Hydroxymethylbilane synthase
hydroxymethylbilane synthase (HemC) is involved in the tetrapolymerisation of porphobilinogen into the hydroxymethylbilane pre-uroporphyrinogen. It catalyses the reaction in a series of stepwise additions of pyrrolylmethyl groups until a hexapyrrole is present at the active centre. The terminal tetrapyrrole is then hydrolysed to yield the product, leaving a cysteine-bound dipyrrole on which assembly continues.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P06983
 (2.5.1.61)
(2.5.1.61)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Escherichia coli K-12 (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1gtk
- Time-resolved and static-ensemble structural chemistry of hydroxymethylbilane synthase
(1.66 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.30.160.40
 3.40.190.10
3.40.190.10  (see all for 1gtk)
(see all for 1gtk)
- Cofactors
- Dipyrromethane cofactor(4-) (1)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:2.5.1.61)
Enzyme Mechanism
- Summary
- Step 1
- Step 2
- Step 3
- Step 4
- Step 5
- Step 6
- Step 7
- Step 8
- Step 9
- Step 10
- Step 11
- Step 12
- Step 13
- Step 14
- Products
- All Steps
Introduction
The enzyme works by stepwise addition of pyrrolylmethyl groups until a hexapyrrole is present at the active centre. A single cycle involved the abstraction of a proton from porphobilinogen substrate by Asp84 to eliminate ammonia and produce the reactive azafulvene intermediate. Asp84 deprotonates the dipyrromethane cofactor, which causes rearrangement of the double bonds an addition to the azafulvene intermediate in a nucleophilic manner. Asp84 deprotonates C4 of the intermediate, causing double bond rearrangement to produce the cofactor elongated by one pyrrole unit. This occurs a further three times. The terminal tetrapyrrole is then hydrolysed to yield the product, leaving a cysteine-bound dipyrrole on which assembly continues.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1gtk) | ||
| Cys242 | Cys242A | This is the residue in the active site to which the cofactor is covalently attached. It is currently still unclear how the cysteine-bound dipyrrole is formed. There are two current alternative mechanisms that have been suggested. Either by a stepwise addition of porphobilinogen to the cysteine [PMID:1522882, PMID:8117733], or by addition of the preuroporphyinogen and thus the first catalytic turnover of the enzyme proceeds via the addition of only a further two porphobilinogen molecules [PMID:8687374]. | covalently attached |
| Asp84 | Asp84A | Acts as a general acid/base. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor, proton relay |
| Arg131, Arg132, Lys83, Arg149, Arg155 | Arg131A, Arg132A, Lys83A, Arg149A, Arg155A | Act to stabilise and activate the substrates and cofactor. | activator, hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
aromatic bimolecular elimination, proton transfer, overall reactant used, overall product formed, intermediate formation, deamination, proton relay, aromatic bimolecular nucleophilic addition, cofactor used, aromatic bimolecular nucleophilic substitution, native state of cofactor regenerated, intermediate terminated, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Woodcock SC et al. (1994), Biochemistry, 33, 2688-2695. Evidence for participation of aspartate-84 as a catalytic group at the active site of porphobilinogen deaminase obtained by site-directed mutagenesis of the hemC gene from Escherichia coli. DOI:10.1021/bi00175a043. PMID:8117733.
- Bung N et al. (2014), PLoS Comput Biol, 10, e1003484-. Structural insights into E. coli porphobilinogen deaminase during synthesis and exit of 1-hydroxymethylbilane. DOI:10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003484. PMID:24603363.
- Roberts A et al. (2013), Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr, 69, 471-485. Insights into the mechanism of pyrrole polymerization catalysed by porphobilinogen deaminase: high-resolution X-ray studies of the Arabidopsis thaliana enzyme. DOI:10.1107/S0907444912052134. PMID:23519422.
- Shoolingin-Jordan PM et al. (1996), Biochem J, 316, 373-376. Discovery that the assembly of the dipyrromethane cofactor of porphobilinogen deaminase holoenzyme proceeds initially by the reaction of preuroporphyrinogen with the apoenzyme. DOI:10.1042/bj3160373. PMID:8687374.
- Louie GV et al. (1992), Nature, 359, 33-39. Structure of porphobilinogen deaminase reveals a flexible multidomain polymerase with a single catalytic site. DOI:10.1038/359033a0. PMID:1522882.
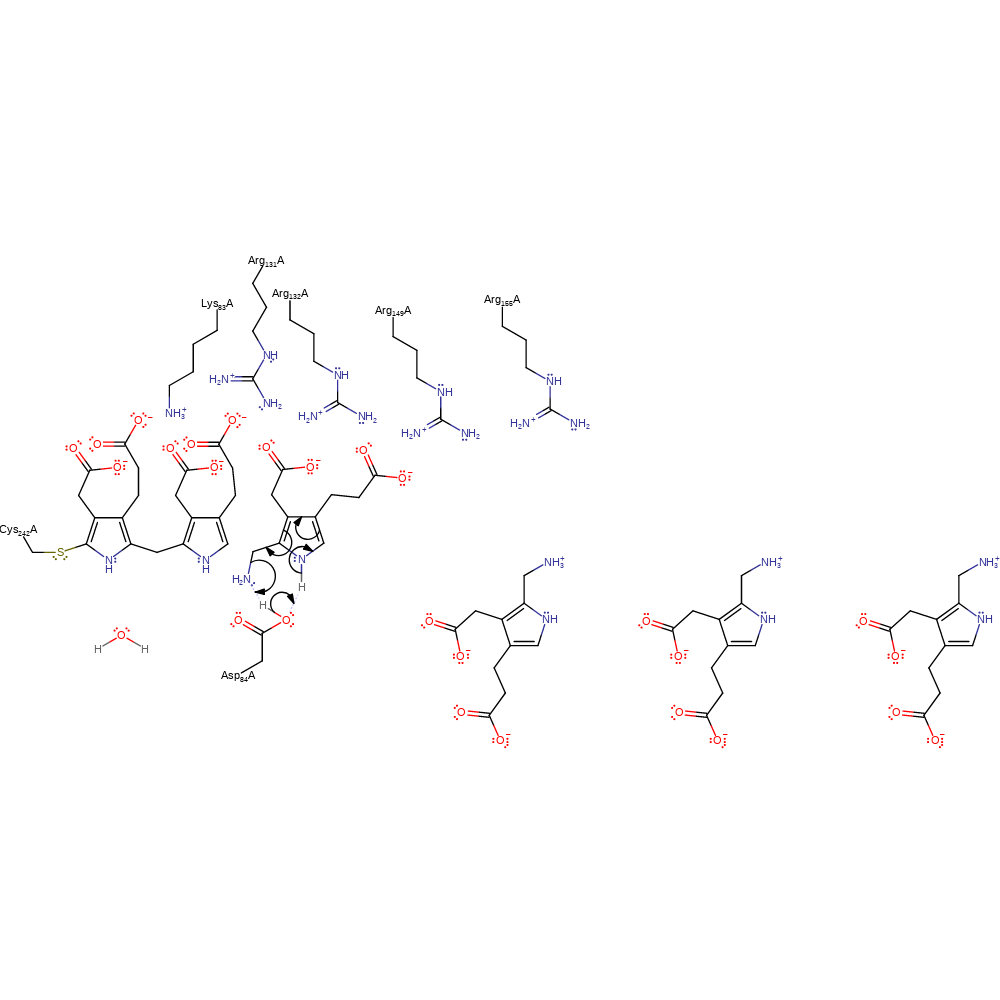
Step 1. Asp84 deprotonates the porphobilinogen substrate, which causes rearrangement of the double bonds to eliminate ammonia and form the reactive azafulvene intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys83A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, activator |
| Asp84A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton relay |
| Arg131A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, activator |
| Arg132A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, activator |
| Cys242A | covalently attached |
| Asp84A | proton donor, proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: aromatic bimolecular elimination, proton transfer, overall reactant used, overall product formed, intermediate formation, deamination, proton relay
Step 2. Asp84 deprotonates the dipyrromethane cofactor, which causes rearrangement of the double bonds an addition to the azafulvene intermediate in a nucleophilic manner.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys83A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, activator |
| Asp84A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton relay |
| Arg131A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, activator |
| Arg132A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, activator |
| Cys242A | covalently attached |
| Asp84A | proton acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: aromatic bimolecular nucleophilic addition, cofactor used, intermediate formation, proton relay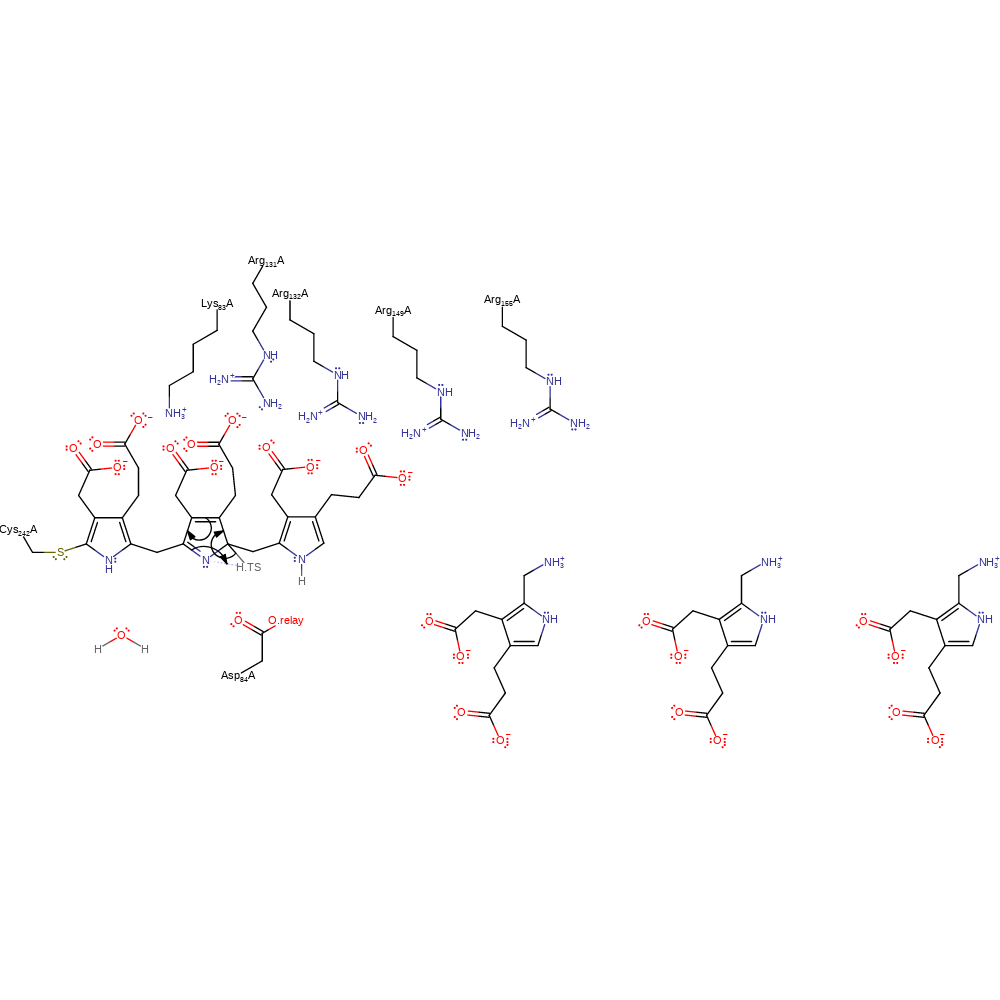
Step 3. Asp84 deprotonates C4 of the intermediate, causing double bond rearrangement to produce the cofactor elongated by one pyrrole unit.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys83A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, activator |
| Asp84A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton relay |
| Arg131A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, activator |
| Arg132A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, activator |
| Cys242A | covalently attached |
| Asp84A | proton donor, proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, intermediate formation, proton relay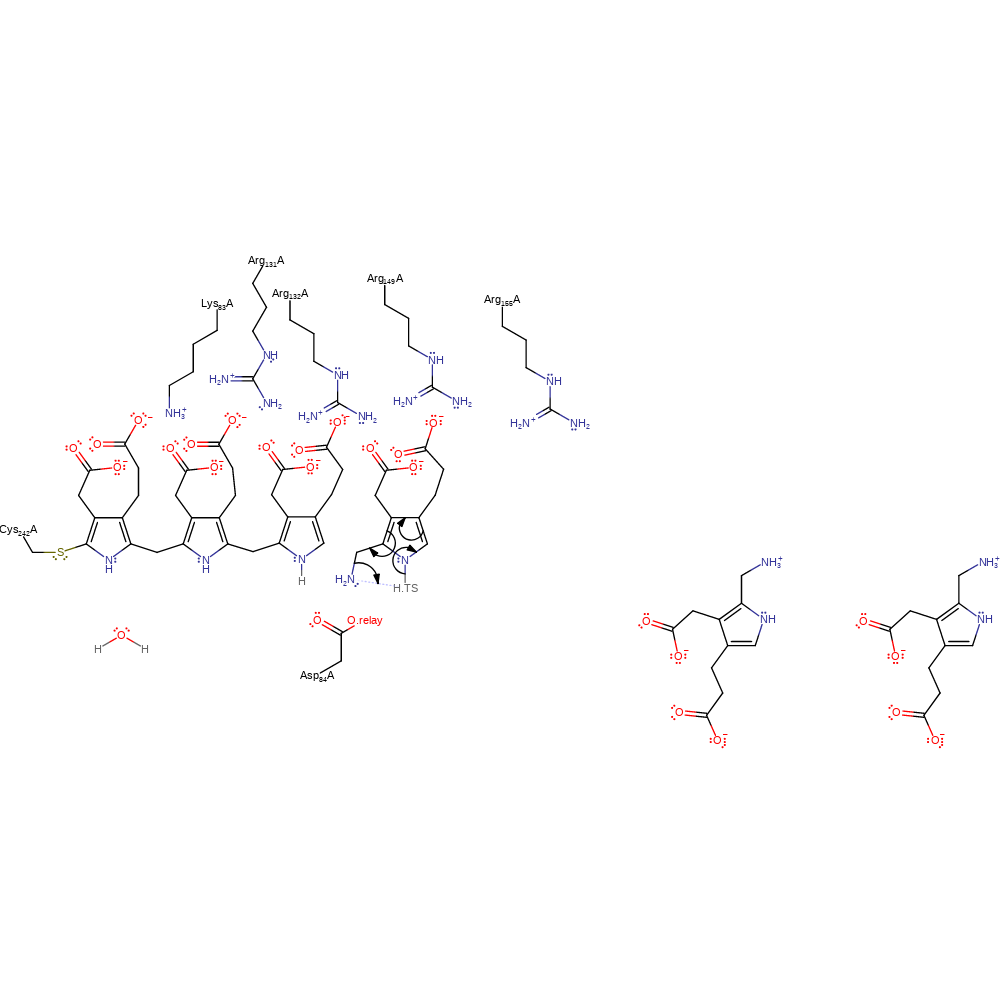
Step 4. Asp84 deprotonates the porphobilinogen substrate, which causes rearrangement of the double bonds to eliminate ammonia and form the reactive azafulvene intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg149A | activator |
| Lys83A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, activator |
| Asp84A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton relay |
| Arg131A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, activator |
| Arg132A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, activator |
| Cys242A | covalently attached |
| Arg149A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp84A | proton donor, proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
ingold: aromatic bimolecular elimination, proton transfer, overall reactant used, overall product formed, intermediate formation, deamination, proton relay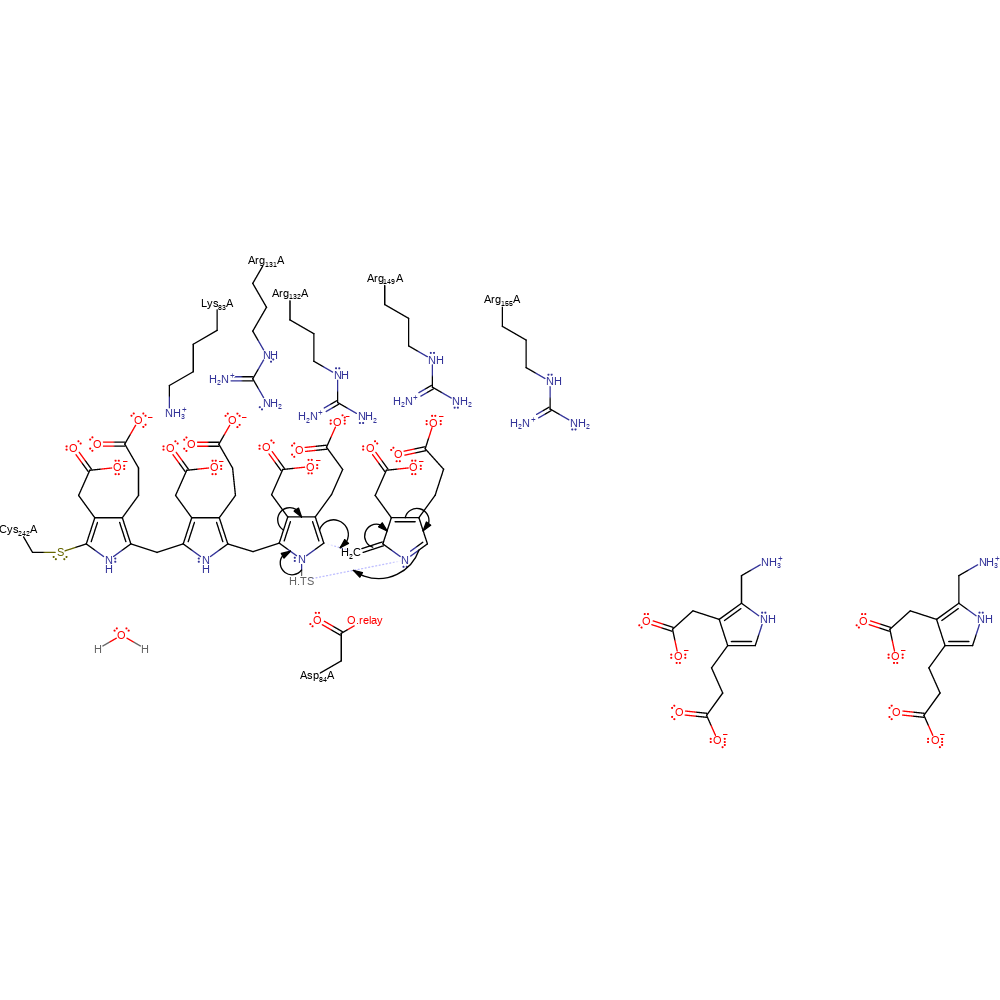
Step 5. Asp84 deprotonates the dipyrromethane cofactor, which causes rearrangement of the double bonds an addition to the azafulvene intermediate in a nucleophilic manner.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys83A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, activator |
| Asp84A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton relay |
| Arg131A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, activator |
| Arg132A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, activator |
| Cys242A | covalently attached |
| Arg149A | activator, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp84A | proton acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: aromatic bimolecular nucleophilic addition, cofactor used, intermediate formation, proton relay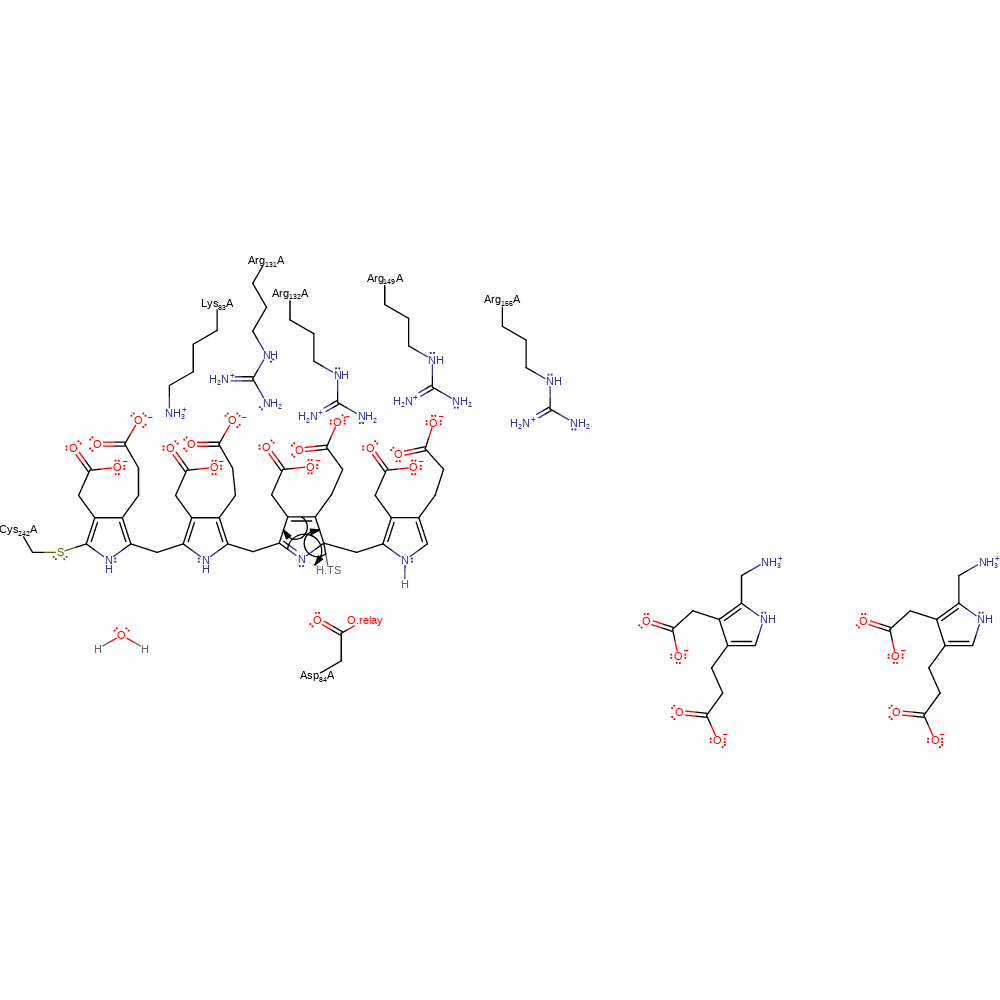
Step 6. Asp84 deprotonates C4 of the intermediate, causing double bond rearrangement to produce the cofactor elongated by one pyrrole unit.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys83A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, activator |
| Asp84A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton relay |
| Arg131A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, activator |
| Arg132A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, activator |
| Cys242A | covalently attached |
| Arg149A | activator |
| Arg149A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp84A | proton acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, intermediate formation, proton relay
Step 7. Asp84 deprotonates the porphobilinogen substrate, which causes rearrangement of the double bonds to eliminate ammonia and form the reactive azafulvene intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg149A | activator |
| Arg155A | activator |
| Lys83A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, activator |
| Asp84A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton relay |
| Arg131A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, activator |
| Arg132A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, activator |
| Cys242A | covalently attached |
| Arg149A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg155A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp84A | proton acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: aromatic bimolecular elimination, proton transfer, overall reactant used, overall product formed, intermediate formation, deamination, proton relay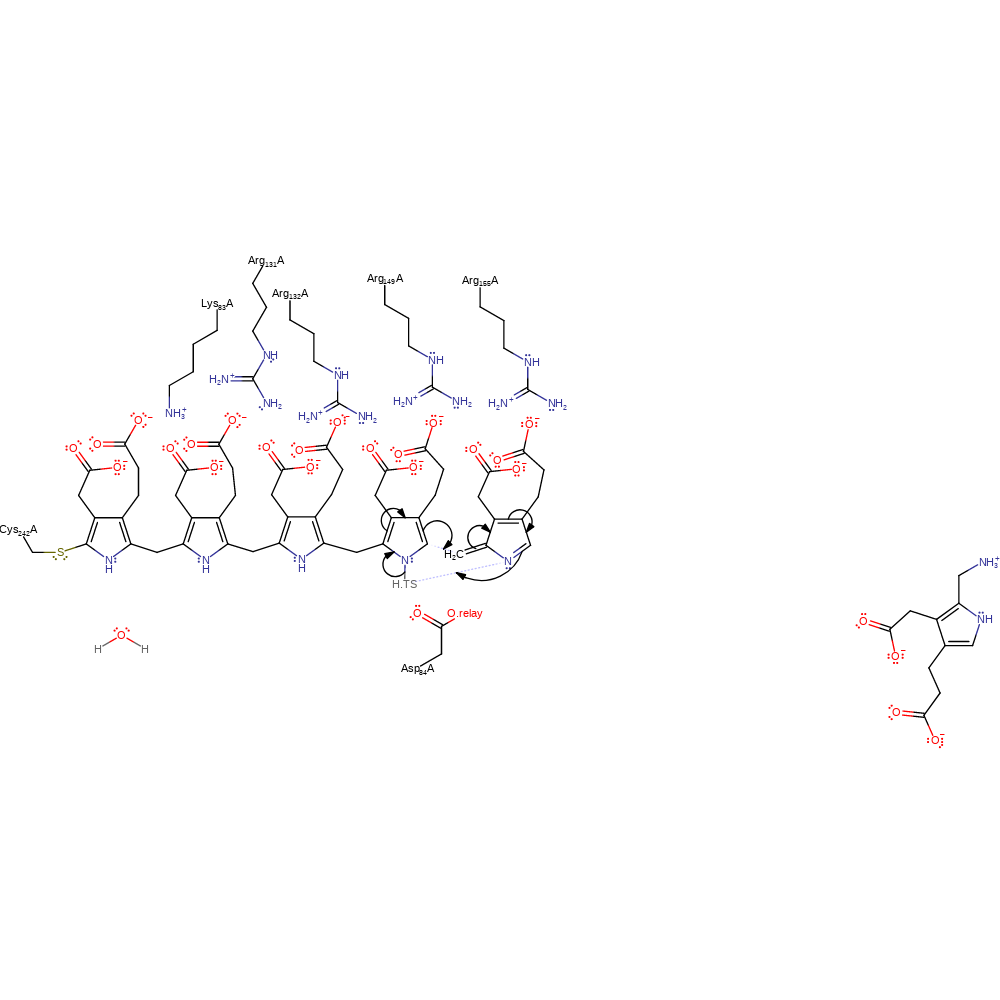
Step 8. Asp84 deprotonates the dipyrromethane cofactor, which causes rearrangement of the double bonds an addition to the azafulvene intermediate in a nucleophilic manner.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys83A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, activator |
| Asp84A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton relay |
| Arg131A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, activator |
| Arg132A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, activator |
| Cys242A | covalently attached |
| Arg149A | activator |
| Arg155A | activator |
| Arg149A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg155A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp84A | proton acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: aromatic bimolecular nucleophilic addition, cofactor used, intermediate formation, proton relay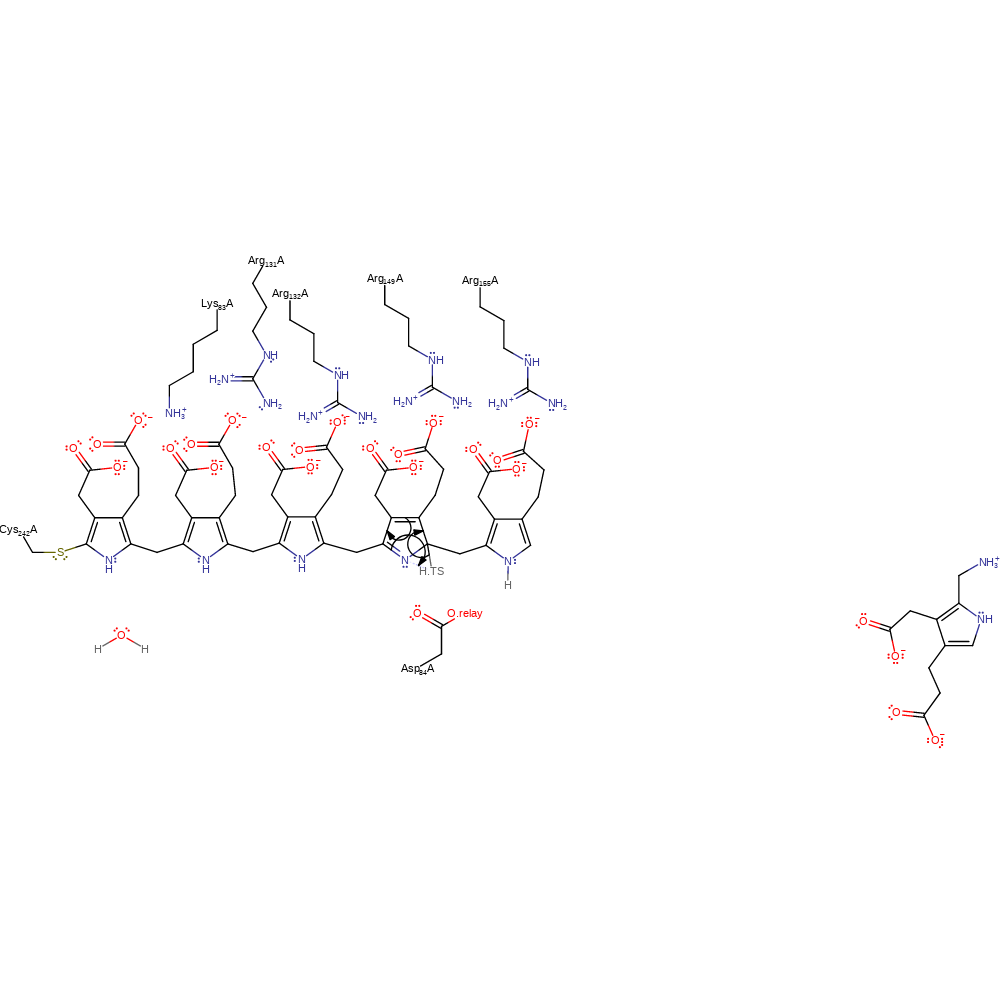
Step 9. Asp84 deprotonates C4 of the intermediate, causing double bond rearrangement to produce the cofactor elongated by one pyrrole unit.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg149A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg155A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys83A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, activator |
| Asp84A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton relay |
| Arg131A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, activator |
| Arg132A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, activator |
| Cys242A | covalently attached |
| Arg149A | activator |
| Arg155A | activator |
| Asp84A | proton acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, intermediate formation, proton relay
Step 10. Asp84 deprotonates the porphobilinogen substrate, which causes rearrangement of the double bonds to eliminate ammonia and form the reactive azafulvene intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys83A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, activator |
| Asp84A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton relay |
| Arg131A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, activator |
| Arg132A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, activator |
| Cys242A | covalently attached |
| Arg149A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg155A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg149A | activator |
| Arg155A | activator |
| Asp84A | proton acceptor, proton donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: aromatic bimolecular elimination, proton transfer, overall reactant used, overall product formed, intermediate formation, deamination, proton relay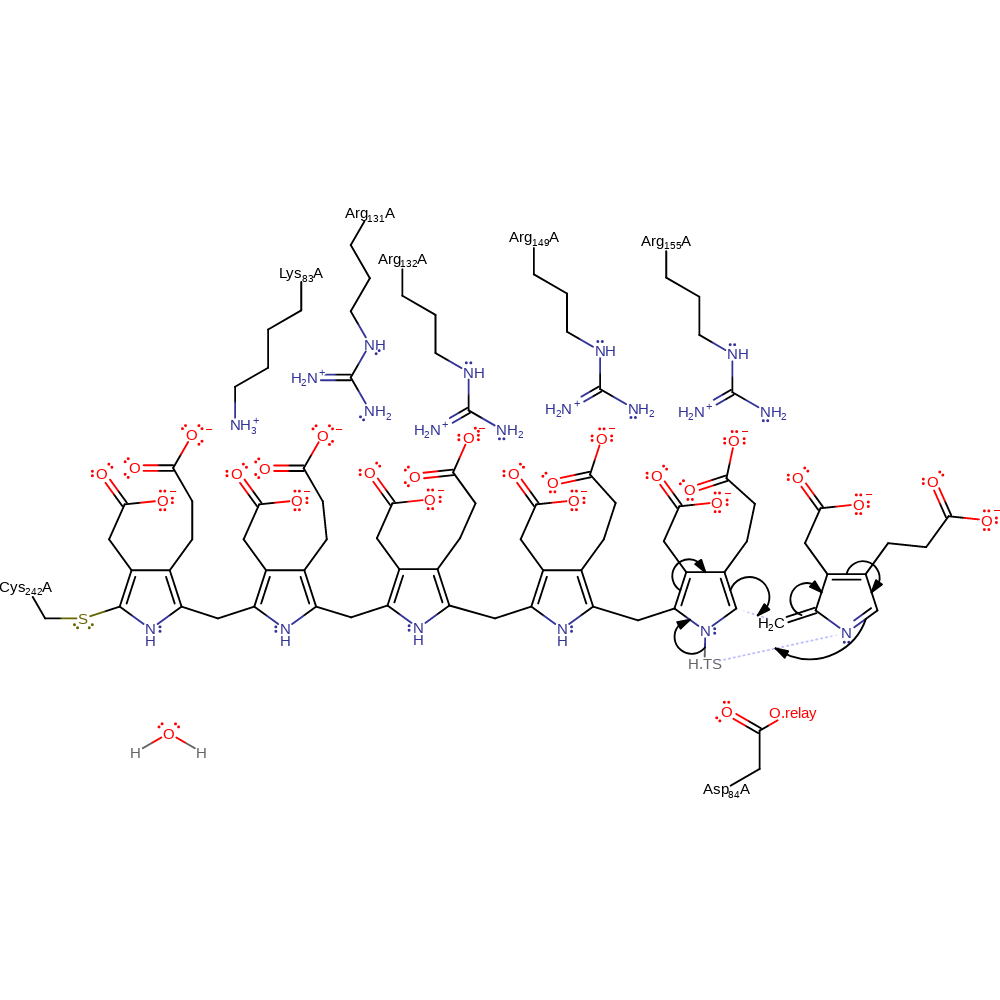
Step 11. Asp84 deprotonates the dipyrromethane cofactor, which causes rearrangement of the double bonds an addition to the azafulvene intermediate in a nucleophilic manner.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys83A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, activator |
| Asp84A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton relay |
| Arg131A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, activator |
| Arg132A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, activator |
| Cys242A | covalently attached |
| Arg149A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg155A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg149A | activator |
| Arg155A | activator |
| Asp84A | proton donor, proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: aromatic bimolecular nucleophilic addition, cofactor used, intermediate formation, proton relay
Step 12. Asp84 deprotonates C4 of the intermediate, causing double bond rearrangement to produce the cofactor elongated by one pyrrole unit.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Arg149A | activator |
| Arg155A | activator |
| Lys83A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, activator |
| Asp84A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton relay |
| Arg131A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, activator |
| Arg132A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, activator |
| Cys242A | covalently attached |
| Arg149A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg155A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp84A | proton donor, proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, intermediate formation, proton relay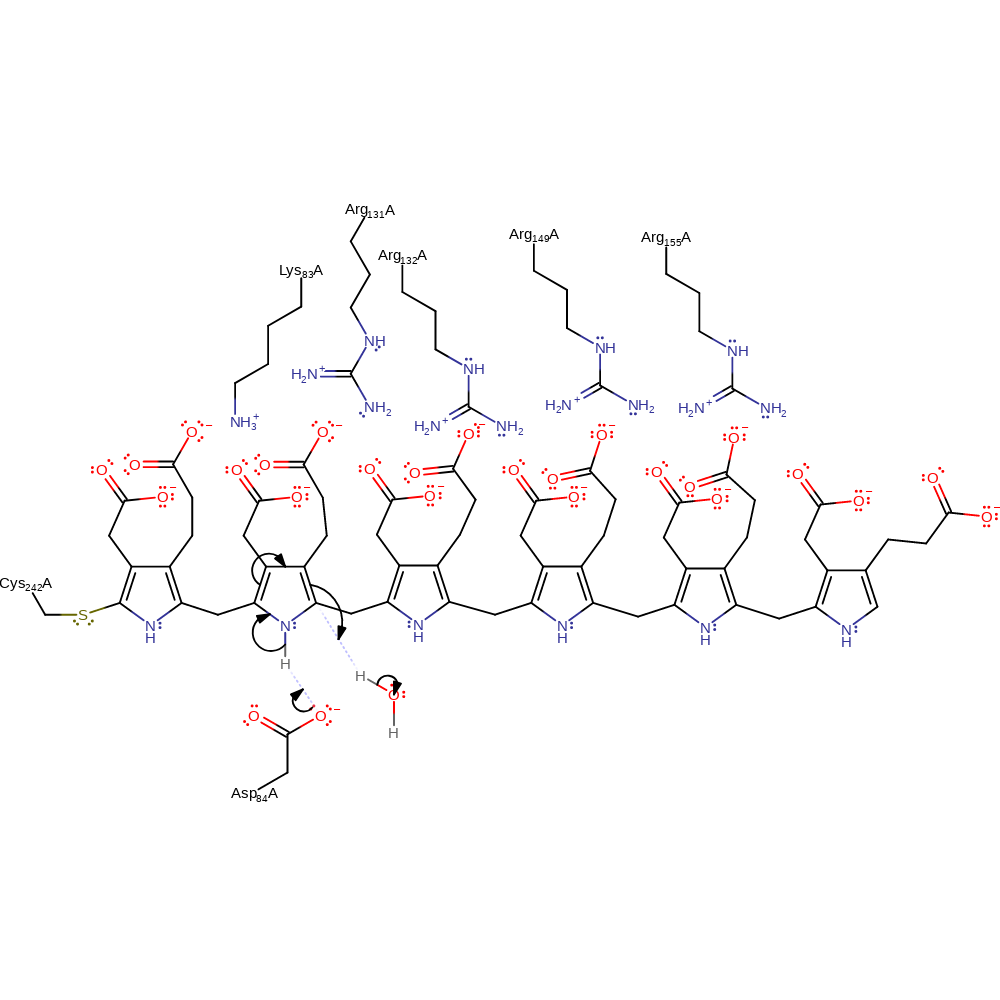
Step 13. Asp84 deprotonates N of the second pyrrole in the chain, causing double bond rearrangement to protonate the chain at the C4 position, this proton comes from a bound water molecule.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys83A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, activator |
| Asp84A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Arg131A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, activator |
| Arg132A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, activator |
| Cys242A | covalently attached |
| Arg149A | activator |
| Arg155A | activator |
| Arg149A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg155A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp84A | proton acceptor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, intermediate formation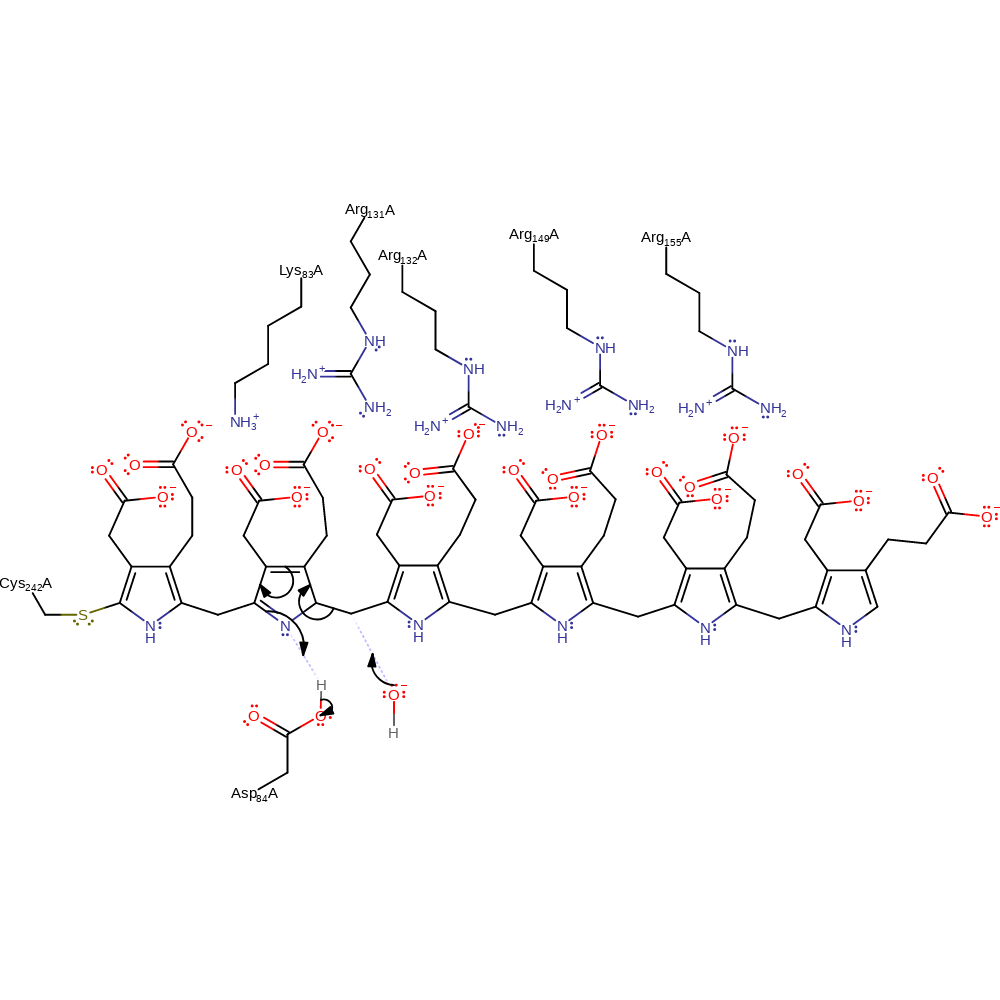
Step 14. The hydroxide initiates a nucleophilic attack on the intermediate in an substitution reaction. The cofactor is re-protonated from Asp84
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Lys83A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, activator |
| Asp84A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| Arg131A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, activator |
| Arg132A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser, activator |
| Cys242A | covalently attached |
| Arg149A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg155A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg149A | activator |
| Arg155A | activator |
| Asp84A | proton donor |




 Download:
Download: