Aristolochene synthase
Aristolochene synthase is a fungal cyclase that catalyses the divalent metal dependent cyclisation of farnesyl diphosphate to the eremophilane sesquiterpene hydrocarbon aristolochene. Based on structural comparison, aristolochene is considered the likely parent hydrocarbon of several eremophilene toxins and bioregulators produced by a variety of filamentous fungi. It is also part of the gene cluster that mediates the biosynthesis of PR-toxin, a bicyclic sesquiterpene belonging to the eremophilane class and acting as a mycotoxin.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
Q03471
 (4.2.3.9)
(4.2.3.9)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Penicillium roqueforti (Blue cheese mold)

- PDB
-
1di1
- CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF ARISTOLOCHENE SYNTHASE FROM PENICILLIUM ROQUEFORTI
(2.5 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
1.10.600.10
 (see all for 1di1)
(see all for 1di1)
- Cofactors
- Magnesium(2+) (3) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Reaction (EC:4.2.3.9)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The cyclisation mechanism is thought to be initiated by the ionisation of the allylic diphosphate ester to the corresponding allylic cation-pyrophosphate ion pair, followed by electrophilic attack at the C10 of the distal double bond and removal of a proton form the cis-C-12 methyl group, resulting in the formation of the intermediate (S)-geracrene A. This intermediate undergoes further cyclisation by protonation at C-6 and intramolecular attack at the resultant carbocation to form the eudesmane cation. Successive 1,2 methyl migration and hydride shift followed by stereospecific deprotonation of H-8si leads to the formation of aristolochene. The observed sequence of anti-migration and syn-deprotonation takes place in a chair-boat conformation. The tight control of the substrate conformation within the enzyme active site is thought to be the main contributing factor to the enzyme's activity. The divalent metal ions (not present in the pdb 1di1) trigger the initial carbocation formation by coordinating the the diphosphate leaving group.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1di1) | ||
| Trp334 | Trp333(295)A | The residue is positioned to stabilise the developing positive charge on C-3 in the eudesmane cation intermediate. | van der waals interaction, steric role, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys206 | Lys206(167)A | The residue is thought to act as a general acid and general base within the cyclisation cascade. Hydrogen bonding interactions suggest Lys206 may be involved in a proton relay from the solvent, mediated by Arg200 and Asp203. Previous structural analysis implicated Tyr72 at the general acid/base catalyst. However, mutagenesis studies have shown the Tyr72Phe mutant to still product aristolochene as the major product (>81%). | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Tyr92, Phe112 | Tyr92(53)A, Phe112(73)A | The aromatic side chain is positioned to stabilise the developing partial positive charge on C-1 in the first step of catalysis, as well as enforcing the substrate into a reactive conformation and controlling the reaction stereochemistry. | van der waals interaction, steric role, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Phe178 | Phe178(139)A | The residue's aromatic side chain is correctly positioned to stabilise the developing positive charge on C-1 in the first step of catalysis. This electrostatic stabilisation of high energy intermediates is achieved without the risk to quenching the carbocation and annihilating catalytic activity. | van der waals interaction, steric role, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
intramolecular electrophilic substitution, overall reactant used, dephosphorylation, cyclisation, intermediate formation, overall product formed, proton transfer, intramolecular electrophilic addition, intermediate terminated, inferred reaction step, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Miller DJ et al. (2008), Org Biomol Chem, 6, 2346-2354. Stereochemistry of eudesmane cation formation during catalysis by aristolochene synthase from Penicillium roqueforti. DOI:10.1039/b804198a. PMID:18563268.
- Miller DJ et al. (2009), Org Biomol Chem, 7, 962-975. 6- and 14-Fluoro farnesyl diphosphate: mechanistic probes for the reaction catalysed by aristolochene synthase. DOI:10.1039/b817194g. PMID:19225680.
- Felicetti B et al. (2004), J Am Chem Soc, 126, 7212-7221. Aristolochene Synthase: Mechanistic Analysis of Active Site Residues by Site-Directed Mutagenesis. DOI:10.1021/ja0499593. PMID:15186158.
- Deligeorgopoulou A et al. (2003), Biochemistry, 42, 7741-7747. Evidence for Differential Folding of Farnesyl Pyrophosphate in the Active Site of Aristolochene Synthase: A Single-Point Mutation Converts Aristolochene Synthase into an (E)-β-Farnesene Synthase†. DOI:10.1021/bi034410m. PMID:12820883.
- Calvert MJ et al. (2002), J Am Chem Soc, 124, 11636-11641. Germacrene A Is a Product of the Aristolochene Synthase-Mediated Conversion of Farnesylpyrophosphate to Aristolochene. DOI:10.1021/ja020762p. PMID:12296728.
- Caruthers JM et al. (2000), J Biol Chem, 275, 25533-25539. Crystal Structure Determination of Aristolochene Synthase from the Blue Cheese Mold, Penicillium roqueforti *. DOI:10.1074/jbc.m000433200. PMID:10825154.
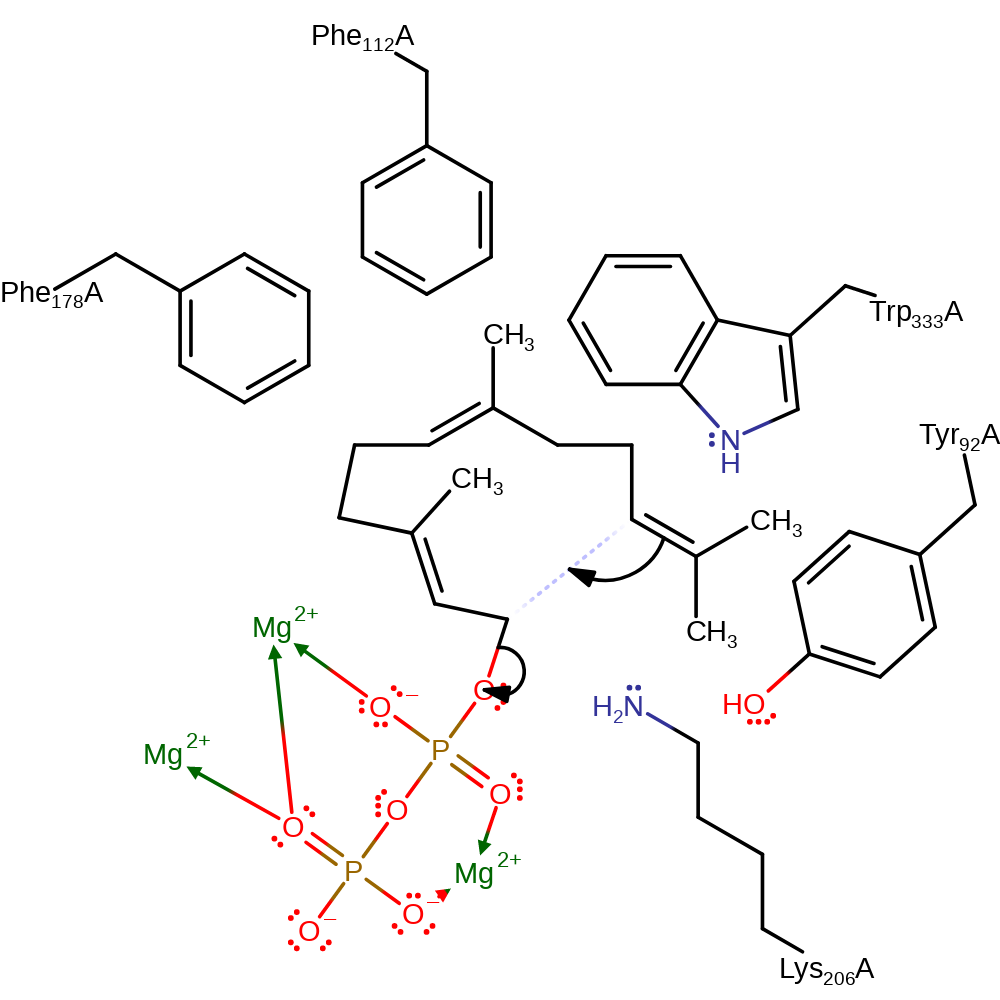
Step 1. Initial carbocation formation is triggered by coordination of the diphospahte leaving group to the divalent metal cation cofactors. The C10-C11 double bond initiates an electrophilic substitution at the C1, eliminating the diphosphate product.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Phe178(139)A | steric role, electrostatic stabiliser, van der waals interaction |
| Tyr92(53)A | steric role, electrostatic stabiliser, van der waals interaction |
| Trp333(295)A | steric role, van der waals interaction |
| Lys206(167)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Phe112(73)A | steric role, electrostatic stabiliser, van der waals interaction |
Chemical Components
ingold: intramolecular electrophilic substitution, overall reactant used, dephosphorylation, cyclisation, intermediate formation, overall product formed
Step 2. Lys206 deprotonates the C12, producing the neutral Germacrene A intermediate. A hydrogen bond network linking Lys206 to the bulk solvent through Asp203 and Arg200 may provide a proton shuttle from the bulk solvent.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Trp333(295)A | steric role, van der waals interaction |
| Phe112(73)A | steric role, electrostatic stabiliser, van der waals interaction |
| Lys206(167)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Tyr92(53)A | steric role, electrostatic stabiliser, van der waals interaction |
| Phe178(139)A | steric role, electrostatic stabiliser, van der waals interaction |
| Lys206(167)A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, intermediate formation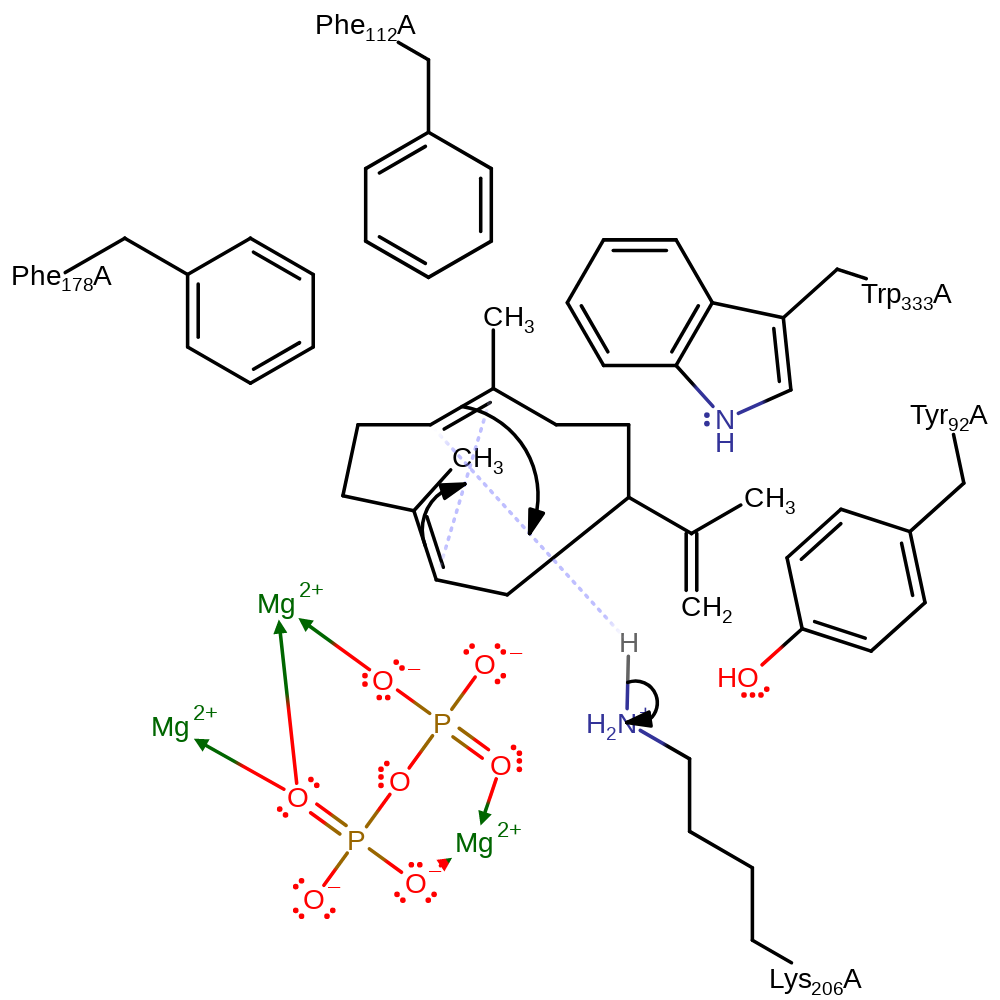
Step 3. The C2-C3 double bond initiates an electrophilic attack on the C7, which causes the protonation of C6 from Lys206 to form the Eudesmane cation intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Trp333(295)A | steric role, electrostatic stabiliser, van der waals interaction |
| Phe112(73)A | steric role, van der waals interaction |
| Lys206(167)A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Tyr92(53)A | steric role, van der waals interaction |
| Phe178(139)A | steric role, van der waals interaction |
| Lys206(167)A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: intramolecular electrophilic addition, proton transfer, intermediate formation, cyclisation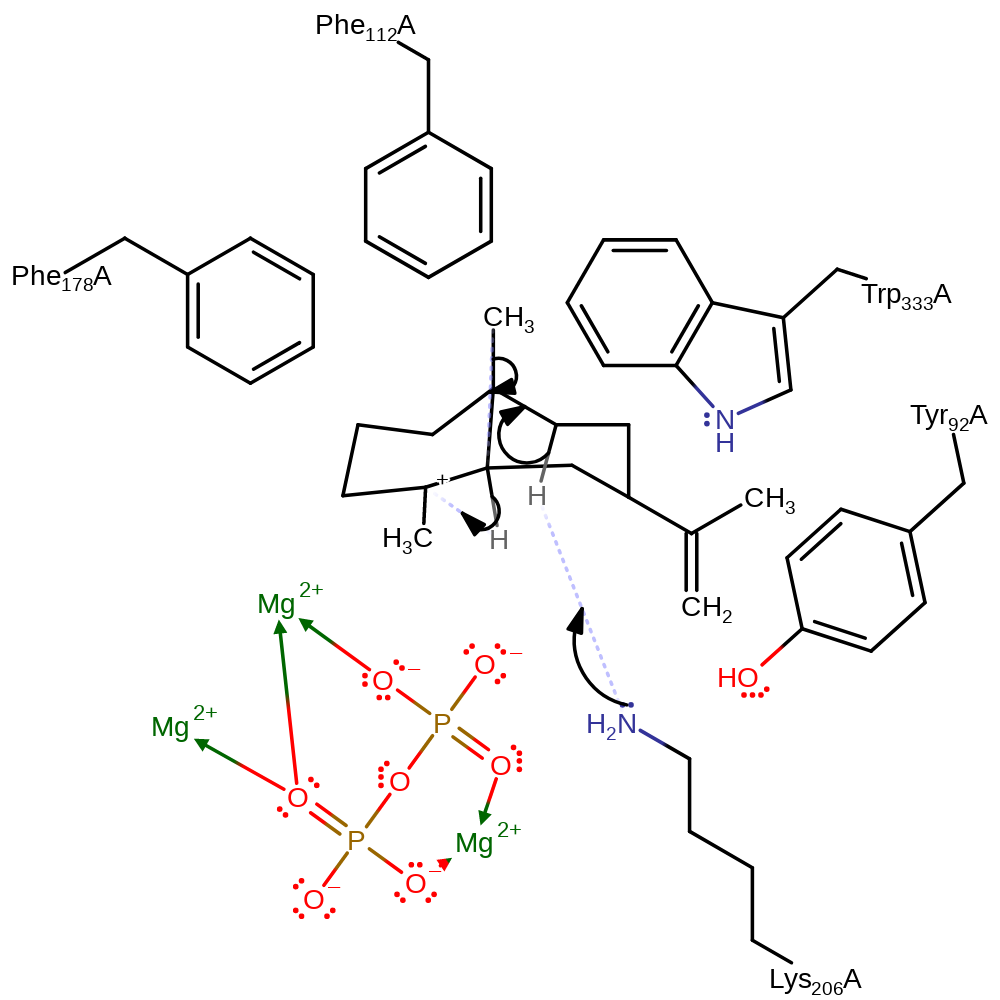
Step 4. Lys206 deprotonates the C8 carbon, which forms a double bond between C8 and C7. This initiates the migration of the C14 methyl from C7 to C8 and a migration of a hydride from C2 to C3 to form the Aristolochene product.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Trp333(295)A | steric role, electrostatic stabiliser, van der waals interaction |
| Phe112(73)A | steric role, van der waals interaction |
| Lys206(167)A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Tyr92(53)A | steric role, van der waals interaction |
| Phe178(139)A | steric role, van der waals interaction |
| Lys206(167)A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: intramolecular electrophilic substitution, proton transfer, intermediate terminated, overall product formed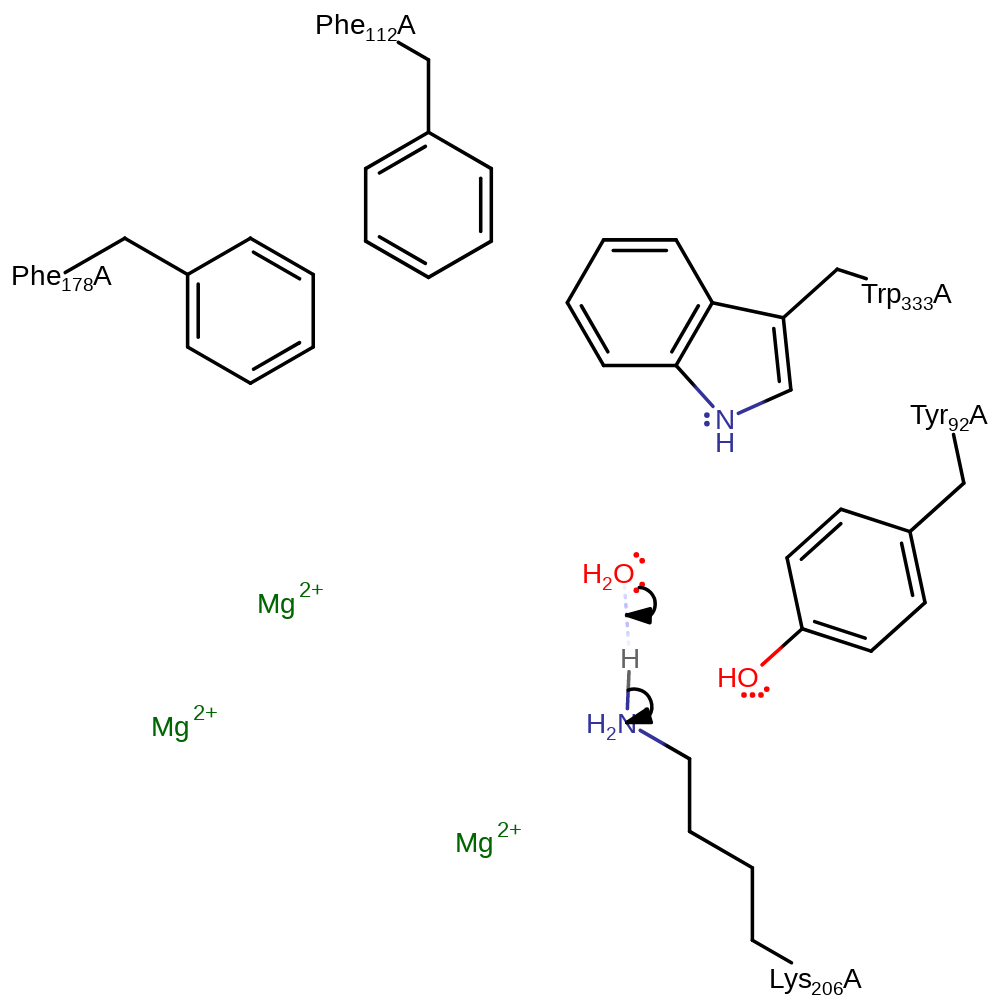
Step 5. Inferred return step. The Lys206 is likely deprotonated via a hydrogen bond network linking Lys206 to the bulk solvent through Asp203 and Arg200.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys206(167)A | hydrogen bond donor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, inferred reaction step, native state of enzyme regeneratedIntroduction
This alternative mechanism is highly similar to the first one, the difference being the eliminated pyrophosphate will act as the predominant general base instead of the lysine. (See the other mechanism for the majority of the references.)
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1di1) |
Chemical Components
intramolecular electrophilic substitution, overall reactant used, dephosphorylation, cyclisation, overall product formed, proton transfer, intramolecular electrophilic addition, hydride transferReferences
- Chen M et al. (2016), Biochemistry, 55, 2864-2874. Probing the Role of Active Site Water in the Sesquiterpene Cyclization Reaction Catalyzed by Aristolochene Synthase. DOI:10.1021/acs.biochem.6b00343. PMID:27172425.

Step 1. Initial carbocation formation is triggered by coordination of the diphospahte leaving group to the divalent metal cation cofactors. The C10-C11 double bond initiates an electrophilic substitution at the C1, eliminating the diphosphate product.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Phe178(139)A | steric role, electrostatic stabiliser, van der waals interaction |
| Tyr92(53)A | steric role, electrostatic stabiliser, van der waals interaction |
| Trp333(295)A | steric role, van der waals interaction |
| Phe112(73)A | steric role, electrostatic stabiliser, van der waals interaction |
Chemical Components
ingold: intramolecular electrophilic substitution, overall reactant used, dephosphorylation, cyclisation, overall product formed
Step 2. The eliminated diposhphate deprotonates the C12, producing the neutral Germacrene A intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr92(53)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Phe112(73)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Phe178(139)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr92(53)A | steric role |
| Phe112(73)A | steric role |
| Phe178(139)A | steric role |
| Trp333(295)A | steric role |
| Tyr92(53)A | van der waals interaction |
| Phe112(73)A | van der waals interaction |
| Phe178(139)A | van der waals interaction |
| Trp333(295)A | van der waals interaction |
Chemical Components
proton transfer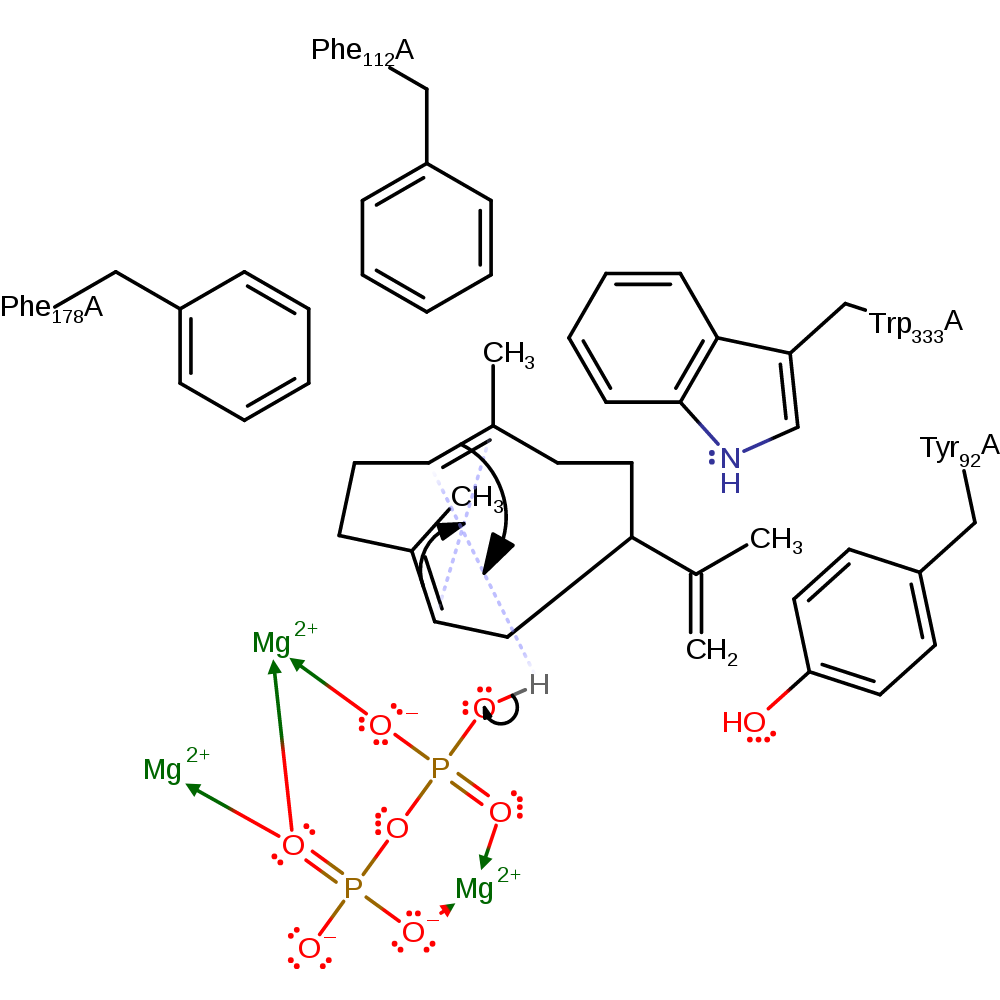
Step 3. The C2-C3 double bond initiates an electrophilic attack on the C7, which causes the protonation of C6 from diphosphate to form the Eudesmane cation intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Trp333(295)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr92(53)A | steric role |
| Phe112(73)A | steric role |
| Phe178(139)A | steric role |
| Trp333(295)A | steric role |
| Tyr92(53)A | van der waals interaction |
| Phe112(73)A | van der waals interaction |
| Phe178(139)A | van der waals interaction |
| Trp333(295)A | van der waals interaction |
Chemical Components
ingold: intramolecular electrophilic addition, proton transfer, cyclisationCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Trp333(295)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Tyr92(53)A | steric role |
| Phe112(73)A | steric role |
| Phe178(139)A | steric role |
| Trp333(295)A | steric role |
| Tyr92(53)A | van der waals interaction |
| Phe112(73)A | van der waals interaction |
| Phe178(139)A | van der waals interaction |
| Trp333(295)A | van der waals interaction |
Chemical Components
hydride transferCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr92(53)A | van der waals interaction |
| Phe112(73)A | van der waals interaction |
| Phe178(139)A | van der waals interaction |
| Trp333(295)A | van der waals interaction |
| Tyr92(53)A | steric role |
| Phe112(73)A | steric role |
| Phe178(139)A | steric role |
| Trp333(295)A | steric role, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
ingold: intramolecular electrophilic substitution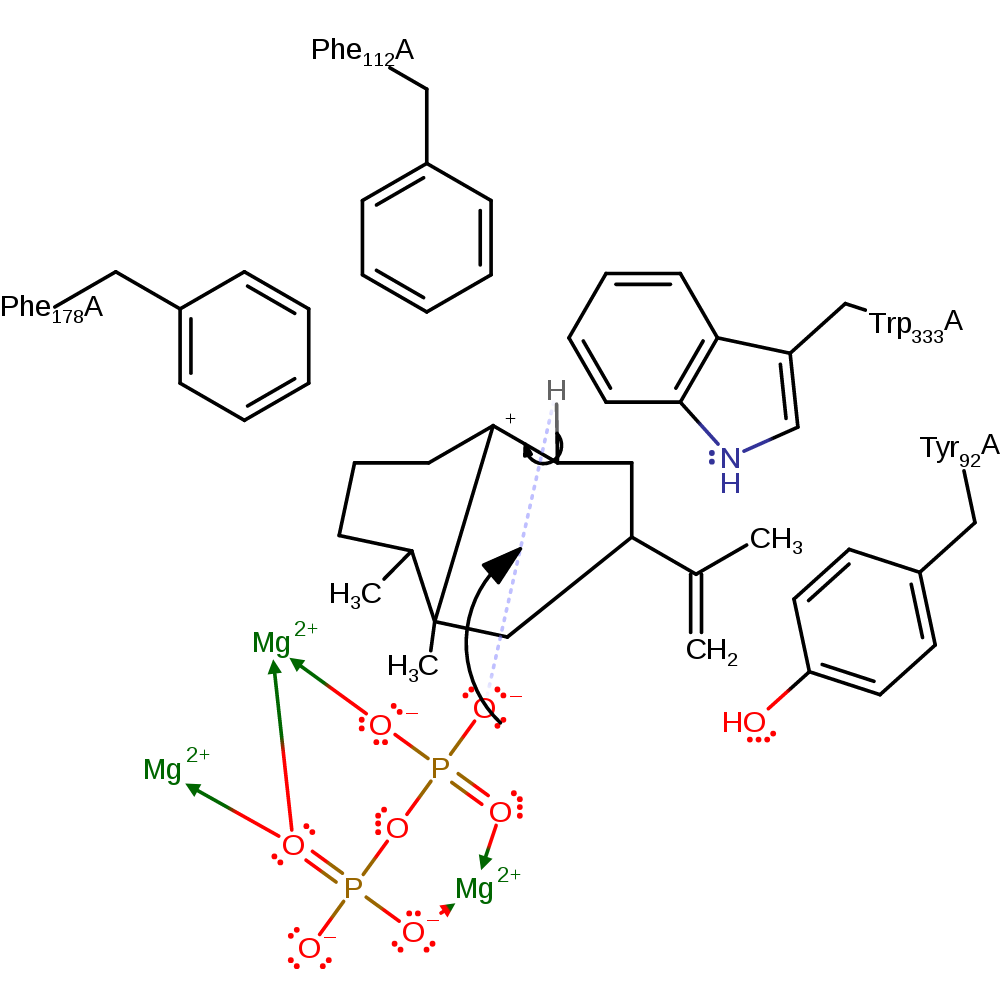
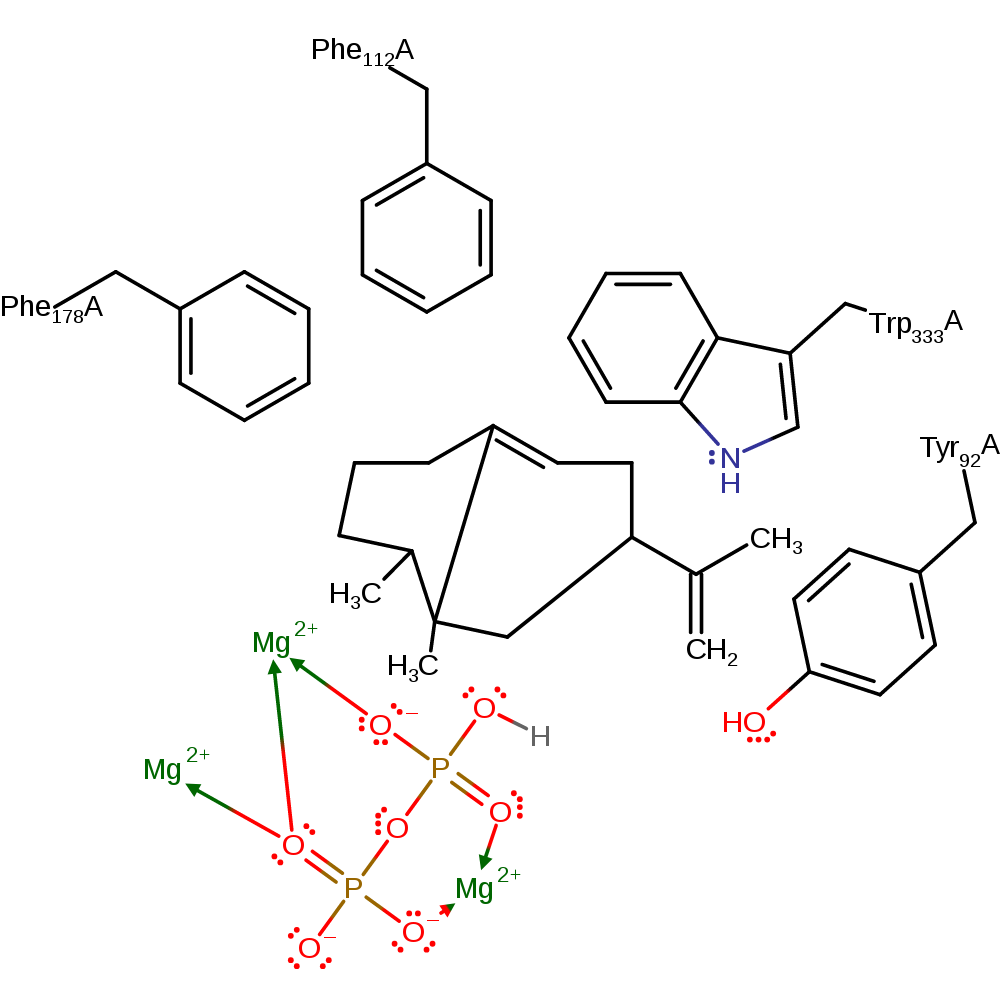
Step 6. Diphosphate deprotonates the C8 carbon, which forms a double bond between C8 and C7.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Tyr92(53)A | van der waals interaction |
| Phe112(73)A | van der waals interaction |
| Phe178(139)A | van der waals interaction |
| Trp333(295)A | van der waals interaction |
| Tyr92(53)A | steric role |
| Phe112(73)A | steric role |
| Phe178(139)A | steric role |
| Trp333(295)A | steric role, electrostatic stabiliser |



 Download:
Download: 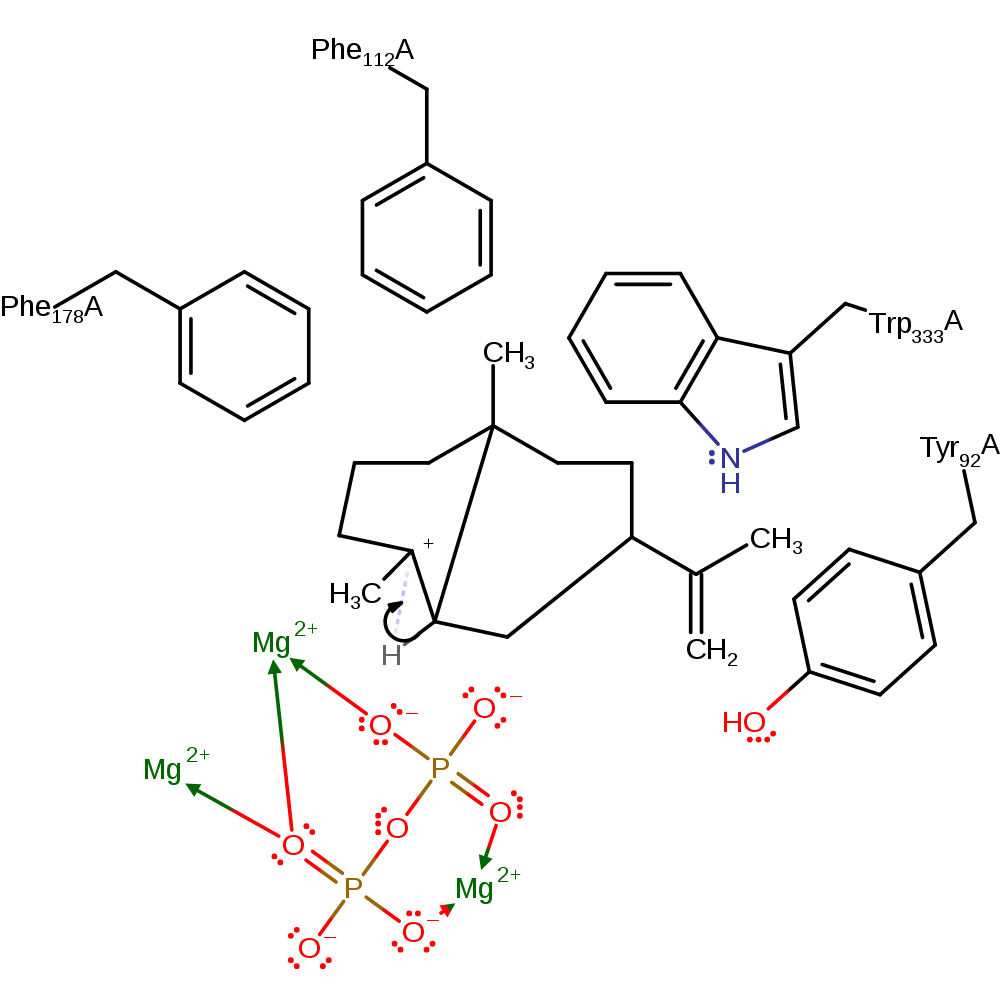

 Download:
Download: