Phosphoenolpyruvate mutase
Phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) mutase catalyses the conversion of PEP to 3-phosphonopyruvate which is the P-C bond forming step of the biosynthetic pathways leading to phosphonate natural products. Phosphonates are secondary metabolites, some of which have antibiotic activity. The structure of the enzyme is that of a modified alpha-beta barrel with only 7 beta sheets in the core of the barrel.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P56839
 (5.4.2.9)
(5.4.2.9)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Mytilus edulis (Blue mussel)

- PDB
-
1pym
- PHOSPHOENOLPYRUVATE MUTASE FROM MOLLUSK IN WITH BOUND MG2-OXALATE
(1.8 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.20.20.60
 (see all for 1pym)
(see all for 1pym)
- Cofactors
- Magnesium(2+) (1) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Reaction (EC:5.4.2.9)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
This mechanism proposal represents the dissociative mechanism with a trigonal metaphosphate intermediate. Here the metaphosphate dissociates from the phosphoenolpyruvate substrate. Followed by an oxyanion initiated a nulceophilic attack of the C3 on the metaphosphate to form the product.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1pym) | ||
| Ser46, Leu48 (main-N), Gly47 (main-N) | Ser46A, Leu48A (main-N), Gly47A (main-N) | Bind the substrate in the correct orientation. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, steric role |
| Arg159, His190, Asn122, Ser123, Lys120 | Arg159A, His190A, Asn122A, Ser123A, Lys120A | Act to stabilise the reactive intermediates, binding the phosphate group and activating it for heterolysis. | promote heterolysis, hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp58 | Asp58A | The initial proposal had Asp58 acting as the phosphoryl carrier [PMID:10378273]. However, subsequent studies have suggested that the disassociative mechanism is more likely in which Asp58 helps activate the phosphate for disassociation from the substrate. | promote heterolysis, metal ligand |
| Asp85, Glu114, Asp87, Asp58 | Asp85A, Glu114A, Asp87A, Asp58A | Coordinate water molecules which coordinate the Mg ion, which stabilizes the reactive intermediates. | hydrogen bond donor, metal ligand, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
heterolysis, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate terminated, overall product formed, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Xu D et al. (2005), J Phys Chem B, 109, 13827-13834. Theoretical Studies of Dissociative Phosphoryl Transfer in Interconversion of Phosphoenolpyruvate to Phosphonopyruvate: Solvent Effects, Thio Effects, and Implications for Enzymatic Reactions. DOI:10.1021/jp051042i. PMID:16852731.
- Xu D et al. (2008), J Phys Chem B, 112, 4102-4108. Ab Initio QM/MM Studies of the Phosphoryl Transfer Reaction Catalyzed by PEP Mutase Suggest a Dissociative Metaphosphate Transition State. DOI:10.1021/jp0776816. PMID:18331021.
- Liu S et al. (2002), Biochemistry, 41, 10270-10276. Dissociative Phosphoryl Transfer in PEP Mutase Catalysis: Structure of the Enzyme/Sulfopyruvate Complex and Kinetic Properties of Mutants†,‡. DOI:10.1021/bi026024v. PMID:12162742.
- Huang K et al. (1999), Structure, 7, 539-548. Helix swapping between two α/β barrels: crystal structure of phosphoenolpyruvate mutase with bound Mg2+–oxalate. DOI:10.1016/s0969-2126(99)80070-7. PMID:10378273.
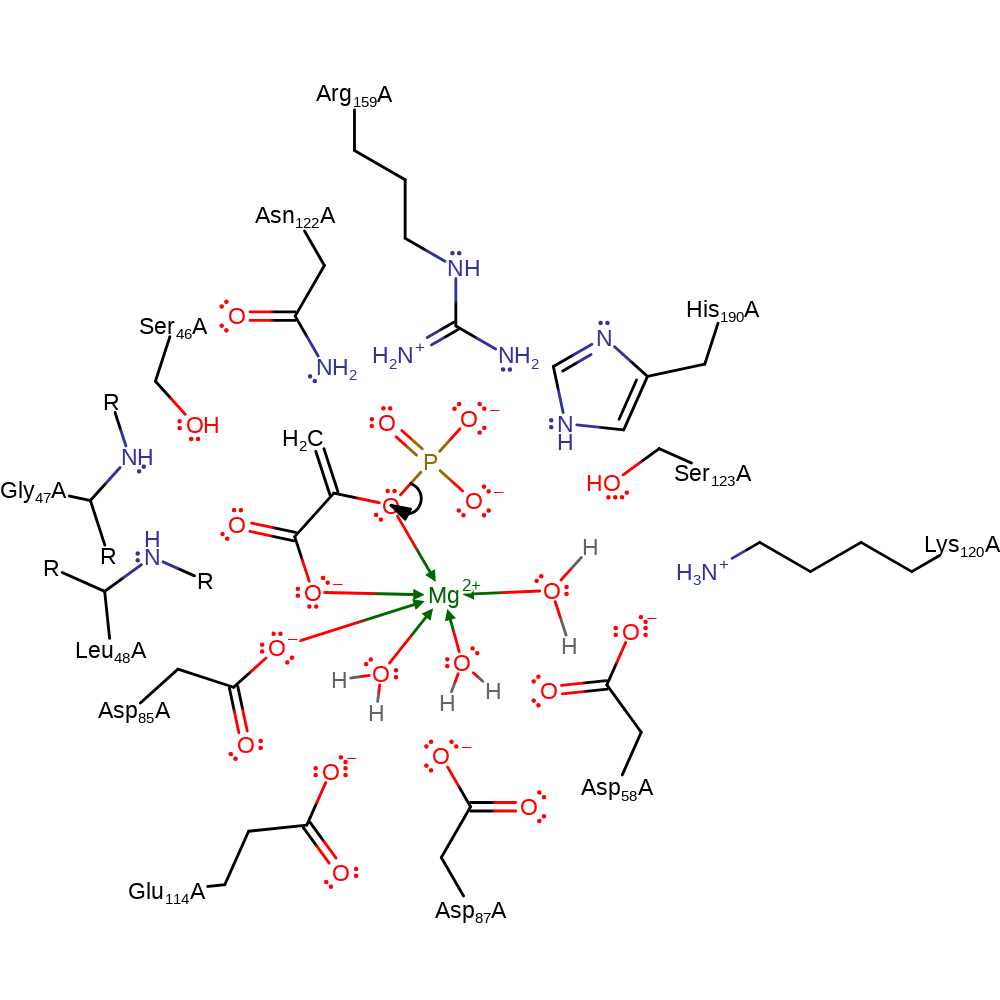
Step 1. The metaphosphate dissociates from the phosphoenolpyruvate substrate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg159A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, promote heterolysis |
| Ser46A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, steric role |
| Leu48A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, steric role |
| Ser123A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, promote heterolysis |
| Asn122A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, promote heterolysis |
| His190A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, promote heterolysis |
| Gly47A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys120A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp58A | metal ligand, promote heterolysis |
| Lys120A | promote heterolysis |
| Gly47A (main-N) | steric role |
| Asp85A | metal ligand |
| Asp87A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu114A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp85A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp87A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu114A | hydrogen bond donor |
Chemical Components
heterolysis, intermediate formation, overall reactant used
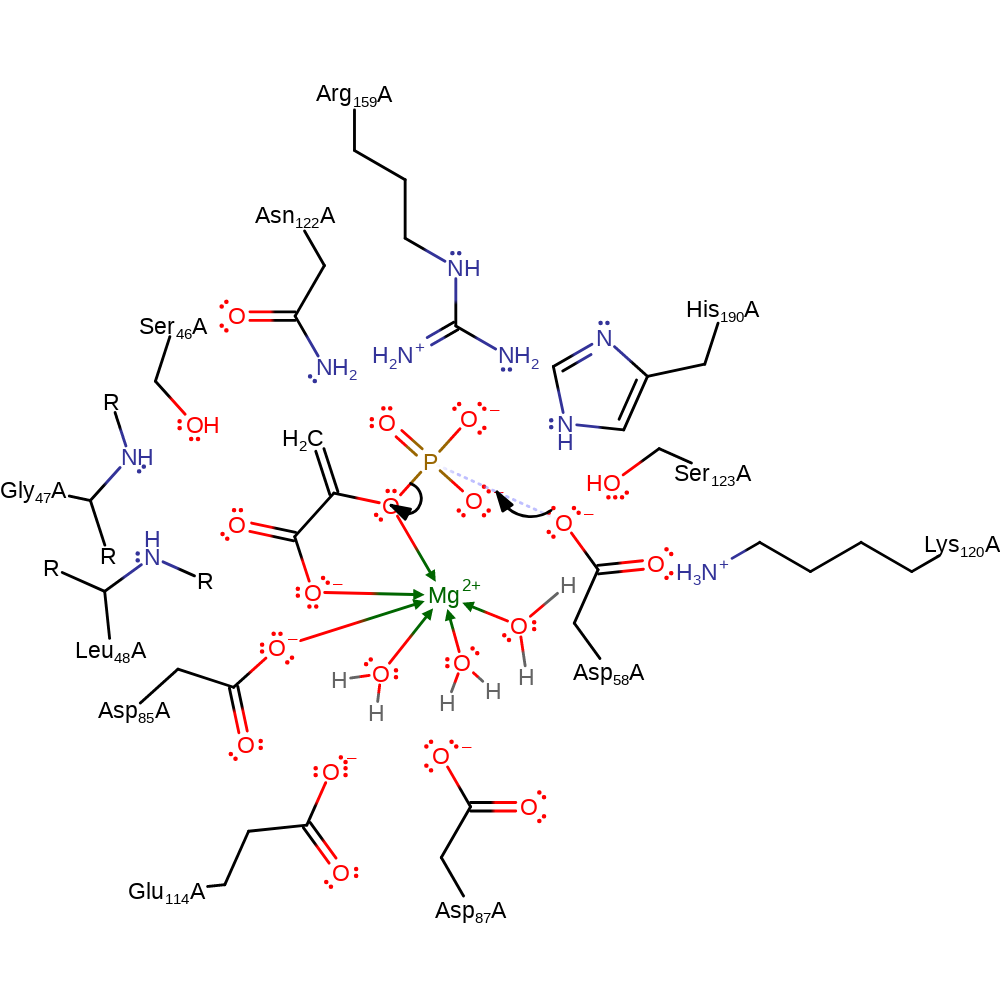
Step 2. The oxyanion initiated a nulceophilic attack of the C3 on the metaphosphate to form the product. The metaphosphate's interactions hole is stationary, whilst the C1-C2 bond os the pyruvate enolate rotates so that the C3-P bond can be formed [PMID:12162742].
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg159A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser46A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, steric role |
| Leu48A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, steric role |
| Ser123A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn122A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His190A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly47A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys120A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly47A (main-N) | steric role |
| Asp85A | metal ligand |
| Asp85A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp87A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu114A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp85A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp87A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu114A | hydrogen bond donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate terminated, overall product formed, native state of enzyme regeneratedIntroduction
This mechanism proposal represents the associative mechanism with a phosphorylated aspartate intermediate. Attack from Asp58 to the phosphate leads to a nucleophilic substitution reaction with oxyanion and phosphorylated aspartate intermediates being formed. This is followed by an oxyanion initiated a nulceophilic attack of the C3 on the phosphate to form the product in a second substitution reaction.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1pym) | ||
| Ser46, Leu48 (main-N), Gly47 (main-N) | Ser46A, Leu48A (main-N), Gly47A (main-N) | Bind the substrate in the correct orientation. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, steric role |
| Arg159, His190, Asn122, Ser123, Lys120 | Arg159A, His190A, Asn122A, Ser123A, Lys120A | Act to stabilize the reactive intermediates and binding the phosphate group. | promote heterolysis, hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp58 | Asp58A | Acts as the phosphoryl carrier | nucleofuge, nucleophile |
| Asp85, Glu114, Asp87, Asp58 | Asp85A, Glu114A, Asp87A, Asp58A | Coordinate water molecules which coordinate the Mg ion, which stabilizes the reactive intermediates. | hydrogen bond donor, metal ligand, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
intermediate formation, overall reactant used, bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, intermediate terminated, overall product formed, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Huang K et al. (1999), Structure, 7, 539-548. Helix swapping between two α/β barrels: crystal structure of phosphoenolpyruvate mutase with bound Mg2+–oxalate. DOI:10.1016/s0969-2126(99)80070-7. PMID:10378273.
- Xu D et al. (2008), J Phys Chem B, 112, 4102-4108. Ab Initio QM/MM Studies of the Phosphoryl Transfer Reaction Catalyzed by PEP Mutase Suggest a Dissociative Metaphosphate Transition State. DOI:10.1021/jp0776816. PMID:18331021.
- Liu S et al. (2002), Biochemistry, 41, 10270-10276. Dissociative Phosphoryl Transfer in PEP Mutase Catalysis: Structure of the Enzyme/Sulfopyruvate Complex and Kinetic Properties of Mutants†,‡. DOI:10.1021/bi026024v. PMID:12162742.
Step 1. Asp58 attacks the phosphate in a nucleophillic substitution reaction, forming a phosphorylated aspartate intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Glu114A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp87A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp85A | metal ligand |
| Lys120A | promote heterolysis, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly47A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser, steric role |
| Arg159A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, promote heterolysis |
| Ser46A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, steric role |
| Leu48A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, steric role |
| Ser123A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, promote heterolysis |
| Asn122A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, promote heterolysis |
| His190A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, promote heterolysis |
| Asp85A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp87A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu114A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp58A | nucleophile |
Chemical Components
intermediate formation, overall reactant used, ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic substitution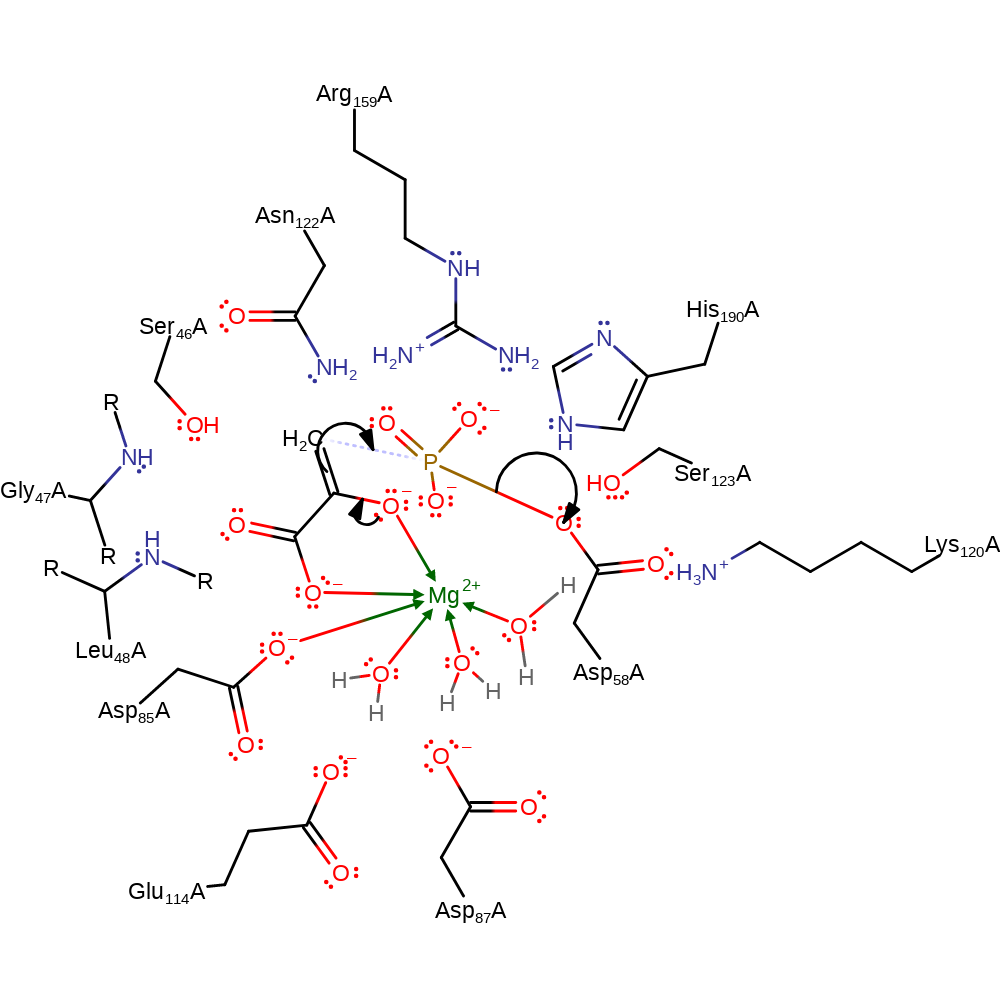
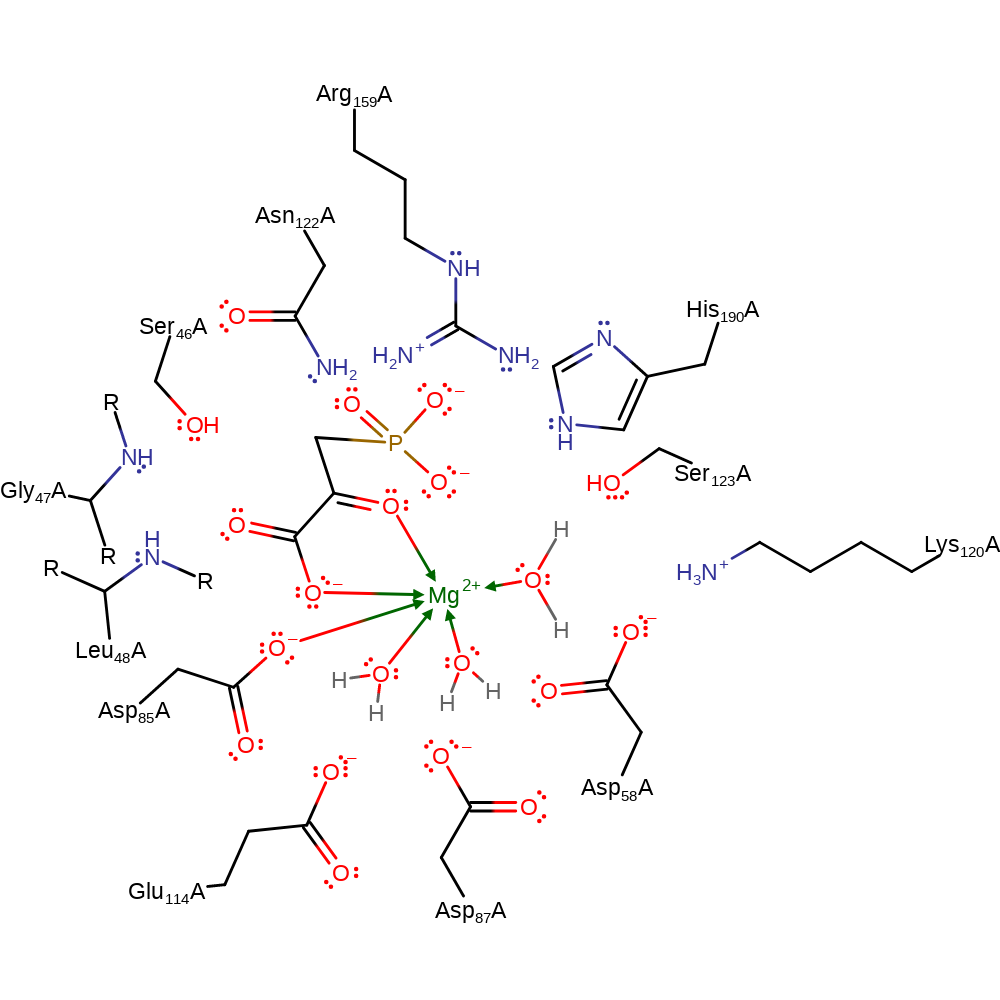
Step 2. There is nucelophilic attack from the C=C bond of the substrate to the Asp bound phosphate leading to the termination of the intermediate and the formation of the product.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Ser46A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Gly47A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Leu48A (main-N) | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp85A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp87A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Glu114A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys120A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asn122A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Ser123A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg159A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| His190A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp85A | metal ligand |
| Ser46A | steric role |
| Gly47A (main-N) | steric role |
| Leu48A (main-N) | steric role |
| Ser46A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Leu48A (main-N) | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp85A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp87A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Glu114A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asn122A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Ser123A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Arg159A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp58A | nucleofuge |



 Download:
Download: 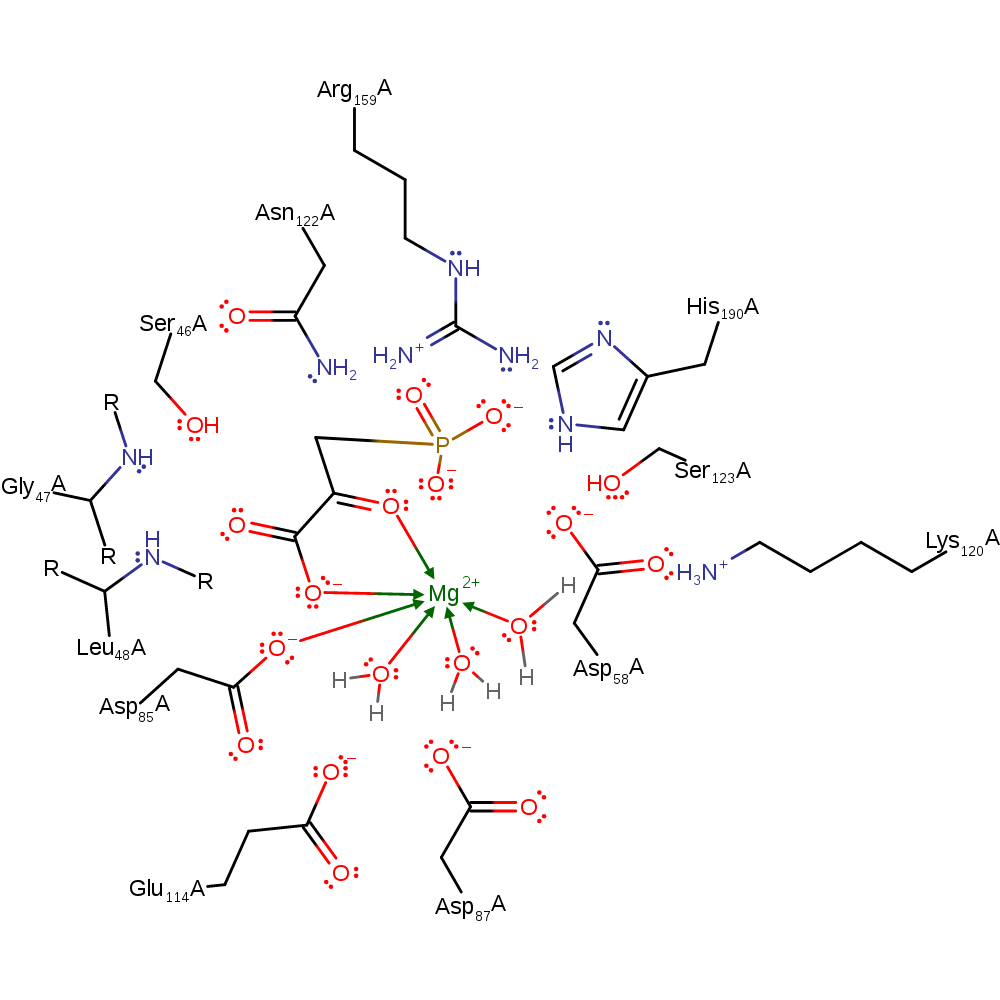 Download:
Download: