Geranyltranstransferase
Geranyltranstransferase is a member of the Isoprenoid Synthase Type I superfamily. It catalyses the metal-dependent formation of (2E,6E)-farnesyl diphosphate from geranyl diphosphate + isopentenyl diphosphate. It is known that the residue at the fifth position before the first DDxxD motif [PMID:12135472], in this case a phenylalanine, is responsible for determining product chain length.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
P08836
 (2.5.1.1, 2.5.1.10)
(2.5.1.1, 2.5.1.10)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Gallus gallus (Chicken)

- PDB
-
1fps
- CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF RECOMBINANT FARNESYL DIPHOSPHATE SYNTHASE AT 2.6 ANGSTROMS RESOLUTION
(2.6 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
1.10.600.10
 (see all for 1fps)
(see all for 1fps)
- Cofactors
- Magnesium(2+) (3) Metal MACiE
Enzyme Reaction (EC:2.5.1.10)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The substrate undergoes heterolysis. The diphosphate product remains associated with the active site, and the cabocation is delocalised over the three terminal carbon atoms of the intermediate. The double bond of isopentenyl diphosphate adds to the terminal carbocation in an electrophilic addition. The diphosphate formed in the initial heterolysis deprotonates the carbon adjacent to the newly formed carbocation, forming a new double bond in the trans,trans-farnesyl diphosphate product.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1fps) | ||
| Asp121 | Asp121(102)A | Forms part of both the Mg1 and Mg2 binding sites. Also helps stabilise the partially closed conformation. | metal ligand |
| Asp257 | Asp257(238)A | Forms part of the Mg3 binding site. | metal ligand |
| Asp258 | Asp258(239)A | Forms part of the Mg3 binding site via a water molecule. | activator |
| Phe112 | Phe112(93)A | The residue at the fifth position before the first DDxxD motif, in this case Phe112 (Phe240 in E. coli) is responsible for determining product chain length [PMID:12135472]. | steric role |
| Phe253 | Phe253(234)A | Helps hold the reactive intermediates in the correct position to ensure erroneous products aren't formed. | steric role |
| Lys71 | Lys71(52)A | Stabilizes fully closed conformation via electrostatic interaction with C-terminal carboxylate of IPP. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp117 | Asp117(98)A | Forms part of both the Mg1 and Mg2 binding sites. | metal ligand |
| Arg126 | Arg126(107)A | Hydrogen bonds to substrate diphosphate stabilising the negative charge. | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys214, Asp188 | Lys214(195)A, Asp188(169)A | Helps stabilise the partially closed conformation. | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
dephosphorylation, heterolysis, overall reactant used, charge delocalisation, bimolecular electrophilic addition, proton transfer, overall product formed, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Hosfield DJ et al. (2004), J Biol Chem, 279, 8526-8529. Structural Basis for Bisphosphonate-mediated Inhibition of Isoprenoid Biosynthesis. DOI:10.1074/jbc.c300511200. PMID:14672944.
- Aaron JA et al. (2010), Pure Appl Chem, 82, 1585-1597. Trinuclear Metal Clusters in Catalysis by Terpenoid Synthases. DOI:10.1351/PAC-CON-09-09-37. PMID:21562622.
- Liang PH (2009), Biochemistry, 48, 6562-6570. Reaction kinetics, catalytic mechanisms, conformational changes, and inhibitor design for prenyltransferases. DOI:10.1021/bi900371p. PMID:19537817.
- Rondeau JM et al. (2006), ChemMedChem, 1, 267-273. Structural basis for the exceptional in vivo efficacy of bisphosphonate drugs. DOI:10.1002/cmdc.200500059. PMID:16892359.
- Liang PH et al. (2002), Eur J Biochem, 269, 3339-3354. Structure, mechanism and function of prenyltransferases. DOI:10.1046/j.1432-1033.2002.03014.x. PMID:12135472.
- Koyama T et al. (2000), Biochemistry, 39, 463-469. Intersubunit Location of the Active Site of Farnesyl Diphosphate Synthase: Reconstruction of Active Enzymes by Hybrid-Type Heteromeric Dimers of Site-Directed Mutants†. DOI:10.1021/bi991621b. PMID:10631008.
- Tarshis LC et al. (1996), Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 93, 15018-15023. Regulation of product chain length by isoprenyl diphosphate synthases. DOI:10.1073/pnas.93.26.15018. PMID:8986756.

Step 1. The substrate undergoes heterolysis. The diphosphate product remains associated with the active site, and the cabocation is delocalised over the three terminal carbon atoms of the intermediate.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp258(239)A | activator |
| Arg126(107)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp121(102)A | metal ligand |
| Asp117(98)A | metal ligand |
| Asp257(238)A | metal ligand |
| Lys214(195)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys71(52)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp188(169)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Phe112(93)A | steric role |
| Phe253(234)A | steric role |
Chemical Components
dephosphorylation, heterolysis, overall reactant used, charge delocalisation
Step 2. The double bond of isopentenyl diphosphate adds to the terminal carbocation in an electrophilic addition. The positive charge in the geranyl carbocation intermediate is delocalised over the three terminal carbons.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp188(169)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp121(102)A | metal ligand |
| Asp117(98)A | metal ligand |
| Asp257(238)A | metal ligand |
| Lys71(52)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg126(107)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys214(195)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Phe112(93)A | steric role |
| Phe253(234)A | steric role |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular electrophilic addition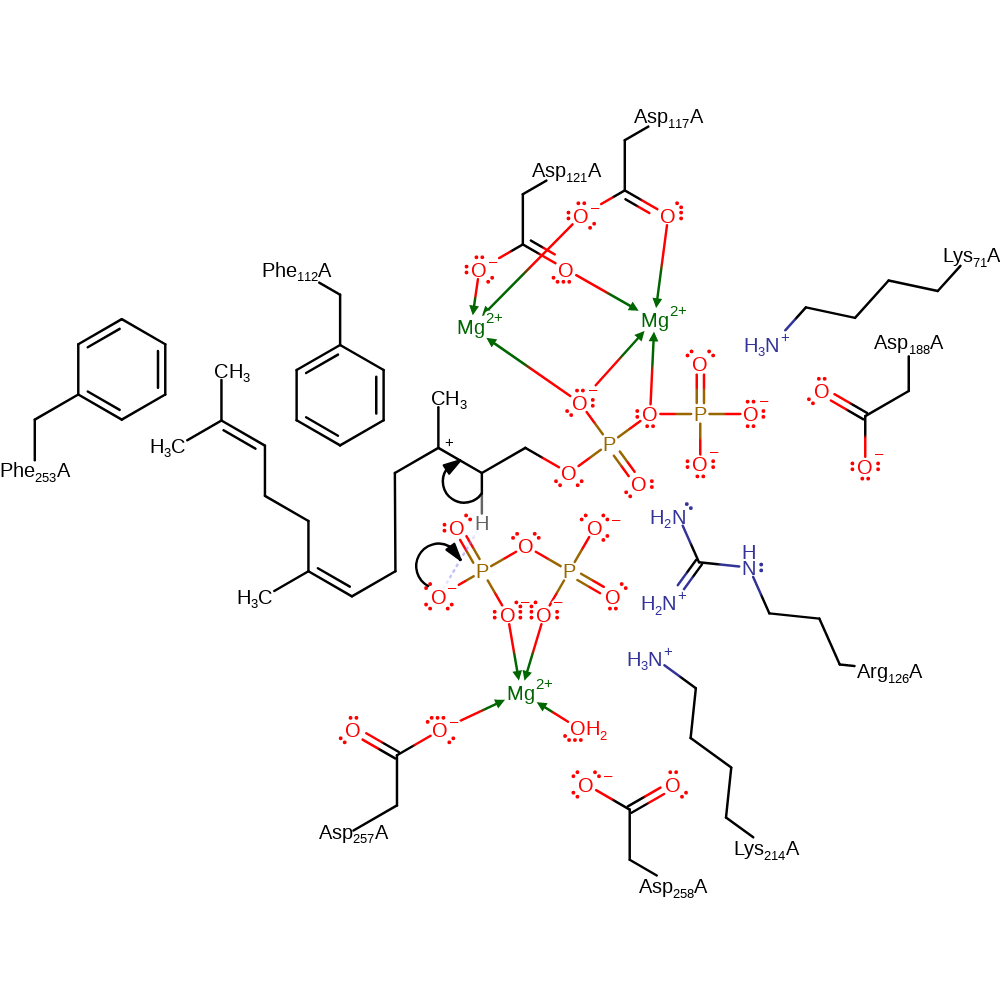
Step 3. The diphosphate formed in the initial heterolysis deprotonates the carbon adjacent to the newly formed carbocation, forming a new double bond in the trans,trans-farnesyl diphosphate product. The product of the reaction moves from the top Mg site to the bottom Mg site upon dissociation of the diphosphate product, ready for another round of elongation. The chain elongation reaction will continue until product chain has reached the residue located at the fifth position before the first DDxxD motif (Phe112 in this case)
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp121(102)A | metal ligand |
| Asp117(98)A | metal ligand |
| Asp257(238)A | metal ligand |
| Phe112(93)A | steric role |
| Phe253(234)A | steric role |
| Lys71(52)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Arg126(107)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp188(169)A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Lys214(195)A | electrostatic stabiliser |




 Download:
Download: