Phosphatidylinositol diacylglycerol-lyase
Phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C (PI-PLC) is a ubiquitous enzyme involved in a vast range of cellular signalling cascades. Prokaryotic PLCs act as virulence factors in some bacteria, catalysing the hydrolysis of the sn-3 phosphodiester bond of phosphatidylinositol (PI) producing diacylglycerol (DAG) and inositol 1-phosphate (I(1)P).
For the bacterial enzyme, the main product is the cyclic intermediate, myo-inositol 1,2-cyclic phosphate, which is rapidly hydrolysed to I(1)P by the eukaryotic PI-PLCs whereas the mammalian enzyme undergoes complete catalysis.
PI-PLC from Bacillus cereus, and the nearly identical enzyme from B. thuringiensis have been used as model systems for the study of IP-PLCs as a whole. Bacterial PI-PLCs are metal-ion-independent. This is in contrast to mammalian PI-PLCs which are Ca(II) dependent. The R69D mutant of B. thuringiensis PI-PLC is calcium dependent and has been used to investigate the role of calcium in catalysis by PI-PLCs [PMID:16042375].
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P14262
 (4.6.1.13)
(4.6.1.13)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Bacillus cereus (Bacteria)

- PDB
-
1ptd
- PHOSPHATIDYLINOSITOL-SPECIFIC PHOSPHOLIPASE C
(2.6 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.20.20.190
 (see all for 1ptd)
(see all for 1ptd)
- Cofactors
- Water (1)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:4.6.1.13)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The first step of the is an intramolecular nucleophilic attack by the C2 hydroxyl of the substrate on the phosphorus producing IP and a myo-inositol 1,2-cyclic phosphate. This is catalysed by His32 and His82 acting as general base and general acid catalysts respectively.
The second step is reverse of the first step but with water acting as the nucleophile. This results in the hydrolysis of a phosphorus-oxygen bond in myo-inositol 1,2-cyclic phosphate to give D-myo-inositol 1-phosphate. However, for the bacterial enzyme, this step is slow and the main product is myo-inositol 1,2-cyclic phosphate.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1ptd) | ||
| His63 | His32A | In the first step His32 is the general base catalyst deprotonating the hydroxyl group on C2 of the substrate so that it may act as an intramolecular nucleophile. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Arg100 | Arg69A | The positive charge on Arg69 stabilises the negatively charged transition state. | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp305 | Asp274A | Asp274 forms a hydrogen bond to with the side chain of His32 and acts as an electrostatic stabiliser. | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His113 | His82A | His82 is the general acid catalyst which protonates the sn-3 oxygen of the DAG leaving group. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Asp64 | Asp33A | Activates His82. | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, intramolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall reactant used, overall product formed, cyclisation, rate-determining step, proton relay, native state of enzyme regenerated, inferred reaction stepReferences
- Hondal RJ et al. (1998), Biochemistry, 37, 4568-4580. Mechanism of Phosphatidylinositol-Specific Phospholipase C: A Unified View of the Mechanism of Catalysis†,‡. DOI:10.1021/bi972646i. PMID:9521777.
- Apiyo D et al. (2005), Biochemistry, 44, 9980-9989. X-ray Structure of the R69D Phosphatidylinositol-Specific Phospholipase C Enzyme: Insight into the Role of Calcium and Surrounding Amino Acids in Active Site Geometry and Catalysis. DOI:10.1021/bi047896v. PMID:16042375.
- Ryan M et al. (2001), Biochemistry, 40, 9743-9750. A Catalytic Diad Involved in Substrate-Assisted Catalysis: NMR Study of Hydrogen Bonding and Dynamics at the Active Site of Phosphatidylinositol-Specific Phospholipase C†. DOI:10.1021/bi010958m. PMID:11583175.
- Kubiak RJ et al. (2001), Biochemistry, 40, 5422-5432. Involvement of the Arg−Asp−His Catalytic Triad in Enzymatic Cleavage of the Phosphodiester Bond†. DOI:10.1021/bi002371y.
- Heinz DW et al. (1998), J Mol Biol, 275, 635-650. Structural and mechanistic comparison of prokaryotic and eukaryotic phosphoinositide-specific phospholipases C. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.1997.1490. PMID:9466937.
- Katan M (1998), Biochim Biophys Acta, 1436, 5-17. Families of phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C: structure and function. DOI:10.1016/s0005-2760(98)00125-8. PMID:9838022.
- Gässler CS et al. (1997), Biochemistry, 36, 12802-12813. Probing the Roles of Active Site Residues in Phosphatidylinositol-Specific Phospholipase C fromBacillus cereusby Site-Directed Mutagenesis†. DOI:10.1021/bi971102d. PMID:9335537.
- Essen LO et al. (1997), Biochemistry, 36, 1704-1718. Structural Mapping of the Catalytic Mechanism for a Mammalian Phosphoinositide-Specific Phospholipase C†,‡. DOI:10.1021/bi962512p. PMID:9048554.
- Moser J et al. (1997), J Mol Biol, 273, 269-282. Crystal structure of the phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C from the human pathogen Listeria monocytogenes. DOI:10.1006/jmbi.1997.1290. PMID:9367761.
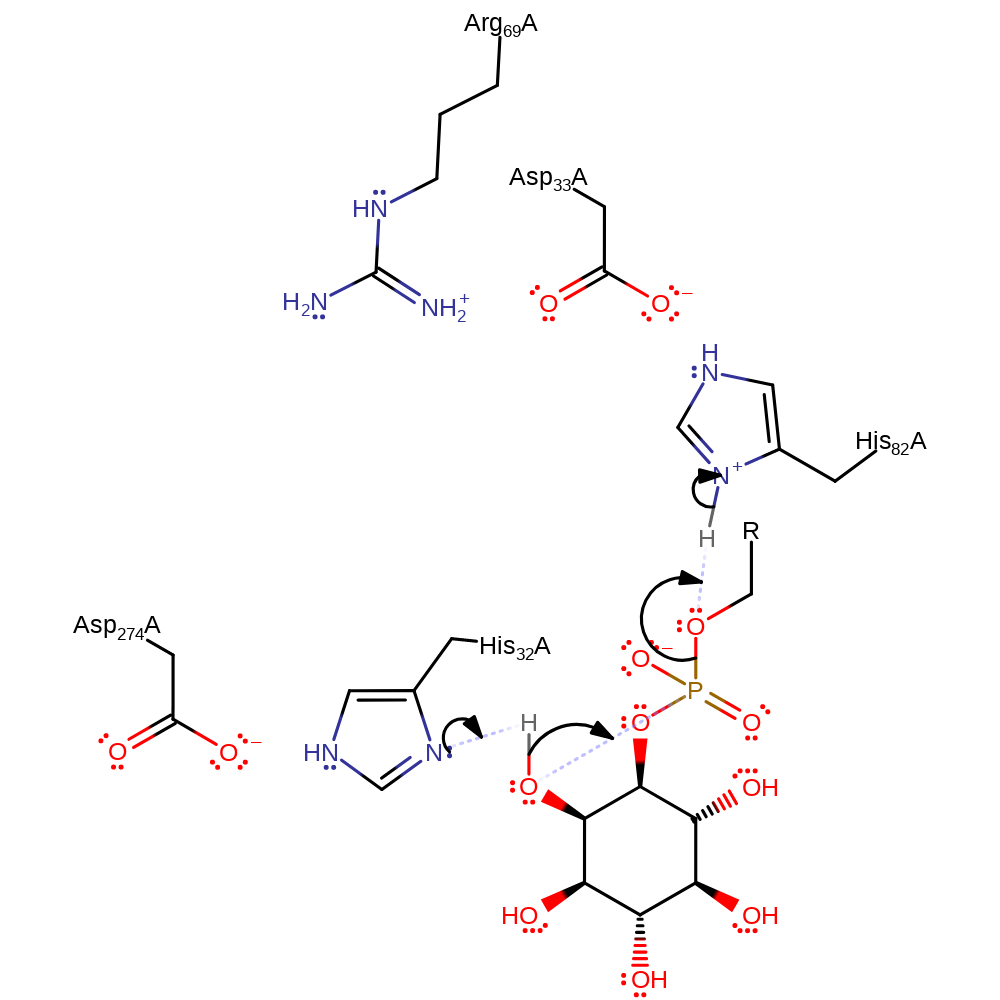
Step 1. His32 deprotonates the hydroxy group adjacent to the phosphate, which initiates an intramolecular nucleophilic addition of the oxyanion to the phosphate, which proceeds through a pentavalent transition state, to eliminate the product alcohol in a substitution reaction, with concomitant deprotonation of His82.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp33A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His82A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Arg69A | hydrogen bond donor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His32A | hydrogen bond donor, hydrogen bond acceptor |
| Asp274A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| His32A | proton acceptor |
| His82A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
proton transfer, ingold: intramolecular nucleophilic substitution, overall reactant used, overall product formed, cyclisation, proton transfer, rate-determining step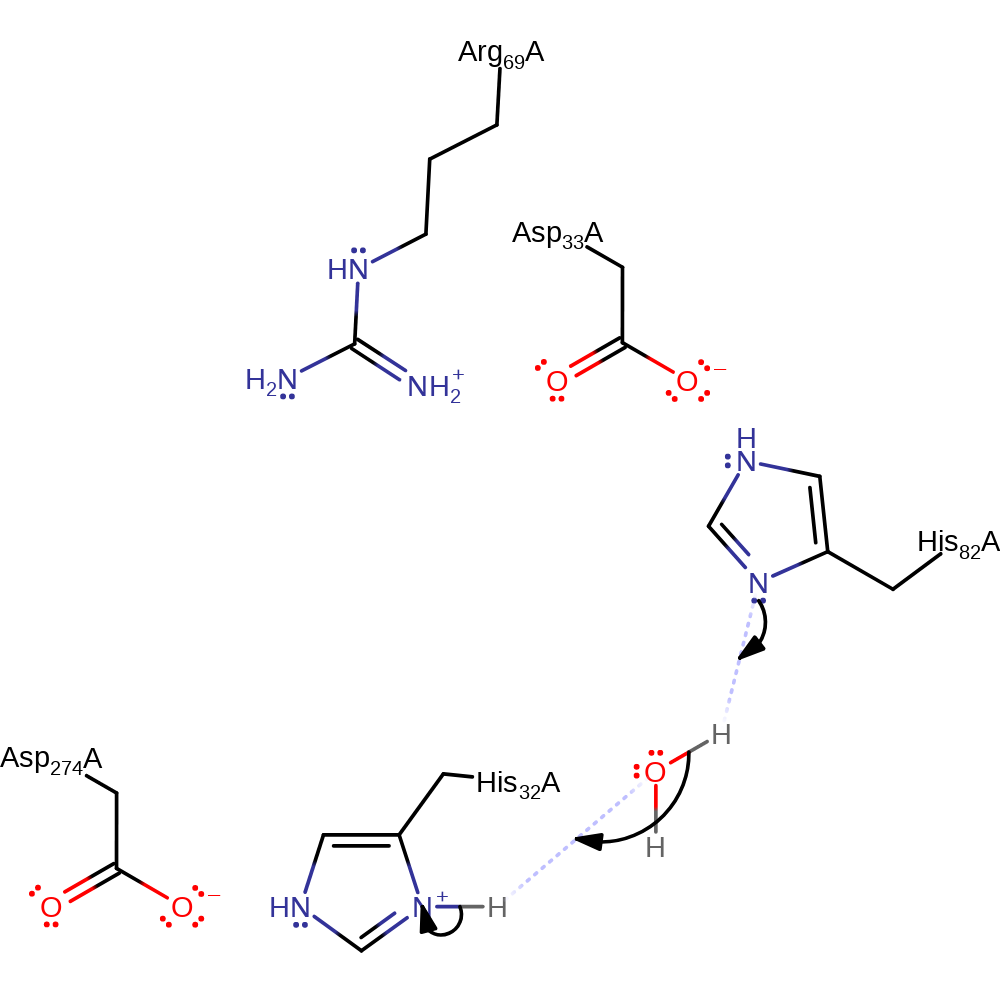
Step 2. His82 deprotonates water, which in turn deprotonates His32 in an inferred step.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp33A | hydrogen bond acceptor |
| His82A | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor |
| His32A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Arg69A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp274A | hydrogen bond acceptor, electrostatic stabiliser |
| His82A | proton acceptor |
| His32A | proton donor |



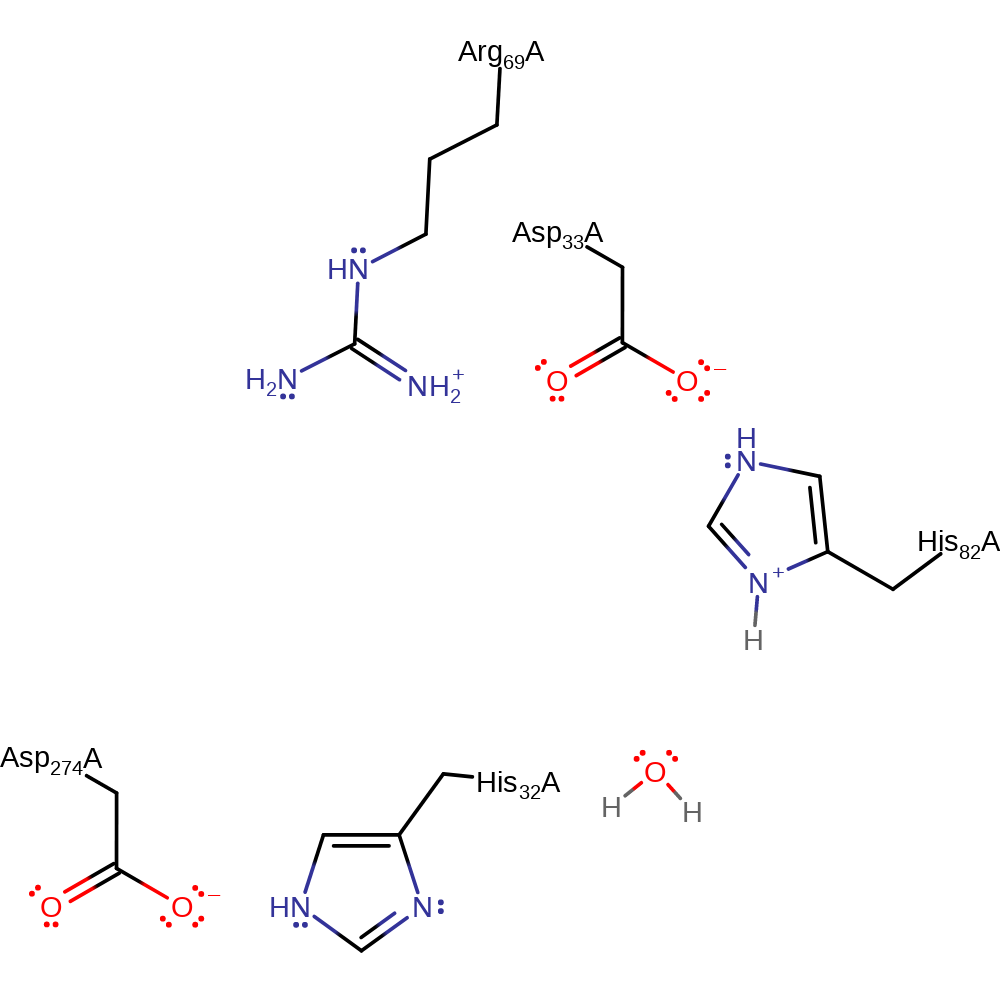 Download:
Download: