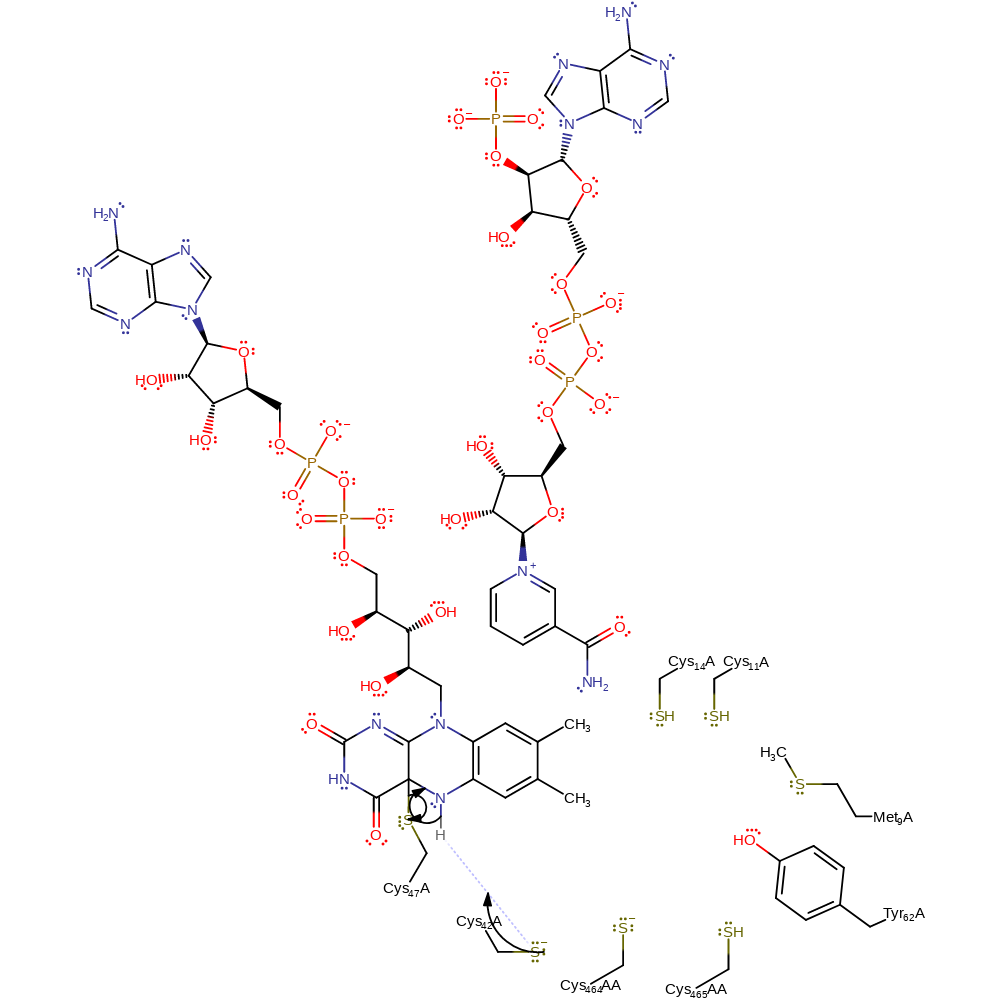
Step 14. Cys136 abstracts a proton from the enzyme-FAD adduct, initiating a reductive elimination of thiolate Cys141.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Met9 | steric role |
| Tyr62 | electrostatic stabiliser, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Cys47A | nucleofuge |
| Cys42A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, elimination (not covered by the Ingold mechanisms), native state of cofactor regenerated, overall product formed, enzyme-substrate complex cleavage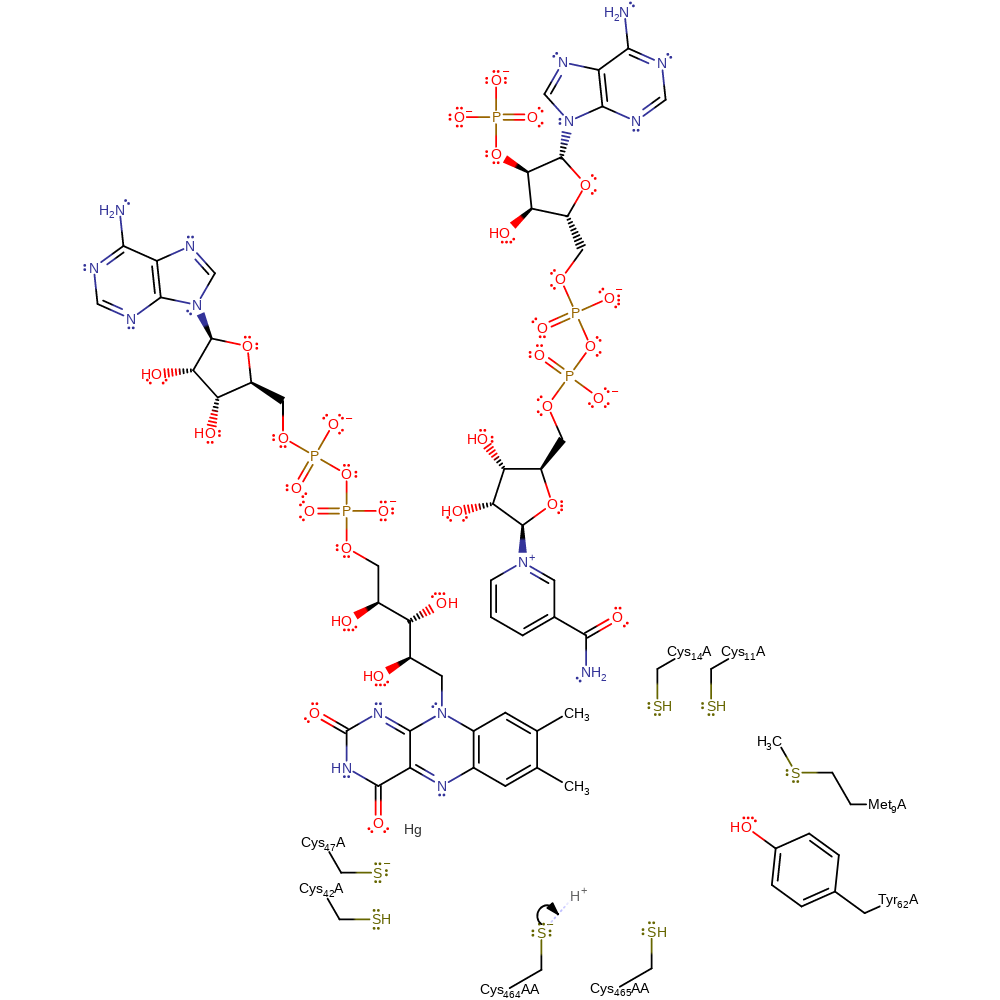
Step 15. The active site is regenerated when Cys558AA is reprotonated. In this inferred return step, the identiy of the proton donor is not clear.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Cys464A(AA) | proton acceptor |





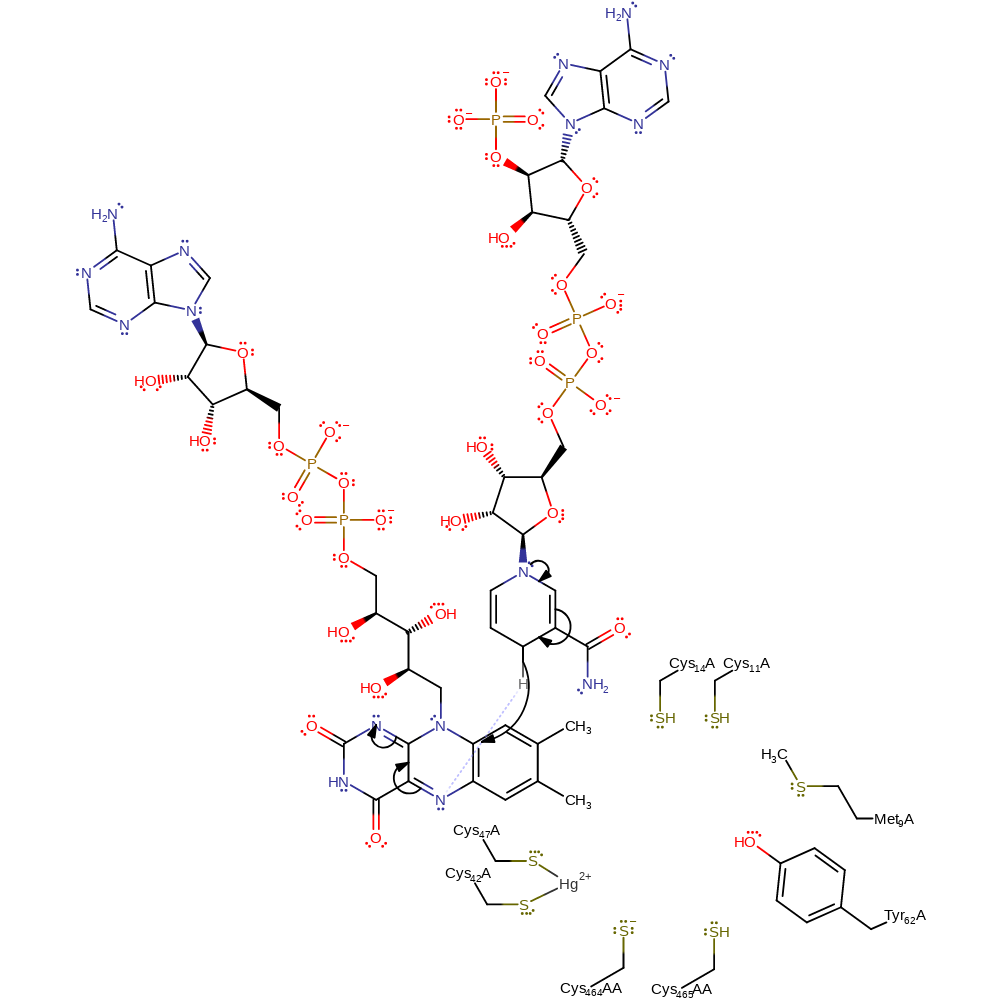
 Download:
Download: 
 Download:
Download: