S-methyl-5'-thioadenosine phosphorylase
S-methyl-5'-thioadenosine phosphorylase (MTAP) catalyses the reversible phosphorylation of S-methyl-5'-thioadenosine (MTA) to adenine and 5-methylthioribose-1-phosphate. It is involved in the breakdown of MTA, a major by-product of polyamine biosynthesis. It is responsible for the first step in the methionine salvage pathway after MTA has been generated from S-adenosylmethionine. It has broad substrate specificity with 6-aminopurine nucleosides as preferred substrates. Despite being also an MTA phosphorylase, the MTAP in thermophilic Sulfolobus solfataricus only has 14% sequence homology to human MTAP.
Reference Protein and Structure
- Sequence
-
Q13126
 (2.4.2.28)
(2.4.2.28)
 (Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
(Sequence Homologues)
(PDB Homologues)
- Biological species
-
Homo sapiens (Human)

- PDB
-
1cg6
- STRUCTURE OF HUMAN 5'-DEOXY-5'-METHYLTHIOADENOSINE PHOSPHORYLASE COMPLEXED WITH 5'-DEOXY-5'-METHYLTHIOADENOSINE AND SULFATE AT 1.7 A RESOLUTION
(1.7 Å)



- Catalytic CATH Domains
-
3.40.50.1580
 (see all for 1cg6)
(see all for 1cg6)
Enzyme Reaction (EC:2.4.2.28)
Enzyme Mechanism
Introduction
The reaction proceeds via a two step mechanism with the formation of an oxocarbenium-like transition state followed by a nucleophilic attack by the phosphate ion at the anomeric carbon in an SN1-like mechanism.
Catalytic Residues Roles
| UniProt | PDB* (1cg6) | ||
| Asp220 | Asp220A | Acts as a general acid/base. This residue is buried in the active site and has a significantly modified pKa, allowing it to be protonated in the ground state of the enzyme. | hydrogen bond acceptor, hydrogen bond donor, proton acceptor, proton donor |
| Asp222 | Asp222A | Binds the substrate and helps to stabilise the oxocarbenium ion formed in the reaction. | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, proton transfer, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, overall product formed, bimolecular nucleophilic addition, intermediate terminated, inferred reaction step, native state of enzyme regeneratedReferences
- Appleby TC et al. (1999), Structure, 7, 629-641. The structure of human 5′-deoxy-5′-methylthioadenosine phosphorylase at 1.7 Å resolution provides insights into substrate binding and catalysis. DOI:10.1016/s0969-2126(99)80084-7. PMID:10404592.
- Guan R et al. (2013), Biochemistry, 52, 8313-8322. Thermodynamic analysis of transition-state features in picomolar inhibitors of human 5'-methylthioadenosine phosphorylase. DOI:10.1021/bi401188w. PMID:24148083.
- Appleby TC et al. (2001), J Biol Chem, 276, 39232-39242. Three-dimensional structure of a hyperthermophilic 5'-deoxy-5'-methylthioadenosine phosphorylase from Sulfolobus solfataricus. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M105694200. PMID:11489901.

Step 1. The glycosidic bond is cleaved to give an oxocarbenium ion that is stabilised by the phosphate in the active site. The adenine that is eliminated is protonated by Asp220. The product of this step is a tautomer of adenine, which will readily tautomerise.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp220A | hydrogen bond donor |
| Asp222A | electrostatic stabiliser |
| Asp220A | proton donor |
Chemical Components
ingold: unimolecular elimination by the conjugate base, proton transfer, intermediate formation, overall reactant used, overall product formed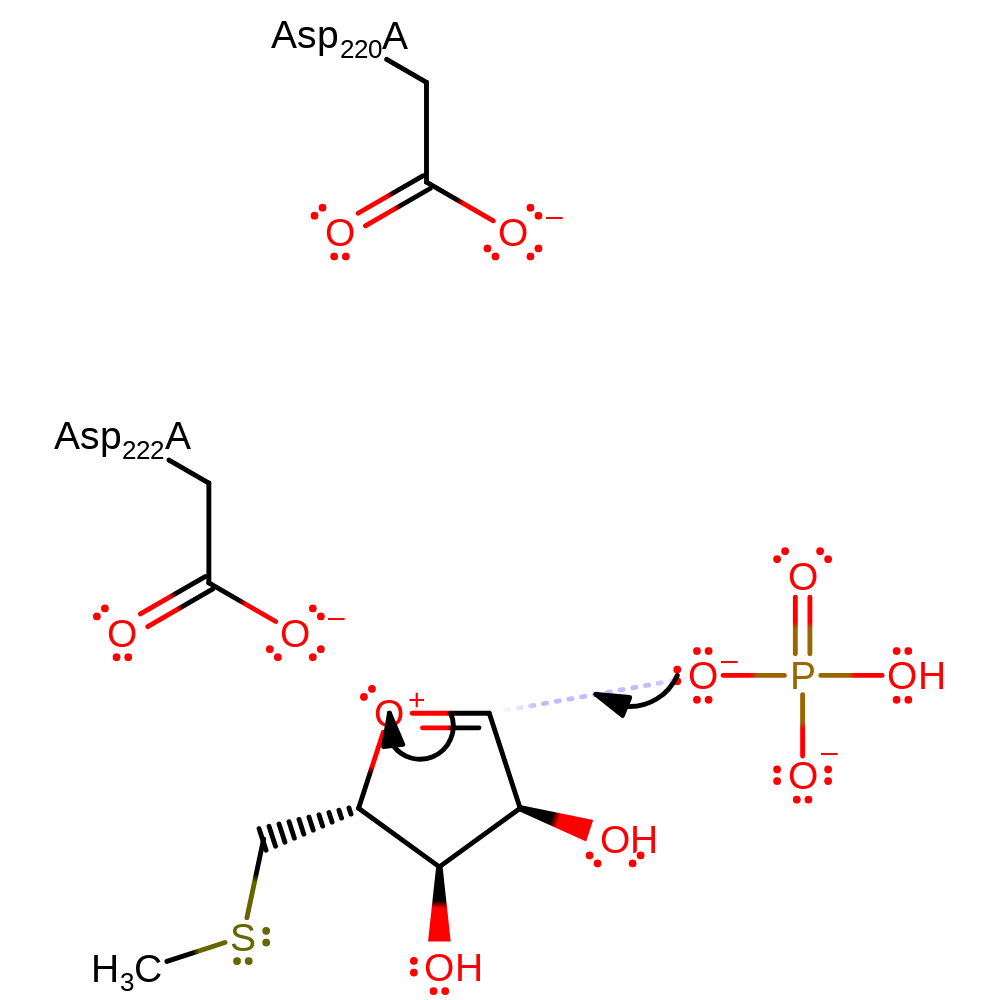
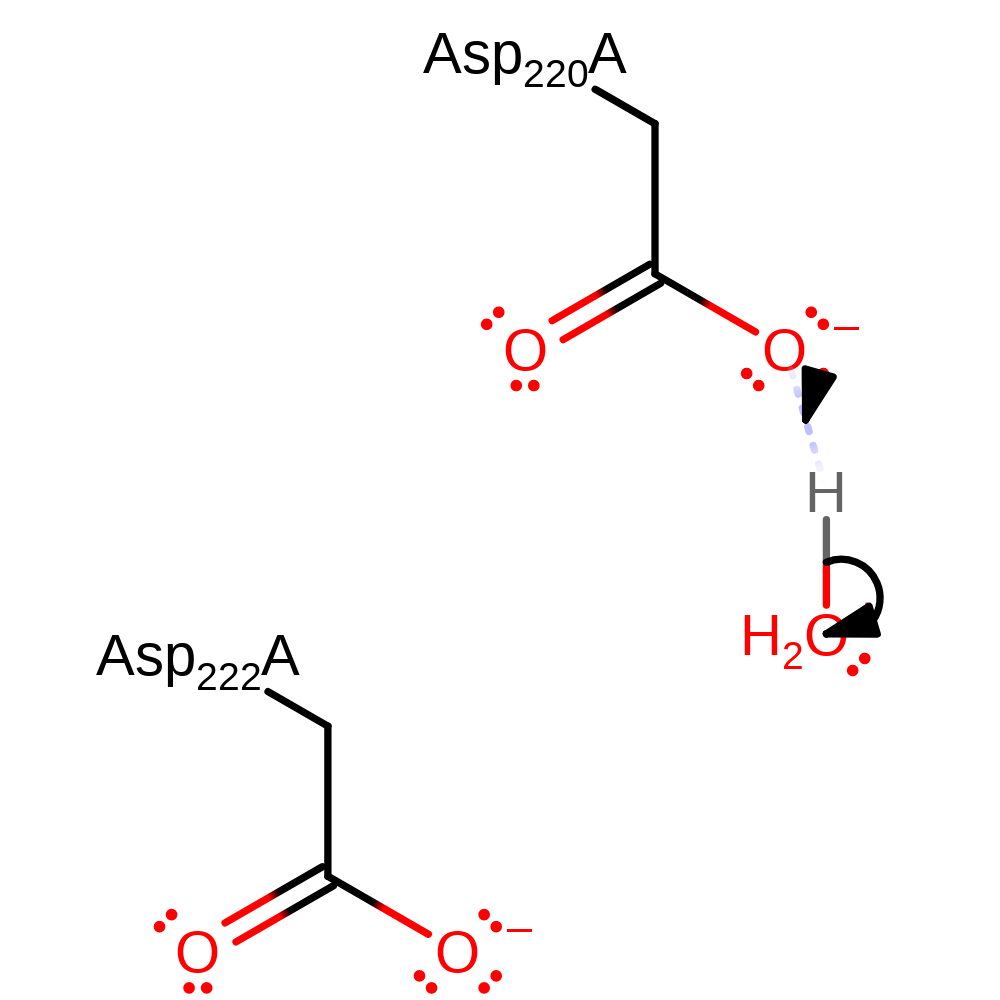
Step 2. Phosphate attacks the oxocarbenium ion intermediate in a nucleophilic addition.
Download: Image, Marvin FileCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp222A | electrostatic stabiliser |
Chemical Components
ingold: bimolecular nucleophilic addition, overall reactant used, intermediate terminated, overall product formedCatalytic Residues Roles
| Residue | Roles |
|---|---|
| Asp220A | hydrogen bond acceptor, proton acceptor |




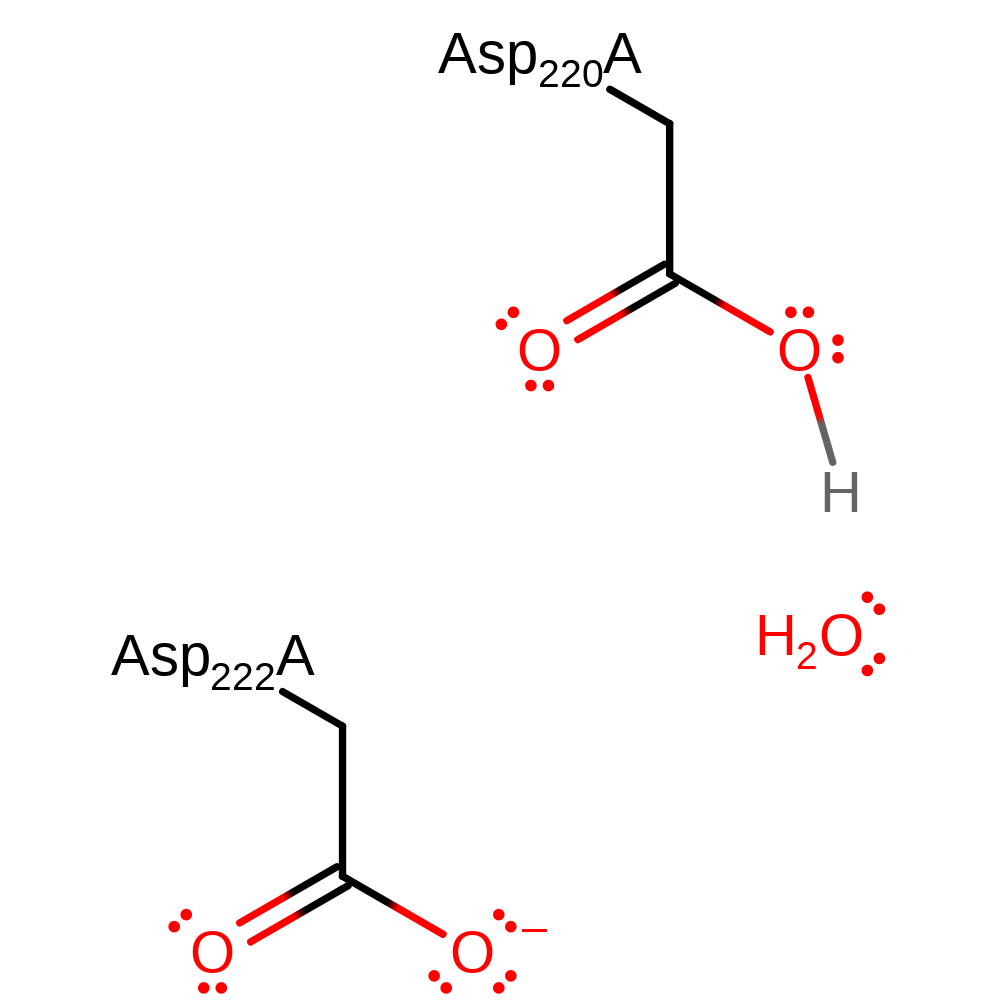 Download:
Download: